Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Basic Electrical Symbols
Enviado por
Michelle Mendoza0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
17 visualizações4 páginasf
Título original
nhhh
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentof
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
17 visualizações4 páginasBasic Electrical Symbols
Enviado por
Michelle Mendozaf
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
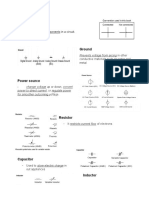
BASIC ELECTRICAL SYMBOLS
1. Earth Electrode - is a metal plate, water pipe, or other conductor of electricity
partially buried in the earth so as to constitute and provide a reliable
conductive path to the ground.
2. Cell - is a device containing electrodes immersed in an electrolyte, used for
generating current or for electrolysis.
3. Battery - is a container consisting of one or more cells, in which chemical energy
is converted into electricity and used as a source of power.
4. Source - is a part of a field-effect transistor from which carriers flow into the
inter-electrode channel.
5. Ideal Source - An ideal source is a theoretical concept of an electric current or
voltage supply (such as a battery) that has no losses and is a perfect
voltage or current supply.
6. Resistor - is a device having resistance to the passage of an electric current.
7. Capacitor - is a device used to store an electric charge, consisting of one or more
pairs of conductors separated by an insulator.
8. Antenna - is an electrical device which converts electric power into radio waves,
and vice versa.
9. Switch Open - is a device for making and breaking the connection in an electric
circuit.
10. Switch Closed - is a device for making and breaking the connection in an electric
circuit.
11. Rotary Switch - is a switch operated by rotation.
12. Open pushbutton - is a push button that makes no electrical contact with the
circuit.
13. Closed pushbutton - is a push button that makes electrical contact with the
circuit.
14. Isolator - is a mechanical switch which isolates a part of circuit from system as
when required.
15. SPST - is a single-pole, single-throw (SPST) switch.
16. SPDT - is single-pole, double-throw (SPDT) switch.
17. DPST - is double-pole, single-throw(DPDT) switch.
18. DPDT - is a double-pole, double-throw (DPDT) switch.
19. Wire - is used to connect the components in a circuit.
20. Test Point - is a location within an electronic circuit that is used to either monitor
the state of the circuitry or to inject test signals.
21. Outward Flow - means flowing outwardly, so inward flow means flowing
inwardly.
22. Electric Motor - is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into
mechanical energy.
23. Potentiometer - is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that
forms an adjustable voltage divider.
24. Attenuator - a device consisting of an arrangement of resistors that reduces the
strength of a radio or audio signal.
25. Three Phase Electric Motor - is a common method of alternating current electric
power generation, transmission, and distribution.
26. Piezoelectric crystal - is the electric charge that accumulates in certain solid
materials
27. Relay - is an electrically operated switch.
28. Electromagnet - is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by
an electric current.
29. Commutator - a device for reversing the direction of flow of electric current.
30. Push button - a button that is pushed to operate an electrical device.
31. Vacuum tube - an electron tube containing a near-vacuum that allows the free
passage of electric current.
32. Anode - the positively charged electrode by which the electrons leave a device.
33. Cathode - the negatively charged electrode by which electrons enter an electrical
device.
34. NPN Transistor - A transistor used to control a high-power LED
35. PNP Transistor – A transistor that use a small base current
36. Phototransistor - is a device that is able to sense light levels and alter the current
flowing between emitter and collector according to the level of light it
receives.
37. Schottky Transistor - is a combination of a transistor and a Schottky diode that
prevents the transistor from saturating by diverting the excessive input
current.
38. Rheostat - an electrical instrument used to control a current by varying the
resistance.
39. Photoresistor - is a light-controlled variable resistor.
40. Thermistor - an electrical resistor whose resistance is greatly reduced by heating,
used for measurement and control.
41. Light bulb - is an electric light with a wire filament heated to such a high
temperature that it glows
42. Oscillatory lamp - is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating
electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave
43. Output Lamp - used for lighting
44. Diode - a semiconductor device with two terminals, typically allowing the flow of
current in one direction only.
45. Zener diode - a form of semiconductor diode in which at a critical reverse voltage
a large reverse current can flow.
