Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Effect of Carbon Dioxide On The Performance of Spark Ignition Engine by Hydrogen Inject With Biogas Fuel
Enviado por
Editor IJTSRDTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Effect of Carbon Dioxide On The Performance of Spark Ignition Engine by Hydrogen Inject With Biogas Fuel
Enviado por
Editor IJTSRDDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
International Journal of Trend in Scientific
Research and Development (IJTSRD)
International Open Access Journal
ISSN No: 2456 - 6470 | www.ijtsrd.com | Volume - 2 | Issue – 4
Effect of carbo
carbonn dioxide on the performance of
Spark Ignition Engine by Hydrogen Inject with Biogas Fuel
Keyur D. Patel
Depart
Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Vad
Vadodara Institute of Engineering,
Kotambi
Kotambi, Vadodara, Gujarat, India
ABSTRACT
Methane and carbon dioxide are the two main as some ash. These waste materials have hazardous
constituents of biogas. One of the reasons of poor effects on the environment, some of them locally,
combustion is the presence of carbon dioxide in the others with more widespread or even global impact.
biogas. Biogas also has traces of nitrogen, hydrogen, Not only does the continued use of large amounts of
oxygen and hydrogen sulphide. Because of a high fossil fuels pose a serious threat to the environment,
investment cost and a heavy infrastructure, only fifty but also the fuels themselves are finite in quantity.
percent of the biogas production upgrades (decrease There are debates amongst experts expe about the
CO2%) by use of water scrubber. so the natural gas extractable amount of fossil fuels. General opinion is
replacement is very ery low. This experiment is that in the beginning of the 21st century almost half of
conducted on modified single cylinder 97.5cc petrol the fossil fuels had already been consumed. The
engine, to work it as a biogas-hydrogen
hydrogen fuel spark known worldwide reserves of petroleum are 1000
ignition engine. Hydrogen added in small amounts billion barrels and these Petroleum reserves are
by HHO generator (hydroxy) kit to decrease predicted to be consumed in about 40 years. Another
concentration of CO2 in biogas power wer and find out problem with petroleum is the emission of pollutants,
the effect of CO2 on the performance. The such as CO2, NOx, CO and hydrocarbons (HC). So,
experimental results show that the large quantity of the world had to search for other sources of fuel and
CO2 present in biogas lowers its calorific value, flame now a day the most useful and eco-friendly
eco source are
velocity and flammability range compared with gaseous fuels.Gaseous fuels have wide flammability
natural gas. So it can be utilized in an IIC engine with limits and can easily form a homogeneous mixture
the hydrogen. with air for good combustion. Thus they will lead to
very low levels of pollutants and can be effectively
Keywords:: Biodiesel, Hydrogen, SI engine, HHO, B
Bio utilized in both spark ignition (SI) and compression
fuel ignition (CI) engines. Moreover, gaseous fuels have
high hydrogen to carbon ratios. Thus very low CO2
I. INTRODUCTION emissions are possible when they are used in IC
In the 20th century, world energy usage has increased Engines. Natural gas and Liquefied Petroleum Gas
significantly
ficantly due to the effect of industrialization, and (LPG) are the readily available petroleum-based
pe fuels,
this increase in usage has resulted in limited while hydrogen, biogas and producer gas can be
petroleum reserves, such as the 1970’s oil crisis [1]. obtained from renewable sources. Renewable fuels
Most of the energy used in the world is sup supplied by will not affect the net CO2 in the environment.Biogas
fossil fuels. Burning of the fossil fuels generates is an attractive source of energy for rural areas. It can
waste materials, mainly emissions to the atmosphere be produced from cow dung and a other animal waste
in the form of combustion fuel gases and dust, as well and also from plant matter such as leaves and water
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 4 | May-Jun
Jun 2018 Page: 78
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) ISSN: 2456-6470
hyacinth – all of which are renewable and available in Biogas cannot be used to run an IC engine directly on
the countryside. Also called “gobar gas”, it is account of its high self ignition temperature.
produced by bacteria, which breaks down organic However, it can be utilized in an IC engine with the
material under air less conditions.This process is dual fuelling approach. The dual fuel engine is
called “anaerobic digestion”. The composition of basically a modified IC engine. In this case, a mixture
biogas, depending on the feed material and the of air and biogas or other gaseous fuel is sucked into
method of digestion, usually lies within the following the engine, compressed and then ignited by a spray of
ranges: 50- 70% methane (CH4), 25-50% CO2, l-5% fuel with a low self-ignition temperature like diesel,
H2, 0.3-3%N2 and various minor impurities, notably vegetable oil or biodiesel, which is called a pilot fuel
hydrogen sulphide (H2S). Hydrogen sulphide [4]. Dual fuel operation always needs a small amount
provides the biogas its bad odder. The presence of of pilot fuel for ignition.
