Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
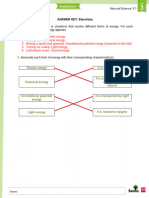
Energy
Enviado por
osamaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Energy
Enviado por
osamaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Name Date Class
Lesson Outline LESSON 1
Forms of Energy
A. What is energy?
1. is the ability to cause change.
2. Energy can cause an object to its position or its motion.
B. Kinetic Energy—Energy of Motion
1. Energy due to motion is .
2. The faster an object moves, the kinetic energy it has.
3. The kinetic energy of an object depends on its as well
as its speed.
4. If two objects move at the same speed, the object with the
mass will have more kinetic energy.
C. Potential Energy—Stored Energy
1. is stored energy.
2. When you are holding a book energy is stored between the book and Earth;
this type of energy is called potential energy. This
type of potential energy stored between an object and Earth depends on the
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
and of the object.
3. Elastic potential energy is energy stored in objects that are compressed
or .
4. When you stretch a rubber band, you are storing
potential energy. When you let go of the rubber band, stored elastic potential
energy is transformed into energy.
5. Food has potential energy, which is the
energy stored in the bonds between atoms. This energy is released when
occur.
D. Energy and Work
1. is the transfer of energy to an object by a force that
makes the object move in the direction of the force.
2. is sometimes described as the ability to do work.
10 Energy and Energy Resources
Name Date Class
Lesson Outline continued
E. Other Forms of Energy
1. Energy can be measured in units of .
2. is the total kinetic energy and potential energy in an
object or group of objects.
3. The energy carried by sound waves is . It is produced
by objects that .
4. All materials are made of atoms and molecules that are always
. The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy of the
particles in matter due to their random motion is .
5. is the energy carried by an electric current.
6. , such as microwaves, can travel through a vacuum.
7. The energy of electromagnetic waves is called .
8. is stored in the nucleus of an atom.
9. The Sun releases nuclear energy when the of atoms
join together.
10. Nuclear power plants release energy by nuclei.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Energy and Energy Resources 11
Name Date Class
Content Practice A LESSON 1
Forms of Energy
Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some terms
might be used more than once or not at all.
electrical energy kinetic mechanical nuclear
potential radiant sound thermal work
1. Energy due to motion is energy.
2. The amount of energy an object has depends on the
object’s speed and mass.
3. Energy that is stored in the nucleus of an atom is energy.
4. The ability to cause change is .
5. energy is stored energy.
6. Energy that is carried by an electric current is energy.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
7. Gravitational, elastic, and chemical are three forms of
energy.
8. The transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied over a distance is
.
9. Energy that is the total of the kinetic energy and potential energy in an object or group
of objects is energy.
10. The energy of atoms and molecules in an object due to their motions is
energy.
11. Energy is the ability to do .
12. Energy carried by electromagnetic waves is called energy.
Energy and Energy Resources 13
Name Date Class
Key Concept Builder LESSON 1
Forms of Energy
Key Concept How is energy related to work?
Directions: On the line before each statement, write T if the statement is true or F if the statement is false.
1. When you lift an object, you do work on the object.
2. When you lift an object higher, you decrease its gravitational potential energy.
3. Work is the transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied over
a distance.
4. An object that has energy can do work.
5. When you lift an object, you increase potential energy.
6. When you lift an object, energy is transferred from the object to you.
7. Energy is the ability to do work.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
8. When a bowling ball hits bowling pins, the pins transfer kinetic energy
to the ball.
9. A ball rolling down a hill has increasing potential energy.
10. When you push a shopping cart, you transfer energy to it.
11. A child climbing a ladder is transforming kinetic energy into potential energy.
12. The child climbing the ladder is doing work.
13. When a pool ball hits another ball and causes it to move, potential energy has
transferred from one ball to the other.
18 Energy and Energy Resources
Name Date Class
Key Concept Builder LESSON 1
Forms of Energy
Key Concept What are different forms of energy?
