Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ar6012 Construction Project Management
Enviado por
Hasna HameedTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ar6012 Construction Project Management
Enviado por
Hasna HameedDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
AR6012 CONSTRUCTION PROJECT MANAGEMENT
UNIT II - INTRODUCTION TO PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Project Network - Events, Activity, Dummy, Network Rules, Graphical Guidelines for Network, Numbering the
Events, Cycles, Development of Network, Steps in development of Network. Work Breakdown Structure, Hierarchies.
1. What is Event?
Event is a specific instant of time at which a particular part of project plan has to be completed. The start or end
of an activity is called event. It doesn’t require time period or resources. Example: in constructing a foundation,
‘completion of excavation’ is an event. A runner touching the finish line is event and running is the activity.
2. What is Activity?
Activity is a task and is part of the project. It consists start and end time-events. It requires a time period and
resources for completion. Example: in constructing a foundation, ‘excavation’ is an activity. Running by a runner in a
track is the activity.
3. What are the steps in Fulkerson’s Rule for
Number the single ‘initial’ event with only arrows coming out of it, as 1 (no arrows enter it)
Neglect all the arrows emerging out of initial event numbered as 1. One or more new initial events will be
present.
Number those event(s) as 2, 3, 4 so on, starting from top to bottom.
Neglect all the arrows emerging out of new initial event(s) numbered as 2, 3, 4 so on. Few more new initial
events will be present.
Repeat step 3.
Repeat step 4 till all the events are numbered.
4. What is Dummy activity?
Dummy activity is an imaginary activity which doesn’t requires neither time nor resources and never affects the
network, but it is used to avoid mistakes in network rules and maintain logic flow of events.
Example: Assume activities A and B start and end at same events 1 and 2 respectively. i. e,
A
1 2
- Incorrect representation
B
3
A - Correct representation using Dummy activity
1
Dummy activity
2
B
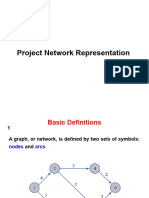
5. What is Network?
Network is a diagrammatic representation of a work plan. It shows the activities, in step-by-step sequence,
leading to the final goal. It shows the inter-dependence between the activities and their sequence. It also gives the
start time, time required and end time for the activities.
Example: the set of 5 major activities in a contracted construction are Briefing, designing, tendering,
construction and commissioning. It can be represented in a network as follows;
Briefing Designing Tendering Construction Commissioning
6. What are the advantages of project network?
Project Network gives clear relationship between the activities and events
It is useful in preparing schedules for highly complicated projects with large activities
It directly provides the time elapsed between 2 activities and hence useful in controlling and rescheduling.
It uses probability for time estimation in projects with uncertainties, such as Research projects
7. What are the Network Rules?
a) Initial node has only outgoing arrows. There must be only one initial node in a network.
1
3
Events 1 and 2 are 2 initial nodes; this is not correct
2
b) An event cannot occur until all the activities leading to it are completed.
c) An event cannot occur twice. There cannot be any network path looping.
1 2
Event 1 is repeating, this is not correct
1 3
d) There must not be any dead ends except final node. There can be only one final node.
4
3
Events 4 and 5 are 2 final nodes; this is not correct
5
e) No activity can start until its preceding event has occurred.
f) One arrow should represent only one activity. Single activity cannot be represented using 2 different arrows.
4
A
3
A Activity A is represented by 2 arrows; 3 – 4 and 4 – 5, this is not correct
5
g) All activities should complete in order to complete the project.
i) Time flow is shown from left to right. It should not be from right to left.
2 1
Flow of time is from right to left; this is not correct
j) Arrow directions should be from left to right and top to bottom (or bottom to top) or combination of above
two (angular).
Additional Questions:
