Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Formulario Confidence Intervals
Enviado por
Lothar Hernández0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
11 visualizações1 páginaFormulario estadística l
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoFormulario estadística l
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
11 visualizações1 páginaFormulario Confidence Intervals
Enviado por
Lothar HernándezFormulario estadística l
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
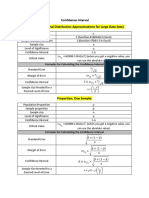
Confidence Intervals for large samples
Parameter Estimator Assumptions Bilateral confidence interval
2
Normal distribution and known 𝜎 𝜎
Mean Sample mean
Sample size greater or equal to 30 (known or 𝑥̅ ± 𝑧𝛼/2 ( )
𝜇 𝑥̅ √𝑛
unknown 𝜎 2 )
Difference between Difference between Normal distributions and known 𝜎12 , 𝜎22
𝜎2 𝜎2
means sample means Sample sizes greater or equal to 30 (known or (𝑥̅1 − 𝑥̅2 ) ± 𝑧𝛼/2 √ 1 + 2
𝜇1 − 𝜇2 𝑥̅1 − 𝑥̅2 unknown 𝜎12 , 𝜎22 ) 𝑛1 𝑛2
Binomial population.
Proportion Sample proportion Sample size greater or equal to 30. 𝑝̂ 𝑞̂
𝑝 𝑝̂ Sampling with replacement or infinite 𝑝̂ ± 𝑧𝛼/2 √
𝑛
population.
Confidence Intervals for variance and ratio of variances
Parameter Estimator Assumptions Bilateral confidence interval
(𝑛 − 1)𝑆 2 2
(𝑛 − 1)𝑆 2
( 2 ≤𝜎 ≤ 2 )
Variance Sample variance Normal population 𝜒𝛼/2 𝜒1−𝛼/2
𝜎2 𝑆2 Sample size 𝑛 Using a right tail distribution
With 𝜈 = 𝑛 − 1
Confidence Intervals for small samples
Parameter Estimator Assumptions Bilateral confidence interval
𝑠
Mean Sample mean Normal population and unknown 𝜎 2 𝑥̅ ± 𝑡𝛼/2 ( )
𝜇 𝑥̅ Sample size less than 30 √𝑛
with 𝜈 = 𝑛 − 1
Você também pode gostar
- Chapter 8. Sampling Distribution and Estimation Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 22 Aug, 2021)Documento1 páginaChapter 8. Sampling Distribution and Estimation Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 22 Aug, 2021)aaxdhpAinda não há avaliações
- Combinations and PermutationsDocumento5 páginasCombinations and PermutationsatchalieuAinda não há avaliações
- StatsandprobaDocumento3 páginasStatsandprobaAndreagale GoAinda não há avaliações
- 215 Final Exam Formula SheetDocumento2 páginas215 Final Exam Formula SheetH.C. Z.Ainda não há avaliações
- Formula SheetDocumento8 páginasFormula SheetLionel HectorAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5: Hypothesis TestingDocumento6 páginasUnit 5: Hypothesis TestingKamlesh PariharAinda não há avaliações
- Standard Normal Distribution Critical Values, ZDocumento3 páginasStandard Normal Distribution Critical Values, Zlbeard501Ainda não há avaliações
- Formula SheetDocumento4 páginasFormula SheetNikki Jean HonaAinda não há avaliações
- Bab 4Documento7 páginasBab 4Hizkia KridAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics Tutorial 1Documento12 páginasStatistics Tutorial 1Natalya LewisAinda não há avaliações
- Normal Distribution: Simple Test of HypothesisDocumento27 páginasNormal Distribution: Simple Test of Hypothesisednalyn ladiaoAinda não há avaliações
- WK 11-Session 11 Notes-Hypothesis Testing (Two Samples) - UploadDocumento12 páginasWK 11-Session 11 Notes-Hypothesis Testing (Two Samples) - UploadLIAW ANN YIAinda não há avaliações
- TestSummary Handout1 v01Documento2 páginasTestSummary Handout1 v01KIM THUyAinda não há avaliações
- BB113 Formula SheetDocumento5 páginasBB113 Formula SheetmubbaahAinda não há avaliações
- ReviewerDocumento1 páginaReviewerchxrlslxrrenAinda não há avaliações
- EDA-HYPOTHESIS-TESTING-FOR-TWO-SAMPLE (With Answers)Documento6 páginasEDA-HYPOTHESIS-TESTING-FOR-TWO-SAMPLE (With Answers)Maryang DescartesAinda não há avaliações
- Cambridge AS Biology 9700 Practical NotesDocumento2 páginasCambridge AS Biology 9700 Practical NotesSafiya Naina100% (1)
- Applied Statistics and Probability For Engineers Chapter - 8Documento13 páginasApplied Statistics and Probability For Engineers Chapter - 8MustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Math in The Modern World Stat LectureDocumento3 páginasMath in The Modern World Stat LectureGylene GardonAinda não há avaliações
- Probability and Statistics Formula SheetDocumento2 páginasProbability and Statistics Formula SheetAl Diego FuseleroAinda não há avaliações
