Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Practice Hwe 1
Enviado por
api-382372564Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Practice Hwe 1
Enviado por
api-382372564Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Practice: HWE #1
Answer each question. Show all work and place final answers in boxes. Remember,
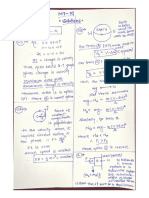
p+q=1
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
1. Given a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium with allele frequencies p =0.9 and q =
0.1, determine the frequencies of the three genotypes AA, Aa and aa. (Starting with an
easy one)
AA = (0.9)2 =0.81
Aa = 2(0.9)(0.1) = 0.18
Aa = (0.1)2 =0.01
2. In a population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the frequency of the recessive
allele is 0.6, find:
a. Frequency of the dominant allele: p = 1- 0.6 = 0.4
b. Percentage of population that is homozygous recessive: (0.6)2 = 0.36 = 36%
c. Percentage of population that is heterozygous: 2(0.4)(0.6) = 0.48 = 48%
d. Percentage of population that is homozygous dominant: (0.4)2 = 0.16 = 16%
3. Allele W for white wool is dominant over allele w for black wool. In a sample of 900
sheep, 9 are black. Assume the population is in HWE. Find:
a. Percentage of the population that is homozygous recessive. 9/900 = 0.01 = 1%
b. Frequency of the recessive allele. q2 = 0.01 → q = 0.1
c. Frequency of the dominant allele. p = 1 - 0.1 = 0.9
d. Percentage of population that is heterozygous. 2(0.1)(0.9) = 0.18 = 18%
e. Percentage of population that is homozygous dominant. p2 = 0.81 = 81%
4. The compound phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) tastes very bitter to most people. The
inability to taste PTC is controlled by a single recessive allele. In the Caucasian
population, about 70% can taste PTC. Assuming the population is in HWE, find:
a. Frequency of the population that is homozygous recessive. 30%
b. Frequency of the recessive allele. q2 = 0.3 → q = 0.55
c. Frequency of the dominant allele. p = 1 - 0.55 = 0.45
d. Percentage of population that is heterozygous. 2(0.55)(0.45) = 0.495 = 49.5%
e. Percentage of population that is homozygous dominant. (0.45)2 = 0.2025 =
20.25%
5. You are investigating a population of 200 people. 145 have brown eyes, a dominant trait,
and 55 have blue eyes, a recessive trait. Assuming the population is in HWE, Find:
a. Frequency of the population that is homozygous recessive. 55/200 = 0.275
b. Frequency of the recessive allele. q2 = 0.275 → q = 0.52
c. Frequency of the dominant allele. p = 1 - 0.52 = 0.48
d. How many (# not the frequency) of the people are homozygous dominant for
brown eyes? p2 = 0.2304 → (0.2304)(200) = 46.08
46 people
e. If everyone reproduces and the population grows to 550 people but remains in
HWE, how many people would you expect to have blue eyes? (0.275)(550) =
151.25
151 people
6. In a tropical forest there is a species of bird that has a variable tail length. In one
population of 2000 birds, 614 have long tails (TT), 973 have medium length tails (Tt),
and 413 birds have short tails (tt). You cannot assume this population is in HWE. Find:
a. Frequency of the population that is homozygous recessive. 413/2000 = 0.2065
b. Frequency of the population that is heterozygous. 973/2000 = 0.4865
c. Frequency of the population that is homozygous dominant. 614/2000 = 0.3070
d. Frequency of the dominant allele. 2(614) + 973 = 2201 → 2201/4000 = 0.55025
e. Frequency of the recessive allele. 2(413) + 973 = 2212 → 1799/4000 = 0.44975
f. If the population WAS in HWE, what would the frequency of the homozygous
recessive genotype be? q2 = 0.2023 = 20.23%
g. If the population WAS in HWE, what would the frequency of the heterozygous
genotype be? 2pq = 2(0.55025)(0.44975) = 0.4949 = 49.49%
h. If the population WAS in HWE, what would the frequency of the homozygous
dominant genotype be? p2 = 0.3028 = 30.28%
i. Compare answers a-c to f-h. Is this population in HWE? Yes.
j. If not, which trait is favored? Also, what mode of selection is occurring? N/a.
