Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Haiti and Its Vulnerability To Natural Disasters
Enviado por
Ericka AlvarezTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Haiti and Its Vulnerability To Natural Disasters
Enviado por
Ericka AlvarezDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Geo file
September 2012
Online 672
Sally Garrington
The Haiti Earthquake 2010 – A Study
of Vulnerability
On 12 January 2010 an earthquake home from family members abroad, was movement in the Enriquillo-
measuring 7 on the Richter scale which in 2008 formed 32% of the Plantain Garden fault system, in the
of magnitude struck the country of country’s GDP. south of the country, that caused the
Haiti, killing over 200,000 people. earthquake which destroyed 60% of
Television footage and journalism In 2004 3,000 people were killed in the country’s capital, Port-au-Prince.
immediately after the ’quake and Haiti due to the impact of Tropical The fault had been locked for over
for the next 12 months showed a Storm Jeanne. Four years later in 250 years, but in January 2010 its
country that was not only devastated 2008 Haiti suffered four damaging energy was released along 65 km of
by the disaster, but even one year hurricanes which left a death toll of the fault, causing land movement of
on was only just emerging from the 800 and huge amounts of damage. 1.8 metres. The epicentre was south
emergency phase and after two years 60% of the harvests were destroyed, west of the capital on the peninsula
is just verging on reconstruction. and there were many landslides and affected several other towns
Why was this? which destroyed lives, homes and (Figure 1).
roads. Haiti only has 2% of its land
Haiti is located in the Caribbean and forested (due to deforestation for Why was Haiti so
forms the western part of the island charcoal manufacture, the main
of Hispaniola, with the Dominican fuel of the poor) so is susceptible
vulnerable?
Republic on the eastern side (Figure to landslides when the heavy rains Although a Richter Scale 7
1). Being in the western hemisphere, come with hurricanes. earthquake can cause much damage,
one might expect it to have a certain it is not only the magnitude of the
amount of wealth, but in fact Haiti hazard that impacts on the outcome
is one of the poorest countries in Haiti and plate margins within a country. There is a Risk
the world. It has a population of 9.8 As well as being in the direct path Equation, set out below:
million but a gross national income of hurricanes, Haiti sits amongst a
(GNI) of only $660 per person per complex set of plate margins (Figure R = HxV
annum, has high levels of infant 1). Although it can be affected by –––––
mortality and a high incidence of movements of destructive plate C
HIV/AIDS (2.2% of the population margins within the Caribbean, it
aged 15-49, which is a very high is the two conservative strike-slip R=Risk H=Hazard
level).The country is heavily faults on the island itself that cause V=Vulnerability C=Capacity to cope
dependent on the remittances sent most impact. In January 2010 it
Figure 1: Location of Haiti and main plate boundaries; inset shows location of Port au Prince and other towns affected by the
earthquake
USA
NORTH AMERICAN
PLATE Caribbean
Sea HAITI
Carrefour
HAITI Gressier
Mexico Bahamas Léogâne Port au Prince
Dominican
Cuba Republic
Jacmel
Epicentre
0 50 km Caribbean Sea
Caribbean Sea
CARIBBEAN
PLATE
Venezuela
COCOS PLATE
Colombia
SOUTH Key
AMERICAN
PLATE BOUNDARIES
PLATE
Transform (Conservative)
NAZCA PLATE Convergent (Destructive)
0 1000 km Divergent (Constructive)
Undefined
Geofile Online © Nelson Thornes 2012
GeoFile Series 30 Issue 1
Fig 672_01 Mac/eps/illustrator 15 s/s
September 2012 no.672 The Haiti Earthquake 2010 – A Study of Vulnerability
Figure 2: Some of the factors affecting Haiti’s vulnerability and capacity to cope systems were in place. Chile is a
much more prosperous country than
Only 50% had access to latrines in Port-au-Prince.
Only 33% had access to clean tap water
Poor building codes. Houses had no earthquake resistance
Haiti, and has a greater capacity to
Poorest country in western hemisphere cope with disasters and emergencies,
Life expectancy – 60 (UK=80)
70% live on less than $2 a day
also being less vulnerable because of
IMR=86 per 1000 (UK=<5),
GNI=$660 pa (UK=41,370 pa) In seismically active region
a more stable system of government
and better disaster planning.
