Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Software Verification: AISC-360-05 Example 001
Enviado por
Zakir KhanDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Software Verification: AISC-360-05 Example 001
Enviado por
Zakir KhanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
AISC-360-05 Example 001
COMPOSITE GIRDER DESIGN
EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION
A series of 45-ft. span composite beams at 10 ft. o/c carry the loads shown
below. The beams are ASTM A992 and are unshored during construction. The
concrete has a specified compressive strength, f c 4 ksi. Design a typical floor
beam with 3-in., 18-gage composite deck and 4 ½ in. normal weight concrete
above the deck, for fire protection and mass. Select an appropriate beam and
determine the required number of ¾ in.-diameter shear studs.
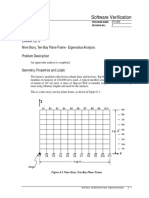
GEOMETRY, PROPERTIES AND LOADING
Member Properties Loading Geometry
W21x55 w = 830 plf (Dead Load) Span, L = 45 ft
E = 29000 ksi w = 200 plf (Construction)
Fy = 50 ksi w = 100 plf (SDL)
w = 1000 plf (Live Load)
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 1
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
TECHNICAL FEATURES OF ETABS TESTED
Composite beam design, including:
Selection of steel section, camber and shear stud distribution
Member bending capacities, at construction and in service
Member deflections, at construction and in service
RESULTS COMPARISON
Independent results are referenced from Example I.1 from the AISC Design
Examples, Version 13.0.
Percent
Output Parameter ETABS Independent
Difference
Pre-composite Mu (k-ft) 333.15 333.15 0.00%
Pre-composite bMn (k-ft) 472.5 472.5 0.00%
Pre-composite Deflection (in.) 2.3 2.3 0.00%
Required Strength Mu (k-ft) 687.5 687.5 0.00%
Full Composite bMn (k-ft) 1027.1 1027.1 0.00%
Partial Composite bMn (k-ft) 770.3 770.3 0.00 %
Shear Stud Capacity Qn 17.2 17.2 0.00 %
Shear Stud Distribution 34 34 0.00%
Live Load Deflection (in.) 1.35 1.30 3.70%
Required Strength Vu (kip) 61.1 61.1 0.00%
Vn (k) 234 234 0.00%
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 2
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
COMPUTER FILE: AISC-360-05 EXAMPLE 001.EDB
CONCLUSION
The ETABS results show an acceptable comparison with the independent results.
The live load deflection differs due to a difference in methodology. In the AISC
example, the live load deflection is computed based on a lower bound value of
the beam moment of inertia, whereas in ETABS, it is computed based on the
approximate value of the beam moment of inertia derived from Equation (C-I3-6)
from the Commentary on the AISC Load and Resistance Factor Design
Specification – Second Edition.
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 3
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
HAND CALCULATION
Properties:
Materials:
ASTM A572 Grade 50 Steel
E = 29,000 ksi, Fy = 50 ksi, wsteel = 490 pcf
4000 psi normal weight concrete
Ec = 3,644 ksi, f c 4 ksi, wconcrete = 145 pcf
Section:
W21x55
d = 20.8 in, bf = 8.22 in, tf = 0.522 in, tw = 0.38 in, h = 18.75 in., rfillet = 0.5 in.
Asteel = 16.2 in2, Ssteel = 109.6 in3, Zsteel = 126 in3, Isteel = 1140 in4
Deck:
tc =4 ½ in., hr = 3 in., sr =12 in., wr = 6 in.
Shear Connectors:
d = ¾ in, h =4 ½ in, Fu = 65 ksi
Design for Pre-Composite Condition:
Construction Required Flexural Strength:
w D 10 77.5 55.125 10
3
0.830125 kip/ft
3
w L 10 20 10 0.200 kip/ft
w u 1.2 0.830125 1.6 0.200 1.31615 kip/ft
wu L 1.31615 45
2 2
Mu 333.15 kip-ft
8 8
Moment Capacity:
b M n b Z s F y 0.9 126 50 12 472.5 kip-ft
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 4
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
Pre-Composite Deflection:
0.830
45 12
4
4 5
5wD L 12
nc 2.31 in.
