Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ps As Icse STD 10 Math Locus
Enviado por
pravingosavi1011_578Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ps As Icse STD 10 Math Locus
Enviado por
pravingosavi1011_578Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
PODAR INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL (ICSE)
Practice sheet-Answer Scheme
Std: X Chapter 14: Locus
Subject: Mathematics
Q 1. AB and CD are two intersecting lines. Find the position of a point at a distance of 2 cm
from AB and 1.8 cm from CD.
Answer Draw a line l parallel to AB at a distance of 2 cm.
Draw a line m parallel to CD at a distance of 1.8 cm.
The point of intersection of lines l and m is the required point.
Q 2. Using only a ruler and compasses construct a ∆ABC in which∠ABC = 120°, AB = 4 cm
and BC = 5cm.
i. Locate point P such that ∠PAB = 90° and BP = CP
ii. Measure the length of BP
Answer 6.5 cm
Q 3. Using only a ruler and compasses construct a quadrilateral ABCD in which
∠ABC = 60°, AB = 6 cm, AD = 5 cm and BC = 5 cm. Mark point D equdistant from
AB and BC.
Answer Angle bisector of ∠ABC
Q 4. Construct a rhombus ABCD with diagonals AC and BD of lengths 8 cm and 6 cm,
respectively. Locate by construction, the point P such that P is equidistant from C and
D, and P is equidistant from AB and AD. Measure the length PC.
Answer 3.1 cm
Q 5. Draw the lines y = –2 and y = 6. Find and draw the locus of the point which is
equidistant from the two given lines.
Answer line y = 2
Q 6. In a quadrilateral ABCD, if the perpendicular bisectors of AB and AD meet at P then
prove that BP = DP.
Q 7. Draw two intersecting lines to include an angle of 30°. Use ruler and compasses to
locate points which are equidistant from these lines and also 2 cm away from the point
of intersection. How many such points exist?
ICSE/X/18-19 Locus page 1 of 5
Answer 4
Q 8. State the locus of a point in a rhombus ABCD which is equidistant:
i. From AB and AD
ii. From the vertices A and C.
Answer i. AC
ii. BD
Q 9. Sketch and describe the locus of the vertices of all triangles with a given base and a
given altitude.
Answer Line parallel to the base at a distance as the altitude.
Q 10. Sketch and describe the locus of the mid-points of all chords parallel to a given chord of
a circle.
Answer Diameter perpendicular to the chord
Q 11. Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 5 cm, BC = 7.5 cm and AC = 6 cm. Construct the
locus of points which are equidistant from:
i. A and B
ii. B and C
Mark a point X, the intersection of the two loci. What is the special name given to the
point?
Answer Circumcentre
Q 12. In a kite ABCD, AB = AD and BC = BD. Prove that the diagonal AC is the
perpendicular bisector of diagonal BD.
Q 13. Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 7 cm, BC = 8 cm and∠ABC = 60°. Locate by
construction, the point P such that P is equidistant from B and C, and P is equidistant
from AB and BC. Measure the length PB.
Answer 4.5 cm
Q 14. Construct a triangle ABC in which BC = 6cm, AB = 9cm and ∠ABC = 60°
i. Construct the locus of all points inside triangle ABC, which are equidistant from
B and C.
ii. Construct the locus of the vertices of the triangle with BC as base, which are
equal in area to triangle ABC.
iii. Marks the point Q in your construction which would make an isosceles triangle
QBC equal in area to triangle ABC.
iv. Measure length CQ.
ICSE/X/18-19 Locus page 2 of 5
Answer 8.3 cm
Q 15. Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 6cm, ∠ABP = 45° and BP = 5cm. Complete the
rectangle ABCD such that
i. P is equidistant from AB and BC, and
ii. P is equidistant from A and D
Q 16. Construct an equilateral triangle ABC in which each side is 5 cm long. Construct a
point O which is equidistant from the three vertices.Construct perpendiculars from O
to each side. Is O equidistant from each side?
