Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Making Art-Introduction
Enviado por
Andrea29110 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
18 visualizações7 páginasThe document discusses key elements of art including process, subject matter, point, line, shape, mass, volume, color, and space. It defines these basic elements and provides examples of how they are used in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional works of art. Specific artworks are mentioned, such as "The Crown Fountain" public sculpture in Chicago, to illustrate concepts like positive and negative space. The document also briefly introduces composition, content, and techniques for comparing and interpreting artworks.
Descrição original:
Título original
Making Art-Introduction.docx
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document discusses key elements of art including process, subject matter, point, line, shape, mass, volume, color, and space. It defines these basic elements and provides examples of how they are used in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional works of art. Specific artworks are mentioned, such as "The Crown Fountain" public sculpture in Chicago, to illustrate concepts like positive and negative space. The document also briefly introduces composition, content, and techniques for comparing and interpreting artworks.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
18 visualizações7 páginasMaking Art-Introduction
Enviado por
Andrea2911The document discusses key elements of art including process, subject matter, point, line, shape, mass, volume, color, and space. It defines these basic elements and provides examples of how they are used in both two-dimensional and three-dimensional works of art. Specific artworks are mentioned, such as "The Crown Fountain" public sculpture in Chicago, to illustrate concepts like positive and negative space. The document also briefly introduces composition, content, and techniques for comparing and interpreting artworks.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 7
Making Art: Introduction 8/19/2015 7:00:00 AM
Processes and Purposes
Process can be affected by demand
People begin to wonder what is art, and started focusing on
different aspects of art
Art becomes an event, and the canvas is the arena
Subject Matter and Meaning
Nonrepresentational art—does not represent anything
Representational art—art that depicts something
Illusionistic—
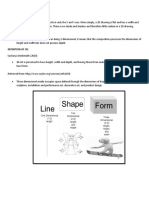
Point, Line, Shape, Mass, Volume, and Color 8/19/2015 7:00:00 AM
What are design elements?
What is composition/design principles?
Point—dot or small, circular shape
Line
Can be actual or implied
Geometrical or gestural
Hatching and crosshatching
Lines can be used to create texture
Lines can give the appearance of weight
Lines can move our eyes and through the intentionally chaotic
constructed space of a sculpture
Shape—can be actual or implied
Shapes are two-dimensional areas with defined or implied
boundaries that can be measured by height and width
Boundary of a shape defined by a line or implied by a difference in
texture or color
Positive and negative shape—when one shape is dominant, it may
be called positive shape and the surrounding shape is called
negative shape
Amorphous shapes lack clarity or precise distinction and are of
uncertain dimension with edges that are difficult to determine
Mass
The illusion of mass may be present in a two-dimensional image
Color
The haystack isn’t important so much as the different color schemes that
represent the changing seasons
Additive Color Processes
Adding colored lights together
Subtractive Color Processes—the mixing of pigments and dies, paints
and material colorants
Polychromatic—a color image that employs a wide range of colors in a
variety of values
Simultaneous Contrast
Two colors, side by side, interact with one another
When complements are placed next to one another, they appear more
intense
Space 8/19/2015 7:00:00 AM
Space is a design element. Places, structures and objects with height,
width, and depth and for creating the illusion of three dimensions on 2-D
surfaces
Actual Space—an expanse with depth, height, and width that surrounds
an object or that an object or that an object occupies
Reliefs often create positive and negative space
2-D Space—bound by height and width; however, spatial illusion is
possible
architectural Space, public sculpture—enhance the quality of life for those
who use it
“The Crown Fountain”—the faces depicted in videos on the glass block
towers are Chicagoans, over a reflecting pool of water
Positive and Negative Space
Virtual Space
Technology allows artists to work with virtual space
A computer constructed environment that appears three
dimensional, allows viewers experiences that seem real
Illusional Space
Indicators of Illusional Space
Foreground, middle ground, background
Size
Overlap
Transparency
Placement
Shakes and shadows
Detail, texture, and pattern
Perspective
Size—nearer is larger
Composition 8/19/2015 7:00:00 AM
How are design elements arranged?