8. How will you represent an Activity in network diagram?
9. What are the types of representation of activity?
10. What are the graphical guidelines of network?
11. What is Work Breakdown Structure?
12. What is skip numbering?
13. Problems in ‘Numbering events’ using Fulkerson’s Rule.
14. Problems in developing a network.
15. What are the rules for Dummy activity?
16. What is: Serial Activity, Parallel Activity, Successor, Predecessor, Immediate Successor, Immediate Predecessor
Você também pode gostar
- CE 751 - LEC 3 - Networking TechniquesDocumento42 páginasCE 751 - LEC 3 - Networking TechniquesPranay VvdAinda não há avaliações
- Construction and Project ManagementDocumento31 páginasConstruction and Project ManagementAnamika MuralidharanAinda não há avaliações
- Network ConstructionDocumento11 páginasNetwork ConstructionDr. Mahmoud Abbas Mahmoud Al-NaimiAinda não há avaliações
- Report By: Bonje, Princess Shara Echin, Kristia Mae Eraya, JingleDocumento17 páginasReport By: Bonje, Princess Shara Echin, Kristia Mae Eraya, JinglesehunkydoryAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - Ii Network AnalysisDocumento37 páginasUnit - Ii Network AnalysisFahad GhansarAinda não há avaliações
- Project ManagementDocumento5 páginasProject ManagementMasumAinda não há avaliações
- Ch-11 PROJECT MANAGEMENTDocumento7 páginasCh-11 PROJECT MANAGEMENTVandana AhujaAinda não há avaliações
- Construction Scheduling Techniques: by Dr. Mahdi DamghaniDocumento28 páginasConstruction Scheduling Techniques: by Dr. Mahdi Damghaniallahmahdiali100% (8)
- Mat611 Topic 4 Network AnalysisDocumento17 páginasMat611 Topic 4 Network AnalysisTyson LukaleAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Path Method and Float AnalysisDocumento30 páginasCritical Path Method and Float AnalysisPriyaAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5Documento21 páginasCH 5Yosef KetemaAinda não há avaliações
- Network Analysis GuideDocumento34 páginasNetwork Analysis GuideGaurang JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- Prakirti Gaur 2319 A03Documento2 páginasPrakirti Gaur 2319 A03Simarleen BhardwajAinda não há avaliações
- SC431 Lecture No. 7 - Construction Planning NetworksDocumento71 páginasSC431 Lecture No. 7 - Construction Planning NetworksJoseph BaruhiyeAinda não há avaliações
- Operation Research Chapter Five 5. Networks and Project ManagementDocumento11 páginasOperation Research Chapter Five 5. Networks and Project ManagementfitsebigAinda não há avaliações
- Project ManagementDocumento63 páginasProject Managementsumitnits007_8936260100% (1)
- Presentation Project PlanningDocumento89 páginasPresentation Project PlanningCheng Eng GanAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Project Planning: PM SR Ruslan Affendy Arshad Frism, Mciob, CCPMDocumento89 páginasIntroduction To Project Planning: PM SR Ruslan Affendy Arshad Frism, Mciob, CCPMzulfadhli zabirAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Management Summary Notes 2Documento4 páginasEngineering Management Summary Notes 2Njuguna WaweruAinda não há avaliações
- Project scheduling techniquesDocumento18 páginasProject scheduling techniquesabhinavAinda não há avaliações
- PM 1Documento44 páginasPM 1Jatin JAinda não há avaliações
- Addis Ababa University Construction Planning and SchedulingDocumento25 páginasAddis Ababa University Construction Planning and SchedulingAdane BelayAinda não há avaliações
- ELEMENTS OF NETWORK PLANNINGDocumento1 páginaELEMENTS OF NETWORK PLANNINGnikita jadwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Management For Engineers - 4Documento29 páginasManagement For Engineers - 4alant k josephAinda não há avaliações
- Hawassa University Project Management Lecture NotesDocumento37 páginasHawassa University Project Management Lecture Notesወይኩን ፍቃድከ100% (1)
- QB SPM Cie 2Documento7 páginasQB SPM Cie 2Arun KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Pert-Cpm PPT 2018Documento43 páginasPert-Cpm PPT 2018HiremathkhushiAinda não há avaliações
- PPET - Project ImplementationDocumento20 páginasPPET - Project ImplementationShawon Moshiur RahamanAinda não há avaliações
- 27-28 Nov Nota Project PlanningDocumento82 páginas27-28 Nov Nota Project PlanningWan Mohamad NoorAinda não há avaliações
- CV4011-PT1 Lecturenote 4-Or - CPM 1516 S1Documento17 páginasCV4011-PT1 Lecturenote 4-Or - CPM 1516 S1Steven KuaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Network FundamentalsDocumento7 páginasChapter 5 Network FundamentalsAD StarlightAinda não há avaliações
- Network Analysis - PERT N CPMDocumento41 páginasNetwork Analysis - PERT N CPMchanchal malooAinda não há avaliações
- MB0049 Unit 05-SLM PDFDocumento31 páginasMB0049 Unit 05-SLM PDFpmg3067100% (1)
