Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ha 5
Enviado por
Shouvik SinhaTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ha 5
Enviado por
Shouvik SinhaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
BRACT’s
Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune-37
Tutorial Booklet :Engineering Mechanics (ES 105)
For
F. Y. B. Tech (ECIT Group)
Formulated by : P.B.Kulkarni
D. E. S. H. (Civil Engg. Department)
w. e. f. Jan 2017 Sem 2
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Tutorial No. 5
Q 1) If motion of particle is defined by y (4 t 3 3 t ) m and ax 12 t m / s2 . If it is known that,
vx 4 m / s at t 0 , calculate resultant velocity and acceleration at t 1 sec .
Ans: v 13.45 m s , a 26.8 m s 2
x2
Q 2) At instant t , position of balloon is defined by x 30 t , y . Determine
100
i) Distance OA at t 2 sec
ii) Velocity and acceleration at t 2 sec .
Ans: OA 69.97 m , v 46.86 m s , a 18 m s 2
Q 3)
Q 4)
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q 5)
Q6)
Problems on n-t system
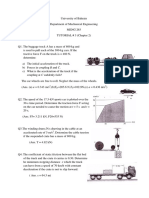
Q 7) To anticipate the dip and hump in the road, the driver of a car applies her brakes to produce a
uniform deceleration. Her speed is 100 km/h at the bottom A of the dip and 50 km/h at the top C of
the hump, which is 120 m along the road from A. If the passengers experience a total acceleration
of 3 m/s2 at A and if the radius of curvature of the hump at C is 150 m, calculate (a) the radius of
curvature at A, (b) the acceleration at the inflection point B, and (c) the total acceleration at C.
Q 8) Determine the maximum speed for each car if the normal acceleration is limited to 0.88g. The
roadway is unbanked and level.
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q 9 ) The two cars A and B enter an unbanked and level turn. They cross line C-C simultaneously,
and each car has the speed corresponding to a maximum normal acceleration of 0.9g in the turn.
Determine the elapsed time for each car between its two crossings of line C-C. What is the relative
position of the two cars as the second car exits the turn? Assume no speed changes throughout
Q 10) A particle moves along the curved path shown. If the particle has a speed of 12m/sec at A at
time and a speed of 14m/sec at B at time , determine the average values of the acceleration of the
particle between A and B, both normal and tangent to the path.
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q11 ) The speed of a car increases uniformly with time from 50 km/h at A to 100 km/h at B during
10 seconds. The radius of curvature of the hump at A is 40 m. If the magnitude of the total
acceleration of the mass center of the car is the same at B as at A, compute the radius of curvature
of the dip in the road at B. The mass center of the car is 0.6 m from the road
Q 12) The figure shows two possible paths for negotiating an unbanked turn on a horizontal portion
of a race course. Path A-A follows the centerline of the road and has a radius of curvature atA = 85
m, while path B-B uses the width of the road to good advantage in increasing the radius of
curvature at B =200m. If the drivers limit their speeds in their curves so that the lateral acceleration
does not exceed 0.8g, determine the maximum speed for each path.
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q 13) Consider the polar axis of the earth to be fixed in space and compute the magnitudes of the
velocity and acceleration of a point P on the earth’s surface at latitude 40° north. The mean
diameter of the earth is 12 742 km and its angular velocity is
Q14 ) The car C increases its speed at the constant rate of as it rounds the curve shown.
If the magnitude of the total acceleration of the car is at the point A where the radius of
curvature is 200 m, compute the speed v of the car at this point.
Q 15) The driver of the truck has an acceleration of 0.4g as the truck passes over the top A of the
hump in the road at constant speed. The radius of curvature of the road at the top of the hump is 98
m, and the center of mass G of the driver (considered a particle) is 2 m above the road. Calculate
the speed v of the truck
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
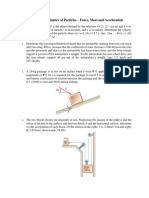
Q 16) A small particle P starts from point O with a negligible speed and increases its speed to a
value where y is the vertical drop from O. When x= 15.5 m , determine the n-
component of acceleration of the particle.
Q 17) The particle P starts from rest at point A at time and changes its speed thereafter at a constant
rate of 2g as it follows the horizontal path shown. Determine the magnitude and direction
of its total acceleration (a) just before point B, (b) just after point B, and (c) as it passes point C.
State your directions relative to the x-axis shown
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q18)
Q 19) At a given instant, the plane moving on curve has speed 500 m / s and acceleration 80 m / s2
as shown. Determine: i)Rate of increase of speed i.e. at , ii)Radius of curvature at point ‘A’.
