Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
M Elf - D: Stresses Under Different Load Applications
Enviado por
MqAshlady0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
26 visualizações1 páginaefwgwe
Título original
8
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoefwgwe
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
26 visualizações1 páginaM Elf - D: Stresses Under Different Load Applications
Enviado por
MqAshladyefwgwe
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
the structure's predicted response Is reasonable.
A key At regions away from discontinuities and points of
component in the validation of software-generated solu- applied loading, the distribution of stress in a member
tions is the engineering judgment of the designer, who having linear elastic material properties is
must be able to visualize the anticipated response of the
Mc (Exp. C.2-3)
structure and approximate values of the results. To this
I
end, the next objective of this article is to provide the back-
where c is the distance from the member's centroidal axis;
ground to the response of ground-supported slabs under
and f is the stress at distance c from the centroidal axis.
different loading scenarios and conditions. These include
tendons not being at the centroid of a slab; tendons having
C.3 STRESSES UNDER DIFFERENT LOAD
unintentional profile, friction, shrinkage, creep, variations
APPLICATIONS
in slab thickness; and concentrated loads.
Figure C.3-1 shows the ground-supported slab that we
C.2 ENGINEERS' BENDING STRESS ASSUMP- will investigate under different prestressing and support
conditions. The slab is assumed to be long enough to have
TIONS
distinct boundary and interior regions. Points A and C
It is common in engineering practice to use the Euler-
represent points at the slab edge, where the tendon anchor-
Bernoulli beam equation when calculating axial and
ages are located. Point B represents a point away from the
bending stresses in beam/slab type members at regions
slab edge.
away from the point of application of any loads or
When a ground-supported slab is cast, the weight of
discontinuities. The key assumption of this equation is
the wet concrete is transferred directly to the ground. The
that plane sections of the member remain plane under a
slab assumes the profile of its support so the curvature in
bending moment.
the slab will initially be the same as that of the supporting
For elastic linear material, commonly assumed, the
Soil. As long as the slab remains in contact with the soil,
moment M in the member is given by bending stresses will only be generated in the slab if there
El is a change In the profile of the soil support. Ignoring tempo-
M (Exp. C.2-1)
it rarily the effects of shrinkage, creep, temperature, and
where E is the modulus of elasticity of the member; I is the settlement, there will be neither bending nor axial stresses
in the slab prior to the application of post-tensioning.
second moment of area of a member's cross section about
Consider the case of a slab on rigid ground support
its centroidal axis; and it is the change in radius of curva-
ture in the member. without any restraint to shrinkage or expansion; in effect,
A slab that is cast over a non-level surface, having an the slab is on roller support. The slab is loaded at its
centroid by an externally applied force P (Fig. C.3-2(a-I));
initial curvature ( I /Ro), will not be subject to a bending
the force is intended to simulate the application of post-
moment, arising from the initial curvature of its support.
tensioning through an anchorage assembly- At a Point B
However, changes in the loading or support conditions,
away from the slab edge, the entire axial force P will be
such as a change in the profile of the soil, can cause a
available, with the stress distributed uniformly over the
change in the slab curvature and a bending moment. For
small displacements, the moment can be calculated from slab thickness (Fig. C.3-2(a-10).
the slab displacement w accordingto the well-known equation
M Elf_d (Exp. C.2-2) B
dx'aw)
soil
where w is the out-of-plane displacement of the slab.
Note that the rigidity of most PT foundations is such Pig. C.3.1—Configuration of a typical ground-supported slab. Points
that the foundation does not strictly follow the soil profile; A and C represent the end conditions, where the post-tensioning
therefore, gaps between the foundation and soil are created anchorages an located. Point B represents the interior condition, away
from the anchorages.
by soil movement.