- Project Management TechniquesDocumento43 páginasProject Management TechniquesBlack MoonAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6 Project Management 71Documento24 páginasChapter 6 Project Management 71Priyansh SainiAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 11Documento52 páginasLecture 11Javeria KhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 PERT-CPMDocumento43 páginasChapter 10 PERT-CPMNISHA NANDALAinda não há avaliações
- Project Network RepresentationDocumento52 páginasProject Network RepresentationEylul KarahanAinda não há avaliações
- Mb0049 Unit 05-SlmDocumento31 páginasMb0049 Unit 05-SlmSarlaJaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- Cv4201 - Civil Engineering Management Operational Research Techniques - Network AnalysisDocumento14 páginasCv4201 - Civil Engineering Management Operational Research Techniques - Network Analysiszzz_monsterAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Path Method Project SchedulingDocumento56 páginasCritical Path Method Project SchedulingAman RajpootAinda não há avaliações
- Mod 6 Network AnalysisDocumento8 páginasMod 6 Network AnalysisVishwas ParakkaAinda não há avaliações
- Pert, CPM and CostDocumento47 páginasPert, CPM and CostAsif KhanAinda não há avaliações
- CPM (Critical Path Method) Arrow Diagram: End Node of This Activity Start Node of This ActivityDocumento11 páginasCPM (Critical Path Method) Arrow Diagram: End Node of This Activity Start Node of This ActivityNaveed FakharAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Pert and CPMDocumento40 páginasChapter 8 Pert and CPMAbdirehman ArabAinda não há avaliações
- Project Management: Topic: Network Diagram (Activity On Arrow)Documento22 páginasProject Management: Topic: Network Diagram (Activity On Arrow)HAMZA ALIAinda não há avaliações
- ACC 104: Management Science: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoDocumento44 páginasACC 104: Management Science: Pamantasan NG CabuyaoHannah MeranoAinda não há avaliações
- Without Logistics Network We Couldn't Have Present Day Goods and Services at Affordable Prices"Documento13 páginasWithout Logistics Network We Couldn't Have Present Day Goods and Services at Affordable Prices"Neetesh SinghAinda não há avaliações
- 03 - 2 Network Analysis - CPM and PERTDocumento32 páginas03 - 2 Network Analysis - CPM and PERTMikealayAinda não há avaliações
- PERT1Documento18 páginasPERT1Mangesh KulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- Unit-4 O.RDocumento18 páginasUnit-4 O.RrengarajanAinda não há avaliações
- Project: Example: Construction of A Bridge, ResidentialDocumento28 páginasProject: Example: Construction of A Bridge, Residentialarpitmittal07Ainda não há avaliações
- CPM PertDocumento18 páginasCPM PertJunaid YAinda não há avaliações
- Network Problem CPM & PertDocumento43 páginasNetwork Problem CPM & PertNiftem Batch BAinda não há avaliações
- CPM PertDocumento21 páginasCPM Pertkabina goleAinda não há avaliações
- Or-Mod 4Documento35 páginasOr-Mod 4Phone PeAinda não há avaliações
- Managing the Unknown: A New Approach to Managing High Uncertainty and Risk in ProjectsNo EverandManaging the Unknown: A New Approach to Managing High Uncertainty and Risk in ProjectsNota: 2 de 5 estrelas2/5 (1)
- Dakshan Chitra PDFDocumento2 páginasDakshan Chitra PDFHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Dakshan ChitraDocumento2 páginasDakshan ChitraHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Other: Contribution Canechle11eDocumento2 páginasOther: Contribution Canechle11eHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- 616 ProposalDocumento16 páginas616 ProposalHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Designing an Autism CenterDocumento7 páginasDesigning an Autism CenterHasna Hameed100% (1)
- UNIT II - Project Programming and Critical Path MethodDocumento10 páginasUNIT II - Project Programming and Critical Path MethodHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Unit I Introduction To PMDocumento34 páginasUnit I Introduction To PMHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Sterling Newsletter 5Documento8 páginasSterling Newsletter 5Hasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Blind SchoolDocumento6 páginasBlind SchoolHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- SummaryDocumento62 páginasSummaryHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- SummaryDocumento62 páginasSummaryHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis Synopsis - Healthy Working EnvironmentDocumento13 páginasThesis Synopsis - Healthy Working EnvironmentHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Rvs School of ArchitectureDocumento3 páginasRvs School of ArchitectureHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Children Are Working Away From HomeDocumento3 páginasChildren Are Working Away From HomeHasna HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Cianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogDocumento1 páginaCianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogMaier MariaAinda não há avaliações
