Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Bhs Inggris Conditional Syechan
Enviado por
Masdd Sda SdsaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Bhs Inggris Conditional Syechan
Enviado por
Masdd Sda SdsaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
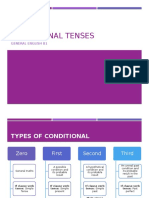
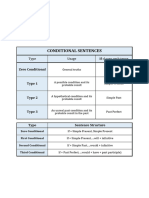
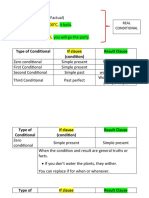
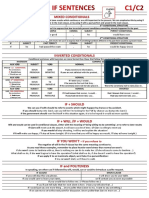
Type If clause Main clause
Zero If + simple simple present
present
Type 1 If + simple simple future
present
Type 2 If + simple present conditional or
past present continuous
conditional
Type 3 If + past perfect conditional or
CONTOH
perfect perfect continuous
conditional
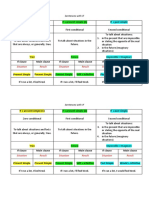
Zero
Mixed type If + past present conditional or PURPOSE OF
If we burn paper, it becomes ash perfect or perfect conditional CONDITIONAL
simple past
If you heat ice, it melts
Conditional sentences
If it rains, the grass get wet are statements
discussing known
Type 1
factors or hypothetical
If it rains, I will stay at home situations and their
If you invite me, I will come to consequences. Complete
conditional sentences
your party
contain a conditional
If he gives her chocolate, she
clause (often referred to
will be happy as the if-clause) and the
If it doesn’t rain, we will go to consequence
the library
CONDITIONAL
Type 2 SENTENCE
If I got scholarship, I would
continue my study in London
If it rained tomorrow, I would
sleep all day
If you went to the bed earlier,
you would not be so tired
Type 3
LANGUAGE FEATURES
If you had studied harder, you
would have passed the exam Type Usage If clause Main clause verb
If it had rained, you would have verb tense tense
gotten wet
If I had accepted that Zero General truths Simple Simple present
present
promotion, I would have been
Type 1 A possible Simple Simple future
working in Milan condition and its present
probable result
Mixed Type
If I had worked harder at Type 2 A hypothetical Simple past Present
school, I would have a better condition and its conditional or
probable result Present
job now continuous
If we had looked at the map, we conditional
wouldn’t be lost Type 3 An unreal past Past Perfect Perfect
If you weren’t afraid of spiders, condition and its conditional
you would have picked it up probable result in
the past
and put it outside
Mixed An unreal past Past perfect Present
type condition and its contditional
probable result in
the present
CONTOH SOAL
1. If I had come to music festival, I would have met Raisa there.
This sentence means ……
a. I didn’t come to the music festival but Raisa there
b. I had come to music festival in order to meet Raisa there
c. I didn’t come to music festival so I didn’t meet Raisa there
d. I come to music festival but I didn’t meet Raisa there
e. I didn’t come to music festival and Raisa was there
Pembahasan:
Pada kalimat diatas, menggunakan bentuk conditional sentence type 3, dengan fakta “unreal condition in the past”
Sehingga, faktanya adalah I didn’t come to music festival so I didn’t meet Raisa there
2. I am not a mechanic, so I can’t fix it.
This sentence means …….
a. If I could be a mechanic, I had fixed it
b. If I have been a mechanic, I would have fixed it
c. If I were a mechanic, I could fix it
d. If I am a mechanic, I could fix it
e. If I could have been a mechanic, I had fixed it
Pembahasan:
Pada kalimat diatas, menggunakan bentuk conditional sentence type 1, dengan fakta yang mungkin terjadi di masa akan
dating, dan faktanya adalah “possibility” di masa datang.
Sehingga, kalimat tersebut bermakna If I am a mechanic, I could fix it
3. …………, I might borrow it from him.