Você também pode gostar
- A BREEDER'S GUIDE TO GENETICS: RELAX, IT'S NOT ROCKET SCIENCENo EverandA BREEDER'S GUIDE TO GENETICS: RELAX, IT'S NOT ROCKET SCIENCEAinda não há avaliações
- HardyWeinburg Problems 2 KeyDocumento1 páginaHardyWeinburg Problems 2 KeyRuhaan TanvirAinda não há avaliações
- Workshop Population GeneticsDocumento4 páginasWorkshop Population Geneticslirianny pachecoAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Problem Set ANSWERSDocumento2 páginasHardy Weinberg Problem Set ANSWERSMaxAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Problem SetDocumento5 páginasHardy Weinberg Problem SetNur Syakira IsmailAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Problem Set KEYDocumento12 páginasHardy Weinberg Problem Set KEYKapil ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- Molecular Biology Chapter 13: Evolution Hardy-Weinberg Practice ProblemsDocumento7 páginasMolecular Biology Chapter 13: Evolution Hardy-Weinberg Practice ProblemsKapil ShindeAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 hardyweinbergprobsANSWERSDocumento7 páginas2015 hardyweinbergprobsANSWERSElan GoldbergAinda não há avaliações
- KEL7 - Population Genetic - 20240403 - 074052 - 0000Documento28 páginasKEL7 - Population Genetic - 20240403 - 074052 - 0000Tri RatnawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy-Weinberg Solved ExamplesDocumento9 páginasHardy-Weinberg Solved ExamplesumaraAinda não há avaliações
- Population Genetics Practice Problems For StudenetsDocumento10 páginasPopulation Genetics Practice Problems For Studenetskaram aliAinda não há avaliações
- 23 How To Do Hardy Weinberg ProblemsDocumento5 páginas23 How To Do Hardy Weinberg ProblemstsrifAinda não há avaliações
- Asses Ment 1Documento3 páginasAsses Ment 1Shakti DaheAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Practice SolutionsDocumento5 páginasHardy Weinberg Practice SolutionsShadan MuAinda não há avaliações
- Problems in Population GeneticsDocumento3 páginasProblems in Population GeneticsBurner AccountAinda não há avaliações
- AP Bio Learning Target - Illustrate Gene Pool Dynamics & MicroevolutionDocumento37 páginasAP Bio Learning Target - Illustrate Gene Pool Dynamics & MicroevolutionJ15Ainda não há avaliações
- Worksheet For Feb 5 - ANSWERS PDFDocumento4 páginasWorksheet For Feb 5 - ANSWERS PDFMary TaklaAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13Documento2 páginasHardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13DontsArtAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13Documento2 páginasHardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13DontsArtAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13Documento2 páginasHardy Weinberg Practice Problem KEY 12-13DontsArtAinda não há avaliações
- 23 How-To-Do-Hardy-Weinberg-ProblemsDocumento5 páginas23 How-To-Do-Hardy-Weinberg-Problemsapi-241528754Ainda não há avaliações
- BiologyDocumento3 páginasBiologywalizadhmariaAinda não há avaliações
- EXTRA CREDIT - Practice Hardy Weinberg QuestionsDocumento2 páginasEXTRA CREDIT - Practice Hardy Weinberg QuestionsLucas Crispi CunhaAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy WeinbergDocumento14 páginasHardy WeinbergAakash ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg Calculation1Documento8 páginasHardy Weinberg Calculation1Rishikaphriya Rauichandran100% (1)
- Hardy WeinbergDocumento27 páginasHardy WeinbergNoor HanisAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg PrincipleDocumento26 páginasHardy Weinberg PrincipleMitzi Noreen Cantillep100% (1)
- Chapter 24-Population GeneticsDocumento72 páginasChapter 24-Population GeneticsJean Pierre RullierAinda não há avaliações
- AP BIO Hardy Weinberg Questions-KeyDocumento3 páginasAP BIO Hardy Weinberg Questions-KeyCasey LynchAinda não há avaliações
- AnswersDocumento19 páginasAnswersSherlock Wesley ConanAinda não há avaliações
- LSM1102 Population GeneticsDocumento81 páginasLSM1102 Population Geneticsgivena2ndchanceAinda não há avaliações
- BIOF11 Tutorial 7Documento5 páginasBIOF11 Tutorial 7Rachna LalAinda não há avaliações