- BoQ East Park Apartment Buaran For ContractorDocumento36 páginasBoQ East Park Apartment Buaran For ContractorDhiangga JauharyAinda não há avaliações
- EE290 Practice 3Documento4 páginasEE290 Practice 3olgaAinda não há avaliações
- Device Interface Device Type (Router, Switch, Host) IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayDocumento2 páginasDevice Interface Device Type (Router, Switch, Host) IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayRohit Chouhan0% (1)
- Common Size Analys3esDocumento5 páginasCommon Size Analys3esSaw Mee LowAinda não há avaliações
- SD-SCD-QF75 - Factory Audit Checklist - Rev.1 - 16 Sept.2019Documento6 páginasSD-SCD-QF75 - Factory Audit Checklist - Rev.1 - 16 Sept.2019Lawrence PeAinda não há avaliações
- The Product Development and Commercialization ProcDocumento2 páginasThe Product Development and Commercialization ProcAlexandra LicaAinda não há avaliações
- Domingo V People (Estafa)Documento16 páginasDomingo V People (Estafa)Kim EscosiaAinda não há avaliações
- IP68 Rating ExplainedDocumento12 páginasIP68 Rating ExplainedAdhi ErlanggaAinda não há avaliações
- Microsoft Word 2000 IntroductionDocumento72 páginasMicrosoft Word 2000 IntroductionYsmech SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- Childrens Ideas Science0Documento7 páginasChildrens Ideas Science0Kurtis HarperAinda não há avaliações
- Factsheet B2B PunchOut en 140623Documento2 páginasFactsheet B2B PunchOut en 140623Curtis GibsonAinda não há avaliações
- 2002, Vol.86, Issues 4, Hospital MedicineDocumento221 páginas2002, Vol.86, Issues 4, Hospital MedicineFaisal H RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Supreme Court rules stabilization fees not trust fundsDocumento8 páginasSupreme Court rules stabilization fees not trust fundsNadzlah BandilaAinda não há avaliações
- Timely characters and creatorsDocumento4 páginasTimely characters and creatorsnschober3Ainda não há avaliações
- Jazan Refinery and Terminal ProjectDocumento3 páginasJazan Refinery and Terminal ProjectkhsaeedAinda não há avaliações
- Brain, Behavior, and Immunity: Alok Kumar, David J. LoaneDocumento11 páginasBrain, Behavior, and Immunity: Alok Kumar, David J. LoaneRinaldy TejaAinda não há avaliações
- JD - Software Developer - Thesqua - Re GroupDocumento2 páginasJD - Software Developer - Thesqua - Re GroupPrateek GahlanAinda não há avaliações
- Problems of Teaching English As A Foreign Language in YemenDocumento13 páginasProblems of Teaching English As A Foreign Language in YemenSabriThabetAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Stations Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasLearning Stations Lesson Planapi-310100553Ainda não há avaliações
- Political Reporting:: Political Reporting in Journalism Is A Branch of Journalism, Which SpecificallyDocumento6 páginasPolitical Reporting:: Political Reporting in Journalism Is A Branch of Journalism, Which SpecificallyParth MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Operation Manual: Auto Lensmeter Plm-8000Documento39 páginasOperation Manual: Auto Lensmeter Plm-8000Wilson CepedaAinda não há avaliações
- PA Inspection Guidelines For Single Site Acceptance: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksDocumento18 páginasPA Inspection Guidelines For Single Site Acceptance: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksDenny WijayaAinda não há avaliações
- Course: Citizenship Education and Community Engagement: (8604) Assignment # 1Documento16 páginasCourse: Citizenship Education and Community Engagement: (8604) Assignment # 1Amyna Rafy AwanAinda não há avaliações
- Victron MultiPlus 48 1200-13-16 Datasheet enDocumento1 páginaVictron MultiPlus 48 1200-13-16 Datasheet enBAHJARI AMINEAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesDocumento15 páginasLesson 2 Mathematics Curriculum in The Intermediate GradesRose Angel Manaog100% (1)
- Philips DVD Player SpecificationsDocumento2 páginasPhilips DVD Player Specificationsbhau_20Ainda não há avaliações
- Restructuring Egypt's Railways - Augst 05 PDFDocumento28 páginasRestructuring Egypt's Railways - Augst 05 PDFMahmoud Abo-hashemAinda não há avaliações
- 14 15 XII Chem Organic ChaptDocumento2 páginas14 15 XII Chem Organic ChaptsubiAinda não há avaliações
- Tender Notice and Invitation To TenderDocumento1 páginaTender Notice and Invitation To TenderWina George MuyundaAinda não há avaliações