Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Chua, Kimberly O. Group 2 2015107174 E201: Work, Energy, and Power
Enviado por
Chua Kimberly0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
19 visualizações5 páginasexp
Título original
Chua Phy11l Exp201
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoexp
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
19 visualizações5 páginasChua, Kimberly O. Group 2 2015107174 E201: Work, Energy, and Power
Enviado por
Chua Kimberlyexp
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 5
Chua, Kimberly O.
GROUP 2
2015107174
E201: WORK, ENERGY, AND POWER
Abstract
The intention of this experiment is to demonstrate how work, power and energy
and its relationship to energy of conservation. According to the law of energy
conservation, “Energy is neither created nor destroyed, but is just changed from
one to another”. Since the energy is the capacity to do work, we can acquire
energy in many forms and through work, it will transfer from one object to another.
Power is used to measure the work done. Based on the results we obtain, the value
of work will increase as the displacement is increased.
Introduction
Work means “A Change in power may be computed
Energy” in Physics. The force comes instantaneously.
from the energy that causes the
object to move at a distance. Work
happens when there is a Methodology
displacement in the direction of the
force. In Math, specifically in
Calculus, it is defined as the integral
of the force over the displacement.
Though force and displacement are
both vector quantities, work has no
direction. The physical capacity of
the system to perform a lot of work is
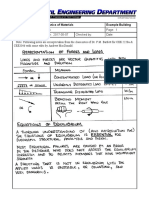
Figure 1.
called Energy.
The image shows all the materials
But also, keep it in mind that if energy
used in the experiment, these are:
exist, it doesn’t always mean that we
1. Dynamic Cart
can do some work. In this experiment,
2. Fan Cart
the definition of work, shall be
3. Two (2) Photogates
defined in a more precise manner
4. Protractor
and that work shall be computed for
5. Spring Balance
a curved path. Power, the time rate
6. Set of Weights
of doing work. Like work and energy,
7. Iron Stand
power is also a scalar quantity. When
8. Smart Timer; and
the rate of work is not constant, the
9. Meter stick
In the first part of the experiment, the balanced.
dynamics track and fan cart serve as
the essential tools. Before starting, it is
needed to make sure that the
dynamics track is leveled on the
table. To check if the track is leveled
horizontally, angle meter is used in this
experiment. When the bubble is at
the center below the zero angle then
it is leveled horizontally. The fan cart’s
fan should also be turned around
wherein the arrow is aiming to zero.
After assembling the track and the
fan cart, the pulley with clamp must
be positioned on the end of the track.
The string with the pan connected on
the other end was attached to the
fan cart. The fancart should be
placed on the track, while the string
should pass over the pulley. Upon For the second part of the
turning on the power of the fan cart experiment, the string from the cart
in a low setting, the direction it goes is was removed. Photogates must be
based where the fan’s direction. The assembled and connected to the
cart must move away from the pan smart timer. The two photogates
to oppose the force. Weights was put were placed in different positions.
on the pan then afterwards the fan Taped the metal fastener to the fan
cart was turned on. If the fan cart cart for the magnet on the cart is not
goes along the orientation of the that capable enough to secure it in
pan, the force is not yet balanced. the position, in a way that it will not
Adding more weights to the pan is bump the photogates but will pass
needed until the correct amount of through its sensors when it moves
weight is reach. It is determined when along the track. The fastener served
fan cart is on a steady position which as an indicator of the fan cart so the
means that the force is now photogate will be able to detect it.
The results that is get from the timer
were used to determine the amount
of work done. Another three trials
were also performed, but this time the
second photogate was moved
further, in order to have a varying
displacement.