Poor planning so limited
Massive rural urban migration as infrastructure
so little employment opportunities.
Huge slums in Port-au-Prince.
The immediate impacts of
HAITI
Unemployment rate put as
high as 90% Factors affecting
Many public services provided
by NGOs and the UN
the earthquake
vulnerability and
capacity to
cope
The Haiti earthquake struck at
Long history of unstable/
ineffectual governments
Lack of a coherent emergency
plan for a disaster
4.53pm. Its epicentre was 25km
south west of the capital causing
In hurricane belt. Suffered large losses in 86% of people in Port-au-Prince widespread devastation, although its
2008 and not fully recovered lived in slum conditions greatest impact was felt in Port-au-
Prince itself. Here there had been a
Poor governance at local Shortage of trained Lack of public awareness of what
and national level health workers and to do in the event of an earthquake massive increase in the population
an underfunded
healthcare system
due to rural-urban migration,
with the majority of people living
in poorly constructed squatter
settlements. These were no match
Figure 3: The impacts of the earthquake
GeoFile Series 30 Issue 1
Fig 672_02 Mac/eps/illustrator 15 s/s for the earthquake, and many lost
Figures NELSON THORNES PUBLISHING Details their lives or were seriously injured
Artist: David Russell Illustration when their homes collapsed. 70%
Magnitude 7 Richter scale of magnitude. Highly damaging
earthquake of buildings in Port-au-Prince
collapsed and most roads were
Mercalli Scale of earthquake Description of effect ‘ruinous’
intensity level 9 blocked by debris. The final death
toll was 230,000, including nearly
65 km rupture Of the Enriquillo -Plantain Garden fault with a 100 UN personnel, many trained
slip of 1.8 metres health workers and a quarter of civil
52 aftershocks Of 4.5 or greater. Largest was on 20/01/10 of service staff. This meant it took
5.9 which caused more building collapse. even longer to get help co-ordinated.
230,000 deaths Due to earthquake or immediate aftermath. Figure 3 summarises some of the
Includes nearly 100 UN personnel and 25% of major impacts of the earthquake.
the country’s civil servants.
6,900 deaths As of November 2011, the number that died Early aid
from the cholera epidemic that followed the
earthquake. Neighbouring Dominican Republic
was amongst the first to give aid,
1.5 million homeless Having to live in tented camps sending in supplies of water, food
60% of infrastructure Area in and around Port-au-Prince and heavy lifting machinery to help
destroyed rescue people from beneath collapsed
70% buildings collapsed In capital Port-au-Prince. 8 hospitals, 9 health buildings. They also made their own
centres, 10 Ministry of Health buildings, 19 hospitals available and permitted
university buildings and training institutes people to cross the border to receive
destroyed. help. Iceland had an emergency
4,000 amputees The rough estimate of how many earthquake
response team in the country within
survivors lost limbs 24 hours. As days passed it became
difficult for relief planes to land, as
4,000 prisoners The number who escaped to freedom from the only part of the airport was usable
Prison Civile when it was destroyed
and there were queues in the skies
$8 billion Cost of damage and losses above Port-au-Prince. Aid ships
had to be turned away from the
Haiti, being such a poor country 2 illustrates many of the reasons devastated port, where the docks
and with limited developed for the country’s vulnerability and were unable to function. A lack of
infrastructure and health services, also why its capacity to cope was co-ordination made the situation
was always going to have poor so limited. A month after Haiti’s worse and initially priority was
capacity to cope. It had not yet earthquake, one of 8.8 on the Richter given to the arrival of security troops
recovered from the damaging scale occurred in Chile, and yet rather than emergency aid.
hurricanes of 2008, and many of only 800 were killed. While Chile
the public services in the country had international aid, the Chilean Many survivors fled to their family
were being run by aid charities and government moved quickly from homes in rural areas, putting extra
the United Nations. It was always the emergency phase through the strain on the villages. However,
going to find it difficult to respond recovery stage to the transition most remained in the city and
resiliently to the disaster and to planning and implementation were camping out on any spare
recover from it. Haiti was extremely phase, because it had a clear disaster open ground, including in front of
vulnerable to any disaster. Figure response plan and the emergency the destroyed presidential palace.