carbon dioxide in the biogas reduces the burning
velocity which ultimately affects the performance of B. Why and how hydrogen will inject?
the engine. Percentage of methane and carbon
dioxide in biogas varies with the maturities of feed
stock, temperature, water content, loading rate of raw
material and bacterial actions. A biogas can act as a
promising (future excellence) alternative fuel by
substituting (to put in place of) considerable amount
of fossil fuels. Biogas, produced by the anaerobic
fermentation of cellulosic biomass materials, is a
clean fuel to run internal combustion engines [2]. Hydrogen is also renewable source, which produces in
II. Applicability of Biogas And Hydrogen In Ic small amount by use of HH0 Generator, and directly
Engines inject into engine with low calorific biogas. Water
contains two Hydrogen atoms (H2) and one Oxygen
A. Why Biogas will useful in IC Engines? molecule. In a combined form they are the abundant
resource known as water. A HHO Generator is a
We know that the economy of India depends to a device that uses electrolysis to convert water into two
large extent on the wheels of transport. However, parts Hydrogen and one part Oxygen. This gas, also
because of a high investment cost and a heavy known as Brown's Gas, is a very clean burning
infrastructure, only fifty percent of the biogas powerful fuel. Through the simple process of running
production is upgraded, and the natural gas electric current through the water, the atoms 'split'
replacement is very low. This renewable energy is back into their original elemental forms. This process
already used for heat and electricity production, but is known as electrolysis. Electrical current runs
the best upgrading solution of this clean energy through the water and all the Hydrogen atoms run
should be the injection into the natural gas grid or the toward the negatively charged electrode, while all the
production of vehicle fuel. Biogas containing more oxygen atoms move toward the positive electrode.
than 45% carbon dioxide caused harsh (rough or
unpleasant to the senses) and irregular running of the III. Theoretical Considerations, Experiment
engine. Similar results were obtained by others, in Setup and Procedure
which increased exhaust emission of the unburned
fuel was found in the region of 45-50% carbon A. Theoretical Consideration
dioxide [3]. The large quantity of CO2 present in S. Orhan Akansu (2007) and E. Porpatham (2012)
biogas lowers its calorific value, flame velocity and conclude that presence of up to 30% carbon dioxide in
flammability range compared with natural gas. The biogas improved the engine performance as compared
self-ignition temperature of biogas is high and hence to the same running with natural gas (96% methane)
it resists knocking which is desirable in SI engines. but percentage of methane and carbon dioxide in
Thus biogas has a high anti-knock index and hence biogas varies with the maturities of feed stock,
biogas engine can use high compression ratios, which temperature, water content, loading rate of raw
can lead to improvement in thermal efficiency. material and bacterial actions [4].
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 4 | May-Jun 2018 Page: 79
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) ISSN: 2456-6470
2456
Theoretical study shows that concentration of CO2 in Dr = diameter of rope
biogas decreases and increases combustible
component of fuel by injecting hydrogen with biogas. W = Total mass supported at rope (kg) S = spring
Also, hydrogen is cleanest world fuels which add with balance (kg)
fossil fuel in engine to increase calorific value, flame
N = pulley speed, RPM
velocity, flammability range of fuel.
Assuming dynamometer efficiency 30% brake power
TABLE I : MASS FRACTION OF COMPONENTS
of the engine.
mass mass fraction 2) Mass of the petrol fuel(kg/hr)
fraction of combustible
of component Mfp= ζp .10-5 .3600/tp
carbon
dioxide here,
CH4 H2 TOTAL
very bad 0.4 0.52 0.015 0.535 ζp = density of petrol (kg/m3)
good biogas 0.3 0.62 0.015 0.635 tp = time taken for consuming 10 ml of petrol (sec)
biogas injected 0.307 0.4 0.242 0.642
3) Mass of gases fuel(kg/hr)
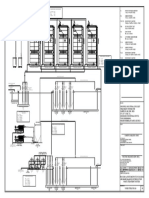
IV. EXPERIMENTAL SET UP Mfg= mb + mh
The experimental apparatus included compressor and Here, mb = mass of biogas (kg/hr)
biogas storage tank, biogas purification, internal
combustion engine and its attachments and H.H.O. mb = ζb . 10-3.3600/ tb
generation kit, biogas injection kit, fuels
fuels-air injection,
Here, ζb = density of biogas (0.85 kg/m3)
dynamometer as shown in Fig. 1. Sufficient biogas
was filled up in biogas storage tank by use of tb = time consume for filling 1 lit (sec)
compressor and distilled water was filled up in HHO
generation kit up to required height withsalt.D.C. Here, mh = mass of hydrogen (kg/hr)
Power was supplied to HHO kit and H HHO gas was
supplied to fuel-air
air injector, also connected biogas mh = ζh . 10-3.3600/ th
storage tank and vacuum pipe with biogas Here, ζh = density of hydrogen (0.089 kg/m3)
injectionkit.