Results and Discussion The relationship between work done
and displacement is also directly
In the first part of the experiment, the
proportional. Whereas the correct
force, work and power of the fan cart
relationship between the work done
was determined. The force of the fan
and power expended is directly
cart was attained by adding the
proportional, because the power is
mass of the pan and the weight
equal to its work over time. So given
added to it and multiplying it to the
that the time is constant, as the work
gravitational acceleration constant,
done increases, the power also
g = 9.8m/s2. Since the fan cart was
increases.
not moving along the dynamics track
when turned on when the added During our experiment, we
weight was placed on the pan that experienced minimal error in the
was connected through the string arrangement of the photogates
and to the cart, the force was proven which affects the outcome of our
to be correct from the experiment. measurement and the photogate’s
For the next part of the experiment, handle itself wasn’t that stable as it
the displacement is the component should be, so the calculation of the
that is changeable per trial which is time, and a slight inaccuracy in the
figured using the positions of the two measurement of the angle and the
photogates. The displacement was height of the mass when a horizontal
measured by subtracting the force was acted to it that made an
distance of the first photogate from impact in our computation.
the second photogate. Using the
smart timer and the photogates, time
was figured. Work was computed by Sample Computation
the force multiplying with the
A. First Part of the Experiment
displacement. Power on the other
Equations to be used:
hand was calculated by dividing the
computed work by time. 𝑊 = 𝑚𝑔
𝑊𝑜𝑟𝑘 𝑊
𝑃𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 = =
𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑇
Conclusion 𝑊𝑜𝑟𝑘 = 𝐹𝑜𝑟𝑐𝑒 × 𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑝𝑙𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡 = 𝐹𝑑
The applied force and the work done
is directly proportional. The work done
Given:
can be determined by getting the
product of the applied force and the Force of the Fan Cart (F)
displacement.
= Weight of the pan + weight Added
When the force increases, given that
time or displacement is constant, the = (0.025kg) (9.8m/s^2)
work done also increases.
= 0.245N
Trial 1 Length of String (L) = 0.225m
Displacement (d) = 0.2m Weight of mass (w) = 2.943N
Time (t) = 0.47s Initial Height (ho) = 0.127m
Work (W) = F (d)
= (0.245N) (0.2m) Trial:
= 0.049J Force = 9N
Power = W / t Final Height (hf) = 0.14m
= (0.049J) / (0.47s) Increase in Height (h) = 0.013m
= 0.1043 Watts Angle (θ) = 30o
Displacement (X) = 0.065m
B. Second Part of the Experiment Work = wL (1-cosθ)
= (2.943N) (0.225m) (1-cosθ)
Equation to be Used:
= 0.039J
𝑊 = 𝑤𝐿(1 − cos 𝜃)
Gravitational Potential Energy
𝐺𝑟𝑎𝑣𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑡𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑃𝑜𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝐸𝑛𝑒𝑟𝑔𝑦 = 𝑈 = (2.943)(0.013)
= 𝑚𝑔ℎ = 0.038 J
Given :
Você também pode gostar
- Lintels Problems - STEEL STRUCTURESDocumento8 páginasLintels Problems - STEEL STRUCTURESDarya Memon100% (1)
- Pile Cap Design 1Documento6 páginasPile Cap Design 1kjpatel2100% (2)
- Lab Report 1 Newtons secondlawofmotion-PHYS101LDocumento7 páginasLab Report 1 Newtons secondlawofmotion-PHYS101LJamie ToriagaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Work Energy and PowerDocumento31 páginasChapter 2 Work Energy and PowerGimarino Lahra MaeAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab FR 4Documento6 páginasPhysics Lab FR 4vada_soAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 3: Conditions For EquilibriumDocumento8 páginasExperiment 3: Conditions For EquilibriumToni Andrei CervalesAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Steel Design PPT in PDFDocumento88 páginasAdvanced Steel Design PPT in PDFaskcmiitmAinda não há avaliações