Geofile Online © Nelson Thornes 2012
September 2012 no.672 The Haiti Earthquake 2010 – A Study of Vulnerability
Eventually tents were flown in and should be stressed that some NGOs continued. Another serious problem
up to 1500 camps were set up all were very well run with minimal was that of rape and other sexual
over Port-au-Prince. Sanitation operating costs and servicing a attacks within the camps. Women
arrangements were hopelessly definite need (see Merlin website at and girls were vulnerable as they
inadequate, and the encampments end of unit). were still in tents which could be
were soon awash with excrement. easily broken into, and they had
There was only one delivery of Later actions little privacy at the latrines or
drinking water a week and so people washing facilities. Many women
were forced to consume untreated By July 2010 98% of the rubble from had lost their husbands and
water, which had a disastrous impact the earthquake remained uncleared felt unprotected in the crowded
later on in the crisis. Cholera spread and 1.6 million people were still conditions. The camps were badly lit
rapidly. living in temporary camps (although at night and there was no policing,
this fell to 1 million by September). and gangs of youths and men were
Communications, including roads, By then many of the original tents carrying out rapes knowing they
and electricity were severely supplied as shelter were falling would not be caught. Although
damaged which hampered attempts apart and much of the funding that Haiti had a poor record of protecting
to distribute aid. After a few days the had been donated was not getting women and girls even before the
unretrieved corpses trapped in the through to those most in need. The earthquake, the situation in the
rubble of buildings began to decay World Bank had cancelled half of camps was far worse, with girls as
in the high heat and humidity and Haiti’s debt and given the country young as ten being attacked.
with thousands of corpses stored in five years before it had to begin
overcrowded morgues there was a repayments of the remaining half.
Cash for work programmes had been The cholera outbreak
need for drastic action if disease was
to be avoided. Most bodies were set up to enable some Haitians to With such crowded and unsanitary
buried in mass graves using earth- support themselves. 20% of all jobs conditions, doctors had been
moving machinery, usually before had disappeared due to the impact of warning about the outbreak of
they could be identified, such was the earthquake. Most buildings that serious disease since the quake
the urgency. had not collapsed in Port-au-Prince occurred. In October 2010 the first
had been assessed as to the safety or case of cholera was identified. Haiti
otherwise of their structure. Some had been cholera-free for over 100
The NGO problem aid money was used to pay Haitian years. When it was announced
As the country did not have an engineers and surveyors to carry out that the particular strain was one
emergency plan in place and the the work. Each building was colour found in south-east Asia, there was
UN had lost so many personnel, tagged after assessment: an uprising of bad feeling against
there was a lack of co-ordination the UN peacekeeping force from
in the first few weeks and it • Red (21%) meaning the building Nepal, from where the disease
was three weeks before the aid would have to be demolished had allegedly been brought in. By
organisations could meet up with • Yellow (26%) for those requiring November 2011 there had been
the Humanitarian Co-ordinator of repairs before reoccupation over 6,900 deaths attributed to
the UN (who was a replacement as • Green (54%) that were safe to the disease and more than 500,000
the original post-holder had died occupy cases reported. The young and the
in the earthquake). Many NGOs elderly are the most vulnerable to
Community-driven development this water-borne disease, which is
flew in to help but most had not
projects were started by the World transmitted by bacteria found in the
investigated what the needs were
Bank which worked with local faeces of infected people. Vomiting
of the survivors. Very few spoke
people to provide the help they and diarrhoea lead to dehydration
French so it was difficult to know
wanted in order to rebuild homes and death can occur within four
what people wanted. There was no
and communities. Homes had to hours, yet cholera can be treated
linkage and so projects were left
comply with building codes and successfully with antibiotics and
half-done; there was duplication
had to be constructed in a hazard rehydration salts. However, there
of aid in some areas, while others
resilient way. However, these was neither enough expertise in the
received no aid at all. With so many
projects were too few to make a disease nor enough medical staff.
