Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
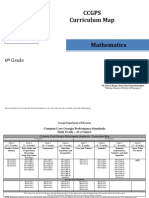
7 Grade Math Ratios & Proportional Relationships CCSS "I Can" Statements
Enviado por
api-2710332470 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
140 visualizações71 páginasTítulo original
7thmathindividualposters1
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
140 visualizações71 páginas7 Grade Math Ratios & Proportional Relationships CCSS "I Can" Statements
Enviado por
api-271033247Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 71
7th Grade Math
Ratios & Proportional
Relationships
CCSS “I Can”
Statements
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.1
I can calculate the unit
rate for real life situations
by breaking down the ratio
(fractions) and dividing to
solve the problem to find
the relationship between
two units.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.2
I can determine that a
proportion is a
statement of equality
between two ratios.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.2.A
I can analyze two ratios
to determine if they are
proportional to one
another with a variety of
strategies (ex: using
tables, graphs or
pictures).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.2.B
I can define the
constant of
proportionality
as a unit rate.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.2.B
I can analyze tables,
graphs, equations,
diagrams and verbal
descriptions to identify
the unit rate.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.2.C
I can represent
proportional
relationships by writing
equations.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.2.D
I can explain what the
points on a graph of a
proportional relationship
mean in terms of a specific
situation and recognize what
(0,0) and (1,r) on a graph
represents, where r is the
unit rate.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.RP.A.3
I can apply proportional
reasoning to solve multistep
ratio and percent problems
(ex: simple interest, tax,
markups, markdowns,
gratuities, commissions, fees,
percent increase and
decrease or percent errors).
7th Grade Math
The Number System
CCSS “I Can”
Statements
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1
I can apply what I have
learned about addition
and subtraction to add
and subtract rational
numbers.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1
I can show addition and
subtraction on a
horizontal or vertical
number line diagram.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1.A
I can describe situations
where opposite quantities
combine to make 0 (ex: A
hydrogen atom has 0
charge because its two
constituents are
oppositely charged.).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1.B
I can represent and
explain how a number
and its opposite have a
sum of 0 and are
additive inverses.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1.B
I can demonstrate and explain how
when adding two numbers p + q:
• if q is positive, the sum of p
and q will be |q| spaces to the
right of p on a number line;
• if q is negative, the sum of p
and q will be |q| spaces to the
left of p on a number line.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1.B
I can explain and justify
why the sum of p + q is
located a distance of |q|
in the positive or
negative direction from
p on a number line.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1.C
I can represent how the
distance between two
rational numbers on a
number line is the
absolute value of their
difference and apply this
to real-world situations.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1.C
I can identify
subtraction of rational
numbers as adding the
additive inverse property
to subtract rational
numbers: p-q=p+(-q).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.1.D
I can use properties of
operations as
strategies to add and
subtract rational
numbers.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2
I can apply what I have
learned about
multiplication and
division of fractions to
multiply and divide
rational numbers.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2.A
I can recognize and describe
the rules when multiplying
signed numbers and apply the
order of operations,
particularly the distributive
property, to multiply rational
numbers (ex: (-1)(-1)=1).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2.A
I can use the products
of rational numbers to
describe real-world
situations.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2.B
I can explain why
integers can be divided
except when the divisor
is 0 and describe why
the quotient is always a
rational number.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2.B
I can understand and
describe the rules when
dividing signed numbers
and integers and
recognize that -(p/q)=(-
p)/q=p/(-q).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2.B
I can use the quotient
of rational numbers to
describe real-world
situations.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2.C
I can identify how
properties of operations
can be used to multiply and
divide rational numbers
(ex: distributive property,
multiplicative inverse property,
multiplicative identity, commutative
property for multiplication and
associative property for multiplication).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.2.D
I can change a rational
number to a decimal
using long division and
explain how the decimal
form of a rational
number stops in zeroes
or repeats.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.3
I can add, subtract,
multiply and divide
rational numbers.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.NS.A.3
I can solve real-world
problems by adding,
subtracting, multiplying
and dividing rational
numbers, including
complex fractions.