- Flow Coefficients of Orifice and Mouthpiece ExperimentDocumento5 páginasFlow Coefficients of Orifice and Mouthpiece ExperimentAshish VermaAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS EXAM REVIEWDocumento18 páginasPHYSICS EXAM REVIEWCha Castillo100% (1)
- Work Power and EnergyDocumento8 páginasWork Power and EnergyJhoanna Rein DuzonAinda não há avaliações
- Science8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Documento23 páginasScience8 q1 Mod3 Potential-And-kinetic-Energy v2Keith Genesis Ruiz AglubaAinda não há avaliações
- Kundt S Tube ExperimentDocumento9 páginasKundt S Tube ExperimentChua Kimberly100% (1)
- Experiment 4: Work, Power and Energy Laboratory ReportDocumento4 páginasExperiment 4: Work, Power and Energy Laboratory ReportRamnuj Orecul SoralcAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 201: Work, Energy, and PowerDocumento5 páginasExperiment 201: Work, Energy, and PowerKeith ManansalaAinda não há avaliações
- PHY11L E201: Work, Energy, and PowerDocumento16 páginasPHY11L E201: Work, Energy, and PowerMikaella TambisAinda não há avaliações
- Work, Energy and Power: Ko, Bhing Liok P., PHY11L/A3Documento6 páginasWork, Energy and Power: Ko, Bhing Liok P., PHY11L/A3bhing koAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Page - 1Documento6 páginasExperiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Page - 1Clemente Abines IIIAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Romar King D. Celebre, 2011104475, BS CEM-2Documento5 páginasExperiment 201 Work, Energy and Power: Romar King D. Celebre, 2011104475, BS CEM-2Romar King CelebreAinda não há avaliações
- Dela Cruz, John Van Russel R. Group 2 2015108536 E201: Work, Energy, and PowerDocumento5 páginasDela Cruz, John Van Russel R. Group 2 2015108536 E201: Work, Energy, and PowerVanz DCAinda não há avaliações
- E201: Work, Energy and Power PALERO JR., Dante MDocumento5 páginasE201: Work, Energy and Power PALERO JR., Dante MRamnuj Orecul SoralcAinda não há avaliações
- Results and Discussion: 0.1372 J 0.5722 S 0.2398 WattsDocumento2 páginasResults and Discussion: 0.1372 J 0.5722 S 0.2398 WattsAnthony FajardoAinda não há avaliações
- E201: Work, Energy and Power POLICIOUS, Mark Angelo FDocumento5 páginasE201: Work, Energy and Power POLICIOUS, Mark Angelo FMark Angelo PoliciosAinda não há avaliações
- This Study Resource Was: Experiment 201 Work, Energy and PowerDocumento5 páginasThis Study Resource Was: Experiment 201 Work, Energy and PowerClemente Abines IIIAinda não há avaliações
- Mapúa Institute of Technology Department of Physics: Experiment 201Documento5 páginasMapúa Institute of Technology Department of Physics: Experiment 201Darwin Lee KatigbakAinda não há avaliações
- MAPUA WORK ENERGY EXPERIMENTDocumento7 páginasMAPUA WORK ENERGY EXPERIMENTRhon AntonioAinda não há avaliações
- Phy11l - E201Documento4 páginasPhy11l - E201Idate PatrickAinda não há avaliações
- Phy11l A4 E201Documento8 páginasPhy11l A4 E201nadaynAinda não há avaliações
- Work Energy TheoremDocumento6 páginasWork Energy TheoremJohn Eric PinedaAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab 6Documento7 páginasPhysics Lab 6Tahsin RahmannAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lab ReportDocumento13 páginasPhysics Lab ReportNaethan VelardeAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 14Documento2 páginasLab 145377773Ainda não há avaliações
- An Introduction To Chemical Energetics and Thermodynamics - 1Documento2 páginasAn Introduction To Chemical Energetics and Thermodynamics - 1Ateneo Blue EaglesAinda não há avaliações
- Work Done by A Variable Force (Vertical)Documento7 páginasWork Done by A Variable Force (Vertical)Hafiezul Hassan50% (2)
- Expt 3 Work Energy Theorem Group 4 Updated 2Documento9 páginasExpt 3 Work Energy Theorem Group 4 Updated 2Damien ManceraAinda não há avaliações
- HPhys Unit 04 UBFPM Packet 2012Documento16 páginasHPhys Unit 04 UBFPM Packet 2012Kelly O'SheaAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Pendulum Experiment IDocumento2 páginasSimple Pendulum Experiment IAmmar ShahzadAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 10Documento24 páginasChap 10uaragieAinda não há avaliações
