Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Activity Intolerance
Enviado por
junex1230 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações2 páginasActivity intolerance related to generalized weakness and pain secondary to sleep deprivation. After 30 mins. Of nursing intervention and management, the patient will be able to: --identify activities and factors that contribute to intolerance -- 5 measures to enhance activity tolerance.
Descrição original:
Direitos autorais
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoActivity intolerance related to generalized weakness and pain secondary to sleep deprivation. After 30 mins. Of nursing intervention and management, the patient will be able to: --identify activities and factors that contribute to intolerance -- 5 measures to enhance activity tolerance.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
1K visualizações2 páginasActivity Intolerance
Enviado por
junex123Activity intolerance related to generalized weakness and pain secondary to sleep deprivation. After 30 mins. Of nursing intervention and management, the patient will be able to: --identify activities and factors that contribute to intolerance -- 5 measures to enhance activity tolerance.
Direitos autorais:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOC, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
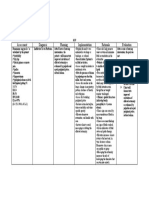
NURSING CARE PLAN
PROBLEM: Activity intolerance
NURSING DIAGNOSIS: Activity Intolerance related to generalized weakness and pain secondary to sleep deprivation
TAXONOMY: Activity-Exercise Pattern
CAUSE ANALYSIS: Pain and weakness limit patient’s activity. Individual has insufficient physiological or psychological energy to endure or complete required or desired daily activites. Lack of
sleep may cause fatigue thereby affecting the physical activity, and decrease responsiveness to external stimuli.
CUES OBJECTIVE NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE: STO: INDEPENDENT: Demonstrate activity tolerance.
Patient report of fatigue or After 30 mins. of nursing Determine cause of activity Determining the cause of a disease Absence of signs and symptoms.
weakness, discomfort. Patient intervention and management, the intolerance can help direct appropriate
verbalized that he had difficulty in patient will able to: interventions
performing his daily activities due to --identify activities and factors that
the pain she felt over right lower contribute to intolerance Monitor and record client’s ability to
quadrant. He also reports of -- 5 measures to enhance activity tolerate activity; note pulse rate,
inadequate sleep at night due to tha tolerance blood pressure, monitor pattern,
pain she felt. dyspnea, use of accessory muscles,
and skin color before and after
LTO: activity.
After 3 days of nursing intervention
and management, the patient will be Teach client the need to pace activity Rest periods decrease oxygen
able to demonstrate activity and rest after meals consumption
tolerance
Observe for pain before activity and, Pain restricts the client from
if possible treat pain before activity. achieving a maximum activity level
and is often exacerbated by
movement.
Encourage client to change position Immobilization and enforced bedrest
from supine to sitting several times in the supine position have
daily and to avoid prolonged bedrest. considerable adverse effects on
nearly every system in the body.
Perform passive range-of-motion Inactivity rapidly contributes to
exercise if client is unable to tolerate muscle shortening and changes in
activity periarticular and cartilaginous joint
structure. These factors contribute to
contracture and limitation of motion
Implement measures to conserve the Measures to conserve the client’s
client’s energy during activity energy enable the client to increase
activity tolerance
Suggest that the client perform Shorter activity periods performed
activities more slowly and for shorter more slowly and more frequent rest
time periods, resting more often, and periods promote optimal
using more assistance as required. performance and achievement levels.
Appropriate assistance ensure safety
and prevents falling.
Instruct client in energy-conserving Energy-saving techniques reduce the
techniques, e.g., sitting to brush energy expenditure, thereby assisting
teeth or comb hair, carrying out in equalization of oxygen supply and
activities at a slower pace. demand.
Encourage progressive activity/ self-
care when tolerated. Provide Gradual activity progression
assistance as needed. prevents a sudden increase in
cardiac workload. Providing
assistance only as needed encourages
independence in performing
activites.
Referrence: Kozier, et. al .Fundamentals of Nursing, 5th edition.
Doenges, et. al. Nursing Care Plans, 6th edition.