7th Grade Math
Expressions &
Equations
CCSS “I Can”
Statements
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.A.1
I can apply properties
of operations to add,
subtract, factor and
expand linear
expressions with
rational coefficients.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.A.1
I can combine like terms
to factor and expand
linear expressions with
rational coefficients
using the distributive
property.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.A.2
I can use properties of
operations to write
equivalent expressions.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.A.2
I can rewrite an
expression in a
different form if
needed.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.3
I can apply properties
of operations to
calculate numbers in
any form and convert
between numerical
forms when necessary.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.3
I can solve multi-step
real-world and
mathematical problems
using positive and negative
rational numbers in any
form (whole numbers,
fractions and decimals).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.3
I can determine if an
answer makes sense
using mental
computation and
estimation strategies.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.4
I can use variables to
represent numbers in real-
world or mathematical
problems and make
reasonable simple
equations and inequalities
to solve problems.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.4.A
I can identify and
fluently solve equations
in the form px+q=r and
p(x+q)=r
(ex: The perimeter of a
rectangle is 54 cm. Its length is
6 cm. What is its width?).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.4.A
I can compare an
arithmetic solution to
an algebraic solution.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.4.B
I can write and solve
word problems leading
to inequalities in the
form px+q>r or px+q<r.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.EE.B.4.B
I can graph and explain
the solution of an
inequality.
7th Grade Math
Geometry
CCSS “I Can”
Statements
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.A.1
I can solve problems
with scale drawings of
geometric figures.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.A.1
I can figure out actual
lengths and areas from
a scale drawing and use
them to create a
different sized scale
drawing.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.A.2
I can draw geometric
shapes with given
conditions either
freehand, with a ruler
and protractor or with
technology.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.A.2
I can recognize and draw a
triangle when given three
measurements: three side
lengths, three angle
measurements or a
combination of side lengths
and angle measurements.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.A.3
I can draw and
describe geometrical
figures including right
rectangular prisms and
right rectangular
pyramids.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.A.3
I can name the two-
dimensional figures
that represent a
particular slice of a
three-dimensional
figure.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.B.4
I can state the
formulas for the area
and circumference of a
circle and use them to
solve problems.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.B.4
I can explain the
relationship between
the circumference and
the area of a circle.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.B.5
I can use properties of
supplementary,
complementary, vertical and
adjacent angles in multi-step
problems to write and solve
simple equations for an
unknown angle in a figure.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.B.6
I can solve problems
involving area, volume
and surface area of
two-and three-
dimensional figures.
7th Grade Math
Statistics & Probability
CCSS “I Can”
Statements
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.A.1
I can understand that
inferences about a
population can be made
by examining a sample.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.A.1
I can understand why
generalizations made
about a population from
a sample are only valid if
the sample represents
that population.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.A.2
I can use data from a
random sampling to draw
conclusions about a
population (ex: Estimate
the mean word length in a
book by randomly sampling
words from the book.).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.A.2
I can generate multiple
samples to gauge
predictions.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.B.3
I can find similarities
and differences in two
different data sets
(including mean, median,
etc.).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.B.4
I can compare and draw
conclusions from two
populations based off
of their means, medians
and/or ranges.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.5
I can recognize and explain
that the probability of a chance
event is a number between 0
and 1 that expresses how likely
an event is to occur.
(ex: When rolling a number cube 600
times, predict that a 3 or 6 would be
rolled roughly 200 times, but probably
not exactly 200 times.).
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.6
I can collect data to
approximate
probability.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.6
I can use probability to
predict the number of
times an event will
occur.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.7
I can investigate,
develop and use
probabilities to help me
solve problems.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.7
I can compare
probabilities to
observed frequencies.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.7.A
I can develop a uniform
probability model and
use it to determine the
probability of an event
occurring.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.7.B
I can develop a
probability model by
observing frequencies
in data developed from
a chance process.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.8
I can find probabilities
of multiple events using
organized lists, tables,
tree diagrams and
simulation.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.8.A
I can use the sample
space to compare the
number of favorable
outcomes to the total
number of outcomes and
determine the probability
of the compound event.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.8.B
I can explain the
outcomes in the sample
space that make up an
event.
CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.SP.C.8.C
I can design and use
simulation to predict
the probability of a
compound event.
