Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Lesson 52
Enviado por
MarcTnnDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lesson 52
Enviado por
MarcTnnDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Lesson Plan
Lesson: Nernst Equation
Aim :
To study the application of the Nernst equation and electrochemical processes.
Learning Outcomes :
By the end of the lesson, students will be able to:
1. use the Nernst equation to calculate the electrode potential, E of half-cell equations
under non-standard conditions.
2. use the Nernst equation to determine the effect of concentration on the e.m.f of the
cell.
3. explain the electrochemical process involved in :
a. the galvanizing of iron
b. dental filling
c. batteries for electric cars
Assumed prior knowledge :
Students should already be familiar with the concept of :
1. electrochemical cells
2. standard electrode potentials.
Underlying Principles
1. Making the invisible, visible.
2. Enabling students to know what to look for.
Time taken to complete the activities : 80 minutes
Differentiation
Questions in the student notes are designed to enable all students to complete the activity.
The pop-up answers are provided for the students to view when they have considered their
responses. Worksheet questions include questions that require recall, understanding and
application of the new concepts learned.
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 1 of 4
Development of Lesson :
No. Steps Strategy Resources
1 Set Induction. • Teacher to quiz students to ensure that
(Ascertaining prior they have the necessary background
knowledge and knowledge.
introducing lesson
topic for the day). Teacher to point out lesson objectives for
the day.
2 Student Activity Teacher to go through Activities 1 - 2 • Courseware
with the students.
• Activity 1 : Nernst equation
Students get to investigate the effect of
changing the concentration of the solution
in a half-cell on the standard cell
potential, e.m.f of the cell. They are also
introduced to the Nernst equation and its
application.
• Activity 2 : Electrochemical processes
Students are shown the electrochemical
processes involved in the corrosion of
metals such as iron and in dental fillings.
They are also shown how galvanaic
cells are connected in series to form the
lead storage battery.
3 Evaluation • Students to answer questions in the • Worksheet
student worksheet on their own.
4 Extension activity • Students to go through the extension • Websites
activities on their own. • Reference
books.
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 2 of 4
Worksheet answers
1. Nernst equation
1.1 a. Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s) E = +0.80 V
0.059 1
Ecell = E − lg
n [Ag + ]
0.059 1
= + 0.80 − lg
1 [0.2]
= +0.84 V
b. Pb4+(aq) + 2e- Pb2+(aq) E = +1.69 V
0.059 [Pb 2+ ]
Ecell = E − lg
n [Pb 4 + ]
0.059 [0.4]
= + 1.69 − lg
2 [0.8]
= +1.70 V
0.059 [Sn 4+ ]
1.2 Nernst equation: Ecell = E − lg
2 [Ag + ] 2 [Sn 2+ ]
0.059
0 = +0.65 − lg K c
2
Kc = 1.08 x 1022
[A very high value for Kc means that the reaction is almost complete and the
equilibrium shifts to the extreme right.]
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 3 of 4
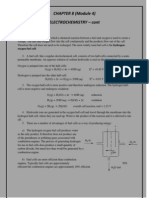
2. Electrochemical Processes
2.1 a. Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s) E = -0.25 V ……..(1)
Ag+(aq) + e- Ag(s) E = +0.80 V …….(2)
b. Ni(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e- E = +0.25 V
(2) x 2 : 2Ag (aq) + 2e-
+
2Ag(s) E = +0.80 V
Ni(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Ni2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
c. +0.25 V + 0.80 V = +1.05 V
0.059 [Ni 2 + ]
d. Ecell = E − lg
n [Ag + ] 2
e. According to the Nernst equation in (d) increasing the concentration of Ni2+
will cause the e.m.f. of the cell to decrease.
0.059 [Ni 2 + ]
f. According to the Nernst equation Ecell = E − lg
n [Ag + ] 2
increasing the concentration of Ag+ will cause the e.m.f. of the cell to increase
g. Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl(s)
Adding Cl- will cause the precipitation of AgCl(s). The concentration of
Ag+(aq) will decrease. According to the Nernst equation, the e.m.f. of the cell
will decrease.