Você também pode gostar
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocumento2 páginasNCP Risk For InfectiontermskipopAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento7 páginasImpaired Skin Integrityprickybiik100% (8)
- NCP AppendicitisDocumento2 páginasNCP AppendicitisArnel Luces Beato100% (1)
- NCP Excess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Ascites and Edema Formation)Documento7 páginasNCP Excess Fluid Volume Related To Compromised Regulatory Mechanism (Ascites and Edema Formation)Aesthea BondadAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 páginasImpaired Skin IntegrityEli AyaseAinda não há avaliações
- NCP - Alteration in ComfortDocumento2 páginasNCP - Alteration in ComfortPatricia CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocumento2 páginasAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 páginasImpaired Gas ExchangeAura Salve Ildefonso Allas100% (3)
- Mpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 páginasMpaired Physical Mobility (Amputation) : Nursing Care PlanTheSweetpea5010% (2)
- Ineffective Renal Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 páginasIneffective Renal Tissue PerfusionHendra Tanjung100% (4)
- Better Photography - April 2018 PDFDocumento100 páginasBetter Photography - April 2018 PDFPeter100% (1)
- Activity Evaluation Form: "Where Children Come First"Documento1 páginaActivity Evaluation Form: "Where Children Come First"TuTitAinda não há avaliações
- Ubi Caritas Guitar Solo Arrangement by Patrick Glenn BalanzaDocumento8 páginasUbi Caritas Guitar Solo Arrangement by Patrick Glenn BalanzaPatrick Glenn BalanzaAinda não há avaliações
- Diarrhea NCP 1Documento1 páginaDiarrhea NCP 1Rhence Efner Saylon50% (2)
- Internet Bill FormatDocumento1 páginaInternet Bill FormatGopal Singh100% (1)
- NCP - Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 páginasNCP - Activity Intolerancejanelee2824Ainda não há avaliações
- Activity Intolerance DeliveryDocumento3 páginasActivity Intolerance Deliveryjunex123100% (2)
- PneumoniaDocumento2 páginasPneumoniaPia MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- NURSING CARE PLAN - SuicidalactDocumento4 páginasNURSING CARE PLAN - SuicidalactJennifer ArdeAinda não há avaliações
- NCP HemothoraxDocumento3 páginasNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Case AnalysisDocumento25 páginasCase AnalysisGerly LagutingAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPaudreyAinda não há avaliações
- Broiler ProductionDocumento13 páginasBroiler ProductionAlexa Khrystal Eve Gorgod100% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 páginasNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP Impaired SkinDocumento2 páginasNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP For UtiDocumento3 páginasNCP For UtiAaron Sanchez100% (1)
- NCP Acute PainDocumento4 páginasNCP Acute PainSj 斗力上Ainda não há avaliações
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective "Masakit Yung Opera Sa Akin" Short Term ObjectiveDocumento12 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Subjective "Masakit Yung Opera Sa Akin" Short Term ObjectiveRaphael FranciscoAinda não há avaliações
- NCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Documento3 páginasNCP (BODY WEAKNESS)Jum ChumAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationgabbyAinda não há avaliações
- NCP EdemaDocumento1 páginaNCP EdemaR Hornilla ArcegaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocumento2 páginasNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07Ainda não há avaliações
- Chinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasChinese General Hospital College of Nursing Nursing Care PlanLoveli Yuchongtian Kiok100% (2)
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocumento3 páginasNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleAinda não há avaliações
- NCP For Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDocumento9 páginasNCP For Disturbed Sensory PerceptionRYAN SAPLADAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocumento3 páginasImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliAinda não há avaliações
- BSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitDocumento12 páginasBSN 3e Duropan Ncp-Knowledge DeficitJane DuropanAinda não há avaliações
- NCPDocumento4 páginasNCPDaniel Garraton0% (1)
- Carpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2009) : IndependentDocumento3 páginasCarpenito-Moyet, L. J. (2009) : IndependentClint DelacruzAinda não há avaliações
- Activity Intolerance R/T Generalized WeaknessDocumento3 páginasActivity Intolerance R/T Generalized Weaknesschanmin limAinda não há avaliações
- Cues/ Evidences Nursing Diagnosi S Scientific Basis Goals and Outcome Criteria Nursing Actions and Nursing Orders Rationale of Nursing Actions EvaluationDocumento5 páginasCues/ Evidences Nursing Diagnosi S Scientific Basis Goals and Outcome Criteria Nursing Actions and Nursing Orders Rationale of Nursing Actions EvaluationCharlene Serino JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocumento4 páginasNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanAinda não há avaliações
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento4 páginasRisk For Decreased Cardiac Outputapi-283482759Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento1 páginaNCP Impaired Physical MobilityCharmaine SolimanAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocumento6 páginasChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyAinda não há avaliações