th = time consume for filling 1 lit (sec)
V. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE
4) Specific fuel consumption
ption (kg /kw.hr)
With starting engine and increasing the speed of
engine and it is measured by tachometer and note SFC = mf/Bp
down spring balance
nce scale at different speed. Mass of
biogas and HHO (lit/sec) were measured and Here, mf = mass of fuel (kg/hr)
calculated from brake power, brake thermal efficiency
5) Brake thermalefficiency
and specific fuel consumption at different speed.
As the power output may be indicated by power or
A. Mathematical Modelling
brake power, therefore thermal efficiency may be
1) Brake Power(kw) expressed as indicated thermal efficiency or as brake
thermal efficiency.
Bp = . Deff .N.(W-S)/60000 .0.3 BTE = Bp.3600.100/ mf.CV
Here, Where, CV = calorific value for fuel (kj/kg) mf = fuel
Deff = (Dp + Dr), Effective diameter of pulley(m)Dp consumption Kg/hr
= diameter ofpulley
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 4 | May-Jun
Jun 2018 Page: 80
VI. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
TABLE I: OBSERVATION TABLE FOR PETROL FUEL ENGINE
Sr. Speed Effective Total mass Spring Density of Time for Mass of fuel, calorific value
diameter of pulley, support balance, petrol, consume for fuel, CV
No. (RPM) Deff ζp (kg/m 10ml mfp
S (kg) 3) (kg/hr)
1 620 0.065 9.9 1.3 772 102 0.272 42000
2 865 0.065 9.9 2 772 83 0.336 42000
3 1115 0.065 9.9 3 772 76 0.365 42000
4 1956 0.065 9.9 4.5 772 65 0.427 42000
TABLE II: RESULT TABLE FOR PETROL FUEL ENGINE
Sr No BP Specific Fuel consumed. Brake thermal efficiency.
(kw) (kg/kw.hr) (%)
1 0.589 0.462 18.55
2 0.76 0.442 19.39
3 0.856 0.427 20.1
4 1.17 0.365 23.46
TABLE III : OBSERVATION TABLE FOR HHO & BIOGAS FUELS ENGINE
Sr. No. Speed Effective Spring mass of mass of Mass calorific value for fuel
(RPM) diameter of balance biogas, mb HHO, mh (KJ/kg)
pulley(Deff) (kg) (S) (kg/hr) (kg/hr) Offuel
mfg (CV)
(kg/hr)
1 590 0.065 1 0.455 0.095 0.55 30000
2 810 0.065 1.9 0.566 0.095 0.661 30000
3 1095 0.065 2.5 0.641 0.095 0.736 30000
4 1780 0.065 4 0.842 0.095 0.937 30000
brake power for both fuels; the SFC continually
TABLE IV: RESULT TABLE FOR HHO & decreases with increase of brake power for petrol
BIOGAS FUELS ENGINE engine but for HHO and BIOGAS engine SFC nearly
remains constant above brake power 0.9.
Sr. BP Specific Brake thermal
No. Fuel efficiency. Effect of BP on Brake Thermal Efficiency
consumed.
brake thermal efficiency of petrol engine is higher
(kw) (kg/kw.hr) (%) compared to HHO and biogas engine at same brake
1 0.584 0.941 12.74 power. Brake thermal efficiency of both fuel engines
2 0.721 0.916 13.08 increases with increase of brake power, but above
3 0.901 0.816 14.69 brake power 0.9 the brake thermal efficiency not
4 1.168 0.802 14.95 much affected with increase of brake power.
Effect of Bp on Specific Fuel consumption: CONCLUSION
At the same brake power, the SFC for petrol is less Based on this experimental work on the use of
than biogas and HHO due to high calorific value of hydrogen to enhance the combustion characteristics of
fuel. The specific fuel consumption is higher at low biogas, the following conclusions are drawn. SFC
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 4 | May-Jun 2018 Page: 81
International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) ISSN: 2456-6470
decreases with increase in brake power for both fuels, 4. E. Porpatham, A. Ramesh and B.