Ans: at 27.36 m s 2 , 3325.5m
Q 20) A particle moves with a constant speed 3 m / s along a parabolic path shown in figure. Find
resulting acceleration at the position when x 0.5 m .
Ans: 5.27
a n 1.7 at t 0
a 1.718 m s 2
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Problems on r- θ system
Q 21) Rotation of the radially slotted arm is governed by ɵ = 0.2t + 0.02t3, where
ɵ is in radians and t is in seconds. Simultaneously, the power screw in the arm
engages the slider B and controls its distance from O according to r = 0.2 +
0.04t2, where r is in meters and t is in seconds. Calculate the magnitudes of the velocity and
acceleration of the slider for the instant when t = 3 s.
Q 22)
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q 23)
Q 24)
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q 25)
Q 26)
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
Q 27)
Q. 28) The particle ‘P’ moves along the spiral with the relation defined by r 10t and (2t ) rad.
Determine position, velocity and acceleration at i) t = 0 sec and ii) t = 0.3 sec.
Ans: i) At t = 0, r = 0, θ=0, v = 10 mm/s along vr , a = 125.6 mm/s2 along aθ
ii) At t = 0.3, r =3mm, θ=1.88 rad, v = 21.34 mm/s, a = 172.65 mm/s2
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
ES 105 Engineering Mechanics (ECIT Group) Tutorials
@ P. B. Kulkarni VIT PUNE (w.e.f 18/08/2016 )
Você também pode gostar
- FormulasDocumento6 páginasFormulasChong SingAinda não há avaliações
- 2016EME1076 Tutorial 1Documento5 páginas2016EME1076 Tutorial 1REan ANandAinda não há avaliações
- Kinematics of Particles All PROBLEMSDocumento19 páginasKinematics of Particles All PROBLEMSصادق سلام محمود شوط100% (1)
- Circular Motion (Ex. 1 & 5)Documento19 páginasCircular Motion (Ex. 1 & 5)PriyankaMishraAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Unit AssignmentDocumento1 página3 Unit AssignmentSagar YadavAinda não há avaliações
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1Documento3 páginasPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 2 Questionss-1AlbertAinda não há avaliações
- Rectilinear KinematicDocumento11 páginasRectilinear KinematicAyyub FakhruddinAinda não há avaliações
- Kinematics Theory + QuestionsDocumento58 páginasKinematics Theory + QuestionsAyushAinda não há avaliações
- Circular Motion Lecture 01Documento60 páginasCircular Motion Lecture 01DEEPAK KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Exercise - 1 To 3 PC Circular Motion ResoDocumento15 páginasExercise - 1 To 3 PC Circular Motion ResoZenith xAinda não há avaliações
- QB Em2 TempDocumento18 páginasQB Em2 Tempanshu kushwahAinda não há avaliações
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Documento3 páginasUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Vivin MathewAinda não há avaliações
- Circular Motion 3Documento41 páginasCircular Motion 3Raja BabuAinda não há avaliações
- DinamicaDocumento7 páginasDinamicaJohn Jairo MarinAinda não há avaliações
- Module 1 Wk3-4Documento36 páginasModule 1 Wk3-4Dyas FerAinda não há avaliações
- Immin111 6007Documento4 páginasImmin111 6007Shreyas ShankerAinda não há avaliações
- Part 1Documento90 páginasPart 1Saeid SamiezadehAinda não há avaliações
- Career Point Sample - 2Documento19 páginasCareer Point Sample - 2Shalini KureelAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 2 NewtonsDocumento4 páginasTutorial 2 Newtons2B Dai Ko DUPLICATEAinda não há avaliações
- T2 Force - AccelerationDocumento4 páginasT2 Force - AccelerationDipesh PanditAinda não há avaliações
- Kinematics Lect 01 NotesDocumento49 páginasKinematics Lect 01 Notesdp67b8ggppAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-KineticsDocumento36 páginasChapter 6-Dynamics-Kinematics-Kineticsعمر صرانAinda não há avaliações
- Work Sheet I & IIDocumento17 páginasWork Sheet I & IIeyobAinda não há avaliações
- PHY 400 - Chapter 6 - Rotational MotionDocumento30 páginasPHY 400 - Chapter 6 - Rotational MotionJacob OrtizAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 2A: Tutorial Tahap Clo-PloDocumento10 páginasTutorial 2A: Tutorial Tahap Clo-PloZariff ZakiAinda não há avaliações