- TUTORIAL 5-jwpnDocumento9 páginasTUTORIAL 5-jwpnINTAN ZURINA BINTI AHMAD EDIDIKAinda não há avaliações
- 1107L Ex.10 Hardy WeinbergDocumento16 páginas1107L Ex.10 Hardy WeinbergCandace PettyAinda não há avaliações
- MT - 1 SolutionsDocumento34 páginasMT - 1 SolutionsShrutiAinda não há avaliações
- 15-Population GeneticsDocumento7 páginas15-Population GeneticsAbbas TalibAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 8: Population Genetics A Large Breeding PopulationDocumento6 páginasLab 8: Population Genetics A Large Breeding PopulationAlejandra EnriquezAinda não há avaliações
- HWDocumento2 páginasHWaudreyannlowAinda não há avaliações
- Population Genetics Practice Problems: Question 4 Section B (10 Marks/ 10minutes)Documento4 páginasPopulation Genetics Practice Problems: Question 4 Section B (10 Marks/ 10minutes)sebastianAinda não há avaliações
- C5.population GeneticsDocumento28 páginasC5.population GeneticsyunohuAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy-Weinberg Genetics Take-Home ANSWERSDocumento3 páginasHardy-Weinberg Genetics Take-Home ANSWERSAndres JacoboAinda não há avaliações
- Answers: Activity 23.1 A Quick Review of Hardy-Weinberg Population GeneticsDocumento6 páginasAnswers: Activity 23.1 A Quick Review of Hardy-Weinberg Population GeneticsR A Y S U N S H I N EAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 3 - Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumDocumento2 páginasAssignment 3 - Hardy-Weinberg EquilibriumViktor SolomonAinda não há avaliações
- 5.2 Hardy-Weinberg LawDocumento23 páginas5.2 Hardy-Weinberg LawjocajoldinAinda não há avaliações
- Biology 4 Tuto 1Documento18 páginasBiology 4 Tuto 1Firdaus ZulkifliAinda não há avaliações
- Population Genetics: Genetic Variation Within A PopulationDocumento26 páginasPopulation Genetics: Genetic Variation Within A PopulationAshleyAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy-Weinberg Review Answers - Extra ResourceDocumento2 páginasHardy-Weinberg Review Answers - Extra ResourceOmar AlwaerAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy Weinberg EquilibriumDocumento7 páginasHardy Weinberg EquilibriumCyrus Flores,Ainda não há avaliações
- CHP 7-Population GeneticsDocumento30 páginasCHP 7-Population GeneticsSIMBA The Lion KingAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 4Documento4 páginasLab 4meera frostAinda não há avaliações
- BIO140 Lect 8a Hardy WeinbergDocumento6 páginasBIO140 Lect 8a Hardy WeinbergAbigail SaballeAinda não há avaliações
- 5 Compressed Notes Population GeneticsDocumento9 páginas5 Compressed Notes Population GeneticsSYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeAinda não há avaliações
- Topic14-Part 2 - Population GeneticsDocumento15 páginasTopic14-Part 2 - Population GeneticsMarshall GorgonzolaAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Hardy-Weinberg Practice ProblemsDocumento1 páginaSolutions Hardy-Weinberg Practice ProblemsEthan J PatelAinda não há avaliações
- 5.2 BioDocumento39 páginas5.2 BioAinaa NajwaaAinda não há avaliações
- 23 Hardy WeinbergDocumento25 páginas23 Hardy WeinbergCruzAinda não há avaliações
- All BIO 4 Sem2Documento753 páginasAll BIO 4 Sem2Farith AfifiAinda não há avaliações
- Population Genetics: Tutorial 5Documento8 páginasPopulation Genetics: Tutorial 5minaAinda não há avaliações
- GeneticsDocumento5 páginasGeneticsmartinsm999Ainda não há avaliações
- Investigating Population Growth SimulationDocumento11 páginasInvestigating Population Growth Simulationapi-3823725640% (3)
- Activity 1 - Whales in TransitionDocumento5 páginasActivity 1 - Whales in Transitionapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Ecological Succession Activity With Colored PicturesDocumento11 páginasEcological Succession Activity With Colored Picturesapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Questions and Answers 1Documento7 páginasQuestions and Answers 1api-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Beach Erosion InfographicDocumento5 páginasBeach Erosion Infographicapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Classification and Kingdom ReviewDocumento3 páginasClassification and Kingdom Reviewapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Virtual Simulation Natural SelectionDocumento6 páginasVirtual Simulation Natural Selectionapi-38237256480% (5)