Answer Yes O is equidistant from each side
Q 17. Using only a ruler and compasses construct ∠ABC = 120°, where AB = BC = 5cm.
i. Mark two points D and E which satisfy the condition that they are equidistant
from both BA and BC.
ii. In the above figure, join AE and EC. Describe the figures
a. ABCD
b. BD
c. ABE
Answer i. rhombus
ii. bisector of∠ABC
iii. triangle
Q 18. Using a ruler and compass only
i. Construct a triangle ABC with BC = 6cm, ∠ABC = 120° and AB = 3.5cm
ii. In the above figure, draw a circle with BC as diameter. Find a point ‘P’ on the
circumference of the circle which is equidistant from AB and BC.
iii. Measure ∠BPC.
Answer ∠BCP = 30°
Q 19. Use a ruler and a pair of compasses to construct ∆ABC in which BC = 4.2cm,
∠ABC = 60° and AB = 5 cm. Construct a circle of radius 2 cm to touch both the arms
of ∠ABC of ∆ABC.
Q 20. Construct an isosceles ∆ABC such that AB = 6 cm, BC = AC = 4 cm. Bisect ∠C
ICSE/X/18-19 Locus page 3 of 5
internally and mark a point P on this bisector such that CP = 5 cm. Find the points Q
and R which are 5 cm away from P and also 5 cm from the line AB.
Q 21. Ruler and compass only may be used in this question..
1. Construct ∆ABC, in which BC = 8 cm, AB = 5 cm and∠ABC = 60°
2. Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from BA
and BC
3. Construct the locus of points inside the triangle which are equidistant from B
and C
4. Mark as P, the point which is equidistant from AB, BC and also equidistant from
B and C
5. Measure and record the length of PB.
Answer 4.5cm
Q 22. Use graph paper for this question. Take 1 cm = 1 unit on both axes. Plot the points
A(2,2), B(8,2), C(11,6) and D(5,6);
i. Name the quadrilateral obtained
ii. Find the locus of the point P such that PA = PB
Answer Parallelogram
straight line x = 5
Q 23. Use graph paper for this question. Plot the points P(3,1), Q(9,1), R(9,7) and S(3,7);
i. Name the quadrilateral obtained
ii. Construct the locus of points equidistant from P and R.
iii. Construct the locus of points equidistant from PS and PQ
Answer i. Square
ii. Diagonal PR
iii. Diagonal QS
Q 24. Using a ruler and compass only. Draw a circle of radius 4 cm and mark two chords AB
and AC of the circle of length 6 cm and 5 cm respectively.
i. Construct the locus of points, inside the circle, that are equidistant from A and
C.
ii. Find the locus of points, inside the circle, that are equidistant from AB and AC.
Answer i. Diameter perpendicular to chord AC
ii. Chord bisecting ∠BAC
ICSE/X/18-19 Locus page 4 of 5
Q 25. Draw a ∆PQR such that PQ = 5.8 cm, RP = 2.9 cm and ∠RQP = 30°. Complete the
trapezium APQR such that A is equidistant from PQ and QR. Find the point M on AQ
which is equidistant from P and Q.
Answer AQ bisector of ∠RQP. M is the pont of intersection of PQ and AQ.
Q 26. Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 6cm, BC = 7cm and∠ABC = 60°. Locate by
construction, the point P such that
i. P is at a distance of 2 cm from BC, and
ii. P is at a distance of 3 cm from C
iii. How many such points exist which satisfy both the loci?
Answer 4 points
Q 27. Plot A(3, –2), B(2,1) and C(10, 3) on graph.
i. Construct the locus of points at a distance of 5 cm from A.
ii. Construct the locus of points equidistant from B and C.
iii. Locate a point P such that PB = PC and P is a distance of 5 cm from A.
iv. Write the co-ordinates of P.
Answer (6, 2)
Q 28. Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 5.6 cm, AC = BC = 9.2 cm. Find the points
equidistant from AB and AC; and also 2 cm from BC. Measure the distance between the
two points obtained.
Answer 4.3 cm
Q 29. Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 5 cm, BC = 7.5 cm and AC = 6 cm. Construct a
circle on diameter BC. Locate a point P on the circle which is equidistant from AB and
BC. Measure∠BPC.