384 E I 384 29, 000 1,140
Design for Composite Flexural Strength:
Required Flexural Strength:
wu 1.2 0.830 1.2 0.100 1.6 1 2.71 kip/ft
wu L 2.68 45
2 2
Mu 687.5 kip-ft
8 8
Full Composite Action Available Flexural Strength:
Effective width of slab:
10.0 45.0 f t
b eff • 2 sides 10.0 ft 11.25 ft
2 8
Resistance of steel in tension:
C Py As F y 16.2 50 810 kips controls
Resistance of slab in compression:
Ac beff t c 10 12 4.5 540 in
2
C 0.85 f 'c Ac 0.85 4 540 1836 kips
Depth of compression block within slab:
C 810
a 1.99 in.
0.85 beff f 'c 0.85 10 12 4
Moment resistance of composite beam for full composite action:
a 2.00
d 1 ( t c hr ) (4.5 3) 6.51 in.
2 2
d 20.8 / 12
M n Py • d 1 Py • 0.9 810 • 6.51 / 12 810 • 1027.1 kip-ft
2 2
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 5
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
Partial Composite Action Available Flexural Strength:
Assume 36.1% composite action:
C 0.361 Py 0.361 810 292.4 kips
Depth of compression block within concrete slab:
C 292.4
a 0.72 in.
0.85 beff f 'c 0.85 10 12 4
a 0.72
d 1 t c hr 4.5 3 7.14 in.
2 2
Compression force within steel section:
P y
C 2 810 292.4 2 258.8 kips
Tensile resistance of one flange:
Fflange b f t f Fy 8.22 0.522 50 214.5 kip
Tensile resistance of web:
Fw eb T t w F y 18.75 0.375 50 351.75 kips
Tensile resistance of one fillet area:
Ffillet Py 2 Fflange Fw eb 2 810 2 214.5 351.2 2 14.6 kips
Compression force in web:
C w eb ( Py C ) / 2 Fflange Ffillet 2 5 8 .8 2 1 4 .5 1 4 .6 2 9 .7 kip s
Depth of compression block in web:
C w eb 29.7
x T 18.76 1.584 in.
F w eb 351.75
Location of centroid of steel compression force measured from top of steel section:
0.5 t f Fflange t f 0.5 rfillet Ffillet t f rfillet 0.5 x C w eb
d2
( Py C ) / 2
0.5 0.522 214.5 0.522 0.5 0.5 14.6 0.522 0.5 0.5 1 .58 29.7
0.467 in.
258.8
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 6
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
Moment resistance of composite beam for partial composite action:
M n C d 1 d 2 Py d 3 d 2
20.8
0.9 292.4 7.14 0.467 810 0.467 12 770.3 kip-ft
2
Shear Stud Strength:
From AISC Manual Table 3.21 assuming one shear stud per rib placed in the
weak position, the strength of ¾ in.-diameter shear studs in normal weight
concrete with f c 4 ksi and deck oriented perpendicular to the beam is:
Q n 17.2 kips
Shear Stud Distribution:
Qn 292.4
n 17 from each end to m id-span, rounded up to 35 total
Qn 17.2
Live Load Deflection:
Modulus of elasticity ratio:
n E E c 29, 000 3, 644 8.0
Transformed elastic moment of inertia assuming full composite action:
Moment Arm
Transformed from
Area Centroid Ay Ay2 I0
Element A (in2) y (in.) (in.3) (in,4) (in.4)
Slab 67.9 15.65 1,062 16,620 115
W21x50 16.2 0 0 0 1,140
84.1 1,062 16,620 1,255
I x I 0 Ay 1, 255 16, 620 17, 874 in.
2 4
1, 062
y 12.6 in.