- Conservation of Energy LabDocumento6 páginasConservation of Energy LabAneesh Malhotra0% (1)
- Laboratory Report in LBYPH11Documento4 páginasLaboratory Report in LBYPH11Bernard Jomari Blancada RazoteAinda não há avaliações
- Work, Energy and Energy Conservation: Learning CompetenciesDocumento4 páginasWork, Energy and Energy Conservation: Learning CompetenciesNathalie SerafinAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 106: Uniform Circular MotionDocumento7 páginasExperiment 106: Uniform Circular MotionJasmin DionisioAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Work and Energy 1Documento14 páginas6 Work and Energy 1John Van Dave TaturoAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Emilio B. Espinosa, Sr. Memorial State College of Agriculture and Technology (Masbate State College) College of EngineeringDocumento24 páginasDr. Emilio B. Espinosa, Sr. Memorial State College of Agriculture and Technology (Masbate State College) College of EngineeringFrancisco, Rizaldy Rodolf G.Ainda não há avaliações
- Work-Energy and ConservationDocumento116 páginasWork-Energy and ConservationMarjorie KhylAinda não há avaliações
- Phy11l Exp5Documento3 páginasPhy11l Exp5Keith Ryan LapizarAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 Labsheet PT4 - Potential Kinetic Energy PDFDocumento4 páginas2020 Labsheet PT4 - Potential Kinetic Energy PDFAkmal HazimAinda não há avaliações
- IAL Physics MechanicsDocumento6 páginasIAL Physics Mechanicsvekariaraj99Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab 4: Work and EnergyDocumento8 páginasLab 4: Work and EnergyWaseem Al-khawajaAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 104: Newton's Second Law of MotionDocumento7 páginasExperiment 104: Newton's Second Law of MotionJaz DionisioAinda não há avaliações
- Work, Power & EnergyDocumento16 páginasWork, Power & EnergyAyush GamerAinda não há avaliações
- Práctica # 2 ElasticidadDocumento7 páginasPráctica # 2 ElasticidadBoris Fernando CalleAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 101 Newton's Second Law of MotionDocumento6 páginasExperiment 101 Newton's Second Law of MotionElle GabrielAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 5: Hooke's LawDocumento8 páginasExperiment 5: Hooke's LawDave Vendivil SambranoAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No: 05: Mass Spring System (SHM)Documento17 páginasExperiment No: 05: Mass Spring System (SHM)Shayan AliAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic Energy and WorkDocumento15 páginasKinetic Energy and WorkMahesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- 7 - Moment of InertiaDocumento11 páginas7 - Moment of Inertiafrank dumbleAinda não há avaliações
- Conservation of Energy ExperimentDocumento3 páginasConservation of Energy ExperimentHaziq HakimieAinda não há avaliações
- Expt-3: Demonstration of Hooke's Law Using Spiral Spring: ObjectiveDocumento8 páginasExpt-3: Demonstration of Hooke's Law Using Spiral Spring: ObjectiveIsmail H. SiddiqueeAinda não há avaliações
- Work 2Documento18 páginasWork 2elenaAinda não há avaliações
- 107 Lab 3Documento7 páginas107 Lab 3Tanvir MahtabAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 4: Measure work, power and energyDocumento4 páginasExperiment 4: Measure work, power and energyRamnuj Orecul SoralcAinda não há avaliações
- Acceleration of A Laboratory CartDocumento3 páginasAcceleration of A Laboratory CartUgur ASİT100% (1)
- LABREP3Documento4 páginasLABREP3Julia LovinoAinda não há avaliações
- Free Fall Experiment AnalysisDocumento12 páginasFree Fall Experiment AnalysisMeritxell Meza VerdeciaAinda não há avaliações
- E205: Hooke's LawDocumento6 páginasE205: Hooke's LawPJ Bundalian100% (2)
- Microx UpdatedDocumento11 páginasMicrox UpdatedChua KimberlyAinda não há avaliações
- Microexit1 600501764134913Documento8 páginasMicroexit1 600501764134913Chua KimberlyAinda não há avaliações
- Phy12 Exit Exam ReviewDocumento9 páginasPhy12 Exit Exam ReviewAngelo Joshua De LeonAinda não há avaliações
- 1.4.1.1 Lab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit ToolsDocumento4 páginas1.4.1.1 Lab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit Toolsmerz asmaAinda não há avaliações