Você também pode gostar
- 6 ThmathindividualpostersDocumento85 páginas6 Thmathindividualpostersapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- 8 Grade Math The Number System CCSS "I Can" StatementsDocumento79 páginas8 Grade Math The Number System CCSS "I Can" Statementsapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- 7th Grade StandardsDocumento8 páginas7th Grade Standardsapi-251069371Ainda não há avaliações
- I Can Math 6Documento6 páginasI Can Math 6api-365969613Ainda não há avaliações
- 6th Grade Math Common Core I Can StatementsDocumento6 páginas6th Grade Math Common Core I Can Statementsapi-233930784Ainda não há avaliações
- "I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade MathDocumento6 páginas"I Can" Common Core!: 6th Grade Mathapi-303193556Ainda não há avaliações
- 8th Grade StandardDocumento7 páginas8th Grade Standardapi-251069371Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 3 OverviewDocumento5 páginasGrade 3 Overviewapi-233351761Ainda não há avaliações
- Math 7 Syllabus 2014-2015Documento5 páginasMath 7 Syllabus 2014-2015api-266524097Ainda não há avaliações
- Overland Trail Curr AnalysisDocumento5 páginasOverland Trail Curr Analysisapi-246119961Ainda não há avaliações
- FKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch3 Student WorkbookDocumento130 páginasFKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch3 Student WorkbookSelvi RamasamyAinda não há avaliações
- Algebra II Standards Final ChartDocumento6 páginasAlgebra II Standards Final Chartapi-273248611Ainda não há avaliações
- 1st Grade Common Core Math StandardsDocumento3 páginas1st Grade Common Core Math Standardsalex1413Ainda não há avaliações
- Standards-K-12 6th GradeDocumento3 páginasStandards-K-12 6th Gradeapi-296039056Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 6 Curriculum MapDocumento6 páginasGrade 6 Curriculum Mapapi-260971765Ainda não há avaliações
- Second Draft of 6-8 Benchmarks With Standards 8-28Documento9 páginasSecond Draft of 6-8 Benchmarks With Standards 8-28justin fellerAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 7 Number System StandardsDocumento2 páginasGrade 7 Number System Standardsapi-282583504Ainda não há avaliações
- I Can Math Check ListDocumento4 páginasI Can Math Check ListPamela PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Common Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeDocumento171 páginasCommon Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeJessicaAinda não há avaliações
- Etr 528 Test Evaluation-Aynur AytekinDocumento32 páginasEtr 528 Test Evaluation-Aynur Aytekinapi-489466485Ainda não há avaliações
- 6thgrade Math I Can StatementsDocumento155 páginas6thgrade Math I Can StatementsRhonda GrossAinda não há avaliações
- 8 ThgradecurriculumDocumento5 páginas8 Thgradecurriculumapi-254290621Ainda não há avaliações
- 6th Grade Math Curriculum MapDocumento6 páginas6th Grade Math Curriculum Mapapi-109360342Ainda não há avaliações
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5Documento20 páginasAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 5establoid1169Ainda não há avaliações
- Math Grade 3 08 11Documento6 páginasMath Grade 3 08 11api-246939068Ainda não há avaliações
- 7th Grade Math I Can StatementsDocumento5 páginas7th Grade Math I Can Statementsapi-260621820Ainda não há avaliações
- FKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch0 MathematicalfoundationDocumento33 páginasFKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch0 MathematicalfoundationSelvi RamasamyAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Quarter Math SkillsDocumento5 páginas2nd Quarter Math Skillsapi-93111231Ainda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Modern Mathematics: A Practical ReviewNo EverandFundamentals of Modern Mathematics: A Practical ReviewAinda não há avaliações
- Sixth Math StandardsDocumento3 páginasSixth Math Standardsapi-233655908Ainda não há avaliações
- Standards-K-12 8th GradeDocumento3 páginasStandards-K-12 8th Gradeapi-296039056Ainda não há avaliações
- Ccss KG MathDocumento8 páginasCcss KG Mathapi-307635338Ainda não há avaliações
- Calculus StandardsDocumento3 páginasCalculus StandardsMahmud Alam NauAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanDocumento7 páginas6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanBecky JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- Stat MatchDocumento44 páginasStat MatchAngelo LorentiAinda não há avaliações
- 7th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocumento6 páginas7th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardAinda não há avaliações
- CCSS Checklist For Math 3rdDocumento9 páginasCCSS Checklist For Math 3rdodie01Ainda não há avaliações
- Website - Grade 3 Math Measurement DataDocumento2 páginasWebsite - Grade 3 Math Measurement Dataapi-546528476Ainda não há avaliações
- Tnready Blueprint g6 MathDocumento9 páginasTnready Blueprint g6 Mathapi-282869532Ainda não há avaliações
- Iskl Grade 7 MathsDocumento5 páginasIskl Grade 7 MathsMathiarasu MuthumanickamAinda não há avaliações
- Third Grade Math May 2014Documento3 páginasThird Grade Math May 2014destiny_eastepAinda não há avaliações
- 1 ST Math Checklists 2Documento6 páginas1 ST Math Checklists 2ddfsfsAinda não há avaliações