Rococo—time of transition
Content—refers to the themes, values, or ideas in a work of art, so distinct
from its form
Comparison and Interpretation 8/19/2015 7:00:00 AM
8/19/2015 7:00:00 AM
Você também pode gostar
- More Tapestry Crochet - Digital - Ventura, CarolDocumento311 páginasMore Tapestry Crochet - Digital - Ventura, CarolPamela Wilkinson100% (9)
- Vocabulary For Visual ArtsDocumento9 páginasVocabulary For Visual ArtsEnrique del CerroAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Drawing by N.D BhattDocumento738 páginasEngineering Drawing by N.D BhattJagadish90% (48)
- Making Copper JewelryDocumento15 páginasMaking Copper Jewelrysimalaura100% (1)
- Teaching Arts ConceptsDocumento40 páginasTeaching Arts Conceptsangel84% (19)
- Performs Basic Exploded Assembly DrawingsDocumento22 páginasPerforms Basic Exploded Assembly DrawingsJOSEPH ONGAinda não há avaliações
- Module Creative Industries PDFDocumento306 páginasModule Creative Industries PDFElla Marie MonteAinda não há avaliações
- Composition and ElementsDocumento32 páginasComposition and ElementssnehaAinda não há avaliações
- Elements 2fprinciples of DesignDocumento4 páginasElements 2fprinciples of Designapi-438083956Ainda não há avaliações
- Elements of DesignDocumento15 páginasElements of DesignnandantharejaAinda não há avaliações
- Time. Examples of Auditory Art Include Music and Poetry.: Auditory Art Is Art That Is Heard at One ParticularDocumento4 páginasTime. Examples of Auditory Art Include Music and Poetry.: Auditory Art Is Art That Is Heard at One Particularnickie jane gardoseAinda não há avaliações
- New Art Around the World Surveys Post-War Developments in Painting and Sculpture GloballyDocumento520 páginasNew Art Around the World Surveys Post-War Developments in Painting and Sculpture GloballyJose Muñoz100% (2)
- Elements of Art and Principles of DesignDocumento52 páginasElements of Art and Principles of DesignLovely JayAinda não há avaliações
- Art Element Principles of Design DefinitionsDocumento4 páginasArt Element Principles of Design Definitionssurafel jaraAinda não há avaliações
- Elements and Principles of ArtsDocumento31 páginasElements and Principles of Artsreynaldo antonioAinda não há avaliações
- ART 6: Art Processes, Elements, and Principles Applied in New TechnologiesDocumento34 páginasART 6: Art Processes, Elements, and Principles Applied in New TechnologiesRey Mark RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Transform your walls into works of art with Jotun Majestic Design paintDocumento20 páginasTransform your walls into works of art with Jotun Majestic Design paintJefry MarkusAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of Art & DesignDocumento24 páginasElements of Art & DesignSatish BAinda não há avaliações
- English As A Second Language Paper 2 Listening: Stage 5Documento6 páginasEnglish As A Second Language Paper 2 Listening: Stage 5Francesco CiocciAinda não há avaliações
- Art AppreciationDocumento24 páginasArt AppreciationRajz UyAinda não há avaliações
- How to Appreciate Art Through Elements, Principles, and PsychologyDocumento43 páginasHow to Appreciate Art Through Elements, Principles, and PsychologyMark Lawrence ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Art AppreciationDocumento46 páginasArt AppreciationNickie Jane GardoseAinda não há avaliações
- Elements and Principle of ArtsDocumento33 páginasElements and Principle of ArtsAljay Singian SalengaAinda não há avaliações
- Gift WrappingDocumento17 páginasGift WrappingDiana de castroAinda não há avaliações
- Art Appreciation Module 3 The Subjects and Elements of ArtDocumento3 páginasArt Appreciation Module 3 The Subjects and Elements of ArtVernadel Apollo100% (1)
- Foxy Crochet ROCKY THE SLEEPING BUNNYDocumento9 páginasFoxy Crochet ROCKY THE SLEEPING BUNNYana100% (4)
- Visual Media and Information: A GuideDocumento52 páginasVisual Media and Information: A Guidetyron plandes100% (2)
- Elements of Fusion, Interrelated and OverlappingDocumento5 páginasElements of Fusion, Interrelated and OverlappingRaynie Rodelas67% (9)
- Grade 12 ReviewerDocumento4 páginasGrade 12 ReviewerKyleen VinluanAinda não há avaliações
- How Elements of Art Shape CreativityDocumento5 páginasHow Elements of Art Shape CreativityMae GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Art AppreciationDocumento12 páginasArt AppreciationJoeciel ValeraAinda não há avaliações