Directions: Write the type of energy next to each clue. Some clues might involve more than one type of energy.
electrical mechanical nuclear radiant sound thermal
1. shooting a basketball
2. the total of the potential energy and kinetic energy in an
object or group of objects
3. a phone ringing
4. the energy of moving atoms
5. Light is an example.
6. energy given off by the Sun
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
7. carried by an electric current
8. Microwaves are an example.
9. Heat is the movement of this.
10. energy that is stored in the nucleus of an atom
11. a radio playing
12. an ocean wave
13. a microwave heating food
Energy and Energy Resources 19
Name Date Class
Lesson Quiz A LESSON 1
Forms of Energy
Multiple Choice
Directions: On the line before each question or statement, write the letter of the correct answer.
1. Energy is the ability to
A. use gravity.
B. hold objects.
C. cause change.
2. A moving truck has more energy than a parked truck.
A. sound
B. kinetic
C. potential
3. A large truck parked on a hill has more energy than a car parked next to it.
A. sound
B. kinetic
C. potential
4. Which situation is an example of work?
A. a person holding several tools
B. a person sitting in a parked car
C. a person hitting a pitched baseball
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
5. Which type of energy is the total energy in an object or group of objects?
A. sound energy
B. radiant energy
C. mechanical energy
Matching
Directions: On the line before each definition, write the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is
used only once.
6. released when nuclei split A. elastic potential energy
7. stored in a stretched rubber band B. thermal energy
C. nuclear energy
8. transferred by heat
D. radiant energy
9. used when your body moves
E. chemical energy
10. carried by electromagnetic waves
22 Energy and Energy Resources
Name Date Class
Lesson Outline LESSON 2
Energy Transformations
A. Changes Between Forms of Energy
1. A microwave oven changes electrical energy to energy.
2. The changes from electrical energy to radiant energy to thermal energy are called
energy .
B. Changes Between Kinetic and Potential Energy
1. When you throw a ball upward, the ball has its greatest speed and the most
energy when it first leaves your hand.
2. As the ball reaches its highest point, the ball gains its greatest
energy.
3. As the ball moves downward, energy decreases
and energy increases.
C. The Law of Conservation of Energy
1. According to the , energy can be transformed from one
form into another or transferred from one region to another, but energy cannot be
created or destroyed.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
2. is a force that resists the motion of one surface over
another.
a. There is always some between any surfaces that are
in contact with each other.
b. As you pedal a bicycle, you do and transfer
to the bicycle.
c. Because of between moving parts of a bicycle, some
of the work you do changes to energy.
d. One way to reduce friction is to apply a(n) to
surfaces that rub against each other.
e. When you apply brakes on a bicycle, the bicycle’s
energy is not destroyed; instead, the bicycle’s energy
is transformed into thermal energy. The amount of
energy remains the same.
Energy and Energy Resources 27
Name Date Class
Lesson Outline continued
D. Using Energy
1. You use energy for cooking and heating.
2. Gas stoves and furnaces change energy from natural gas
into thermal energy.
3. During photosynthesis, plants transform energy from
the Sun into chemical energy stored in food.
4. Your body changes the chemical energy stored in food into
energy as you move and into
energy, which keeps your body temperature high.
5. A television transforms energy into sound energy and
energy.
6. Many devices you use every day are powered by energy
from electrical power plants.
7. With battery-powered devices, energy is transformed
into electrical energy for power.
8. When energy changes form, some energy is always
released. Scientists often refer to this energy that cannot be used
as .
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
9. Cars transform most of the chemical energy in gasoline into
energy.
28 Energy and Energy Resources
Name Date Class
Content Practice A LESSON 2
Energy Transformations
Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Some terms
might be used more than once.
electrical energy transformation friction kinetic
law of conservation of energy potential radiant thermal
1. According to the , energy cannot be created or destroyed.
2. A change from electrical energy to radiant energy to thermal energy is called
a(n) .
3. A force that resists the motion of one surface over another
is .
4. A microwave oven changes energy to radiant energy to
energy.
5. Suppose you are shooting a basketball toward a hoop. As the ball rises in the air, its
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
energy increases and its
decreases.
6. As the ball falls back toward the floor, its energy increases
and its decreases.
7. Friction transforms some mechanical energy into energy.
8. You use a lamp to change energy into
energy.