46. Schottky diode - is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a
semiconductor with a metal.
47. Tunnel Diode - a two-terminal semiconductor diode using tunneling electrons to
perform high-speed switching operations.
48. Fuse - is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent
protection of an electrical circuit.
49. Circuit Breaker - an automatic device for stopping the flow of current in an
electric circuit as a safety measure.
50. Delay - is energized by means of a pulse into the control circuit in an electrically
controlled time-delay switch
51. Inductor/Coil - a component in an electric or electronic circuit that possesses
inductance.
52. Variable Inductor - movable element which may be adjusted to different
positions or adjusted to vary its physical dimensions to change the
effective inductance from one value to another.
53. Buzzer - audio signaling device
54. Speaker – used as a sound amplifier
55. Variable capacitor - is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and
repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically
56. Electrolytic Capacitor - is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is
made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization.
57. Transformer - is a static electrical device that transfers electrical energy between
two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction.
58. Oscillator - a device for generating oscillating electric currents or voltages by
nonmechanical means.
59. Amplifier - is an electronic device that can increase the power of a signal
60. Timer IC-555 - is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, pulse
generation, and oscillator applications
61. Thyristor SCR - is a four-layer (P-N-P-N) semiconductor device that contains
three PN junctions in series and is represented by the symbol as shown.
62. Diac - is a full-wave or bi-directional semiconductor switch that can be turned on
in both forward and reverse polarities.
63. Power Converter – is an electrical or electro-mechanical device for converting
electrical energy.
64. Inverter - is an electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to
alternating current (AC)
65. Bridge Rectifier - uses four individual rectifying diodes connected in a closed loop
“bridge” configuration to produce the desired output.
66. Wrench - turns nuts, bolts, pipes, etc.
67. Screwdriver - used for the turning the screws
68. Drill - designed to drill holes and drive screws
69. Cutter/ Utility Knife - designed to cut wood, cardboard, and other materials.
70. Drill bits – is a cutting tool which is used to create holes.
References:
https://www.edrawsoft.com/basic-electrical-symbols.php
https://www.electrical-symbols.com/electric-electronic-symbols/electrical-
symbols.htm
Merriam Webster Dictionary
https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/power/thyristor.html
https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/diode/diode_6.html
https://interestingengineering.com/10-tools-every-engineer-fix-things
Você também pode gostar
- Electronic Components - Functions& SymbolsDocumento3 páginasElectronic Components - Functions& SymbolsGil Nacario91% (58)
- ServiceNow Certified System AdministratoDocumento19 páginasServiceNow Certified System Administratocamis_vieiraAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics Mini Dictionary by GadgetronicxDocumento49 páginasElectronics Mini Dictionary by GadgetronicxObby JhonAinda não há avaliações
- Resistor Capacitor Inductor Transistor DiodeDocumento2 páginasResistor Capacitor Inductor Transistor Diodelekz re100% (2)
- ByD DemoScript Project MGMTDocumento21 páginasByD DemoScript Project MGMTLakhbir SinghAinda não há avaliações
- 200 Basic Electronic Terms FinalDocumento8 páginas200 Basic Electronic Terms FinalShairyl Ü TablanteAinda não há avaliações
- DEFINITIONSDocumento6 páginasDEFINITIONSRaymond Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Dictionary of Terms in ElectronicsDocumento7 páginasDictionary of Terms in ElectronicsIrza Aditya MahendraAinda não há avaliações
- A Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToDocumento2 páginasA Double Pole Double Throw (DPDT) Switch Is A Switch That Has 2 Inputs and 4 Outputs Each Input Has 2 Corresponding Outputs That It Can Connect ToPaulo Taganas MendiolaAinda não há avaliações