- ENGN 37 HomeworkDocumento25 páginasENGN 37 HomeworkLucia AntoniusAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 3Documento3 páginasTutorial 3Vivin MathewAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics Ex1Documento1 páginaDynamics Ex1dinalamin195Ainda não há avaliações
- Repeat Paper 02 Edexcel PhysicsDocumento7 páginasRepeat Paper 02 Edexcel PhysicsWajira Sanjaya PereraAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 6 Tangential and Normal Components of Acceleration: OverviewDocumento8 páginasLesson 6 Tangential and Normal Components of Acceleration: OverviewNadjer C. AdamAinda não há avaliações
- 09-08-15 SR - Iit-Iz-Co-Spark Jee Adv Rpta-2 (2013 p2) Q'paperDocumento33 páginas09-08-15 SR - Iit-Iz-Co-Spark Jee Adv Rpta-2 (2013 p2) Q'paperKumar Prasad100% (1)
- A9R833Documento15 páginasA9R833Alejandro AguirreAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial Chapter 12 (Chapter 1 & 2 Mac 2017)Documento8 páginasTutorial Chapter 12 (Chapter 1 & 2 Mac 2017)Firdaus AriffAinda não há avaliações
- Physics I Problems PDFDocumento1 páginaPhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 AssignmentDocumento17 páginasChapter 2 Assignmentramel sigueAinda não há avaliações
- Transportation EngineeringDocumento11 páginasTransportation EngineeringStphn FmlrAinda não há avaliações
- 634618365995252500Documento12 páginas634618365995252500Akashdeep RamnaneyAinda não há avaliações
- Phase-1 Jee-Main Gtm-6 Final Question Paper NarayanaDocumento28 páginasPhase-1 Jee-Main Gtm-6 Final Question Paper NarayanaShrenik Jain100% (2)
- PhysicsDocumento14 páginasPhysicsSevyAinda não há avaliações
- Phyf4 Chap2Documento179 páginasPhyf4 Chap2Mohd AzlanAinda não há avaliações
- Circular MotionDocumento15 páginasCircular MotionMruthyumJaya Rao.KakarlaAinda não há avaliações
- Annual Question 2016Documento3 páginasAnnual Question 2016Er Saurabh SinhaAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics TutorialDocumento23 páginasMechanics TutorialDipesh PanditAinda não há avaliações
- R (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageDocumento4 páginasR (4.0 CM + (2.5 CM/S) I + (5.0 CM/S) T J: - (A) Find The Magnitude and Direction of The Dot's AverageOlojo Oluwasegun EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- 2021B MECD323 Deber3Documento2 páginas2021B MECD323 Deber3Darwin MoranAinda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Physics SoloutionDocumento9 páginasFundamentals of Physics Soloution8310032914Ainda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 2Documento5 páginasTutorial 2Vivin MathewAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial TwoDocumento5 páginasTutorial TwoParas gurungAinda não há avaliações
- Revision Plan-II (DPP # 2) - Physics - EnglishDocumento12 páginasRevision Plan-II (DPP # 2) - Physics - EnglishBhriguKansra50% (2)
- PMS Midterm Fall2021 2022Documento7 páginasPMS Midterm Fall2021 2022fareedongodAinda não há avaliações
- Forces and Motion: Revision Paper 01-Edexcel IGCSE in PhysicsDocumento6 páginasForces and Motion: Revision Paper 01-Edexcel IGCSE in PhysicsWajira Sanjaya PereraAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1011 (Nov)Documento10 páginasEngineering Mechanic Sem 1 Session 1011 (Nov)Amirul AizatAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Mechanics Problem Sheet - 4 Module - 4 Kinematics of ParticlesDocumento12 páginasEngineering Mechanics Problem Sheet - 4 Module - 4 Kinematics of ParticlesCams SenoAinda não há avaliações
- Sheet (5) - Dynamics PDFDocumento2 páginasSheet (5) - Dynamics PDFahmedmohammeda829Ainda não há avaliações
- 2018b Mec4a4-Gr1 Deber6Documento7 páginas2018b Mec4a4-Gr1 Deber6DaLcAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsNo EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2No EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- The Principles and Pracitce of Navigation - A FROST - 1991)Documento161 páginasThe Principles and Pracitce of Navigation - A FROST - 1991)AVINASH ANAND RAOAinda não há avaliações