9. When you use a battery, you transform chemical energy stored in the battery to
energy.
10. The exhaust from a car contains energy that cannot be
used. Scientists often refer to this energy that cannot be used as waste energy.
30 Energy and Energy Resources
Name Date Class
Key Concept Builder LESSON 2
Energy Transformations
Key Concept What is the law of conservation of energy?
Directions: In the diagram below, a ball has just been thrown and is about to be caught. Use the diagram to
answer each question.
At the ball’s highest point its
kinetic energy is zero and its
potential energy is maximum. C.
Total
energy
KEPE
Kinetic energy is D.
decreasing, and potential
energy is increasing.
Total Kinetic energy is
energy decreasing, and potential
KEPE energy is increasing.
B.
Total
energy
Kinetic energy is KEPE
maximum, and potential
energy is minimum.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Total E.
A. energy
KEPE
Kinetic energy is
maximum, and
potential energy
is minimum.
Total
energy
KEPE
1. At which stage is kinetic energy at the maximum value?
2. At which stage is potential energy at its minimum?
3. At which stage is the kinetic energy zero?
4. At which stage is the potential energy at the maximum value?
5. Which stage has increasing kinetic energy and decreasing potential energy?
6. Which stage has decreasing kinetic energy and increasing potential energy?
34 Energy and Energy Resources
Name Date Class
Lesson Quiz A LESSON 2
Energy Transformations
Multiple Choice
Directions: On the line before each question or statement, write the letter of the correct answer.
1. An energy occurs when energy changes from one type to another type.
A. increase
B. conversion
C. transformation
2. What happens to potential energy when a ball is tossed into the air?
A. It never changes.
B. It increases as the ball approaches its highest point.
C. It decreases as the ball approaches its highest point.
3. According to the law of conservation of energy, energy cannot
A. be created or destroyed.
B. transferred from one region to another.
C. transformed from one form into another.
4. When a ball is thrown into the air, its kinetic energy is lowest
A. at its highest point.
B. at the moment it is released.
C. as it begins to fall back to the ground.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
5. What type of energy transformation occurs during photosynthesis?
A. Radiant energy becomes chemical energy.
B. Thermal energy becomes chemical energy.
C. Nuclear energy becomes mechanical energy.
Matching
Directions: On the line before each definition, write the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is
used only once.
6. transforms gravitational potential energy into A. friction
kinetic energy
B. lubricant
7. transforms mechanical energy into thermal energy C. electric heater
8. transforms radiant energy into sound energy D. cell phone
9. force that reduces kinetic energy and produces E. a marble falling off a
heat table
10. reduces friction’s creation of thermal energy
Energy and Energy Resources 41
Name Date Class
Content Vocabulary LESSON 3
Energy Resources
Directions: An analogy is a relationship between two pairs of words. An analogy can be written in the following
manner: a is to b as c is to d. For example, apple is to fruit as celery is to vegetable. In the analogies that
follow, one of the terms is missing. On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each
sentence.
fossil fossil fuel inexhaustible energy resource
nonrenewable energy resource nuclei renewable energy resource
1. Fossil fuel is to as solar energy is to inexhaustible energy
resource.
2. Power plant is to power plants as nucleus is to .
3. Wind is to as coal is to nonrenewable energy resource.
4. Coal is to as kinetic energy is to energy.
5. Nonrenewable energy resource is to as petroleum is to
hydroelectric energy.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
6. is to dinosaur skeleton as energy is to the Sun.
Energy and Energy Resources 45
Name Date Class
Lesson Outline LESSON 3
Energy Resources
A. Sources of Energy
1. Most of the energy that we use every day originally came from
the .
2. A small amount of energy that reaches Earth’s surface comes
from .
B. Electric Power Plants
1. produce most of the energy people use in their daily lives.
2. The three main sources of energy used in electric power plants are
, energy in uranium,
and power from falling water.
C. Nonrenewable Energy Resources
1. A(n) is an energy source that is used much faster than
it is replaced or is available in limited amounts.