NGOs there was a replication of
large impact. In addition the World The lack of clean drinking water
their needs too. Lots of money was
Bank funded supplementary food and the problem of the disposal of
spent on buying transport vehicles
for 200,000 children aged 6-23 human wastes meant that the disease
and arranging accommodation
months as well as funding schools really got a grip within the country,
for the aid workers so operational
for 140,000 children within camps. and it is now assessed as endemic.
costs were sometimes higher than
New water supply systems were set Although the number of cases is
the amount of help that eventually
up in six rural locations as part of falling at present, it is thought that
got to the population. Most NGOs
the move to encourage people to stay once the rainy season returns in
tended to be operating in a top-down
in the countryside rather than add to 2012, there will be a resurgence of
way, delivering what they felt was
the pressures in Port-au-Prince. cholera cases.
needed. An overall co-ordinator was
needed to determine the ‘three Ws’:
Who? (which NGO), What ? (what Problems in the camps Haiti a year on
they are offering) and Where? (their Few of the camps had competent Gradually the country is beginning
location), to avoid duplication and camp managers and the problems to recover; for example, health
to provide a focus on actual needs. It of water supply and sanitation care in Port-au-Prince is of a
Geofile Online © Nelson Thornes 2012
September 2012 no.672 The Haiti Earthquake 2010 – A Study of Vulnerability
better quality now than before the Figure 4: Park’s model (or hazard response curve) adapted for Haiti
earthquake, but what will happen
Improvement
when the NGOs leave? There is a Normality
need for a long-term strategy. Many
of the survivors are traumatised Jan 12th Planning for future
is underway. Limited
2010
by the events they have witnessed, implementation
Quality of Life
and thousands of amputees are left
without hope of a job or any other Jan 12th 2011
Not yet fully
means of making a living. Some of recovered
the Haitian nurses who worked for Greater disruption
the NGOs have opted to continue as more vulnerable Longer to recover because
of poor capacity to cope
working for them elsewhere, or to
leave the country to go to the USA Pre disaster Emergency relief Rehabilitation Reconstruction
where they will receive better pay. Time
Haiti’s brain drain continues at a
time when it is most desperately in Figure 5: Haiti’s Action Plan for National Recovery and Development
need of its skilled workers. As of
Area of Focus What it involves
January 2011 the relief appeal stood
at over $1 billion, 72% of what is 1.Territorial Rebuilding GeoFileDecentralisation
Series 30 Issue 1of services away from Port-
required. 810,000 people are still au-Prince. Land reform
Fig 672_04 Mac/eps/illustrator 15 s/s ensuring clear laws
in the camps but 700,000 have now for land tenure.
NELSON THORNES PUBLISHING
Artist: David Russell Illustration
left, 35,000 to move to transitional 2. Economic Rebuilding Modernisation and further development of
shelters before finally moving back agricultural, manufacturing, construction and
into a house. 95% of the children in tourism sectors.
the earthquake zone have returned 3. Social Rebuilding Aim for universal primary education, an
to school, which is one positive sign improved and expanded Higher Education
of recovery. Figure 4 shows Park’s sector and a healthcare system that operates
model adapted to show the situation nationwide and not just in urban areas.
in Haiti. Haiti is only now beginning 4. Institutional Rebuilding Modernise the legal framework of the
to move into the reconstruction country and get the core state functions
phase; it has a long way to go before up and running – eventually independently
it can get back even to any level of of aid. Have clear targets for transparency
normality. and accountability in government actions to
reduce corruption levels.
Conclusion
stockpiles and bottled water. There
Haiti is a vulnerable country with a will be more co-ordination and Website resources
long history of unstable government working with the military in order to http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/in_depth/
and has had a number of severe clear roads to access areas to receive americas/2010/haiti_earthquake/
disasters to contend with during aid. Foreign aid will be responsible default.stm - BBC page dedicated
the last 10 years. However, the aid to a Haitian co-ordinator who will to news and short videos of the
to the country in response to the direct what aid is sent where and earthquake and its aftermath.
earthquake and the highlighting who will have an overview. Camps
of its problems has led to some http://www.merlin.org.uk/haiti?gcli
need to be organised with security d=CNWP8dmw2rACFcQKfAod2H
positive results. On 31 March 2010 in mind to protect the vulnerable,
the Haitian government presented g6zA - Haiti pages of the site of the
especially women and girls. NGO Merlin
to the UN its Plan of Action for
Recovery and Development (Figure In 2010 the international aid
5). There is a recognised need for agencies tended to take over and
the training of more health workers they undermined Haiti’s ability to
and offering jobs to keep them in the respond. Although Haiti was not
country. Teachers are to be trained well prepared, its people know what
in dealing with traumatised children they need after a disaster. It is to be
and there is to be the development of hoped that with better co-ordination
manufacturing industries, with the and different priorities Haiti will be
help of the EU and the World Bank. better able to face any future natural
disasters.