Answer 90°
Q 30. Construct a triangle ABC with AB = 4 cm, BC = 6.5 cm and AC = 8.5 cm. Through A,
draw a line parallel to BC. Locate a point P on this line which is equidistant from B and
C. What type of triangle is BPC?
Answer Isosceles
ICSE/X/18-19 Locus page 5 of 5
Você também pode gostar
- PS As ICSE STD 10 Math Section FormulaeDocumento4 páginasPS As ICSE STD 10 Math Section Formulaepravingosavi1011_578Ainda não há avaliações
- Don Bosco Park Circus Class 10 Physics Preboards Paper Icse 2024Documento7 páginasDon Bosco Park Circus Class 10 Physics Preboards Paper Icse 2024utsavdutta7d11dpsmAinda não há avaliações
- Prelim Physics ICSEDocumento3 páginasPrelim Physics ICSEsagart233732Ainda não há avaliações
- 2nd Bai Avabai ICSE10 Maths PE-1 20-21-UnprotectedDocumento7 páginas2nd Bai Avabai ICSE10 Maths PE-1 20-21-Unprotecteddinesh lalwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions To Me N Mine Psa-Ix PDFDocumento86 páginasSolutions To Me N Mine Psa-Ix PDFJayendra Pandey0% (2)
- Trigonometry-3 Jee Main and AdvancedDocumento4 páginasTrigonometry-3 Jee Main and AdvancedMd Rizwan AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Test Paper - 3 Pattern: Mht-Cet: Please Read The Following Instructions CarefullyDocumento16 páginasTest Paper - 3 Pattern: Mht-Cet: Please Read The Following Instructions CarefullyThe mind SetterAinda não há avaliações
- Iiser Question Papers With SolutionDocumento56 páginasIiser Question Papers With SolutionAdamhilldwfww100% (1)
- Me and Mine Maths....Documento140 páginasMe and Mine Maths....Vaibhav Ambure75% (4)
- Human Digestive Sysytem Icse BoardDocumento40 páginasHuman Digestive Sysytem Icse BoardJagrity SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Ray Optics Lecture UnacademyDocumento57 páginasRay Optics Lecture UnacademyAbhishek ShuklaAinda não há avaliações
- VPM Classes - Ugc Net Law - Mock Paper (P1 & P2 - New Pattern) - 48 Pages 2716374358 PDFDocumento48 páginasVPM Classes - Ugc Net Law - Mock Paper (P1 & P2 - New Pattern) - 48 Pages 2716374358 PDFHarish BhattAinda não há avaliações
- HCL PDFDocumento13 páginasHCL PDFjoycepeterAinda não há avaliações
- Clat PDFDocumento3 páginasClat PDFMayank GandhiAinda não há avaliações
- Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Worksheet Class10 Y1539856429ssolutions ICSE Physics WorksheetDocumento102 páginasHttps App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Worksheet Class10 Y1539856429ssolutions ICSE Physics WorksheetDhruv ParikhAinda não há avaliações
- 06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFDocumento5 páginas06 - BIO IX ICSE Respiration in Plants PDFthe lillyAinda não há avaliações
- Impulse and Momentum ForkvpyDocumento9 páginasImpulse and Momentum ForkvpyRishabh RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE Chemistry Nayak Tutorials Question BankDocumento34 páginasICSE Chemistry Nayak Tutorials Question BankA.K. LohaniAinda não há avaliações
- Podar International School (Icse) Practice Sheet STD: X Chapter: 4 Linear Inequations Subject: MathematicsDocumento2 páginasPodar International School (Icse) Practice Sheet STD: X Chapter: 4 Linear Inequations Subject: Mathematicspravingosavi1011_578100% (2)
- 10th Maths 2016-17 SDV Sa-1 Question Paper-13Documento2 páginas10th Maths 2016-17 SDV Sa-1 Question Paper-13Naveen ShankarAinda não há avaliações
- ICS VVM Full With Final Cover Page 2pdfDocumento97 páginasICS VVM Full With Final Cover Page 2pdfHemanth HemuAinda não há avaliações
- Compulsary Mathematics - Class 10Documento348 páginasCompulsary Mathematics - Class 10Rüpësh ẞhäñdårîAinda não há avaliações
- Vii - (Vol-1) Number SystemDocumento10 páginasVii - (Vol-1) Number SystemRajee100% (1)
- Surface Area 10Documento2 páginasSurface Area 10Smaranil GuchaitAinda não há avaliações
- GST SolutionDocumento7 páginasGST SolutionRohan MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- 8th STD FormulaDocumento1 página8th STD FormulaNitesh Matta100% (1)
- Computer Applications Icse10th Ans MDocumento371 páginasComputer Applications Icse10th Ans Mgroup projectAinda não há avaliações