2. are the remains of ancient organisms that can be
burned as an energy source.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
a. Fossil fuels take of years to form, and they are being
used up much faster than they can be replaced.
b. and natural gas form from microscopic marine
organisms whose remains are subject to increasing temperature and pressure for
millions of years.
c. forms on land from remains of ancient plants that
come under strong pressure.
d. Most of the burned in the United States is used to
generate electricity in power plants.
e. Most of the burned in the United States is used to
heat buildings.
f. Burning natural gas produces less than burning other
fossil fuels does.
46 Energy and Energy Resources
Name Date Class
Lesson Outline continued
g. Burning fossil fuels releases substances that can mix with water in the atmosphere
and form , which can damage the environment.
h. Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide, which causes
, a rise in Earth’s average temperature.
3. People can transform nuclear energy from uranium into
thermal energy.
a. Uranium is a(n) energy resource because it is no
longer being formed inside Earth.
b. Nuclear power plants do not release into the air.
c. Nuclear power plants produce wastes that are and
can cause great damage to living things.
D. Renewable Energy Resources
1. A(n) is an energy resource that is replaced as fast as
or faster than it is used.
2. In a(n) power plant, the kinetic energy from falling
water is converted into electrical energy.
3. is radiant energy from the Sun.
4. A(n) , such as solar energy, is one that can’t be used up.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
5. Solar cells convert solar energy into energy.
6. Wind is a(n) energy resource that can be used to
generate electricity.
7. Thermal energy produced inside Earth is called .
8. Materials from plants and animals that people burn are
called .
9. In the United States, the most common biofuel used in cars
is .
E. Conserving Energy Resources
1. About 86 percent of the energy used in the United States comes
from , a nonrenewable energy resource.
2. energy is one way to make our natural resources last
longer.
Energy and Energy Resources 47
Você também pode gostar
- What is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionNo EverandWhat is Charge? – The Redefinition of Atom - Energy to Matter ConversionAinda não há avaliações
- Nature of SurroundingsDocumento7 páginasNature of SurroundingsJe VisualsAinda não há avaliações
- 6 - 13 FORMS of EnergyDocumento30 páginas6 - 13 FORMS of EnergyDennis Limosnero MayorAinda não há avaliações
- Verdiflor, Jessa MaeDocumento1 páginaVerdiflor, Jessa MaeChristine Joy LitanaAinda não há avaliações
- Items Form of Energy: Long Test 2 - Science 6Documento2 páginasItems Form of Energy: Long Test 2 - Science 6kate corveraAinda não há avaliações
- Forms of EnergyDocumento14 páginasForms of EnergyMckenrie AnasAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Exemplar in Science 8 Week 3Documento6 páginasLesson Exemplar in Science 8 Week 3Joyce PerezAinda não há avaliações
- Types of EnergyDocumento3 páginasTypes of EnergyPABLO REYNERIO CRUZ ROCHA100% (1)
- Ì (SK$M) Bdieej + - Ä-U-Ä-U Ì (SK$M) Bdieej + - Ä-U-Ä-U: Physical Science Physical ScienceDocumento14 páginasÌ (SK$M) Bdieej + - Ä-U-Ä-U Ì (SK$M) Bdieej + - Ä-U-Ä-U: Physical Science Physical SciencePhạm SửuAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 2Documento2 páginasLesson 2Roderick DacaoAinda não há avaliações
- Energy and ChemistryDocumento27 páginasEnergy and Chemistry中村カズハAinda não há avaliações
- Envi Sci - Module 2, Unit 3Documento5 páginasEnvi Sci - Module 2, Unit 3Roshin TejeroAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Transfer WorksheetsDocumento2 páginasEnergy Transfer WorksheetsChris HarrisAinda não há avaliações
- (Owls) Answers Reading Essentials c.3 Energy, Work, and SimpleDocumento3 páginas(Owls) Answers Reading Essentials c.3 Energy, Work, and SimpleLucas JamesAinda não há avaliações
- Energy GZ 2019Documento56 páginasEnergy GZ 2019geetub1Ainda não há avaliações
- Sol Eva U3Documento4 páginasSol Eva U3Felipe RojasAinda não há avaliações