There are plans to decentralise so
that resources are put into rural areas
to act as a counterweight to the pull
of Port-au-Prince. Micro-finance is Focus Questions
being offered to enable small-scale
entrepreneurs to begin businesses 1 Using Figures 1 and 2 explain why, when a natural disaster occurs in
that will hopefully provide more jobs Haiti, it is so vulnerable to the impacts and has limited capacity to cope.
in the future.
2 ‘The response to the Haitian earthquake could have been better
Haiti is beginning to draw up a managed.’ Discuss.
Disaster Plan which includes food
Geofile Online © Nelson Thornes 2012
Você também pode gostar
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
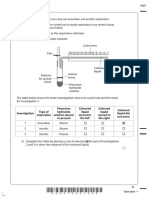
- 3 L-Dopa Can Be Used To Treat People With Parkinson's Disease. Using L-Dopa For A LongDocumento2 páginas3 L-Dopa Can Be Used To Treat People With Parkinson's Disease. Using L-Dopa For A LongEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Course List For The English Literature ... He University of Queensland, AustraliaDocumento1 páginaCourse List For The English Literature ... He University of Queensland, AustraliaEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Brain Jan 2015Documento1 páginaBrain Jan 2015Ericka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- June 2013 Immune ResponseDocumento5 páginasJune 2013 Immune ResponseEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Ial BioDocumento8 páginasIal BioEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Weisel and Hubel Studied The Development of Vision During The Critical WindowDocumento5 páginas4 Weisel and Hubel Studied The Development of Vision During The Critical WindowEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- EnvironmentalDocumento98 páginasEnvironmentalEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Coasts Case StudiesDocumento6 páginasCoasts Case StudiesEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Global InterdependenceDocumento107 páginasGlobal InterdependenceEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- UG022514 International GCSE in Economics 4EC0 For WebDocumento57 páginasUG022514 International GCSE in Economics 4EC0 For Web212852Ainda não há avaliações
- 6953 01 Que 20160527Documento20 páginas6953 01 Que 20160527Ericka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Respiration Rate of A Rat.: 2 The Diagram Below Shows The Apparatus That Could Be Used To Measure TheDocumento2 páginasRespiration Rate of A Rat.: 2 The Diagram Below Shows The Apparatus That Could Be Used To Measure TheEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 0510 w15 QP 22Documento16 páginas0510 w15 QP 22Gurpreet GabaAinda não há avaliações
- Jan 2010 Immune Response and Infectious DiseaseDocumento3 páginasJan 2010 Immune Response and Infectious DiseaseEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 2016 JanDocumento6 páginas2016 JanEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 June 6bi05 PDFDocumento3 páginas2015 June 6bi05 PDFEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- The Dramaturgy of Discomfort in Richard IIDocumento9 páginasThe Dramaturgy of Discomfort in Richard IIEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
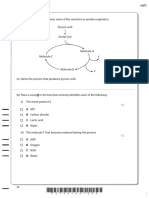
- 5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationDocumento3 páginas5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 JanDocumento2 páginas2015 JanEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 June 6bi05Documento3 páginas2015 June 6bi05Ericka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 3 The Apparatus Shown in The Diagram Below Was Used To Measure The Rate ofDocumento3 páginas3 The Apparatus Shown in The Diagram Below Was Used To Measure The Rate ofEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 June RDocumento4 páginas2013 June REricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationDocumento3 páginas5 The Diagram Below Summarises Some of The Reactions in Aerobic RespirationEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Florence (Flo-Jo) Griffith-Joyner's World Record of 10.49 Seconds For The 100 MDocumento2 páginas2 Florence (Flo-Jo) Griffith-Joyner's World Record of 10.49 Seconds For The 100 MEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) - The Diagram Below Shows The Structure of HIV. Enzyme A Glycoproteins Enzyme BDocumento5 páginasImmunodeficiency Virus (HIV) - The Diagram Below Shows The Structure of HIV. Enzyme A Glycoproteins Enzyme BEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- June 2016 Ial Immune ResponseDocumento6 páginasJune 2016 Ial Immune ResponseEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Death of A Salesman Scene Breakdown With Sound CuesDocumento1 páginaDeath of A Salesman Scene Breakdown With Sound CuesEricka AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Statistics Questions Practice W2 Final 1Documento23 páginasStatistics Questions Practice W2 Final 1Ameen Hussain Fahmy100% (1)