Você também pode gostar
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNo EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Beam Column Base Plate DesignDocumento10 páginasBeam Column Base Plate DesignSPUD1100% (3)
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNo EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (4)
- Beam-Column Base Plate DesignDocumento10 páginasBeam-Column Base Plate Designthegerman34Ainda não há avaliações
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsNo EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsNota: 3 de 5 estrelas3/5 (2)
- C.6 of Stress: LarbeiimieemDocumento1 páginaC.6 of Stress: LarbeiimieemMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Elastic Foundation BeamDocumento157 páginasChapter 2 Elastic Foundation BeamyangAinda não há avaliações
- Integral Bridges and The Modelling of Soil-Structure InteractionDocumento10 páginasIntegral Bridges and The Modelling of Soil-Structure Interactionkevin_au18Ainda não há avaliações
- Analysis and Design of Structural Sandwich Panels: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNo EverandAnalysis and Design of Structural Sandwich Panels: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Calculation of Spring Stiffness of A PileDocumento6 páginasCalculation of Spring Stiffness of A PilescshekarAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignNo EverandLecture Notes on Reinforced Concrete DesignAinda não há avaliações
- Web Buckling in Castellated Beams: A. A. Aglan, R. G. RedwoodDocumento14 páginasWeb Buckling in Castellated Beams: A. A. Aglan, R. G. RedwoodmokhtazulAinda não há avaliações
- Vesic 1975 Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocumento27 páginasVesic 1975 Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundationst.w.c.100% (2)
- Strength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainNo EverandStrength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Section1 Unit3Documento16 páginasSection1 Unit3jbsAinda não há avaliações
- Fault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureNo EverandFault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureMarion Y. ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- Foundations: A. Site Foundation Conditions. Subsurface SoilDocumento16 páginasFoundations: A. Site Foundation Conditions. Subsurface Soiladaneteferi100% (1)
- Analysis Procedure for Earthquake Resistant StructuresNo EverandAnalysis Procedure for Earthquake Resistant StructuresAinda não há avaliações
- Simplified Analysis of Offshore Piles U N D E R Cyclic Lateral LoadsDocumento10 páginasSimplified Analysis of Offshore Piles U N D E R Cyclic Lateral LoadskamalAinda não há avaliações
- JL-67-April Design of Anchorage Zone Reinforcement in Prestressed Concrete Beams PDFDocumento13 páginasJL-67-April Design of Anchorage Zone Reinforcement in Prestressed Concrete Beams PDFVictor Miranda AcuñaAinda não há avaliações
- Beam Column Base Plate DesignDocumento10 páginasBeam Column Base Plate DesignFar HanAinda não há avaliações
- Designing Piles ForDrag ForceDocumento37 páginasDesigning Piles ForDrag ForceReemALMousawiAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic Soil Pile InteractionDocumento39 páginasSeismic Soil Pile InteractionLuis Alonso SAAinda não há avaliações
- Calculating Mast and Rigging PDFDocumento19 páginasCalculating Mast and Rigging PDFMarian Igescu100% (1)
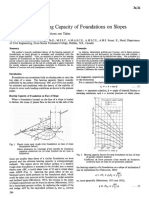
- Meyerhof (1957) - The Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Foundations On Slopes PDFDocumento3 páginasMeyerhof (1957) - The Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Foundations On Slopes PDFMunnaz67% (3)
- ETM RC - 1 Chapter - Three (LSDforShear)Documento27 páginasETM RC - 1 Chapter - Three (LSDforShear)Fekadu DebelaAinda não há avaliações
- Deformation Analysis For Prestressed Concrete Beams: by J. WarwarukDocumento14 páginasDeformation Analysis For Prestressed Concrete Beams: by J. WarwarukRahil QureshiAinda não há avaliações
- 8a. Hibbeler - 8th - Deflection and Elastic Beam TheoryDocumento8 páginas8a. Hibbeler - 8th - Deflection and Elastic Beam TheoryNadiaAinda não há avaliações
- 2023 - Zeng Et Al - Cyclic P-Y Curve Model of Unidirectional Loaded Pile in Sand Considering TheDocumento12 páginas2023 - Zeng Et Al - Cyclic P-Y Curve Model of Unidirectional Loaded Pile in Sand Considering Theee SsAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic Stability of Earth Slopes With Tension Crack: Research ArticleDocumento15 páginasSeismic Stability of Earth Slopes With Tension Crack: Research ArticleAlonso TazaAinda não há avaliações
- RUDDY - Ponding of Concrete Deck FloorsDocumento9 páginasRUDDY - Ponding of Concrete Deck FloorsmarinamoviaAinda não há avaliações
- The Stability of The Slopes of Earth Dams-ReiniusDocumento9 páginasThe Stability of The Slopes of Earth Dams-ReiniusAnonymous GnfGTwAinda não há avaliações
- Plates and SlabsDocumento63 páginasPlates and SlabsMelkamu DemewezAinda não há avaliações
- FERDIN 1 (1) - Removed - Removed (1) - RemovedDocumento3 páginasFERDIN 1 (1) - Removed - Removed (1) - RemovedGildardo VillalpbosAinda não há avaliações
- Ilovepdf MergedDocumento39 páginasIlovepdf MergedAizon SusulanAinda não há avaliações
- Foundation EngineeringDocumento90 páginasFoundation EngineeringAnonymous 2R2pCtCDAinda não há avaliações
- Deflection Due To PrestressDocumento85 páginasDeflection Due To PrestresscamilleAinda não há avaliações