- KS3 LeaP Q4 M2 WEEK 5 SCI G 9 WORKPOWERENERGY MARY JEAN BARRERADocumento6 páginasKS3 LeaP Q4 M2 WEEK 5 SCI G 9 WORKPOWERENERGY MARY JEAN BARRERAtolisAinda não há avaliações
- Various Forms of EnergyDocumento2 páginasVarious Forms of EnergyRhianna TetlowAinda não há avaliações
- Energy TransformationDocumento4 páginasEnergy TransformationJerome OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Physical Dimensions and PropagationDocumento9 páginasPhysical Dimensions and Propagationgodsblessings8000Ainda não há avaliações
- Types of EnergyDocumento1 páginaTypes of EnergyAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADER100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Power and Energy SourcesDocumento6 páginasChapter 1 - Power and Energy SourcesRyan A. RamosAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER I - Concept of Work Energy and PowerDocumento2 páginasCHAPTER I - Concept of Work Energy and PowerEllaisa Molina Grabanzor0% (1)
- Energies 7th GradeDocumento8 páginasEnergies 7th GradeMaria AlejandraAinda não há avaliações
- Physics - Notes: EnergyDocumento2 páginasPhysics - Notes: EnergyShannenAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Energy: Energy at A Glance, 2015Documento4 páginasIntroduction To Energy: Energy at A Glance, 2015Balanuța IanaAinda não há avaliações
- Science9 Quarter 4 Module 5Documento16 páginasScience9 Quarter 4 Module 5Joan D. Roque80% (5)
- Work and Energy: Part A. Vocabulary ReviewDocumento2 páginasWork and Energy: Part A. Vocabulary ReviewForeignnX PhayyAinda não há avaliações
- MODULE 1 EnergyDocumento19 páginasMODULE 1 EnergyMark Cidric RoqueroAinda não há avaliações
- Physics 7 Second TermDocumento34 páginasPhysics 7 Second TermMohamed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3. Kinetic and Potential EnergyDocumento11 páginasLesson 3. Kinetic and Potential Energyellenquest528Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan in Electric Motor and GeneratorDocumento15 páginasLesson Plan in Electric Motor and GeneratorMELIE BAGARES88% (8)
- PHYSICSDocumento6 páginasPHYSICSJARIYAAinda não há avaliações
- Learners Copy Phys Scie Mod 4Documento16 páginasLearners Copy Phys Scie Mod 4Lynlyn ClorAinda não há avaliações
- Science 6 Q3 W3Documento9 páginasScience 6 Q3 W3John Rich Caidic100% (1)
- Introduction To Energy: Energy at A Glance, 2016Documento4 páginasIntroduction To Energy: Energy at A Glance, 2016subashreeAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Education: Individual Output On Unpacked MelcsDocumento2 páginasDepartment of Education: Individual Output On Unpacked MelcsBalagtas VinaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Energy WebnotesDocumento1 páginaChapter 4 Energy WebnotesOlivia DraherAinda não há avaliações
- EnergyDocumento2 páginasEnergyBrent PatarasAinda não há avaliações
- Phy Xi Chap 1 Physical-World WebDocumento2 páginasPhy Xi Chap 1 Physical-World WebVikash SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- DLP G8 Q1 WK 3 D2 (12) JaneDocumento7 páginasDLP G8 Q1 WK 3 D2 (12) JaneCathy MoronioAinda não há avaliações
- 2b.potential EnergyDocumento7 páginas2b.potential Energyfakhar.0917Ainda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento6 páginasDetailed Lesson PlanAllanRey Alegria BejarAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento6 páginasDetailed Lesson PlanMelanie Tagudin TrinidadAinda não há avaliações
- Key Words: Apparatus For Measuring The Amount of Heat Involved in A Chemical ReactionDocumento2 páginasKey Words: Apparatus For Measuring The Amount of Heat Involved in A Chemical ReactionChutimaAinda não há avaliações
- Energy LawDocumento32 páginasEnergy LawMichelle Gutierrez SibayanAinda não há avaliações
- Module 2. Melcs Lesson 2. Unpacking and Combining Melcs Into Learning ObjectivesDocumento2 páginasModule 2. Melcs Lesson 2. Unpacking and Combining Melcs Into Learning ObjectivesAriel Olar CuevasAinda não há avaliações
- Work, Energy & Power..Documento39 páginasWork, Energy & Power..Abdul rafay ImranAinda não há avaliações
- Shs Physical Science 12 Curriculum GuideDocumento10 páginasShs Physical Science 12 Curriculum Guideclay adrian100% (2)