SFC of biogas and HHO fuel engine is higher than Nagalingam,“Effect of compression ratio on the
petrol engine due to low calorific value of fuel. BTE performance and combustion of a biogas fuelled
increases with increase in brake power for both the spark ignition engine”, Fuel, 95(2012): 247.
cases but the BTE of biogas is somewhat lower
compared to petrol engine because the SFC of petrol 5. S.S.Kapdi,“Biogas scrubbing,compression and
is lower. storage: perspective and prospectus in Indian
context Centre for Rural Development and
REFERENCES Technology”, Indian Institute of Technology, New
Delhi, India. (2004).
1. M. Canakci , “Combustion characteristics of a
turbocharged DI compression ignition engine 6. Keyur patel,” Experimentation study on spark
fueled with petroleum diesel fuels and biodiesel”, ignition Engine by hydrogen with biogas fuel”,
Bio resource Technology, 98(2007): 1167. VIER Journal of Engineering Research, Issue -4
(2017), pp 79-82.
2. E. Porpatham, A. Ramesh and B. Nagalingam,
“Investigation on the effect of concentration of 7. European commission, Energy for future,
methane in biogas when used as a fuel for a spark Renewable sources of energy white paper for a
ignition engine”, Fuel, 87(2008): 1651. community strategy and action plan, com,
Brussels (1997).
3. S. Bari, “Effect of carbon dioxide on the
performance of biogas/diesel dual-fuel engine”,
School of Mechanical Engineering, University
Sains, Malaysia, (1996): 1007.
@ IJTSRD | Available Online @ www.ijtsrd.com | Volume – 2 | Issue – 4 | May-Jun 2018 Page: 82
Você também pode gostar
- Citizen Care BIO CNG Projects DetailsDocumento39 páginasCitizen Care BIO CNG Projects Detailspriyank sharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Waste Management Project: Municipality of Zaragoza Nueva EcijaDocumento54 páginasSolid Waste Management Project: Municipality of Zaragoza Nueva EcijaElias Buenavente100% (1)
- Biogas Production-A Review On Composition, Fuel Properties, Feed Stock and Principles of Anaerobic DigestionDocumento13 páginasBiogas Production-A Review On Composition, Fuel Properties, Feed Stock and Principles of Anaerobic DigestionTrần Thanh SơnAinda não há avaliações
- Renewable Hydrogen Technologies: Production, Purification, Storage, Applications and SafetyNo EverandRenewable Hydrogen Technologies: Production, Purification, Storage, Applications and SafetyLuis M GandiaNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- Green Carbon Dioxide: Advances in CO2 UtilizationNo EverandGreen Carbon Dioxide: Advances in CO2 UtilizationGabriele CentiAinda não há avaliações
- Biogas Plant: Biogas Digester Design, Gas Production and PurificationNo EverandBiogas Plant: Biogas Digester Design, Gas Production and PurificationAinda não há avaliações
- BiogasDocumento46 páginasBiogasSiddharth KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- CO2 Content in Biogas Affects Engine Performance and NOx EmissionsDocumento9 páginasCO2 Content in Biogas Affects Engine Performance and NOx EmissionsVương HoàngAinda não há avaliações
- A Review On Continuous Carbon Capturing Methods and UtilisationDocumento8 páginasA Review On Continuous Carbon Capturing Methods and UtilisationBandiDevendraReddyAinda não há avaliações
- A Review On Biogas As An Alternative FuelDocumento7 páginasA Review On Biogas As An Alternative FuelResearch ParkAinda não há avaliações
- Maximizing Bio-Gas Production from Sewage and Food WasteDocumento8 páginasMaximizing Bio-Gas Production from Sewage and Food Wasteadeel rafiqAinda não há avaliações
- Biogas - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsDocumento12 páginasBiogas - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsanirudhAinda não há avaliações
- Thermal Science and Engineering Progress: Deepalika, Vijay Kumar, Akhilesh Kumar ChoudharyDocumento25 páginasThermal Science and Engineering Progress: Deepalika, Vijay Kumar, Akhilesh Kumar ChoudharyThanh Binh TranAinda não há avaliações
- I.C. Engines Using Bio-gas for Renewable EnergyDocumento7 páginasI.C. Engines Using Bio-gas for Renewable EnergyAman Goyal (B19ME004)Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0360319920331566 MainDocumento13 páginas1 s2.0 S0360319920331566 Mainjenny lopezAinda não há avaliações
- EACFMDocumento15 páginasEACFMMDLAinda não há avaliações