- 333-010 Part1 PDFDocumento1 página333-010 Part1 PDFpmali2Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Flexural Analysis (Part 1) (Compatibility Mode)Documento41 páginasChapter 3 Flexural Analysis (Part 1) (Compatibility Mode)Umair RazaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction of Concentrated Loads in Plates and Shells: KR 12/R2 A 1/2kDocumento38 páginasIntroduction of Concentrated Loads in Plates and Shells: KR 12/R2 A 1/2ksamil68Ainda não há avaliações
- Elastic Analysis of Ground-Floor Slabs Under Multiple Loads: A. A. Abbas, M. N. Pavlovic and M. D. KotsovosDocumento15 páginasElastic Analysis of Ground-Floor Slabs Under Multiple Loads: A. A. Abbas, M. N. Pavlovic and M. D. KotsovosDulio Nils MHAinda não há avaliações
- Concreto Pretensado-NAWY - Cap 7 PDFDocumento82 páginasConcreto Pretensado-NAWY - Cap 7 PDFCarlos Alberto Pacheco SierraAinda não há avaliações
- SEISMIC VULNERABILITY and RETROFIT OF RC PDFDocumento5 páginasSEISMIC VULNERABILITY and RETROFIT OF RC PDFHoracio GutierrezAinda não há avaliações
- Laterally LoadedDocumento13 páginasLaterally LoadedbiniAinda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Foundation EngineeringDocumento43 páginasAn Introduction To Foundation EngineeringkamaAinda não há avaliações
- Interaction of Concrete and Curved Reinforcement As Applied To Construction PracticeDocumento29 páginasInteraction of Concrete and Curved Reinforcement As Applied To Construction PracticepicottAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic Design of Tunnels: Wang', MunfakhzDocumento10 páginasSeismic Design of Tunnels: Wang', MunfakhzGabriel SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- Excavation Induced Building Response by Laminate Beam MethodDocumento6 páginasExcavation Induced Building Response by Laminate Beam MethodvttrlcAinda não há avaliações
- Section 3 Design Principles: A. General 1. ScopeDocumento17 páginasSection 3 Design Principles: A. General 1. ScopeRizalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 Design of Shallow FoundatinDocumento30 páginasChapter 3 Design of Shallow FoundatinYIBELTAL EBABU100% (2)
- Chap.4.torsion DesignDocumento45 páginasChap.4.torsion DesignChalachew MesfinAinda não há avaliações
- Seismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Slab-Column Connections With Thin Plate StirrupsDocumento9 páginasSeismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Slab-Column Connections With Thin Plate StirrupsangthiankongAinda não há avaliações
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocumento4 páginasInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDavisAinda não há avaliações
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocumento4 páginasInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringJosé Luis Romero ValeroAinda não há avaliações
- Module - 1Documento45 páginasModule - 1naveenAinda não há avaliações
- Bearing CapacityDocumento22 páginasBearing CapacityMohamed HemedaAinda não há avaliações
- Resistencia de Materiales-Manuel-Romero-García-ByPrialeDocumento418 páginasResistencia de Materiales-Manuel-Romero-García-ByPrialeLuis RebañoSagrado100% (3)
- 180.60 Punching Shear Stress Check ParametersDocumento1 página180.60 Punching Shear Stress Check ParametersMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- Computation of Post-Tensioned Slab Deflection Under Construction LoadsDocumento6 páginasComputation of Post-Tensioned Slab Deflection Under Construction LoadsMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- Beam-Type Punching Shear: D D D D DDocumento1 páginaBeam-Type Punching Shear: D D D D DMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- FL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalDocumento1 páginaFL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- MAT85 AdvDocumento1 páginaMAT85 AdvMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 4.8.7 Constant Force and Variable Force Design There Are Two Schemes in Common Use For TheDocumento2 páginas4.8.7 Constant Force and Variable Force Design There Are Two Schemes in Common Use For TheMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- ConcreteDocumento1 páginaConcreteMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- Large Roofs and Sports Stadiums: Wind Loading and Structural Response Lecture 20 Dr. J.D. HolmesDocumento22 páginasLarge Roofs and Sports Stadiums: Wind Loading and Structural Response Lecture 20 Dr. J.D. HolmesMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- FL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalDocumento1 páginaFL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- TN 180 Stress Check and Rebar Verification USDocumento11 páginasTN 180 Stress Check and Rebar Verification USHieuAinda não há avaliações
- 10 RaftDocumento13 páginas10 RaftMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 9Documento1 página9MqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 423 Minutes Spring 08-AsDocumento9 páginas423 Minutes Spring 08-AsMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- FL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalDocumento1 páginaFL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- FL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalDocumento1 páginaFL Psi (11.10) : V Is The Shear Carried Through The Critical Section by The Tendons (VerticalMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 4Documento1 página4MqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 4Documento1 página4MqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- CR CR : Second SupportDocumento1 páginaCR CR : Second SupportMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 12Documento2 páginas12MqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- TL ES+CR+ + Re: (A Force OagramDocumento1 páginaTL ES+CR+ + Re: (A Force OagramMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- CR CR : Second SupportDocumento1 páginaCR CR : Second SupportMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 12Documento2 páginas12MqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- TL ES+CR+ + Re: (A Force OagramDocumento1 páginaTL ES+CR+ + Re: (A Force OagramMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 11Documento1 página11MqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- 10.3.3 Seating Losses Due To Seating of StrandDocumento1 página10.3.3 Seating Losses Due To Seating of StrandMqAshladyAinda não há avaliações