- Overland TrailDocumento8 páginasOverland Trailapi-245623862Ainda não há avaliações
- Algebra 1 Math Alt Ast 1516 Edits-1Documento4 páginasAlgebra 1 Math Alt Ast 1516 Edits-1api-293898864Ainda não há avaliações
- Yearly Math Lesson Plan (2012) Form 5Documento19 páginasYearly Math Lesson Plan (2012) Form 5Nie Anthon100% (1)
- 8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocumento6 páginas8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Algebra F Semester 1 Topics 2011-2012: Chapter 1 GoalsDocumento2 páginasAdvanced Algebra F Semester 1 Topics 2011-2012: Chapter 1 Goalsapi-168512039Ainda não há avaliações
- Math Grade 5 08 11Documento6 páginasMath Grade 5 08 11api-246939068Ainda não há avaliações
- 6th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocumento6 páginas6th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardAinda não há avaliações
- Eighth Grade Math May 2014Documento2 páginasEighth Grade Math May 2014destiny_eastepAinda não há avaliações
- Math Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Documento4 páginasMath Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Lino Garcia63% (8)
- Matlab III: Graphics and Data AnalysisDocumento39 páginasMatlab III: Graphics and Data Analysiswan ismail ibrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Ade Level Scope - grade6.SP - EditsDocumento6 páginasAde Level Scope - grade6.SP - Editscguanajuato5416Ainda não há avaliações
- Seventh Math StandardsDocumento3 páginasSeventh Math Standardsapi-233655908Ainda não há avaliações
- Reader 133ADocumento164 páginasReader 133AIv ChenAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6: How to Do Forecasting Regression by AnalysisDocumento7 páginasChapter 6: How to Do Forecasting Regression by AnalysisSarah Sally SarahAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 5 "I Can " Statements Number Strand: Whole Numbers To 1 000 000Documento8 páginasGrade 5 "I Can " Statements Number Strand: Whole Numbers To 1 000 000api-231547982Ainda não há avaliações
- Walk The Line 7Documento3 páginasWalk The Line 7api-279576217Ainda não há avaliações
- G MTH 2 st20 Ccss Ican Stmnts 20120528Documento8 páginasG MTH 2 st20 Ccss Ican Stmnts 20120528api-324573119Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide MarchDocumento67 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide Marchapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Unique Learning System Presentation Shared 2Documento30 páginasUnique Learning System Presentation Shared 2api-271033247100% (1)
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide AprilDocumento69 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide Aprilapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide February Part 2Documento39 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide February Part 2api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide AugustDocumento96 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide Augustapi-271033247100% (1)
- Usr Local SRC EducationDocumento9 páginasUsr Local SRC Educationapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Energy All AroundDocumento30 páginasEnergy All AroundVeronica BaileyAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide February Part 2Documento39 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide February Part 2api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide February Part 1Documento90 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide February Part 1api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
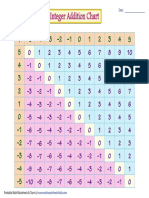
- Addition Subtraction Chart Display1Documento1 páginaAddition Subtraction Chart Display1api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide DecemberDocumento44 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide Decemberapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide AugustDocumento96 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide Augustapi-271033247100% (1)
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide JanuaryDocumento74 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide Januaryapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Usr Local SRC EducationDocumento12 páginasUsr Local SRC Educationapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- A e Ai I e WorksheetsDocumento24 páginasA e Ai I e Worksheetsapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide October Part 2Documento33 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide October Part 2api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
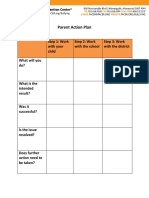
- Parent Action PlanDocumento1 páginaParent Action Planapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Essential Elements Math Pacing Guide October Part 1Documento81 páginasEssential Elements Math Pacing Guide October Part 1api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- PndbrochureDocumento2 páginasPndbrochureapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Bullying Aanhpi Massa FactsDocumento1 páginaBullying Aanhpi Massa Factsapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Dolch Sight Words Flash Cards 1st 1Documento41 páginasDolch Sight Words Flash Cards 1st 1api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Dolch Sight Words Flash Cards 3rdDocumento41 páginasDolch Sight Words Flash Cards 3rdapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Module 6: Comparing and Ordering DecimalsDocumento45 páginasModule 6: Comparing and Ordering DecimalsalfierapisuraAinda não há avaliações