- Case Study ComparisonDocumento3 páginasCase Study Comparisonapi-38237256450% (2)
- Speciation ActivityDocumento5 páginasSpeciation Activityapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Complex Inheritance Pattern PracticeDocumento3 páginasComplex Inheritance Pattern Practiceapi-38237256450% (2)
- Cytogenetics Report For G-Banded KaryotypeDocumento3 páginasCytogenetics Report For G-Banded Karyotypeapi-3823725640% (1)
- The Mystery of 7th DeathsDocumento3 páginasThe Mystery of 7th Deathsapi-382372564100% (1)
- Lab Introduction To Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento3 páginasLab Introduction To Gel Electrophoresisapi-382372564100% (1)
- Ap Lab MeiosisDocumento6 páginasAp Lab Meiosisapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Data Tables For Alien Gene AnalysisDocumento3 páginasData Tables For Alien Gene Analysisapi-382372564100% (3)
- Bikini Bottom GeneticsDocumento3 páginasBikini Bottom Geneticsapi-38237256420% (5)
- Alien Translation ActivityDocumento12 páginasAlien Translation Activityapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Ap Photosynthesis LabDocumento6 páginasAp Photosynthesis Labapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Ap Cellular Respiration LabDocumento8 páginasAp Cellular Respiration Labapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Lactase Enzyme LabDocumento7 páginasLactase Enzyme Labapi-382372564100% (1)
- Constructing A Model of AtpDocumento7 páginasConstructing A Model of Atpapi-3823725640% (1)
- Molecule Building LabDocumento7 páginasMolecule Building Labapi-382372564Ainda não há avaliações
- Hand Sanitizer Soap Lab ReportDocumento6 páginasHand Sanitizer Soap Lab Reportapi-382372564100% (2)
- Vocabulary Frame GeneticsDocumento4 páginasVocabulary Frame GeneticsSonia Patricia Gomez RinconAinda não há avaliações
- Punnett Square WorksheetDocumento2 páginasPunnett Square WorksheetAlyssa ReaAinda não há avaliações
- Dihybrid Cross WorksheetsDocumento2 páginasDihybrid Cross Worksheetsapi-307565882100% (1)
- 1-OG Genetics PowerpointDocumento54 páginas1-OG Genetics PowerpointElizabeth DeanAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics ProblemsDocumento4 páginasGenetics Problemsapi-265883279Ainda não há avaliações
- Dihybrid WorksheetDocumento6 páginasDihybrid Worksheetapi-298247873Ainda não há avaliações
- Pedigree AnalysisDocumento18 páginasPedigree AnalysisSanjeet YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics Test Review Grade 8Documento3 páginasGenetics Test Review Grade 8Paui Parado EranAinda não há avaliações
- Keshav Malhotra - Dihybrid CrossDocumento3 páginasKeshav Malhotra - Dihybrid Crossneliwok622Ainda não há avaliações
- Genetics Problems - Answer Key-1Documento9 páginasGenetics Problems - Answer Key-1Sapes YtAinda não há avaliações
- PedigreeDocumento24 páginasPedigreeAnte MihaljevićAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics WebquestDocumento2 páginasGenetics WebquestMariah ElieAinda não há avaliações
- Science 9 Module 5Documento4 páginasScience 9 Module 5Cherry DerramasAinda não há avaliações
- Module 7Documento17 páginasModule 7Joana TabuenaAinda não há avaliações
- Science Activity SheetsDocumento4 páginasScience Activity SheetsRose Ann Chavez100% (1)
- Gene ManipulationDocumento46 páginasGene ManipulationFRITZ PATAWARANAinda não há avaliações
- Genetics Solution Manual - Chapter 3Documento22 páginasGenetics Solution Manual - Chapter 3amarka01Ainda não há avaliações
- 07 - Pedigree Exercise - LynnDocumento4 páginas07 - Pedigree Exercise - LynnSebastián Eduardo González BalcázarAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 3.4 WorksheetDocumento5 páginasTopic 3.4 WorksheetYixuan PENGAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 14 Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocumento9 páginasChapter 14 Mendel and The Gene IdeaJUNG LEEAinda não há avaliações