84.1
2
I tr I x A y 17, 874 82.6 12.6 4, 458 in
2 4
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 7
Software Verification
PROGRAM NAME: ETABS
REVISION NO.: 4
Effective moment inertia assuming partial composite action:
I equiv I s Q n Py I tr I s 1,140 0.361 4, 458 1,140 3,133 in
4
I eff 0 .7 5 I eq u iv 0 .7 5 3,1 3 3 2, 3 5 0 in
4
4
5w L L
4
5 1 12 30 12
LL 1.35 in.
384 E I eff 384 29, 000 2, 350
Design for Shear Strength:
Required Shear Strength:
wu 1.2 0.830 1.2 0.100 1.6 1 2.71 kip/ft
wu L 2.71 45
Vu 61.1 kip-ft
2 2
Available Shear Strength:
V n • 0.6 • d • t w • Fy 1.0 • 0.6 • 20.8 • 0.375 • 50 234 kips
AISC-360-05 Example 001 - 8
Você também pode gostar
- AISC DG11 2nd Edition Example 001 PDFDocumento12 páginasAISC DG11 2nd Edition Example 001 PDFMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- Model Analysis of Plane Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo EverandModel Analysis of Plane Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionAinda não há avaliações
- Ram Connection ManualDocumento152 páginasRam Connection ManualMauricio Coronado Neira100% (2)
- Tutorial Ram ConectionDocumento17 páginasTutorial Ram ConectionFOXMEXAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Analysis MethodDocumento31 páginasDirect Analysis MethodgayalamAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Eccentricities in Load Bearing WallsDocumento8 páginasCalculating Eccentricities in Load Bearing WallsMbleekAinda não há avaliações
- Column SpliceDocumento2 páginasColumn SpliceMdShahbazAhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Ly and LZ Concept DiscussedDocumento2 páginasLy and LZ Concept DiscussedalayshahAinda não há avaliações
- Steel Cap Plate Connections DesignDocumento18 páginasSteel Cap Plate Connections DesignVinoth KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Concrete ShearWallDocumento34 páginasDesign of Concrete ShearWallOmar HadriAinda não há avaliações
- Shear Wall With Boundary ElementDocumento4 páginasShear Wall With Boundary ElementArnel DodongAinda não há avaliações
- RC Stair SlabsDocumento3 páginasRC Stair SlabsAssad Mohammed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Steel HangerDocumento2 páginasDesign of Steel HangerMostafa Saleh100% (1)
- GTG Beam Formwork DesignDocumento32 páginasGTG Beam Formwork DesignshihabAinda não há avaliações
- PROKON - Plane Frame - Analysis - Example - BeamDocumento44 páginasPROKON - Plane Frame - Analysis - Example - BeamJames RamAinda não há avaliações
- Section Modulus Equations and Calculators Common Shapes: Got It!Documento4 páginasSection Modulus Equations and Calculators Common Shapes: Got It!Fatih AdamAinda não há avaliações
- Steel Connection Guide 211 EnuDocumento64 páginasSteel Connection Guide 211 EnuAnonymous TRthlKkWWAinda não há avaliações
- Portal Frame Practice ProblemsDocumento10 páginasPortal Frame Practice ProblemsBoyzz ChinAinda não há avaliações
- Connection Types: Simple (Shear) ConnectionsDocumento5 páginasConnection Types: Simple (Shear) Connectionsmahhor82_635643838Ainda não há avaliações
- تصميم الكمرات بطريقة ultimate PDFDocumento42 páginasتصميم الكمرات بطريقة ultimate PDFqaisalkurdyAinda não há avaliações
- CSA A23.3 DeflectionsDocumento11 páginasCSA A23.3 Deflections700spymaster007Ainda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Circular Flat Slab in Residential Building Using STAAD ProDocumento42 páginasAnalysis of Circular Flat Slab in Residential Building Using STAAD ProKarthik Naidu67% (6)
- Broadway Hilti - Handrail BaseDocumento4 páginasBroadway Hilti - Handrail Basexpertsteel100% (1)
- Typical Anchor BoltsDocumento33 páginasTypical Anchor BoltslucianduAinda não há avaliações
- Design of CorbelDocumento32 páginasDesign of CorbelSathish Kumar Civil100% (1)
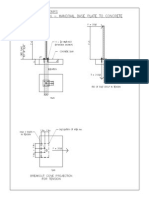
- Axially Loaded Columns - Base Plate DesignDocumento2 páginasAxially Loaded Columns - Base Plate DesignaomareltayebAinda não há avaliações
- CSA S16-14 Example 002fgfDocumento7 páginasCSA S16-14 Example 002fgfBoby CuliusAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis Report Tensile Canopy - HOCKEY STADIUM - R0 - ADocumento23 páginasAnalysis Report Tensile Canopy - HOCKEY STADIUM - R0 - ANeeraj KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Cold Form DesignDocumento32 páginasCold Form DesignKilaru HareeshAinda não há avaliações