- Compressed Air: Stäubli Invents Active SafetyDocumento12 páginasCompressed Air: Stäubli Invents Active SafetyAlper SakalsizAinda não há avaliações
- Snorkel TM16 PartsDocumento261 páginasSnorkel TM16 Partskirk sutherlandAinda não há avaliações
- Flanges2 BS1560Documento12 páginasFlanges2 BS1560venthan_kalaiAinda não há avaliações
- Pages From Ganz - Turbina-3Documento1 páginaPages From Ganz - Turbina-3palanaruvaAinda não há avaliações
- Three Phase Separator Sizing (Double Weir 1)Documento3 páginasThree Phase Separator Sizing (Double Weir 1)Saeid Rahimi MofradAinda não há avaliações
- RP551Documento281 páginasRP551HalotropiaAinda não há avaliações
- Ode - 21a2kv25Documento2 páginasOde - 21a2kv25meomimi9457Ainda não há avaliações
- T Bolt Specs PDFDocumento2 páginasT Bolt Specs PDFrefaeAinda não há avaliações
- Astm E111-97Documento7 páginasAstm E111-97Uri Sterin100% (2)
- Spong, Block - The PendubotDocumento2 páginasSpong, Block - The Pendubotaleong1Ainda não há avaliações
- 4B3.9G2 So10737Documento72 páginas4B3.9G2 So10737Alexis SanchezAinda não há avaliações
- SyllabusDocumento22 páginasSyllabusSohael AftabAinda não há avaliações
- Sheetpile CalculationDocumento2 páginasSheetpile CalculationTeddy TPAinda não há avaliações
- KC FLT 8809008 enDocumento24 páginasKC FLT 8809008 enAnonymous l05hkK4yUV50% (4)
- Ufgs 41 22 13.15Documento60 páginasUfgs 41 22 13.15Abdul wahid ButtAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Tecnico Nissan Sentra 2008Documento9 páginasManual Tecnico Nissan Sentra 2008Anderson Luiz Manfredini Mendes0% (2)
- The Concise Valve V IDocumento174 páginasThe Concise Valve V Ikagasaw023Ainda não há avaliações
- Problem Set 2.projectile MotionDocumento9 páginasProblem Set 2.projectile MotionChristian OconAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 13-EditedDocumento24 páginasPHYSICAL SCIENCE MODULE 13-EditedEricha Solomon88% (8)
- Lpile Group ModuleDocumento2 páginasLpile Group ModuleMUHAMMAD ALIAinda não há avaliações
- 2.6 Force Pulley SystemDocumento8 páginas2.6 Force Pulley SystemOmkara HiteshAinda não há avaliações
- MarutiDocumento286 páginasMarutiMarcelo DominguezAinda não há avaliações
- First Law Applied To Engineering SystemsDocumento8 páginasFirst Law Applied To Engineering Systemsguy100% (1)
- Pulsar 150 Ug4 MAY 14Documento75 páginasPulsar 150 Ug4 MAY 14Nadeem AnsariAinda não há avaliações
- IPBR Flush Bottom Ball ValveDocumento2 páginasIPBR Flush Bottom Ball Valvedevang asherAinda não há avaliações
- MarioniDocumento45 páginasMarionifarmakisdAinda não há avaliações
- Blast Valve PV-KK-WDocumento2 páginasBlast Valve PV-KK-WyousufbashaAinda não há avaliações
- Automated Tugger AGV's For Factory AutomationDocumento2 páginasAutomated Tugger AGV's For Factory Automationservice9046Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit Homework Momentum Its Conservation Ans KeyDocumento6 páginasUnit Homework Momentum Its Conservation Ans KeyKristyne Olicia100% (1)
- Cromax 42CrMo4 4140Documento3 páginasCromax 42CrMo4 4140Iñigo Fernandez de LabastidaAinda não há avaliações
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNo EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansAinda não há avaliações
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeNo EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (59)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindAinda não há avaliações
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetNo EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (10)
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignNo EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (137)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNo EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!No EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNo EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (21)
- The Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisNo EverandThe Finite Element Method: Linear Static and Dynamic Finite Element AnalysisNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksNo EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.No EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationNo EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (18)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityNo EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Rocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyNo EverandRocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (5)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignNo EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (19)
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbNo EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (15)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesNo EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (3)