- BIO2141 Mendelian GeneticsDocumento136 páginasBIO2141 Mendelian GeneticsMelissa AkayezuAinda não há avaliações
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 3Documento23 páginasScience: Quarter 4 - Module 3Cristina AguinaldoAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Mendelian Genetics Preliminary ActivitiesDocumento7 páginas1 Mendelian Genetics Preliminary ActivitiesJenny PartozaAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan Nov 29, 2021Documento2 páginasAdobe Scan Nov 29, 2021Bryan GonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Hardy-Weinberg Homework Questions /30Documento4 páginasHardy-Weinberg Homework Questions /30LucatneoAinda não há avaliações
- "Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerDocumento5 páginas"Mendelian Genetics": General Biology 2 ReviewerFayza Jalil Balading100% (1)
- Pedigree WorksheetDocumento3 páginasPedigree Worksheetmowehe4417Ainda não há avaliações
- Genetics: Mendel and The Gene IdeaDocumento59 páginasGenetics: Mendel and The Gene IdeaRathod Sasidhar NaikAinda não há avaliações
- Spongebob Genetics 1Documento2 páginasSpongebob Genetics 1api-43582966933% (3)
- Top 3 Breeding Methods Used For Cross-Pollinated CropsDocumento16 páginasTop 3 Breeding Methods Used For Cross-Pollinated CropsPuput Kurniawan IswantoAinda não há avaliações
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNo EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (18)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNo EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (393)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNo EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNo EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (517)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNo EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessAinda não há avaliações
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNo Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (33)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNo EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeAinda não há avaliações
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNo EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNo EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (216)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorAinda não há avaliações
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNo EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (812)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNo EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (11)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperNo EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (16)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)No EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (411)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNo EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (397)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNo EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (52)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNo EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (110)
- An Eagle Named Freedom: My True Story of a Remarkable FriendshipNo EverandAn Eagle Named Freedom: My True Story of a Remarkable FriendshipAinda não há avaliações
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNo EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (65)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNo EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (595)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveNo EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (66)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignNo EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (39)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsNo EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2083)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueNo EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (38)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNo EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (115)