- Sewage Sludge To Bio-Fuel A Review On The Sustainable Approach of Transforming Sewage Waste To Alternative Fuel PDFDocumento25 páginasSewage Sludge To Bio-Fuel A Review On The Sustainable Approach of Transforming Sewage Waste To Alternative Fuel PDFPiyush SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Biogas Supply To Diesel EngineDocumento7 páginasBiogas Supply To Diesel EngineZubair Shaikh100% (1)
- Biogas and Biofuel Project ReportDocumento14 páginasBiogas and Biofuel Project Reportvedant hiwarkarAinda não há avaliações
- Renewable Energy: Murat Kadir YesilyurtDocumento18 páginasRenewable Energy: Murat Kadir YesilyurtMUHAMMAD ABIEL PRADIPTAAinda não há avaliações
- Renewable Energy: Murat Kadir YesilyurtDocumento18 páginasRenewable Energy: Murat Kadir YesilyurtHadiAgungSAinda não há avaliações
- ECONOMIC ROOTS OF HYDROGEN PRODUCTION IN PAKISTANDocumento51 páginasECONOMIC ROOTS OF HYDROGEN PRODUCTION IN PAKISTANOsama Aadil SaadiAinda não há avaliações
- A Detailed Review of The Impacts of Diesel Biofuel Mixes With Nanofluid AdditionsDocumento5 páginasA Detailed Review of The Impacts of Diesel Biofuel Mixes With Nanofluid AdditionsEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S2214785322000396 MainDocumento5 páginas1 s2.0 S2214785322000396 MainBalaji BhukyaAinda não há avaliações
- Hypothesis On Using Biogas and HydrogenDocumento4 páginasHypothesis On Using Biogas and HydrogeniaetsdiaetsdAinda não há avaliações
- NictDocumento10 páginasNictAKSHAT TIWARIAinda não há avaliações
- Bio EtanolDocumento8 páginasBio EtanolWahyudi PanggabeanAinda não há avaliações
- Green Hydrogen: An Najah National University Faculty of Graduate StudiesDocumento11 páginasGreen Hydrogen: An Najah National University Faculty of Graduate StudiesMajedaAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Gas As Alternet Fuel in Ic EngineDocumento24 páginasBio Gas As Alternet Fuel in Ic Engineapi-3706848100% (6)
- 1 s2.0 S0360319923029476 MainDocumento15 páginas1 s2.0 S0360319923029476 MainSivani PAinda não há avaliações
- Production of Ammonia by Biomass GasificationDocumento220 páginasProduction of Ammonia by Biomass GasificationAdeel ArifAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper 8Documento3 páginasResearch Paper 8Anuraag MJAinda não há avaliações
- Liu, 2022 - CO2 Negative SMS and Other Biomasses ConversionDocumento8 páginasLiu, 2022 - CO2 Negative SMS and Other Biomasses ConversionCarolina Restrepo LondoñoAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Hydroxy and Hydrogen Gas Addition On Die - 2018 - International JournaDocumento9 páginasEffect of Hydroxy and Hydrogen Gas Addition On Die - 2018 - International Journajenny lopezAinda não há avaliações
- Effects of Oxyhydrogen Gas Induction On The Performance of A Small-Capacity Diesel EngineDocumento14 páginasEffects of Oxyhydrogen Gas Induction On The Performance of A Small-Capacity Diesel EngineNam stareAinda não há avaliações
- Experimental Investigation of BiogasDocumento2 páginasExperimental Investigation of BiogasNazif MisnanAinda não há avaliações
- CO2 Variation of BiogasDocumento6 páginasCO2 Variation of BiogashelenAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Gas As Alternet Fuel in Ic EngineDocumento20 páginasBio Gas As Alternet Fuel in Ic EngineShizuka NaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S136403211730182X MainDocumento12 páginas1 s2.0 S136403211730182X Mainabhishek sharma0% (1)
- 1Documento11 páginas1SuryaAinda não há avaliações
- CFD Analysis of Biodiesel Blends Combustion Using Ansys FluentDocumento6 páginasCFD Analysis of Biodiesel Blends Combustion Using Ansys FluentabdullaalakourAinda não há avaliações
- The Influence of Hydrogen Addition On The Combustion CharacteristicsDocumento13 páginasThe Influence of Hydrogen Addition On The Combustion CharacteristicsjorgearoncancioAinda não há avaliações
- Biomass For Power and Energy Generation: Narsimhulu SankeDocumento5 páginasBiomass For Power and Energy Generation: Narsimhulu SankeHiteshAinda não há avaliações
- Bio-Coal: A Renewable and Massively Producible Fuel From Lignocellulosic BiomassDocumento9 páginasBio-Coal: A Renewable and Massively Producible Fuel From Lignocellulosic Biomassekouedjen KarolAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction of Bio GasDocumento15 páginasIntroduction of Bio GasShashankBoazAinda não há avaliações
- Alves 2013Documento11 páginasAlves 2013Atif zahoorAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Biogas Purification To Reduce Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)Documento7 páginasDesign of Biogas Purification To Reduce Carbon Dioxide (CO2) and Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)Karen Joy BabidaAinda não há avaliações