- X - Cbse Maths Pre-Mid Term Exam - FinalDocumento7 páginasX - Cbse Maths Pre-Mid Term Exam - FinalMahadas ThanmayeeAinda não há avaliações
- 1st AVM Juhu ICSE10 Maths PrePrelim 2021-UnprotectedDocumento6 páginas1st AVM Juhu ICSE10 Maths PrePrelim 2021-Unprotecteddinesh lalwaniAinda não há avaliações
- Mock PB 23-1Documento11 páginasMock PB 23-1Kshitij YadavAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE Class 10 Maths SyllabusDocumento8 páginasICSE Class 10 Maths Syllabusprash_hingeAinda não há avaliações
- Cbse Class 10 Maths Question Paper 2020 PDFDocumento11 páginasCbse Class 10 Maths Question Paper 2020 PDFSabir100% (1)
- 10th Icse Question Bank 22.07.13Documento15 páginas10th Icse Question Bank 22.07.13Vishal Jalan100% (1)
- Imp Ques Maths X PDFDocumento5 páginasImp Ques Maths X PDFMuskan KukrejaAinda não há avaliações
- Maths 01 Real Number Class 10 Practice QuestionsDocumento5 páginasMaths 01 Real Number Class 10 Practice Questionssamarth mishraAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocumento6 páginasGeometry and TrigonometryFranc VenturaAinda não há avaliações
- Co-Ordinate X ClassDocumento2 páginasCo-Ordinate X ClassCRPF SchoolAinda não há avaliações
- Dont Lose ThisDocumento6 páginasDont Lose Thisapi-269875058Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of PollutionDocumento2 páginasTypes of PollutionaishaAinda não há avaliações
- 04 Linear Equation in Two Variable Subjective QuestionsDocumento5 páginas04 Linear Equation in Two Variable Subjective Questionsshweta_angel90Ainda não há avaliações
- Class X Mathematics Preboard 2023Documento6 páginasClass X Mathematics Preboard 2023Neema TheteAinda não há avaliações
- Compound AnglesDocumento2 páginasCompound AnglesHimanshu GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- 01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsDocumento9 páginas01 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Periodic Properties& VariationsNatasha DalalAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE Class 9 Heron's FormulaDocumento5 páginasCBSE Class 9 Heron's Formulavinod1577100% (1)
- Respaper Soils in India Geography Notes Class 10 Icse by Priyanshu SinghDocumento5 páginasRespaper Soils in India Geography Notes Class 10 Icse by Priyanshu SinghprashanthAinda não há avaliações
- Solution To Mnm-Eng-Ix 2nd Term Pws Total Pages 72 PDFDocumento72 páginasSolution To Mnm-Eng-Ix 2nd Term Pws Total Pages 72 PDFpipraniaejaj1Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemical Reaction and EquationDocumento6 páginasChemical Reaction and EquationamitAinda não há avaliações
- Class X Maths Chapterwise QuestionsDocumento13 páginasClass X Maths Chapterwise QuestionsJuveria100% (1)
- Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocumento61 páginasLinear Equations in Two VariablesNoel SabuAinda não há avaliações
- Class-X Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Documento2 páginasClass-X Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Apex Institute50% (2)
- X ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFDocumento9 páginasX ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFthe lillyAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 3 20200Documento5 páginasICSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 3 20200Subhajit BakshiAinda não há avaliações
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsDocumento2 páginasICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsSagnik MajumderAinda não há avaliações
- Class 9 QuadrilateralDocumento6 páginasClass 9 QuadrilateralVarshini PeraAinda não há avaliações
- SampleQue 7thStd ForAllSchools CompleteBookDocumento30 páginasSampleQue 7thStd ForAllSchools CompleteBookPP0% (1)
- CBSE Class 8 Mathematics Paper 1 2014Documento4 páginasCBSE Class 8 Mathematics Paper 1 2014Anurag SaikiaAinda não há avaliações
- Delhi Public School Assignment No - 1: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento4 páginasDelhi Public School Assignment No - 1: Multiple Choice QuestionsAyush jhaAinda não há avaliações