- Connection DesignDocumento33 páginasConnection Designjesus curielAinda não há avaliações
- Drop Panel CalculationDocumento2 páginasDrop Panel Calculationsandiok86Ainda não há avaliações
- Steel Design DetailDocumento2.471 páginasSteel Design DetailPark WaAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Steel StructuresDocumento1 páginaAdvanced Steel StructuresRohan KulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- Discussion - Design of W-Shapes For Combined Bending and TorsionDocumento2 páginasDiscussion - Design of W-Shapes For Combined Bending and TorsionnaimAinda não há avaliações
- Generation of Rebar Objects Using Results from Analysis and DesignDocumento22 páginasGeneration of Rebar Objects Using Results from Analysis and DesignАндрей Николаевич ГоревAinda não há avaliações
- Unbraced LengthsDocumento8 páginasUnbraced LengthsZoran MilutinovicAinda não há avaliações
- SAP2000 Introductory TutorialDocumento62 páginasSAP2000 Introductory Tutorialanon_443224320100% (1)
- Super Composite ColumnDocumento2 páginasSuper Composite ColumnCheng Por EngAinda não há avaliações
- A How-To-Approach To Notional LoadsDocumento4 páginasA How-To-Approach To Notional Loadsshare4learnAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Analysis & Design Report - GutterDocumento10 páginasStructural Analysis & Design Report - GutterAie BantuganAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Steel Design Project: Calculation SheetDocumento14 páginasStructural Steel Design Project: Calculation SheetJoey Johnson100% (2)
- Load Case, Load Combination, Modal Case Options. Choose The Load Case To Be DisplayedDocumento5 páginasLoad Case, Load Combination, Modal Case Options. Choose The Load Case To Be DisplayedLivia15Ainda não há avaliações
- Knee ConnectionsDocumento13 páginasKnee ConnectionsNag RajAinda não há avaliações
- ACI 318-14 RC Shear Wall Design - Short Walls PDFDocumento9 páginasACI 318-14 RC Shear Wall Design - Short Walls PDFHuzil FernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Lattice Girder Design for Roof StructureDocumento12 páginasLattice Girder Design for Roof StructureMock Khang Hi100% (1)
- PRYING9.xls AISC Prying Action AnalysisDocumento5 páginasPRYING9.xls AISC Prying Action AnalysisCarlos Valverde PortillaAinda não há avaliações
- AISC-360-05 Example 001 PDFDocumento8 páginasAISC-360-05 Example 001 PDFMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- AISC-360-10 Example 001 PDFDocumento9 páginasAISC-360-10 Example 001 PDFMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- AISC-360-16 EXAMPLEDocumento8 páginasAISC-360-16 EXAMPLEMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- Software Verification: AISC-360-10 Example 001Documento9 páginasSoftware Verification: AISC-360-10 Example 001Davico HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- AISC-360-10 Example 002 - Composite Girder Design Verified in ETABSDocumento9 páginasAISC-360-10 Example 002 - Composite Girder Design Verified in ETABSMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- Software Verification: AISC-360-16 Example 003Documento5 páginasSoftware Verification: AISC-360-16 Example 003alejandro mantillaAinda não há avaliações
- AISC DG02 Example 003 PDFDocumento7 páginasAISC DG02 Example 003 PDFMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- ACI 318-08 Example 001Documento5 páginasACI 318-08 Example 001RMM100% (1)
- Software Verification of Composite Beam DesignDocumento8 páginasSoftware Verification of Composite Beam Designalejandro mantillaAinda não há avaliações
- AISC DG02 Example 004 PDFDocumento11 páginasAISC DG02 Example 004 PDFMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- AISC 360-05 Example 001 PDFDocumento7 páginasAISC 360-05 Example 001 PDFHendrik TaupanAinda não há avaliações
- EC-4-2004 Example 001 PDFDocumento8 páginasEC-4-2004 Example 001 PDFMohamed Abo-ZaidAinda não há avaliações