- Fuel Processing Technology: Ahmad Tavasoli, Masoumeh G. Ahangari, Chirayu Soni, Ajay K. DalaiDocumento11 páginasFuel Processing Technology: Ahmad Tavasoli, Masoumeh G. Ahangari, Chirayu Soni, Ajay K. DalaiJaydeep PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Dnv-Position Paper Co2 Utilization Tcm4-445820Documento20 páginasDnv-Position Paper Co2 Utilization Tcm4-445820lhphong021191Ainda não há avaliações
- 11 ACV HidrogenoDocumento15 páginas11 ACV Hidrogenoluis felipe hernandez capachoAinda não há avaliações
- How To Setup Bio Gas PlantDocumento5 páginasHow To Setup Bio Gas PlantMunish BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Steam gasificationofbiomasswithCaOascatalystforhydrogen RichsyngasproductionDocumento7 páginasSteam gasificationofbiomasswithCaOascatalystforhydrogen Richsyngasproductionrizkyfahmisaputra27Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment: Name Class Subject Topic Reg No# Submitted ToDocumento12 páginasAssignment: Name Class Subject Topic Reg No# Submitted ToAli AyanAinda não há avaliações
- Biomethane Plants Based On Municipal Solid WasteDocumento17 páginasBiomethane Plants Based On Municipal Solid WasteRocky KhareAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S2590174522000794 MainDocumento13 páginas1 s2.0 S2590174522000794 Mainrabie letaifAinda não há avaliações
- Use of Biomass Gas in Running Internal Combustion Engine To Generate Electricity-A ReviewDocumento7 páginasUse of Biomass Gas in Running Internal Combustion Engine To Generate Electricity-A Reviewkashipuranataraj69Ainda não há avaliações
- R V College of EngineeringDocumento16 páginasR V College of EngineeringSantosh DoddamaniAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment-Shashank Kumar Singh-67Documento15 páginasAssignment-Shashank Kumar Singh-67ShashankBoazAinda não há avaliações
- Biomass: The Ultimate Source of Bio Energy: Sushmita Mohapatra, Kasturi GadgilDocumento4 páginasBiomass: The Ultimate Source of Bio Energy: Sushmita Mohapatra, Kasturi GadgilRaghu RamAinda não há avaliações
- Lit 15Documento3 páginasLit 15basireddykasireddy005Ainda não há avaliações
- Clean Energy Catalyst: Green Hydrogen Revolutionizing RefiningNo EverandClean Energy Catalyst: Green Hydrogen Revolutionizing RefiningAinda não há avaliações
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementNo EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementAinda não há avaliações
- Activating Geospatial Information For Sudans Sustainable Investment MapDocumento13 páginasActivating Geospatial Information For Sudans Sustainable Investment MapEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainable EnergyDocumento8 páginasSustainable EnergyEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Educational Unity Embracing Diversity For A Stronger SocietyDocumento6 páginasEducational Unity Embracing Diversity For A Stronger SocietyEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Design Simulation and Hardware Construction of An Arduino Microcontroller Based DC DC High Side Buck Converter For Standalone PV SystemDocumento6 páginasDesign Simulation and Hardware Construction of An Arduino Microcontroller Based DC DC High Side Buck Converter For Standalone PV SystemEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Collective Bargaining and Employee Prosocial Behaviour in The Hospitality Sector in Port HarcourtDocumento10 páginasCollective Bargaining and Employee Prosocial Behaviour in The Hospitality Sector in Port HarcourtEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Women Before and After Islam With Special Reference To ArabDocumento3 páginasWomen Before and After Islam With Special Reference To ArabEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges Faced by The Media in An Attempt To Play Their Roles in Public Awareness On Waste Management in Buea and DoualaDocumento18 páginasChallenges Faced by The Media in An Attempt To Play Their Roles in Public Awareness On Waste Management in Buea and DoualaEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD)Documento13 páginasInternational Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD)Editor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial Intelligence A Boon in Expanding Online Education Through Social Media and Digital Marketing Post Covid 19Documento9 páginasArtificial Intelligence