- The White Tiger and Post ColonialismDocumento8 páginasThe White Tiger and Post Colonialismagustinabsas100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (121)
- Between God Ethnicity and Country An Approach To The Study of Transnational ReligionDocumento31 páginasBetween God Ethnicity and Country An Approach To The Study of Transnational ReligionoktaguzelAinda não há avaliações
- Latin American RevolutionDocumento13 páginasLatin American Revolutionr2tc6jtnrvAinda não há avaliações
- United States Treaties and Other Interna PDFDocumento1.147 páginasUnited States Treaties and Other Interna PDFNazmul IslamAinda não há avaliações
- Haitian-Jewish Relations WwII Refs - Leiderman Aug'16Documento46 páginasHaitian-Jewish Relations WwII Refs - Leiderman Aug'16leidermanAinda não há avaliações
- Entry Test Grade 8 2022Documento3 páginasEntry Test Grade 8 2022Гульбану АбикеноваAinda não há avaliações
- Covert Action Information Bulletin 48Documento68 páginasCovert Action Information Bulletin 48Pierre AbramoviciAinda não há avaliações
- Baltimore Afro-American Newspaper, April 17, 2010Documento20 páginasBaltimore Afro-American Newspaper, April 17, 2010The AFRO-American NewspapersAinda não há avaliações
- HaitiDocumento1 páginaHaitiReshanth VangalapudiAinda não há avaliações
- Presidentes de HaitiDocumento6 páginasPresidentes de Haitilucre_ankAinda não há avaliações
- Crime and Violence in The Caribbean - Full ReportDocumento223 páginasCrime and Violence in The Caribbean - Full ReportccentroaméricaAinda não há avaliações
- Stewardship Plan For The National Parks and Natual Areas of HaitiDocumento355 páginasStewardship Plan For The National Parks and Natual Areas of Haitintres100% (1)
- Public Rights Private CommerceDocumento20 páginasPublic Rights Private CommercezuluagadavidAinda não há avaliações
- Cuba in The World The World in CubaDocumento319 páginasCuba in The World The World in Cubawladimir.gonzalezAinda não há avaliações
- Teachers Without Borders Annual Report 2011Documento11 páginasTeachers Without Borders Annual Report 2011Teachers Without BordersAinda não há avaliações
- Reading PersepolisDocumento20 páginasReading Persepolisapi-278760277100% (1)
- The Haitian RevolutionDocumento4 páginasThe Haitian Revolutionapi-381731617Ainda não há avaliações
- KROHN HANSEN 2001 Social AnthropologyDocumento28 páginasKROHN HANSEN 2001 Social AnthropologyJoseph SepulvedaAinda não há avaliações
- Resolução 1542Documento4 páginasResolução 1542Michelle AntonioAinda não há avaliações
- Voodoo Book ListDocumento3 páginasVoodoo Book ListLuís TenorioAinda não há avaliações
- Research Paper On NgoDocumento7 páginasResearch Paper On Ngogz8jpg31100% (1)
- Hannibal Price - The Haytian QuestionDocumento120 páginasHannibal Price - The Haytian QuestionDoru BarbuAinda não há avaliações
- LOPAS SA Company Profile - ENDocumento63 páginasLOPAS SA Company Profile - ENCyril Jean-BaptisteAinda não há avaliações
- Gender Assessment AnnexDocumento112 páginasGender Assessment AnnexGaspar Ciro PiercamilliAinda não há avaliações
- Haiti Earthquake Thesis StatementDocumento8 páginasHaiti Earthquake Thesis Statementmichellespragueplano100% (2)
- HAITIDocumento2 páginasHAITIMicashella ApanayAinda não há avaliações
- Kate RamseyDocumento31 páginasKate RamseyJoanna Da HoraAinda não há avaliações
- UNICEF Haiti Orphanage Report English - 2014 PDFDocumento158 páginasUNICEF Haiti Orphanage Report English - 2014 PDFTimothy SchwartzAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation of Stories of Change Project 'Haiti - Let Agogo'Documento83 páginasEvaluation of Stories of Change Project 'Haiti - Let Agogo'OxfamAinda não há avaliações
- 02 EngDocumento16 páginas02 EngRatnani AshishAinda não há avaliações