- PlanDocumento1 páginaPlanZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 10 PDFDocumento1 página10 PDFZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Road CulvertDocumento1 páginaRoad CulvertZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Stbu 10 00010 PDFDocumento13 páginasStbu 10 00010 PDFZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Stairs DetailDocumento1 páginaStairs DetailZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Footing EstimationDocumento3 páginasFooting EstimationZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- 2Documento1 página2Zakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Culverts Cross SectionDocumento1 páginaTypes of Culverts Cross SectionZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Comparing RCC, Steel and Composite Structures for 30-Storey BuildingDocumento6 páginasComparing RCC, Steel and Composite Structures for 30-Storey Buildingnvc_vishwanathanAinda não há avaliações
- Anchore PDFDocumento2 páginasAnchore PDFZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Verification ManualDocumento457 páginasVerification ManualKay OlokoAinda não há avaliações
- Example 06Documento2 páginasExample 06Ihab El AghouryAinda não há avaliações
- SummaryDocumento3 páginasSummaryZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Pile Foundation Us CropDocumento186 páginasPile Foundation Us CropZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Scale A4 and A3Documento1 páginaScale A4 and A3Zakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Guidelines For The Design of High Mast Pole FoundationDocumento62 páginasGuidelines For The Design of High Mast Pole Foundationolomu100% (8)
- NokarOnline Survey Results for ServantsDocumento2 páginasNokarOnline Survey Results for ServantsZakir KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Custom Objects, Fields, Tabs, Related Lists, List ViewsDocumento7 páginasCustom Objects, Fields, Tabs, Related Lists, List ViewsAjay GhugeAinda não há avaliações
- RPGS Complete Lecture Note1 Inpdf Compressed1Documento203 páginasRPGS Complete Lecture Note1 Inpdf Compressed1Purusottam PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics T (954/1) Functions QuizDocumento1 páginaMathematics T (954/1) Functions QuizmasyatiAinda não há avaliações
- DBMS Queries OverviewDocumento98 páginasDBMS Queries OverviewAbhinay YadavAinda não há avaliações
- LP Galvo Scanner LaserphotoDocumento16 páginasLP Galvo Scanner LaserphotoCostin DinamaxAinda não há avaliações
- Control of Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output ProcessesDocumento27 páginasControl of Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output Processesmeseret sisayAinda não há avaliações
- Metodo Fotometrico para La Determinación de La Concentración de Ozono AtmosféricoDocumento8 páginasMetodo Fotometrico para La Determinación de La Concentración de Ozono AtmosféricoVarinia ZubiletaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital-To-Analog Converter ICs SB Vol11 Issue5Documento12 páginasDigital-To-Analog Converter ICs SB Vol11 Issue5Hooman KaabiAinda não há avaliações
- Generator Protection Application GuideDocumento106 páginasGenerator Protection Application GuideJorge Alberto Chavarría Sacasa100% (1)
- Green Building Store MVHR Brochure-File032484Documento9 páginasGreen Building Store MVHR Brochure-File032484Anthi ValavaniAinda não há avaliações
- Abstract Load Balancing 1Documento3 páginasAbstract Load Balancing 1Naveen AbhiAinda não há avaliações
- Chieftain 2100X (2-Deck) Data SheetDocumento1 páginaChieftain 2100X (2-Deck) Data SheetbrianAinda não há avaliações
- Spe 58987 Propped Fracturing in Gas Carbonate Formations MexicoDocumento12 páginasSpe 58987 Propped Fracturing in Gas Carbonate Formations MexicoJose Gregorio FariñasAinda não há avaliações
- Navisworks BasicTrainingDocumento54 páginasNavisworks BasicTrainingMadhankumarAinda não há avaliações
- Model For Calculating The Refractive Index of DiffDocumento5 páginasModel For Calculating The Refractive Index of DiffNANAinda não há avaliações
- LSE MA100 Background CheckDocumento5 páginasLSE MA100 Background CheckAlternative EgoAinda não há avaliações
- CS5371 Theory of Computation: Lecture 1: Mathematics Review I (Basic Terminology)Documento23 páginasCS5371 Theory of Computation: Lecture 1: Mathematics Review I (Basic Terminology)Kamal WaliaAinda não há avaliações