- Art App. Group 1 ReportDocumento43 páginasArt App. Group 1 ReportChris MacaraegAinda não há avaliações
- S5 Studio notesDocumento16 páginasS5 Studio notesMwebembezi GodwinAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Visual Art ReviewerDocumento7 páginasReading Visual Art ReviewerJun Francis TabusaoAinda não há avaliações
- LAS Arts 6 Q2 W1Documento5 páginasLAS Arts 6 Q2 W1Darwin Ignacio DI ChannelAinda não há avaliações
- Crea 2110Documento141 páginasCrea 2110DryZlaAinda não há avaliações
- Composition (Visual Arts) : The Art of PaintingDocumento33 páginasComposition (Visual Arts) : The Art of PaintingerokuAinda não há avaliações
- Art Appreciation ActivityDocumento2 páginasArt Appreciation ActivityJohn Warren MestiolaAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Art Elements and PrinciplesDocumento11 páginasDigital Art Elements and PrinciplesMatt The idkAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2 Art Elements and Principle Group 1Documento5 páginasLesson 2 Art Elements and Principle Group 1Regine QuijanoAinda não há avaliações
- UntitledDocumento19 páginasUntitledJuliane keith MartinAinda não há avaliações
- Arts For Elem LectureDocumento18 páginasArts For Elem LectureJoyce AgustinAinda não há avaliações
- Artapp Module 03 Elements of ArtsDocumento11 páginasArtapp Module 03 Elements of ArtsKent Maloloy-onAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment in Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionDocumento2 páginasAssignment in Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionJullie SolanoAinda não há avaliações
- SESSION-1 Mapeh 10Documento33 páginasSESSION-1 Mapeh 10LEAH MARIEAinda não há avaliações
- Art TypesDocumento25 páginasArt TypesKapil SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Depth and VolumeDocumento5 páginasDepth and VolumeSajid HolyAinda não há avaliações
- Art Appreciation BlehDocumento4 páginasArt Appreciation Blehjay rickAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Design Is About Creating and Making The General Aesthetics of A Product ConsistentDocumento10 páginasVisual Design Is About Creating and Making The General Aesthetics of A Product Consistentsha catsAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of Art Are Stylistic Features That Are inDocumento3 páginasElements of Art Are Stylistic Features That Are injeziel dolorAinda não há avaliações
- Contemporary Arts LectureDocumento12 páginasContemporary Arts Lecturemomo momoAinda não há avaliações
- AA - Principles of ArtDocumento2 páginasAA - Principles of ArtHiledeAinda não há avaliações
- BA0005L ModulesDocumento32 páginasBA0005L ModulesMathieu Zeph EstacionAinda não há avaliações
- E Tech Module2 Word PDFDocumento14 páginasE Tech Module2 Word PDFTomori MoAinda não há avaliações
- Art HistoryDocumento44 páginasArt HistoryMoises Rodriguez0% (1)
- Visual MediaDocumento20 páginasVisual MediaRobel ManaloAinda não há avaliações
- Elements of ArtDocumento53 páginasElements of ArtRina PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- HumanitiesDocumento61 páginasHumanitiesKhate Tria De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- The Visual Language Handouts EditedDocumento8 páginasThe Visual Language Handouts EditedLara Concepcion CabigoAinda não há avaliações
- Humanities 1 - Principles of ArtDocumento7 páginasHumanities 1 - Principles of Artmarangen125100% (3)
- 2a 2d Design Introduction PDFDocumento11 páginas2a 2d Design Introduction PDFVijay VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Article On Elements of ArtDocumento11 páginasArticle On Elements of ArtDherry's Jhean Batara BalisiAinda não há avaliações
- AAP Reviewer 2ND QuarterDocumento9 páginasAAP Reviewer 2ND QuarterDesiree BermeoAinda não há avaliações
- Visual Information and MediaDocumento22 páginasVisual Information and MediaIrish MiguelAinda não há avaliações
- Creative Imagination, Especially in The Production of Decorative Objects." However, The ThingDocumento4 páginasCreative Imagination, Especially in The Production of Decorative Objects." However, The ThingHyde ParkAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 6Documento16 páginasLecture 6Ahmed NasserAinda não há avaliações
- Reviwer MApehDocumento16 páginasReviwer MApehMary Rose CalamayanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction to Art, Craft and Design ElementsDocumento51 páginasIntroduction to Art, Craft and Design ElementsClifford Mwanja100% (1)