- Test-Statistics List: Test Statistics For Finding The Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis TestingDocumento1 páginaTest-Statistics List: Test Statistics For Finding The Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis TestingRojan PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- Distribution Test Statistic / Formula ConditionsDocumento10 páginasDistribution Test Statistic / Formula ConditionsNatalya Lewis0% (1)
- 2.1 Plotting For Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)Documento2 páginas2.1 Plotting For Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)RajaAinda não há avaliações
- Cheat Sheet PDFDocumento4 páginasCheat Sheet PDFSaif ali KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 9. One-Sample Hypothesis Tests Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 21 Aug, 2021)Documento1 páginaChapter 9. One-Sample Hypothesis Tests Nguyen Thi Thu Van (This Version Is Dated On 21 Aug, 2021)aaxdhpAinda não há avaliações
- GB Academy Equation ListDocumento16 páginasGB Academy Equation ListfaysalnaeemAinda não há avaliações
- STA1510 Chapter 8 SummaryDocumento3 páginasSTA1510 Chapter 8 SummaryLeigh MakanAinda não há avaliações
- Z Test (Standard Normal Distribution) (N 30) : 1) Confidence Interval For MeanDocumento10 páginasZ Test (Standard Normal Distribution) (N 30) : 1) Confidence Interval For MeanAniruddha PhalakAinda não há avaliações
- Stat 101 - Measures of Dispersion, Skewness, and KurtosisDocumento2 páginasStat 101 - Measures of Dispersion, Skewness, and KurtosisAbbey La FortezaAinda não há avaliações
- Stat - Prob Q3 Module 8Documento18 páginasStat - Prob Q3 Module 8dwyanesisneros19Ainda não há avaliações
- Tests of SignificanceDocumento36 páginasTests of SignificanceSanchit SinghalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 - Part 1 - Group 2Documento48 páginasChapter 4 - Part 1 - Group 2Ahmad SalahuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics: Dealing With Skewed DataDocumento7 páginasStatistics: Dealing With Skewed DataAbhijeetAinda não há avaliações
- Manual in Stat5Documento1 páginaManual in Stat5Lyanna MormontAinda não há avaliações
- New9Topic - Two Sample Inference (Corrected)Documento57 páginasNew9Topic - Two Sample Inference (Corrected)2p6jt8wkg8Ainda não há avaliações
- Statistical Intervals For A Single SampleDocumento31 páginasStatistical Intervals For A Single SampleBui Tien DatAinda não há avaliações
- Statistic PartBDocumento10 páginasStatistic PartBAnkit ChatterjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Est Diff MeanDocumento41 páginasEst Diff Meanariba shoukatAinda não há avaliações
- Module 6-2Documento8 páginasModule 6-2Ho Uyen Thu NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 10 Estimating Population MeansDocumento5 páginasLesson 10 Estimating Population MeansSamleedigiprintsAinda não há avaliações
- 2024-Lecture 09Documento29 páginas2024-Lecture 09Nguyễn TâmAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionDocumento5 páginasStatistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionAndrea GamutanAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Mean and Variance of The Sampling Distribution ofDocumento14 páginas2 Mean and Variance of The Sampling Distribution ofMerry Greece Ayes100% (1)
- Mean and Proportion of 2 Independent PopulationsDocumento5 páginasMean and Proportion of 2 Independent PopulationsAina Nasha RoszailullailAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Lim - Midterm HandoutsDocumento3 páginasPre Lim - Midterm HandoutsJanica SamsonAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics and Probability Module 6: Week 6: Third QuarterDocumento7 páginasStatistics and Probability Module 6: Week 6: Third QuarterALLYSSA MAE PELONIAAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3-MSDA 3055Documento44 páginasLecture 3-MSDA 3055dhaval galaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Two - Estimation (STA408)Documento46 páginasChapter Two - Estimation (STA408)BadnazAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 26 CompactDocumento5 páginasLecture 26 CompactDela Cruz DearAinda não há avaliações
- FormulaSheet Test 1Documento6 páginasFormulaSheet Test 1bestreview7Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 - Sampling Distributions CLTDocumento17 páginasChapter 7 - Sampling Distributions CLTBui Tien DatAinda não há avaliações
- STAT273 - CHAPTER 06 (Summer)Documento6 páginasSTAT273 - CHAPTER 06 (Summer)Abood RainAinda não há avaliações
- CQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DDocumento15 páginasCQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DAmr AlShenawyAinda não há avaliações