a. Were the novel his
b. The novel were his
c. If his the novel
d. If the novel him
e. If his the novel
Pembahasan:
Penggunaan might menunjukkan pada bentuk conditional sentence type 2 dengan pattern subject + past tense + subject +
might/would/could
Seharusnya: If the novel were his, I might borrow it from him
Penggunaan inversi/pembalikan digunakan dalam kalimat tersebut, sehingga were the novel his, I might borrow it from
him
Você também pode gostar
- ConditionalDocumento23 páginasConditionalLance Nicole VillasisAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals and SunjunctivesDocumento7 páginasConditionals and SunjunctivesRachel WellinsAinda não há avaliações
- CONDITIONALDocumento95 páginasCONDITIONALmmmmmAinda não há avaliações
- CONDITIONALDocumento25 páginasCONDITIONALShiella Mae Vispo100% (1)
- 2.godina IF Clauses 0, 1, 2 TabelaDocumento2 páginas2.godina IF Clauses 0, 1, 2 TabelaMarijam SafargalijevaAinda não há avaliações
- 07 CONDITIONAL - RevDocumento20 páginas07 CONDITIONAL - RevBima Dwi Priya SAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional 2pagesDocumento2 páginasConditional 2pagesTechArea GamingAinda não há avaliações
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocumento7 páginasClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaAinda não há avaliações
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocumento8 páginasClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaAinda não há avaliações
- The Zero ConditionalDocumento4 páginasThe Zero ConditionalKim SeorinAinda não há avaliações
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocumento8 páginasClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaAinda não há avaliações
- ConditionalsDocumento11 páginasConditionalsPetra StefanescuAinda não há avaliações
- Name:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentencesDocumento4 páginasName:Hosea Roinaldo Class:XII MIPA 2/19 Conditional SentenceshosearoinaldoAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional Sentences G 9 ENGDocumento3 páginasConditional Sentences G 9 ENGEnas MujaliAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional SentencesDocumento4 páginasConditional SentencesRekaman IstiAinda não há avaliações
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocumento5 páginasClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaAinda não há avaliações
- CONDITIONALDocumento27 páginasCONDITIONALBjp MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals: English For Level IvDocumento4 páginasConditionals: English For Level IvJuan Felipe SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- ConditionalsDocumento8 páginasConditionalsIngridAinda não há avaliações
- GE B1 - Conditional TensesDocumento10 páginasGE B1 - Conditional TensesSadhvi SitaAinda não há avaliações
- Clauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyDocumento6 páginasClauses Exercise: 1. The Jury Believed That The Man Was GuiltyJohn PalutlaAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional SentenceDocumento2 páginasConditional SentenceBunnarin ChrunAinda não há avaliações
- If Clause Group 5Documento24 páginasIf Clause Group 5FauzanAinda não há avaliações
- Clasa A VIII A B ConditionalsDocumento9 páginasClasa A VIII A B ConditionalsLiliana GheorgheAinda não há avaliações
- If ClauseDocumento16 páginasIf ClauseNabilah Mukti RifahmiAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals ExplanationDocumento8 páginasConditionals ExplanationDoris ELianaAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals PDFDocumento2 páginasConditionals PDFminimunhozAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals ExplanationDocumento8 páginasConditionals ExplanationJota Fagua MuñozAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseDocumento4 páginasConditional Sentence Type Usage If Clause Verb Tense Main Clause Verb TenseStancu AlinAinda não há avaliações
- ConditionalsDocumento20 páginasConditionalsshinneulyoungAinda não há avaliações
- IF - Conditional SentencesDocumento4 páginasIF - Conditional SentencesChirine AyoubAinda não há avaliações
- The Zero ConditionalDocumento5 páginasThe Zero ConditionalEduard Hernan Cardona VillamilAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional Sentence TypeDocumento6 páginasConditional Sentence TypeHarsh SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- If Conditional: With Reza and FaisaDocumento9 páginasIf Conditional: With Reza and FaisaSyifaa ZuchrufAinda não há avaliações
- If Cond Sentence+ImperativeDocumento18 páginasIf Cond Sentence+Imperativefarrelarifin7Ainda não há avaliações
- ConditionalsDocumento11 páginasConditionalsКоля МогильниковAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional SentencesDocumento7 páginasConditional SentencesmirindaokasAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional and Subjunctive MoodsDocumento20 páginasConditional and Subjunctive MoodsCyndi De VriesAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals All InfographicsDocumento8 páginasConditionals All Infographicsamajida fadia rAinda não há avaliações
- If Clause LessonDocumento8 páginasIf Clause LessonMega NandaAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional - English Grammar - EFDocumento2 páginasConditional - English Grammar - EFNameless 00Ainda não há avaliações
- A'la Faradisil Jannah Rangkuman Sasing Bab 1-5Documento13 páginasA'la Faradisil Jannah Rangkuman Sasing Bab 1-5A'la Faradisil Jannah XI MIPA 3Ainda não há avaliações
- Conditional Sentences (C1 - C2)Documento1 páginaConditional Sentences (C1 - C2)MaryoriRamírez100% (1)
- Conditional: Simple Present If Simple FutureDocumento2 páginasConditional: Simple Present If Simple FutureFlor Viviana CASTAÑO VELANDIAAinda não há avaliações