A Boon in Expanding Online Education Through Social Media and Digital Marketing Post Covid 19Editor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Deconstructing The Hijra Narrative Reimagining Trans Identities Through Literary PerspectivesDocumento6 páginasDeconstructing The Hijra Narrative Reimagining Trans Identities Through Literary PerspectivesEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- An Analysis On The Use of Image Design With Generative AI TechnologiesDocumento4 páginasAn Analysis On The Use of Image Design With Generative AI TechnologiesEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Differential Equations Third Order Inhomogeneous Linear With Boundary ConditionsDocumento6 páginasDifferential Equations Third Order Inhomogeneous Linear With Boundary ConditionsEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- A Pharmaceutical Review On Kaanji and Its Wide Range of ApplicabilityDocumento6 páginasA Pharmaceutical Review On Kaanji and Its Wide Range of ApplicabilityEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- An Investigation of The Temperature Effect On Solar Panel Efficiency Based On IoT TechnologyDocumento7 páginasAn Investigation of The Temperature Effect On Solar Panel Efficiency Based On IoT TechnologyEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Sustainable Development A PrimerDocumento9 páginasSustainable Development A PrimerEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- To Assess The Knowledge and Attitude of Non Professionals Regarding COVID 19 Vaccination A Descriptive StudyDocumento4 páginasTo Assess The Knowledge and Attitude of Non Professionals Regarding COVID 19 Vaccination A Descriptive StudyEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Concept of Shotha W.S.R To Arishta LakshanaDocumento3 páginasConcept of Shotha W.S.R To Arishta LakshanaEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Consumers' Impulsive Buying Behavior in Social Commerce PlatformsDocumento5 páginasConsumers' Impulsive Buying Behavior in Social Commerce PlatformsEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- A Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Art Therapy To Reduce Depression Among Old Age Clients Admitted in Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Thandalam, ChennaiDocumento5 páginasA Study To Assess The Effectiveness of Art Therapy To Reduce Depression Among Old Age Clients Admitted in Saveetha Medical College and Hospital, Thandalam, ChennaiEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Dashamooladi Niruha Basti Followed by Katibasti in The Management of "Katigraha" W.R.S To Lumbar Spondylosis A Case StudyDocumento3 páginasRole of Dashamooladi Niruha Basti Followed by Katibasti in The Management of "Katigraha" W.R.S To Lumbar Spondylosis A Case StudyEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Effectiveness of Video Teaching Program On Knowledge Regarding 5Fs of Disease Transmission Food, Finger, Fluid, Fomite, Faces Among Children at Selected Setting, ChennaiDocumento3 páginasEffectiveness of Video Teaching Program On Knowledge Regarding 5Fs of Disease Transmission Food, Finger, Fluid, Fomite, Faces Among Children at Selected Setting, ChennaiEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Risk, Capital Adequacy and Liquidity Performance of Deposit Money Banks in NigeriaDocumento12 páginasFinancial Risk, Capital Adequacy and Liquidity Performance of Deposit Money Banks in NigeriaEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Importance of Controlled CreditDocumento3 páginasImportance of Controlled CreditEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Evan Syndrome A Case ReportDocumento3 páginasEvan Syndrome A Case ReportEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- H1 L1 Boundedness of Rough Toroidal Pseudo Differential OperatorDocumento8 páginasH1 L1 Boundedness of Rough Toroidal Pseudo Differential OperatorEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges in Pineapple Cultivation A Case Study of Pineapple Orchards in TripuraDocumento4 páginasChallenges in Pineapple Cultivation A Case Study of Pineapple Orchards in TripuraEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Knowledge Related To Diabetes Mellitus and Self Care Practice Related To Diabetic Foot Care Among Diabetic PatientsDocumento4 páginasKnowledge Related To Diabetes Mellitus and Self Care Practice Related To Diabetic Foot Care Among Diabetic PatientsEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- An Approach To The Diagnostic Study On Annavaha Srotodusti in Urdwaga Amlapitta WSR To Oesophagogastroduodenoscopic ChangesDocumento4 páginasAn Approach To The Diagnostic Study On Annavaha Srotodusti in Urdwaga Amlapitta WSR To Oesophagogastroduodenoscopic ChangesEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- A Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Reproductive Age Women in Selected Community ThrissurDocumento4 páginasA Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Reproductive Age Women in Selected Community ThrissurEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- A Study On Human Resource AccountingDocumento3 páginasA Study On Human Resource AccountingEditor IJTSRDAinda não há avaliações
- Scope of Poultry Waste Utilization: D.Thyagarajan, M.Barathi, R.SakthivadivuDocumento7 páginasScope of Poultry Waste Utilization: D.Thyagarajan, M.Barathi, R.SakthivadivuDave De Los MartirezAinda não há avaliações
- Waste Water StoryDocumento18 páginasWaste Water StoryAbishek ThiyagarajanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Anaerobic Digestion Engineering: Michael ChesshireDocumento32 páginasIntroduction To Anaerobic Digestion Engineering: Michael ChesshireAnonymous i9ytPrBlenAinda não há avaliações
- P&ID and Mass Balance Production Waste 130921-B-ModelDocumento1 páginaP&ID and Mass Balance Production Waste 130921-B-ModelmaizanazaAinda não há avaliações
- Valorization Food Waste Hydrogen - FuelDocumento11 páginasValorization Food Waste Hydrogen - FuelSinai PamfiliAinda não há avaliações
- Comercial Splash - Biogas - ElsenbruchDocumento37 páginasComercial Splash - Biogas - ElsenbruchANIL KUMAR KAinda não há avaliações
- Resource Recovery Assessment at A Pulp Mill Wastewater Treatment Plant in UruguayDocumento9 páginasResource Recovery Assessment at A Pulp Mill Wastewater Treatment Plant in UruguayElSujeto 999 :3Ainda não há avaliações
- Digester Mass BalanceDocumento31 páginasDigester Mass BalanceMusawenkosi Ncube0% (1)
- Final ZLD (Draft) 1Documento25 páginasFinal ZLD (Draft) 1raghavendran raghuAinda não há avaliações
- Biogas: Big Change Starts SmallDocumento8 páginasBiogas: Big Change Starts Smallkassambara18499Ainda não há avaliações
- Didacta Re BiomasDocumento4 páginasDidacta Re BiomasAntonAinda não há avaliações
- Biopolymers in Wastewater TreatmentDocumento4 páginasBiopolymers in Wastewater Treatmentبارق التجاريةAinda não há avaliações
- Water Supply Engineering NotesDocumento19 páginasWater Supply Engineering NotesAshraf Hussain BelimAinda não há avaliações
- A Guide For Bioreactor Landfill OperationDocumento46 páginasA Guide For Bioreactor Landfill OperationPatrick SipatelaAinda não há avaliações
- Ansi Asabe Ep403.4 Feb2011Documento6 páginasAnsi Asabe Ep403.4 Feb2011StephanAinda não há avaliações
- Pipe Compost Units in Every HouseDocumento7 páginasPipe Compost Units in Every HouseLakshmi Cg0% (1)
- Revelstoke Sewage Treatment Plant Odour Control ReportDocumento56 páginasRevelstoke Sewage Treatment Plant Odour Control ReportAlexCooperRTRAinda não há avaliações
- Bioenergy Conversion and BiofuelsDocumento17 páginasBioenergy Conversion and BiofuelsNguyễn ThuAinda não há avaliações
- Micros TrainingDocumento6 páginasMicros TrainingRajesh Chandra MisraAinda não há avaliações
- VCS PD-Zhoukou Swine Farm Biogas Recovery Project in HenanDocumento101 páginasVCS PD-Zhoukou Swine Farm Biogas Recovery Project in HenanafreenrahmanAinda não há avaliações
- Commercial Composting GuideDocumento4 páginasCommercial Composting GuideShiva ChiramshiAinda não há avaliações
- T-Zed Nature - Rebeiro - Chryslene - Paper PDFDocumento11 páginasT-Zed Nature - Rebeiro - Chryslene - Paper PDFsiskaAinda não há avaliações
- Dranco Technology Digest Organic WasteDocumento7 páginasDranco Technology Digest Organic Wastemime840% (1)
- ICA and Me e A Subjective ReviewDocumento40 páginasICA and Me e A Subjective ReviewCalcetinAinda não há avaliações
- Solid Waste ManagementDocumento10 páginasSolid Waste ManagementCharisse Jordan CruzAinda não há avaliações
- General Guidelines For The Disposal of CarcassesDocumento18 páginasGeneral Guidelines For The Disposal of CarcassesSuraj_SubediAinda não há avaliações
- CL0052 SMDocumento12 páginasCL0052 SMRoddy MantuanoAinda não há avaliações
- Potential of Biomass For Bioenergy in Pakistan BasDocumento13 páginasPotential of Biomass For Bioenergy in Pakistan Bastaha zafarAinda não há avaliações