© 2003 Ministry of Education Malaysia. All Rights Reserved. Page 4 of 4
Você também pode gostar
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (I)Documento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (I)MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 2 03Documento45 páginasChemistry Form 6 Sem 2 03Ng Swee Loong StevenAinda não há avaliações
- Module PPinang Sem 1Documento131 páginasModule PPinang Sem 1Heng Wei PinAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Documento0 páginaPhysics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Choe Kok HuanAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 50Documento3 páginasLesson 50MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 40Documento5 páginasLesson 40MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: K and K For Heterogeneous SystemDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: K and K For Heterogeneous SystemMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Introduction To Ionic EquilibriumDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Introduction To Ionic EquilibriumMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Acid-Base TitrationDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Acid-Base TitrationMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)Documento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 41Documento4 páginasLesson 41MarcTnn100% (1)
- Lesson 29Documento3 páginasLesson 29MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Shape of MoleculesDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Shape of MoleculesMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan:: 80 MinutesDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan:: 80 MinutesMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 21Documento5 páginasLesson 21MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3Documento5 páginasLesson 3MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Some of Their PropertiesDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan: Some of Their PropertiesMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (I)Documento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (I)MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Semester 3 DefinitionDocumento1 páginaChemistry Semester 3 DefinitionYong ChoonAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 42Documento4 páginasLesson 42MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- STPM 2023 SEM 2 Mock AnsDocumento2 páginasSTPM 2023 SEM 2 Mock AnsHannah KaienAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (II)Documento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (II)MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 40Documento3 páginasLesson 40MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Proposal For Chemistry Project STPM 2016Documento2 páginasProposal For Chemistry Project STPM 2016Voon Keat Nicholas Thoo100% (1)
- Lesson 39Documento3 páginasLesson 39MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (IV)Documento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (IV)MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Sem 1 Q &A PDFDocumento9 páginasChem Sem 1 Q &A PDFevacuate clashAinda não há avaliações
- STPM Chemistry Form 6 NotesDocumento5 páginasSTPM Chemistry Form 6 NotesAfz Min100% (3)
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: First and Second Order ReactionDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: First and Second Order ReactionMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Marking Scheme For Term 2 Trial Exam, STPM 2019 (Gbs Melaka) Section A (45 Marks)Documento7 páginasMarking Scheme For Term 2 Trial Exam, STPM 2019 (Gbs Melaka) Section A (45 Marks)Michelles JimAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: The Mass SpectrometerDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: The Mass SpectrometerMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Water (STPM)Documento5 páginasWater (STPM)mei chyiAinda não há avaliações
- STPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFDocumento1 páginaSTPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFChris LauAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Ionic and Covalent BondingDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Ionic and Covalent BondingMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: First Row D-Block ElementsDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: First Row D-Block ElementsMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 2Documento52 páginasChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 Chapter 2Yuzamrah Awang NohAinda não há avaliações
- Proposal For Chemistry Project STPM 2015Documento4 páginasProposal For Chemistry Project STPM 2015Joel Yeong100% (1)
- MOCK - TEST - (Chemistry) - Term 1 - 2015Documento19 páginasMOCK - TEST - (Chemistry) - Term 1 - 2015Ung Hie HuongAinda não há avaliações
- Electrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMDocumento10 páginasElectrochemistry - Cont Module 4 STPMPavithiranAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 41Documento3 páginasLesson 41MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Chemistry 2014Documento83 páginasManual Chemistry 2014AlexTanYun-KaiAinda não há avaliações
- Inorganic Chemistry STPMDocumento113 páginasInorganic Chemistry STPMThilagavathy SethuramahAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Report DraftDocumento19 páginasPhysics Report DraftViola Voon Li WeiAinda não há avaliações
- Ujian Sem2 Physics STPM 2017Documento9 páginasUjian Sem2 Physics STPM 2017Bestah Joewellster TeoAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2Documento12 páginasChemistry STPM Semester 2 Group 2Chong Yin Ping100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding HybridisationDocumento7 páginasChemical Bonding HybridisationCherry T CYAinda não há avaliações
- STPM Chemistry 2003 - Paper 1Documento18 páginasSTPM Chemistry 2003 - Paper 1Steve_Sam93Ainda não há avaliações
- STPM Chemistry Form 6Documento5 páginasSTPM Chemistry Form 6BabasChong100% (1)
- STPM Project 2017Documento10 páginasSTPM Project 2017LiuJiewChuanAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 49Documento3 páginasLesson 49MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 2)Documento13 páginasModule 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 2)Steven LeeAinda não há avaliações
- A Level Chemistry Core Practical 10 - Electrochemical CellsDocumento5 páginasA Level Chemistry Core Practical 10 - Electrochemical CellsshellodkomaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter6-Electrochemistry (Part 3)Documento33 páginasChapter6-Electrochemistry (Part 3)BagusprPrasetyoAinda não há avaliações
- Electrochemistry FR Worksheet Answers Key PDFDocumento22 páginasElectrochemistry FR Worksheet Answers Key PDFEmily toaAinda não há avaliações
- Practical 4 Postlab ReportDocumento8 páginasPractical 4 Postlab Reportgracebrewster123Ainda não há avaliações
- 12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 02 PDFDocumento2 páginas12 Chemistry Electrochemistry Test 02 PDFShreyash KolekarAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasLesson PlanMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of ElectrolysisDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Uses of ElectrolysisMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Dun DownloadDocumento1 páginaDun DownloadMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasLesson PlanMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Heat Energy ChangeDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Heat Energy ChangeMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 49Documento3 páginasLesson 49MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Standard Cell PotentialMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 45Documento4 páginasLesson 45MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 48Documento3 páginasLesson 48MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasLesson PlanMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsDocumento3 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Colligative Properties of SolutionsMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemDocumento5 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 41Documento4 páginasLesson 41MarcTnn100% (1)
- Lesson 42Documento4 páginasLesson 42MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: The Base Dissociation ConstantMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: PH and pOHDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: PH and pOHMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)Documento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Le Chatelier's Principle (II)MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Zero Order ReactionDocumento4 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: Zero Order ReactionMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: For Homogeneous SystemsMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 28Documento5 páginasLesson 28MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 29Documento3 páginasLesson 29MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 21Documento5 páginasLesson 21MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: First and Second Order ReactionDocumento6 páginasLesson Plan: Lesson: First and Second Order ReactionMarcTnnAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 27Documento4 páginasLesson 27MarcTnnAinda não há avaliações