- Ray OpticsDocumento41 páginasRay OpticsHannah VsAinda não há avaliações
- Ultra-Low-Power Wireless Systems - Energy-Efficient Radios For The Internet of Things PDFDocumento11 páginasUltra-Low-Power Wireless Systems - Energy-Efficient Radios For The Internet of Things PDFnhatvpAinda não há avaliações
- Record results of toy soldier experiment times with different massesDocumento42 páginasRecord results of toy soldier experiment times with different massesTeoh Han Jie100% (1)
- IgE Level Effect of Phyllanthus Acidus Leaf ExtractDocumento5 páginasIgE Level Effect of Phyllanthus Acidus Leaf Extractkhatami muhammadAinda não há avaliações
- Mech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) NotesDocumento45 páginasMech Vi Non Traditional Machining (10me665) Notesnikhil0% (1)
- Class XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementDocumento29 páginasClass XII Computer Project - Hotel ManagementLakshmi Puthiyedath71% (7)
- OOPS AbapDocumento188 páginasOOPS Abapraky036950% (2)
- Name: Fatema Saeed Grade Level:: Lesson Plan TemplateDocumento3 páginasName: Fatema Saeed Grade Level:: Lesson Plan Templateapi-340688378Ainda não há avaliações
- Smartdek Design ManualDocumento48 páginasSmartdek Design ManualranddyAinda não há avaliações
- HM130 5Documento1 páginaHM130 5AntonelloAinda não há avaliações
- Na2xckbr2y Rev 08Documento1 páginaNa2xckbr2y Rev 08dardakAinda não há avaliações
- Flight Planning For ATTDocumento106 páginasFlight Planning For ATTTienek Lee100% (1)
- Measure Runoff and Soil Loss at Erosion Plots in TanzaniaDocumento19 páginasMeasure Runoff and Soil Loss at Erosion Plots in TanzaniaMohd Sofiyan Bin SulaimanAinda não há avaliações
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseNo EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (50)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindAinda não há avaliações
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionNo EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (10)
- Introduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNo EverandIntroduction to Applied Thermodynamics: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsNo EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationNo EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (18)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNo EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceNo EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (9)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedNo EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionNo EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Quantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationNo EverandQuantum Mechanics 4: Spin, Lasers, Pauli Exclusion & Barrier PenetrationNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (1)
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkNo EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Control of Power Electronic Converters and Systems: Volume 1No EverandControl of Power Electronic Converters and Systems: Volume 1Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityNo EverandThe Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (115)
- Oil and Gas Pipelines: Integrity and Safety HandbookNo EverandOil and Gas Pipelines: Integrity and Safety HandbookAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Foundations for Offshore Wind TurbinesNo EverandDesign of Foundations for Offshore Wind TurbinesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Rolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsNo EverandRolling Bearing Tribology: Tribology and Failure Modes of Rolling Element BearingsAinda não há avaliações
- Machinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeNo EverandMachinery Failure Analysis Handbook: Sustain Your Operations and Maximize UptimeNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (4)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessAinda não há avaliações
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityNo EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsAinda não há avaliações