- CH 5 MomentsDocumento22 páginasCH 5 MomentsisamalhassanAinda não há avaliações
- Complex NumbersDocumento15 páginasComplex NumbersAnonymous jUaHPNGx9lAinda não há avaliações
- (Lecture Notes in Mathematics 830) James A. Green (Auth.) - Polynomial Representations of GLN (1980, Springer) (10.1007 - BFb0092296) - Libgen - LiDocumento123 páginas(Lecture Notes in Mathematics 830) James A. Green (Auth.) - Polynomial Representations of GLN (1980, Springer) (10.1007 - BFb0092296) - Libgen - LiTrần Duy ThanhAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 9 PDFDocumento20 páginasUnit 9 PDFpoojaAinda não há avaliações
- Alexander Horned SphereDocumento3 páginasAlexander Horned SphereDARKOVUKICAinda não há avaliações
- Edexcel IAL C34 - SAM PaperDocumento5 páginasEdexcel IAL C34 - SAM PaperSahil KananiAinda não há avaliações
- Fractaldimensionin Architecture An Explorationof Spatialdimension 2017Documento107 páginasFractaldimensionin Architecture An Explorationof Spatialdimension 2017Ar ReshmaAinda não há avaliações
- Center of MassDocumento3 páginasCenter of MassMartha Glorie Manalo WallisAinda não há avaliações
- Scott Robertson How To DrawDocumento208 páginasScott Robertson How To DrawJorge Braddock50% (2)
- DAY 1 VectorsDocumento24 páginasDAY 1 VectorsPrecious MiñozaAinda não há avaliações
- WTW 158 - Calculus 1 Class NotesDocumento27 páginasWTW 158 - Calculus 1 Class NotesCAinda não há avaliações
- Navigation Map ProjectionsDocumento38 páginasNavigation Map Projectionsbittu692Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter #4 Bending Stress: Simple Bending Theory Area of Second Moment Parallel Axes Theorem Deflection of Composite BeamDocumento30 páginasChapter #4 Bending Stress: Simple Bending Theory Area of Second Moment Parallel Axes Theorem Deflection of Composite Beamlayiro2Ainda não há avaliações
- Mathematics: Self-Learning Module 6Documento12 páginasMathematics: Self-Learning Module 6Tabada NickyAinda não há avaliações
- Circle EquationDocumento7 páginasCircle EquationbirrajAinda não há avaliações
- Safal Maths HandbookDocumento40 páginasSafal Maths HandbookbadarishpAinda não há avaliações
- TD 7 1st PT 22Documento4 páginasTD 7 1st PT 22MarivicVichoMonsayacAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics Resource Package: Quarter I Subject: MATH Date: - Day 3 Content StandardDocumento9 páginasMathematics Resource Package: Quarter I Subject: MATH Date: - Day 3 Content StandardEric John ROSALEJOSAinda não há avaliações
- Icem 2d Car MeshingDocumento34 páginasIcem 2d Car MeshingAmber Dixon100% (1)
- Monday, 9 November 2020 - Morning Unit 1: Non-Calculator Higher TierDocumento24 páginasMonday, 9 November 2020 - Morning Unit 1: Non-Calculator Higher TierBDPV02Ainda não há avaliações
- Features Located To A PatternDocumento4 páginasFeatures Located To A PatternJuan Posada GAinda não há avaliações
- Crisfield M A Vol 2 Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures Advanced TopicsDocumento509 páginasCrisfield M A Vol 2 Non-Linear Finite Element Analysis of Solids and Structures Advanced TopicsIffat Siddqiue0% (1)
- 00 Dobot Blockly WorkbookDocumento182 páginas00 Dobot Blockly Workbookdborcic61Ainda não há avaliações
- M2L2 LNDocumento8 páginasM2L2 LNnagesha_basappa865Ainda não há avaliações
- Metric SpaceDocumento12 páginasMetric SpaceSelvia Eko100% (1)
- Claus Michael Ringel, Jan Schröer - Representation Theory of Algebras I - Modules (Preliminary Version Feb 10, 2009) (2009) PDFDocumento283 páginasClaus Michael Ringel, Jan Schröer - Representation Theory of Algebras I - Modules (Preliminary Version Feb 10, 2009) (2009) PDFJonhatan Castillo BarajasAinda não há avaliações
- Final NMDocumento17 páginasFinal NMMausoomAinda não há avaliações
- 08aaa Full Yr 12 ReviewDocumento31 páginas08aaa Full Yr 12 ReviewSnorkAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 3rd Edition AnswersDocumento1 páginaCalculus Graphical Numerical Algebraic 3rd Edition AnswersVeerendra cbse0% (1)