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Documento2 páginasCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16Ainda não há avaliações
- NCP PpwardDocumento15 páginasNCP PpwardKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- NCP BMDocumento1 páginaNCP BMSourabh MehraAinda não há avaliações
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDocumento2 páginasProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Documento6 páginasIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.Ainda não há avaliações
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 páginasActivity Intolerancepooper123Ainda não há avaliações
- Risk For InjuryDocumento2 páginasRisk For InjuryRo-anne AkuAinda não há avaliações
- Burns - Skin Integrity, ImpairedDocumento2 páginasBurns - Skin Integrity, Impairedmakyofrancis20Ainda não há avaliações
- Problem PrioDocumento2 páginasProblem PrioYsrael Alcantara100% (1)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 páginasAssessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodolfo Bong SemaneroAinda não há avaliações
- Glaucoma NCPDocumento4 páginasGlaucoma NCPChantal CaraganAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKSDocumento3 páginasAssessment Healt H Patte RN Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome (Edit) Intervention (Edit) Evaluation (EDIT) Rema RKStflorenzAinda não há avaliações
- NCP (Fatigue)Documento3 páginasNCP (Fatigue)Edrick SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocumento3 páginasImpaired Urinary EliminationDenise Republika100% (1)
- MoblityDocumento2 páginasMoblityReyes MikkoAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocumento4 páginasAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentMina RacadioAinda não há avaliações
- Subjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesDocumento4 páginasSubjective Data: Baseline Data of Client.: Reference: Nurse's Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Interventions, and RationalesJor GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento3 páginasActivity IntoleranceRaidis PangilinanAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care PlansDocumento3 páginasNursing Care PlansAvonne SabileAinda não há avaliações
- BS en Iso 06509-1995 (2000)Documento10 páginasBS en Iso 06509-1995 (2000)vewigop197Ainda não há avaliações
- Neelima A Kulkarni ResumeDocumento3 páginasNeelima A Kulkarni ResumeAcademics LecturenotesAinda não há avaliações
- Onset Hobo Trade T Cdi 5200 5400 User ManualDocumento3 páginasOnset Hobo Trade T Cdi 5200 5400 User Manualpaull20020% (1)
- Paramount Healthcare Management Private Limited: First Reminder Letter Without PrejudiceDocumento1 páginaParamount Healthcare Management Private Limited: First Reminder Letter Without PrejudiceSwapnil TiwariAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Three: Tools For Exploring The World: Physical, Perceptual, and Motor DevelopmentDocumento43 páginasChapter Three: Tools For Exploring The World: Physical, Perceptual, and Motor DevelopmentHsieh Yun JuAinda não há avaliações
- Dehn Brian Intonation SolutionsDocumento76 páginasDehn Brian Intonation SolutionsEthan NealAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes 3A - Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure 2019Documento19 páginasLecture Notes 3A - Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure 2019Lena BacaniAinda não há avaliações
- ARC-232, Material Construction 2Documento4 páginasARC-232, Material Construction 2danishali1090Ainda não há avaliações
- A SURVEY OF ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MIDGE (Diptera: Tendipedidae)Documento15 páginasA SURVEY OF ENVIRONMENTAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE MIDGE (Diptera: Tendipedidae)Batuhan ElçinAinda não há avaliações
- Kefauver Harris AmendmentsDocumento7 páginasKefauver Harris AmendmentsAnil kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper On Air QualityDocumento4 páginasResearch Paper On Air Qualityluwahudujos3100% (1)
- Manual: Functional SafetyDocumento24 páginasManual: Functional SafetymhaioocAinda não há avaliações
- Redirection & PipingDocumento16 páginasRedirection & PipingPraveen PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Microeconomics Term 1 SlidesDocumento494 páginasMicroeconomics Term 1 SlidesSidra BhattiAinda não há avaliações
- Health and Safety For The Meat Industry: Guidance NotesDocumento198 páginasHealth and Safety For The Meat Industry: Guidance NotesPredrag AndjelkovicAinda não há avaliações
- PH of Soils: Standard Test Method ForDocumento3 páginasPH of Soils: Standard Test Method ForYizel CastañedaAinda não há avaliações
- Advent Wreath Lesson PlanDocumento2 páginasAdvent Wreath Lesson Planapi-359764398100% (1)
- Aquaculture - Set BDocumento13 páginasAquaculture - Set BJenny VillamorAinda não há avaliações
- CL RouterAndSwitches AE Kn1of3 AnswerDocumento19 páginasCL RouterAndSwitches AE Kn1of3 Answereugene ngAinda não há avaliações
- TrellisDocumento1 páginaTrellisCayenne LightenAinda não há avaliações
- List of Phrasal Verbs 1 ColumnDocumento12 páginasList of Phrasal Verbs 1 ColumnmoiibdAinda não há avaliações
- Karthik ResumeDocumento2 páginasKarthik ResumeArun Raj AAinda não há avaliações
- Part Time Civil SyllabusDocumento67 páginasPart Time Civil SyllabusEr Govind Singh ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- ArcGIS Shapefile Files Types & ExtensionsDocumento4 páginasArcGIS Shapefile Files Types & ExtensionsdanangAinda não há avaliações
- Particle BoardDocumento1 páginaParticle BoardNamrata RamahAinda não há avaliações