- Accounting Information SystemsDocumento3 páginasAccounting Information SystemsChua KimberlyAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz # 1Documento19 páginasQuiz # 1Argie FloresAinda não há avaliações
- 1.4.1.1 Lab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit ToolsDocumento4 páginas1.4.1.1 Lab - Researching Network Attacks and Security Audit Toolsmerz asmaAinda não há avaliações
- Obstacles, decision methods, objectives & frameworksDocumento3 páginasObstacles, decision methods, objectives & frameworksChua KimberlyAinda não há avaliações
- Emg20 Q1 OtDocumento6 páginasEmg20 Q1 OtChua KimberlyAinda não há avaliações
- 01.1.1 - OrientationDocumento10 páginas01.1.1 - OrientationChua KimberlyAinda não há avaliações
- Kundt S Tube ExperimentDocumento3 páginasKundt S Tube ExperimentChua KimberlyAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Block Machine Foundation in STAADPRODocumento3 páginasDesign of Block Machine Foundation in STAADPROVivek DhutAinda não há avaliações
- TUDelft MBD LectureDocumento8 páginasTUDelft MBD Lecturestarling1001408Ainda não há avaliações
- Chap05 StaticFailureDocumento9 páginasChap05 StaticFailureFatih AŞCIAinda não há avaliações
- Rolling Disk Lab Report Applied DynamicsDocumento7 páginasRolling Disk Lab Report Applied DynamicsAliAinda não há avaliações
- Ch-8 Motion: Difference Between Uniform and Non Uniform MotionDocumento4 páginasCh-8 Motion: Difference Between Uniform and Non Uniform MotionBdbdhrhrjruhrhrAinda não há avaliações
- The Classical Mechanics of Non-Conservative SystemsDocumento5 páginasThe Classical Mechanics of Non-Conservative Systemshmalikn7581Ainda não há avaliações
- Jasmine Tran - Unit 2 Free Response Question - Ap Calc PortfolioDocumento2 páginasJasmine Tran - Unit 2 Free Response Question - Ap Calc Portfolioapi-574938628Ainda não há avaliações
- Equation Sheet For ThermodynamicsDocumento3 páginasEquation Sheet For ThermodynamicsQuazar001Ainda não há avaliações
- Calculating Currents in a Wheatstone Bridge NetworkDocumento10 páginasCalculating Currents in a Wheatstone Bridge NetworkMadhavan KAinda não há avaliações
- Armfield F1 21 Datasheet v2b Web 1Documento1 páginaArmfield F1 21 Datasheet v2b Web 1Ibrahim ALsultanAinda não há avaliações
- MAE 318 Homework 1 F17Documento2 páginasMAE 318 Homework 1 F17ZarghamKhanAinda não há avaliações
- Materials QDocumento41 páginasMaterials QEses SAinda não há avaliações
- CIVE 192 - Summer - Course Notes Part 1Documento21 páginasCIVE 192 - Summer - Course Notes Part 1DrewAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture Notes PPT 4 PDFDocumento17 páginasLecture Notes PPT 4 PDFDrRoja A RAinda não há avaliações
- Oscillations, Waves and OpticsDocumento25 páginasOscillations, Waves and OpticsTushar GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- z.2. Sertifikat + Materi Seminar Internasional Usm 2022 (Lengkap)Documento6 páginasz.2. Sertifikat + Materi Seminar Internasional Usm 2022 (Lengkap)Sutarno -Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics- Enthalpy of Reaction and Hess’s LawDocumento3 páginasThermodynamics- Enthalpy of Reaction and Hess’s LawMaggie GilliganAinda não há avaliações
- Edexcel M3 NotesDocumento44 páginasEdexcel M3 NotesNani AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- S. Boon-Long C. Laguerie J.P. Couderc - Mass Transfer From Suspended Solids To A Liquid in Agitated VessDocumento7 páginasS. Boon-Long C. Laguerie J.P. Couderc - Mass Transfer From Suspended Solids To A Liquid in Agitated VessAntung PutraAinda não há avaliações
- Funds of Inertial Navigation Satellite Based Positioning and Their Integration PDFDocumento44 páginasFunds of Inertial Navigation Satellite Based Positioning and Their Integration PDFCaehhsegffAinda não há avaliações
- FrictionDocumento6 páginasFrictionElle HeartfiliaAinda não há avaliações
- Xtract V 3 0 8Documento72 páginasXtract V 3 0 8Don Ing Marcos LeónAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanism Design: A SeriesDocumento3 páginasMechanism Design: A Seriesamirmasood kholojiniAinda não há avaliações