- Ee Def & TermsDocumento16 páginasEe Def & TermsRaymond John PeruchoAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical ComponentsDocumento5 páginasElectrical ComponentsJohn Damever BalanquitAinda não há avaliações
- Electronic ComponentDocumento1 páginaElectronic ComponentJedediah D. MagannonAinda não há avaliações
- CT PeriodicDocumento2 páginasCT PeriodicJ.P. SumandoAinda não há avaliações
- Bu RSW 1 and 2Documento7 páginasBu RSW 1 and 2ANGELU MARIE GUMIRANAinda não há avaliações
- SimbolDocumento26 páginasSimboldrion67Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronic ComponentsDocumento6 páginasElectronic ComponentsEmey SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical MaterialsDocumento2 páginasElectrical MaterialsAira Acob MagnoAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical and ElectronicsDocumento3 páginasElectrical and Electronicsmaddie demecilloAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsDocumento6 páginasExperiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsAdesh Bhortakke100% (2)
- FEEEDocumento56 páginasFEEEnetra msajjan100% (1)
- Tugas Minggu 12Documento10 páginasTugas Minggu 12Juliyanti HasibuanAinda não há avaliações
- Substation, Electrical EngineeringDocumento21 páginasSubstation, Electrical EngineeringayushiborkarAinda não há avaliações
- Interview QuestionsDocumento3 páginasInterview QuestionsJeevaAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical SystemDocumento16 páginasElectrical SystemCjoy MañiboAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.Documento7 páginasDefinition of Electrical Terms and Electrical Units.julianaquino1203Ainda não há avaliações
- Electronic Materials-G5Documento15 páginasElectronic Materials-G5Joana MendoAinda não há avaliações
- Familiarization of Electrical DevicesDocumento14 páginasFamiliarization of Electrical DevicesJerome BricenioAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical EngineeringDocumento7 páginasStudy of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical Engineeringnational printersAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ElectronicsDocumento10 páginasBasic ElectronicsFrancess Mae AlonzoAinda não há avaliações
- Paraskevi Hofioni - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocumento20 páginasParaskevi Hofioni - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525648840Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of Diagram and SymbolsDocumento7 páginasTypes of Diagram and SymbolsPrince John Rabano100% (1)
- Electronic Components Functions Amp Symbols PDFDocumento3 páginasElectronic Components Functions Amp Symbols PDFCrichelleMaeAinda não há avaliações
- Building UtilitiesDocumento89 páginasBuilding Utilitiesalezandro del rossiAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principal of Electrical CircuitryDocumento19 páginasBasic Principal of Electrical CircuitryAreeba ParvezAinda não há avaliações
- SCIENCE m15Documento2 páginasSCIENCE m15vidal.keith011006Ainda não há avaliações
- Circuits WordDocumento2 páginasCircuits WordPatrick GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Resistors: PotentiometerDocumento48 páginasResistors: PotentiometerjojoAinda não há avaliações
- Electronics SymbolsDocumento7 páginasElectronics SymbolsStudy SharyAinda não há avaliações
- Power ElexDocumento38 páginasPower ElexTin PelingonAinda não há avaliações
- TP Elec PDFDocumento3 páginasTP Elec PDFchroeun sokayAinda não há avaliações
- Export DocumentDocumento37 páginasExport DocumentEunjeru EspedidoAinda não há avaliações
- Electric Circuit - An Electrical Device That Provides A Path For Electrical CurrenDocumento1 páginaElectric Circuit - An Electrical Device That Provides A Path For Electrical CurrenUda PieAinda não há avaliações
- Ed Lab Manual-2Documento82 páginasEd Lab Manual-2Akhil VinnakotaAinda não há avaliações
- Electro 1 Student FileDocumento6 páginasElectro 1 Student FileHarveyBidañaAinda não há avaliações
- 11Б electricians second lessonDocumento6 páginas11Б electricians second lessondilyana666Ainda não há avaliações
- P.E.S. College of Engineering, Aurangabad.: Project ReportDocumento25 páginasP.E.S. College of Engineering, Aurangabad.: Project ReportShaikh Ibrahim0% (1)