- Loci Class XDocumento4 páginasLoci Class XDsr dAinda não há avaliações
- Solution:: Long Answer Type Questions (4 Marks)Documento25 páginasSolution:: Long Answer Type Questions (4 Marks)rai venugopalAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Right-Angled Triangle TrigonometryDocumento9 páginasNon-Right-Angled Triangle TrigonometryMohammad AliAinda não há avaliações
- ESci 110 - N046 - Lesson 8.1 AssessmentDocumento4 páginasESci 110 - N046 - Lesson 8.1 AssessmentIvy PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Very Short Answer Questions - Introduction To Trigonometry - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF DownloadDocumento9 páginasVery Short Answer Questions - Introduction To Trigonometry - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Downloadkrishnatsharma5432Ainda não há avaliações
- DPP JeeDocumento6 páginasDPP JeeMAG MarvelAinda não há avaliações
- TestDocumento14 páginasTestapi-355808066Ainda não há avaliações
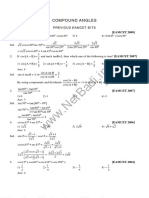
- Cos Sin 2 2 Sin: Formule Trigonometrice 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19Documento2 páginasCos Sin 2 2 Sin: Formule Trigonometrice 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19Stefan DumitriuAinda não há avaliações
- Ebook College Algebra and Trigonometry 6Th Edition Lial Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento68 páginasEbook College Algebra and Trigonometry 6Th Edition Lial Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrosakien8871yc100% (12)
- Ioqm DPP-3Documento1 páginaIoqm DPP-3tanishk goyalAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHDocumento18 páginasChapter 17 I Lines & Planes in 3D ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Sharygin 2013Documento16 páginasSharygin 2013Đào Quang ĐứcAinda não há avaliações
- Answers To Coursebook Exercises: 5 AnglesDocumento2 páginasAnswers To Coursebook Exercises: 5 AnglesMufeed JarrarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 3 Lesson 2 Video Asa Aas HL NotesDocumento2 páginasUnit 3 Lesson 2 Video Asa Aas HL Notesapi-264764674Ainda não há avaliações
- Worksheets TrianglesDocumento5 páginasWorksheets TrianglesJowhie Anne ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Defined TermsDocumento11 páginasDefined TermsSantanah Daxene Daylo100% (2)
- Swap Sector & Wrong Azimuth - JBDocumento19 páginasSwap Sector & Wrong Azimuth - JBPaulus SihombingAinda não há avaliações
- Circles AssignmentDocumento2 páginasCircles AssignmentpiyushAinda não há avaliações
- Geometry Triangles PDFDocumento20 páginasGeometry Triangles PDFPratyush Acharya100% (2)
- C2 January 2006 Mark SchemeDocumento6 páginasC2 January 2006 Mark SchemesheenaAinda não há avaliações
- AC Lesson LectureDocumento56 páginasAC Lesson LectureMKAinda não há avaliações
- Plane Geometry 1Documento9 páginasPlane Geometry 1Rehman AhabathAinda não há avaliações
- 12th Complex One Marks TestDocumento3 páginas12th Complex One Marks TestSenthil Kumar Ganesan100% (2)
- Heights & Distances PDFDocumento19 páginasHeights & Distances PDFTanishque SinghAinda não há avaliações
- JR Maths-1bDocumento35 páginasJR Maths-1bsharanvarmavegirajuAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Trig WS3 Paper1 Ans PDFDocumento44 páginas3 Trig WS3 Paper1 Ans PDFArvind GargAinda não há avaliações
- Cie Igcse o Level Maths Topic 4Documento24 páginasCie Igcse o Level Maths Topic 4Nayeem HakimAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Course On 3-DDocumento66 páginasSimple Course On 3-DCartmanTaiAinda não há avaliações
- A Stronger Form of The Steiner-Lehmus TheoremDocumento3 páginasA Stronger Form of The Steiner-Lehmus TheoremAliBenMessaoudAinda não há avaliações
- Incenter Symmetry, Euler Lines, and Schiffler Points: Guyen E IldbergerDocumento9 páginasIncenter Symmetry, Euler Lines, and Schiffler Points: Guyen E IldbergerJeffersonAinda não há avaliações
- Dominik's DocumentDocumento116 páginasDominik's DocumentLouis JamesAinda não há avaliações
- Plane Trigonometry Oct 2021Documento7 páginasPlane Trigonometry Oct 2021Benjie MorenoAinda não há avaliações