- 17 1+energy An+overviewDocumento3 páginas17 1+energy An+overviewjessielaine80Ainda não há avaliações
- ENERGYDocumento16 páginasENERGYdodoAinda não há avaliações
- Energy EvsDocumento11 páginasEnergy EvsSOMYA AGARWALAinda não há avaliações
- Energy QuizDocumento2 páginasEnergy QuizvioletaAinda não há avaliações
- Required IB Physics DefinitionsDocumento7 páginasRequired IB Physics DefinitionsКатерина ДьомкінаAinda não há avaliações
- Module - Material Science and EngineeringDocumento8 páginasModule - Material Science and EngineeringNikkie NazaAinda não há avaliações
- Energy and EnvironmentDocumento39 páginasEnergy and EnvironmentAkinwunmi OpeyemiAinda não há avaliações
- Different Forms of EnergiesDocumento9 páginasDifferent Forms of EnergiessaraAinda não há avaliações
- Curriculum Implementation MatrixDocumento11 páginasCurriculum Implementation MatrixReymart VillapeñaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Energy ConversionDocumento77 páginasChapter 1 Introduction To Energy ConversionBewnet GetachewAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System - Print - QuizizzDocumento5 páginasRespiratory System - Print - QuizizzosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Writing A Lab ReportDocumento26 páginasWriting A Lab ReportosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Read To LearnDocumento5 páginasRead To LearnosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 - Energy Notes - CompleteDocumento22 páginasChapter 5 - Energy Notes - CompleteosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 Energy Review - Print - QuizizzDocumento5 páginasChapter 5 Energy Review - Print - QuizizzosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Forms of Energy - Print - QuizizzDocumento6 páginasForms of Energy - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Calculating Acceleration - Print - QuizizzDocumento6 páginasCalculating Acceleration - Print - QuizizzosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory System - Print - QuizizzDocumento5 páginasRespiratory System - Print - QuizizzosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3 - Moving Cellular Material: Student Labs and Activities Appropriate ForDocumento20 páginasLesson 3 - Moving Cellular Material: Student Labs and Activities Appropriate ForosamaAinda não há avaliações
- The Heart - Print - QuizizzDocumento5 páginasThe Heart - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Excretory System - Print - QuizizzDocumento4 páginasExcretory System - Print - Quizizzosama0% (1)
- Cell Theory and Types of Microscopes - Print - QuizizzDocumento4 páginasCell Theory and Types of Microscopes - Print - QuizizzosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic Energy Worksheet: The Energy Due To MotionDocumento1 páginaKinetic Energy Worksheet: The Energy Due To MotionosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Transport & Homeostasis - Print - QuizizzDocumento3 páginasCell Transport & Homeostasis - Print - Quizizzosama100% (1)
- Study Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemDocumento3 páginasStudy Guide: Section 2: The Respiratory SystemosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Study Guide: Section 1: The Circulatory SystemDocumento4 páginasStudy Guide: Section 1: The Circulatory SystemosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Concept Mapping Circulatory Respiratory and Excretory Systems EditableDocumento2 páginasConcept Mapping Circulatory Respiratory and Excretory Systems EditableosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Section Quick Check Organization of The Nervous System EditableDocumento2 páginasSection Quick Check Organization of The Nervous System EditableosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Research SampleDocumento11 páginasResearch SampleosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Microscope LabelingDocumento1 páginaMicroscope LabelingosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Monohybrid Cross PhenotypeDocumento2 páginasMonohybrid Cross PhenotypeosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3 Classifying OrganismsDocumento33 páginasLesson 3 Classifying OrganismsosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Your Task For Today Is To Watch The 10 Minutes' Video Posted in Classera Under The NameDocumento1 páginaYour Task For Today Is To Watch The 10 Minutes' Video Posted in Classera Under The NameosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology H.W 11.2Documento1 páginaBiology H.W 11.2osamaAinda não há avaliações