- Electric Circuit and Circuit ElementsDocumento12 páginasElectric Circuit and Circuit ElementsDr-Eng Amir ElsafraweyAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Electronics NotesDocumento5 páginasBasic Electronics NotesRolando Carlos FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Electronics: "2 Sample Circuits"Documento3 páginasBasic Electronics: "2 Sample Circuits"Jove TumimbangAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of Electrical TermDocumento2 páginasDefinition of Electrical TermLuis Carlos100% (1)
- Cabt 10Documento15 páginasCabt 10محمد خالدAinda não há avaliações
- Electricity & ElectronicsDocumento82 páginasElectricity & ElectronicsCassandra Noreen Pacayra SantosAinda não há avaliações
- Task Performanc E IN T.L.E.: Balmores, Jose Pascual P. Gr. 8 - OLHTDocumento4 páginasTask Performanc E IN T.L.E.: Balmores, Jose Pascual P. Gr. 8 - OLHTErika BalmoresAinda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Documento6 páginasPower Electronics: Semester 7 Electronics Engineering: What Is Power Electronics and Explain Its Block Diagram?Asha DurafeAinda não há avaliações
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocumento12 páginasEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical System Component-AkpDocumento6 páginasElectrical System Component-Akpvirgilio ayadAinda não há avaliações
- Workshop Practice IIDocumento8 páginasWorkshop Practice IISurendra GhalanAinda não há avaliações
- Utilities Assignment 1 1Documento5 páginasUtilities Assignment 1 1Ernest VincentAinda não há avaliações
- BLE - Module 4Documento139 páginasBLE - Module 4David ManiAinda não há avaliações
- Eee221 (SR) PPDocumento15 páginasEee221 (SR) PPMehedi HasanAinda não há avaliações
- HahshshshDocumento2 páginasHahshshshMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 2 Help - 2Documento5 páginasCH 2 Help - 2Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Publication 2Documento1 páginaPublication 2Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Layout - Lab PDFDocumento1 páginaLayout - Lab PDFMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Forms CoverPageDocumento1 páginaForms CoverPageMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell SiteDocumento10 páginasCell SiteLgu SikatunaAinda não há avaliações
- Plate 2Documento7 páginasPlate 2Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- FORDDocumento8 páginasFORDMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- LABSA ProposalDocumento10 páginasLABSA ProposalMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- PD Ca (ClO) 2Documento3 páginasPD Ca (ClO) 2Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento2 páginasAssignment 1Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Front Page - EmagsDocumento5 páginasFront Page - EmagsMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Highlighted - For Enbal Equation 18 - ADocumento8 páginasHighlighted - For Enbal Equation 18 - AMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Packed Bed SO3Documento112 páginasPacked Bed SO3Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- GHJKDocumento79 páginasGHJKMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Design ScheduleDocumento2 páginasPlant Design ScheduleMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Abdul Equip ListDocumento1 páginaAbdul Equip ListMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- LABSA Storage TankDocumento3 páginasLABSA Storage TankMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation 1Documento3 páginasPresentation 1Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation 1Documento3 páginasPresentation 1Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Cruz, Carl David C. HUM 002 - 9:00 TTHDocumento2 páginasCruz, Carl David C. HUM 002 - 9:00 TTHMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Labsa ParametersDocumento2 páginasLabsa ParametersMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Water Supply QualityDocumento35 páginasWater Supply QualityMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Abstract Castor Oil BackupDocumento1 páginaAbstract Castor Oil BackupMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Plant Design ScheduleDocumento2 páginasPlant Design ScheduleMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Process1 DraftDocumento11 páginasProcess1 DraftMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Labsa RefDocumento1 páginaLabsa RefMichelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- PhilippinesDocumento29 páginasPhilippinesVenus Cartagena100% (1)