- BullyingbrochureDocumento2 páginasBullyingbrochureapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- DCL Factsheet 201010Documento2 páginasDCL Factsheet 201010api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Proc SafegdsDocumento25 páginasProc Safegdsapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Wasb 2021-AprilDocumento36 páginasWasb 2021-Aprilapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Wasb 2020-11-NovemberDocumento36 páginasWasb 2020-11-Novemberapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Wasb 2021-MayDocumento36 páginasWasb 2021-Mayapi-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- New-Member-Handbook-2021 Web-1Documento68 páginasNew-Member-Handbook-2021 Web-1api-271033247Ainda não há avaliações
- Spain Usa ExtraditionDocumento2 páginasSpain Usa ExtraditionAdrian BirdeaAinda não há avaliações
- Easy Gluten Free RecipesDocumento90 páginasEasy Gluten Free RecipesBrandon Schmid100% (1)
- Accounting Notes - 1Documento55 páginasAccounting Notes - 1Rahim MashaalAinda não há avaliações
- Death and DickinsonDocumento12 páginasDeath and DickinsonHarshita Sohal100% (1)
- Practise Active and Passive Voice History of Central Europe: I Lead-InDocumento4 páginasPractise Active and Passive Voice History of Central Europe: I Lead-InCorina LuchianaAinda não há avaliações
- Agile Process ModelsDocumento15 páginasAgile Process ModelsShadrack KimutaiAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 4 Science Quiz Bee QuestionsDocumento3 páginasGrade 4 Science Quiz Bee QuestionsCecille Guillermo78% (9)
- AIX For System Administrators - AdaptersDocumento2 páginasAIX For System Administrators - Adaptersdanielvp21Ainda não há avaliações
- MCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Documento11 páginasMCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Hiya ShahAinda não há avaliações
- The Man of Sorrows Wednesday of Holy Week Divine IntimacyDocumento5 páginasThe Man of Sorrows Wednesday of Holy Week Divine IntimacyTerri ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- 6-Modul - PTI412 - IoT-1-2020Documento17 páginas6-Modul - PTI412 - IoT-1-202020200801015 Joko SulistyoAinda não há avaliações
- State of Indiana, County of Marion, SS: Probable Cause AffidavitDocumento1 páginaState of Indiana, County of Marion, SS: Probable Cause AffidavitIndiana Public Media NewsAinda não há avaliações
- KINGS OF TURKS - TURKISH ROYALTY Descent-LinesDocumento8 páginasKINGS OF TURKS - TURKISH ROYALTY Descent-Linesaykutovski100% (1)
- Sosai Masutatsu Oyama - Founder of Kyokushin KarateDocumento9 páginasSosai Masutatsu Oyama - Founder of Kyokushin KarateAdriano HernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Court of Appeals: DecisionDocumento11 páginasCourt of Appeals: DecisionBrian del MundoAinda não há avaliações
- Expectations for Students and ParentsDocumento15 páginasExpectations for Students and ParentsJasmine TaourtiAinda não há avaliações
- Model Test Paper Maths CBSE Class IX - IIIDocumento8 páginasModel Test Paper Maths CBSE Class IX - IIIAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VAinda não há avaliações
- Wallace, 2009Documento20 páginasWallace, 2009florAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Lesson Writing Unit: Personal Recount For Grade 3 SEI, WIDA Level 2 Writing Kelsie Drown Boston CollegeDocumento17 páginas6 Lesson Writing Unit: Personal Recount For Grade 3 SEI, WIDA Level 2 Writing Kelsie Drown Boston Collegeapi-498419042Ainda não há avaliações
- ABAP Program Types and System FieldsDocumento9 páginasABAP Program Types and System FieldsJo MallickAinda não há avaliações
- Master ListDocumento26 páginasMaster ListNikhil BansalAinda não há avaliações
- Heat Wave Action Plan RMC 2017Documento30 páginasHeat Wave Action Plan RMC 2017Saarthak BadaniAinda não há avaliações
- Eng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionDocumento2 páginasEng10 LPQ3_4 Coherence and CohesionNiña RasonableAinda não há avaliações
- Zeal Study 10th English Synonym Unit 1 - 7Documento24 páginasZeal Study 10th English Synonym Unit 1 - 7viaanenterprises2008Ainda não há avaliações
- Military Divers ManualDocumento30 páginasMilitary Divers ManualJohn0% (1)
- Aerospace & Aviation Job RolesDocumento74 páginasAerospace & Aviation Job RolesBharat JainAinda não há avaliações
- 19-Year-Old Female With Hypokalemia EvaluatedDocumento5 páginas19-Year-Old Female With Hypokalemia EvaluatedMohammed AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 ACI Airport Economics Report - Preview - FINAL - WEB PDFDocumento12 páginas2015 ACI Airport Economics Report - Preview - FINAL - WEB PDFDoris Acheng0% (1)
- Salzer Panel Accessories Price List - 01st January 2019Documento40 páginasSalzer Panel Accessories Price List - 01st January 2019Chandra SekaranAinda não há avaliações
- Guest Speaker SpeechDocumento12 páginasGuest Speaker SpeechNorhana Manas83% (82)