- ConditionalsDocumento19 páginasConditionalsantonio.1898Ainda não há avaliações
- Situation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFDocumento1 páginaSituation Result Situation Result Situation Result: Sentences With IFKenia AquinoAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional SentencesDocumento1 páginaConditional Sentencescampus.headAinda não há avaliações
- ConditionalulDocumento3 páginasConditionalulsimina antonAinda não há avaliações
- CONDITIONALSDocumento2 páginasCONDITIONALSJudith Contreras JaraAinda não há avaliações
- ConditionalsDocumento5 páginasConditionalsMarcia TrellesAinda não há avaliações
- Amanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalDocumento4 páginasAmanda. T Xii A 2: ConditionalGeraldine SitanggangAinda não há avaliações
- IF ClauseDocumento1 páginaIF ClauseMaria PascuAinda não há avaliações
- Providing (Or Provided), As (Or So) Long As, and On Condition ThatDocumento1 páginaProviding (Or Provided), As (Or So) Long As, and On Condition Thatgusti annisaAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional ClausesDocumento4 páginasConditional ClausesBojana JovanovskaAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals - Theory (B1)Documento2 páginasConditionals - Theory (B1)damianAinda não há avaliações
- Conditional Sentences (C1-C2)Documento1 páginaConditional Sentences (C1-C2)Cristina-Luciana IonescuAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals Explanation Powerpoint Grammar Guides 64539Documento8 páginasConditionals Explanation Powerpoint Grammar Guides 64539Samuel HavristiucAinda não há avaliações
- Conditionals Chart: Grammar & UsageDocumento15 páginasConditionals Chart: Grammar & UsageDanielle MacAlpineAinda não há avaliações
- Genigraphics Poster Template 36x48aDocumento1 páginaGenigraphics Poster Template 36x48aMenrie Elle ArabosAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Sensor Nodes in Underwater Sensor Networks: Yu Yang, Zhang Xiaomin, Peng BO, Fu YujingDocumento5 páginasDesign of Sensor Nodes in Underwater Sensor Networks: Yu Yang, Zhang Xiaomin, Peng BO, Fu Yujinghari9923Ainda não há avaliações
- Python Fundamentals: ModularityDocumento19 páginasPython Fundamentals: ModularityVFisaAinda não há avaliações
- Clauses of Contrast and Purpose Whatever, Whenever, Etc.Documento5 páginasClauses of Contrast and Purpose Whatever, Whenever, Etc.CARLOS VILLAMIZAR MONROYAinda não há avaliações
- Word-Order-In-English - Vi2 PDFDocumento6 páginasWord-Order-In-English - Vi2 PDFwahyu chandra wijayaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 01 - Assignments CSE115 (SAM)Documento11 páginasWeek 01 - Assignments CSE115 (SAM)Fake PrioAinda não há avaliações
- Objectives of The System For Autistic Children SchoolDocumento5 páginasObjectives of The System For Autistic Children SchoolmoAinda não há avaliações
- Post-Implementation Steps For SAP Note 3295909Documento5 páginasPost-Implementation Steps For SAP Note 3295909luizhm0reiraAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Libre Office - WriterDocumento448 páginasManual Libre Office - WriterpowerpuffpurpleAinda não há avaliações
- Rainbow Class 7Documento94 páginasRainbow Class 7Yassilya GhizlaneAinda não há avaliações
- How To Paraphrase in The IELTS TestDocumento6 páginasHow To Paraphrase in The IELTS TestNgọc Quân TrươngAinda não há avaliações
- Starvert: Compact & Powerful DriveDocumento44 páginasStarvert: Compact & Powerful DriveSamir AtabAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial - Creating Forms PDFDocumento9 páginasTutorial - Creating Forms PDFBlashko GjorgjievAinda não há avaliações
- PA3000 en Arch 1011122Documento78 páginasPA3000 en Arch 1011122lifgarygarcia100% (1)
- EvalExam2 Geometry SET ADocumento2 páginasEvalExam2 Geometry SET AEngr. HLDCAinda não há avaliações
- Materi Ajar InfographicsDocumento17 páginasMateri Ajar InfographicsZona Putra Jaya MandiriAinda não há avaliações
- 09 - Chapter2Documento81 páginas09 - Chapter2Kamalakkannan MuniappanAinda não há avaliações
- ĐỀ KT ANH 7 GIỮA KÌ 2Documento6 páginasĐỀ KT ANH 7 GIỮA KÌ 2Đặng HuyềnAinda não há avaliações
- Al MumtahinaDocumento9 páginasAl MumtahinaAyesha KhanAinda não há avaliações
- World Languages Committee BookletDocumento75 páginasWorld Languages Committee BookletmarthaAinda não há avaliações
- Multi Format LFDocumento17 páginasMulti Format LFIssac NewtonAinda não há avaliações
- Definition and Essence in Aristotle's Metaphysics VII 4Documento26 páginasDefinition and Essence in Aristotle's Metaphysics VII 4Shayok SenguptaAinda não há avaliações
- International Journal For Clergy July 1990: J. Robert Spangler, Longest Serving Ministry Editor, RetiresDocumento32 páginasInternational Journal For Clergy July 1990: J. Robert Spangler, Longest Serving Ministry Editor, RetiresDaniel HalápiAinda não há avaliações
- Part 2 Picture Description: para Empezar La ComparaciónDocumento5 páginasPart 2 Picture Description: para Empezar La ComparaciónMariola Valencia EstévezAinda não há avaliações
- A Look at Architypal CriticismDocumento9 páginasA Look at Architypal Criticismseeker03Ainda não há avaliações
- PIC18 Starter Kit User GuideDocumento46 páginasPIC18 Starter Kit User GuideDamith Buddhika Sri WimalarathnaAinda não há avaliações
- HabilitationDocumento186 páginasHabilitationAland MediaAinda não há avaliações
- Active Level 2 SsDocumento2 páginasActive Level 2 SsMehran EltAinda não há avaliações
- BGP Regular Expressions ExamplesDocumento2 páginasBGP Regular Expressions ExamplesSon Tran Hong NamAinda não há avaliações
- Tehnici de Argumentare 56Documento52 páginasTehnici de Argumentare 56Alexandru IvanAinda não há avaliações