- PD Ca (ClO) 2Documento3 páginasPD Ca (ClO) 2Michelle MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- 5751-1957 Hydrographic Surveying PDFDocumento85 páginas5751-1957 Hydrographic Surveying PDFMichelle Mendoza100% (1)
- Architectural Design Case Studies: Useful Online ResourcesDocumento3 páginasArchitectural Design Case Studies: Useful Online Resourcesnysidlibrary100% (1)
- AutoCAD NotesDocumento17 páginasAutoCAD NotesKriss_PsAinda não há avaliações
- Data-Driven and Physics-Informed Deep Learning Operators For Solution of Heat Conduction EquationDocumento8 páginasData-Driven and Physics-Informed Deep Learning Operators For Solution of Heat Conduction EquationStephen PanAinda não há avaliações
- VPLS Autodiscovery BGP Based-CiscoDocumento34 páginasVPLS Autodiscovery BGP Based-Ciscokirantbhat19834099Ainda não há avaliações
- Huawei LTE ENodeB CabinetsDocumento41 páginasHuawei LTE ENodeB CabinetsSyed Mohsin Ghani100% (1)
- CSS Border Properties: ST NDDocumento11 páginasCSS Border Properties: ST NDSubhadeep PandaAinda não há avaliações
- Steps To Replace Spare Parts of KX5600Documento5 páginasSteps To Replace Spare Parts of KX5600Freire Jose FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- Azure DevOps - User CreationDocumento68 páginasAzure DevOps - User CreationInge SmitAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Conceptualized InteractionDocumento32 páginasChapter 2 Conceptualized InteractionnancyAinda não há avaliações
- EE 6351 - Electrical Drives and Controls (EDC) QBDocumento160 páginasEE 6351 - Electrical Drives and Controls (EDC) QBkannanchammyAinda não há avaliações
- Acquisition Plan Template - Updated 9.1.21Documento19 páginasAcquisition Plan Template - Updated 9.1.21Edgar De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Control RoomDocumento24 páginasControl Roomsarsan nedumkuzhi maniAinda não há avaliações
- Key Brand Elements: How-To GuideDocumento7 páginasKey Brand Elements: How-To GuideDemand MetricAinda não há avaliações
- Amesim English s01Documento20 páginasAmesim English s01Chetan P BhatAinda não há avaliações
- Slide Sosialisasi PULDATANDocumento52 páginasSlide Sosialisasi PULDATANKJSB LALU UBAI ABDILLAH - PHLN 2022Ainda não há avaliações
- Subject: Technical and Cost Proposal of Online Manpower Management System IntegratedDocumento12 páginasSubject: Technical and Cost Proposal of Online Manpower Management System IntegratedMainuddin BhuiyanAinda não há avaliações
- Gbat V Mock (3) IctDocumento8 páginasGbat V Mock (3) Ictfeddy anddy0% (1)
- 06944eb5513ef244ec882693720db20aDocumento409 páginas06944eb5513ef244ec882693720db20aRatanieri0% (1)
- Rre Ry Ry1 A2a MP014 Pe CH STX B01 DWG 00901Documento1 páginaRre Ry Ry1 A2a MP014 Pe CH STX B01 DWG 00901md_rehan_2Ainda não há avaliações
- 29-CHT06 Honda Steering Wheel ControlDocumento4 páginas29-CHT06 Honda Steering Wheel Controlalexandre fleureauAinda não há avaliações
- Week8 HomeworkDocumento3 páginasWeek8 Homeworkyashar2500Ainda não há avaliações
- Diploma in Information Technology Coursework: Subject: Web Design Subject Code: DIT2283Documento15 páginasDiploma in Information Technology Coursework: Subject: Web Design Subject Code: DIT2283Karthigeyan SenthanAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Accounting Tables Used in Business Planning and Consolidation NW 10.0Documento20 páginasFinancial Accounting Tables Used in Business Planning and Consolidation NW 10.0SarathBabu BandarupalliAinda não há avaliações
- EWM Transaction CodesDocumento22 páginasEWM Transaction CodesChuks Osagwu100% (1)
- Curso Mantenimiento HyPET HPP4Documento230 páginasCurso Mantenimiento HyPET HPP4FabianQuitianAinda não há avaliações
- Month: January 2020 Cash BookDocumento9 páginasMonth: January 2020 Cash BookAbidAinda não há avaliações
- 701MRF de PDFDocumento92 páginas701MRF de PDFPetros TsenesAinda não há avaliações
- Control Systems (CS) : Lecture-17 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionDocumento18 páginasControl Systems (CS) : Lecture-17 Routh-Herwitz Stability CriterionAdil KhanAinda não há avaliações