- The Elements of ArtDocumento7 páginasThe Elements of ArtAeleu JoverzAinda não há avaliações
- North Africa and Southwest AsiaDocumento4 páginasNorth Africa and Southwest AsiaAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Portfolio Entry #4 Due December 8, 2015 What Is Art For?Documento2 páginasPortfolio Entry #4 Due December 8, 2015 What Is Art For?Andrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Discussion JournalDocumento3 páginasDiscussion JournalAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- The Pacific RealmDocumento14 páginasThe Pacific RealmAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- North Africa and Southwest AsiaDocumento4 páginasNorth Africa and Southwest AsiaAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Medieval ArtDocumento3 páginasMedieval ArtAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- HW 11Documento2 páginasHW 11Andrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Medieval ArtDocumento3 páginasMedieval ArtAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Making Art IntroductionDocumento3 páginasMaking Art IntroductionAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Comparison WK SheetDocumento2 páginasComparison WK SheetAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- MuseumsDocumento1 páginaMuseumsAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Asia NotesDocumento18 páginasAsia NotesAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Poetry Response "The Convergence of The Twain"Documento2 páginasPoetry Response "The Convergence of The Twain"Andrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Describes Describes Demonstrating CollideDocumento2 páginasDescribes Describes Demonstrating CollideAndrea2911Ainda não há avaliações
- CHLOE It en Poliform 0 Cat30b79e67Documento4 páginasCHLOE It en Poliform 0 Cat30b79e67mohamed abdelwahabAinda não há avaliações
- Hotel Thilanka Restaurant & Parking 01-03-2016Documento8 páginasHotel Thilanka Restaurant & Parking 01-03-2016Dinuka MalinthaAinda não há avaliações
- M3M Latitude Gurgaon 9871424442 Sector 65 GurgaonDocumento13 páginasM3M Latitude Gurgaon 9871424442 Sector 65 GurgaonSaxenaramanAinda não há avaliações
- Coach Carl JohnsonDocumento1 páginaCoach Carl Johnsonscriber9Ainda não há avaliações
- CREATIVE WRITING HandoutsDocumento12 páginasCREATIVE WRITING HandoutsRussel AporboAinda não há avaliações
- Senior Project Proposal FormDocumento3 páginasSenior Project Proposal FormkAinda não há avaliações
- Buddy DoyleDocumento2 páginasBuddy DoyleAntonio DekoAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Review 2010Documento13 páginasAnnual Review 2010ArtlinkEdinburghAinda não há avaliações
- Test 1: GRE Real 19Documento6 páginasTest 1: GRE Real 19pe_ter_panAinda não há avaliações
- Fall 2014 Class ScheduleDocumento6 páginasFall 2014 Class SchedulekbdsinfoAinda não há avaliações
- Information About Louis Welsh's The Cutting RoomDocumento13 páginasInformation About Louis Welsh's The Cutting RoomMalena BerardiAinda não há avaliações
- Giovanni Sforza President and DesignerDocumento86 páginasGiovanni Sforza President and DesignerHalil YamanAinda não há avaliações
- NEW Products FOR 2019: America'S Leading Manufacturer of Innovative Water-Based Wood FinishesDocumento12 páginasNEW Products FOR 2019: America'S Leading Manufacturer of Innovative Water-Based Wood Finishesalattar98Ainda não há avaliações
- A619864s0 RevDocumento1 páginaA619864s0 RevWill MermaAinda não há avaliações
- TextileDocumento31 páginasTextileRalucaFlorentinaAinda não há avaliações
- HinamatsuriDocumento3 páginasHinamatsuripungky_wahyuAinda não há avaliações
- 182758why The Biggest "Myths" About Average Cost For Popcorn Ceiling Removal May Actually Be RightDocumento5 páginas182758why The Biggest "Myths" About Average Cost For Popcorn Ceiling Removal May Actually Be RightpbauchbiyqAinda não há avaliações
- Toon Artist - GuideDocumento8 páginasToon Artist - GuideTettsAinda não há avaliações
- San Diego Art Institute Journal May/June 2010Documento8 páginasSan Diego Art Institute Journal May/June 2010MediaAinda não há avaliações
- TLE 7 Second Periodical Exam. 2023-2024Documento3 páginasTLE 7 Second Periodical Exam. 2023-2024Kate AzucenaAinda não há avaliações