- Probability Distribution: - Discrete - ContinuousDocumento5 páginasProbability Distribution: - Discrete - ContinuousEavie OngAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Statistical & Internal ValidityDocumento58 páginas03 Statistical & Internal ValidityAssan AchibatAinda não há avaliações
- Chapters 7,8,9Documento4 páginasChapters 7,8,9sarkarigamingytAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of FormulasDocumento1 páginaSummary of FormulasneotechAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignNo EverandSample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Biostatistics for Geneticists and Epidemiologists: A Practical ApproachNo EverandBasic Biostatistics for Geneticists and Epidemiologists: A Practical ApproachAinda não há avaliações
- Bayesian Inference For Categorical Data PDFDocumento48 páginasBayesian Inference For Categorical Data PDFLili CRAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 21sjit PQT QBDocumento66 páginas2020 21sjit PQT QB4019 Arvind VenkatAinda não há avaliações
- Econometrics Final Exam Questions: Full Name - Altynai Kubatova - Group - Fin-18Documento2 páginasEconometrics Final Exam Questions: Full Name - Altynai Kubatova - Group - Fin-18Altynai KubatovaAinda não há avaliações
- Fpsyg 11 01300Documento11 páginasFpsyg 11 01300Hung TranAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Business Statistics 1st Edition Freed Solutions ManualDocumento38 páginasUnderstanding Business Statistics 1st Edition Freed Solutions Manualagabnadebooq100% (14)
- Basic Statistical ToolsDocumento45 páginasBasic Statistical ToolsfarjanaAinda não há avaliações
- Flood FrequencyDocumento35 páginasFlood FrequencyHarish Kumar MahavarAinda não há avaliações
- Bayes Intro PT 2Documento13 páginasBayes Intro PT 2awelAinda não há avaliações
- Helicopter PaperDocumento42 páginasHelicopter PaperGandi SuhartinahAinda não há avaliações
- Square Root LawDocumento3 páginasSquare Root LawGambit KingAinda não há avaliações
- 'Yatham Padma' 8 May 2022Documento82 páginas'Yatham Padma' 8 May 2022Padma yathamAinda não há avaliações
- 3-1-Lossless CompressionDocumento10 páginas3-1-Lossless CompressionMuhamadAndiAinda não há avaliações
- Detection Estimation and Modulation Theory Solution ManualDocumento82 páginasDetection Estimation and Modulation Theory Solution ManualUfuk Tamer33% (3)
- Point Estimation and Interval Estimation: Learning ObjectivesDocumento58 páginasPoint Estimation and Interval Estimation: Learning ObjectivesVasily PupkinAinda não há avaliações
- Yates' Chapter 6, 10: Stochastic Processes & Stochastic FilteringDocumento16 páginasYates' Chapter 6, 10: Stochastic Processes & Stochastic FilteringMohamed Ziad AlezzoAinda não há avaliações
- Case Problem 2 Harbor Dunes Golf CourseDocumento2 páginasCase Problem 2 Harbor Dunes Golf CourseSomething ChicAinda não há avaliações
- Mahardika Angeli Fortuna - 20320183 - TeamTeaching1 - Colaboratory-DikonversiDocumento6 páginasMahardika Angeli Fortuna - 20320183 - TeamTeaching1 - Colaboratory-Dikonversiade tan rezaAinda não há avaliações
- Difference Between RERDocumento2 páginasDifference Between RERShahzaib BhuttoAinda não há avaliações
- SCI 1020 - wk2Documento4 páginasSCI 1020 - wk2Luk Ee RenAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 23:: Control ChartsDocumento11 páginasUnit 23:: Control ChartstarrteaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 8fhjgDocumento9 páginasChapter 7 8fhjgJimmy LyAinda não há avaliações
- Sample Size PilotDocumento5 páginasSample Size PilotmsriramcaAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Methods ModuleDocumento22 páginasQuantitative Methods ModuleJean LeysonAinda não há avaliações
- Activity No 2 StatDocumento2 páginasActivity No 2 StatRodin PaspasanAinda não há avaliações
- A-Detailed-Lesson-Plan-in-Statistics and ProbabilityDocumento6 páginasA-Detailed-Lesson-Plan-in-Statistics and ProbabilityEllen VilladolidAinda não há avaliações
- Geomitric DistributionDocumento18 páginasGeomitric DistributionTaanzAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Computer NetworksDocumento288 páginasAnalysis of Computer NetworksItalo Dias100% (1)
- Report DOE2Documento28 páginasReport DOE2bellbeshAinda não há avaliações
- SPSS Series 3 Repeated Measure ANOVA and MANOVA PDFDocumento52 páginasSPSS Series 3 Repeated Measure ANOVA and MANOVA PDFUzaima SiddiquiAinda não há avaliações
- Beck y Katz 2011Documento24 páginasBeck y Katz 2011María Marta MarotoAinda não há avaliações