- Domains and Kingdoms: Study GuideDocumento6 páginasDomains and Kingdoms: Study GuideosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Study Guide: Section 1: Animal CharacteristicsDocumento5 páginasStudy Guide: Section 1: Animal CharacteristicsosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Week 5 Research Skills and CitationDocumento7 páginasWeek 5 Research Skills and CitationosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Cut Out The Pictures and Stick Them On in The Right OrderDocumento3 páginasCut Out The Pictures and Stick Them On in The Right OrderosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Essentials For Biology (PDF - Io)Documento5 páginasReading Essentials For Biology (PDF - Io)osamaAinda não há avaliações
- Worksheet 18.2 P A - R E: ART Eaction NergyDocumento2 páginasWorksheet 18.2 P A - R E: ART Eaction NergyosamaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 8 Energy of A Tossed BallDocumento5 páginasLab 8 Energy of A Tossed BallvincinugeAinda não há avaliações
- SP2g and 2hDocumento3 páginasSP2g and 2hjmdpro9Ainda não há avaliações
- Lesson1 WindenergycalcDocumento3 páginasLesson1 WindenergycalcLuis Augusto CarvalhoAinda não há avaliações
- Rube Goldberg Lesson PlansDocumento15 páginasRube Goldberg Lesson PlansanusridharAinda não há avaliações
- Mock TestDocumento4 páginasMock TestRufa NarioAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 002 100%Documento14 páginasQuiz 002 100%jrence100% (1)
- AS Level Physics Revision NotesDocumento39 páginasAS Level Physics Revision NotesjoshuaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Check Answer Key Energy Transfer in CollisionsDocumento6 páginasLesson Check Answer Key Energy Transfer in CollisionsMary Jane Victoria RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- "Understanding Car Crashes-It's Basics Physics" Teacher's Guide For Grades 9-12Documento5 páginas"Understanding Car Crashes-It's Basics Physics" Teacher's Guide For Grades 9-12Nicolas BenedetiAinda não há avaliações
- Bentuk Bentuk EnergiDocumento25 páginasBentuk Bentuk Energisebastian harveyAinda não há avaliações
- Cl-7 Ch-3 EnergyDocumento10 páginasCl-7 Ch-3 EnergyShalu AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Workenergyandpower 140122001755 Phpapp01 PDFDocumento52 páginasWorkenergyandpower 140122001755 Phpapp01 PDFKiron SheiqAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Dynamics (Newton's Laws of Motion)Documento62 páginas3-Dynamics (Newton's Laws of Motion)王玟靖Ainda não há avaliações
- Force Motion and Energy Lesson PlanDocumento5 páginasForce Motion and Energy Lesson Planapi-629351965Ainda não há avaliações
- Physic Source PDFDocumento4 páginasPhysic Source PDFRomel AlojadoAinda não há avaliações
- 5b WorkEnergyPowerDocumento20 páginas5b WorkEnergyPowershallou sashimiAinda não há avaliações
- AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocumento7 páginasAP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple Choicedipankar65Ainda não há avaliações
- Conceptest Clicker Questions: Physics, 4 EditionDocumento47 páginasConceptest Clicker Questions: Physics, 4 EditionstephensreenivasulutAinda não há avaliações
- The Physics of GolfDocumento41 páginasThe Physics of GolfSmartAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Exemplar 1 1Documento11 páginasDetailed Lesson Exemplar 1 1john.erolesAinda não há avaliações
- Subject:: Tow Class Lecture OneDocumento8 páginasSubject:: Tow Class Lecture Oneasad gango saeedAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic and Potential Energy WSDocumento3 páginasKinetic and Potential Energy WSNheilzen Aelee Velasco MercaderAinda não há avaliações
- Half Course Test FiitjeeDocumento19 páginasHalf Course Test FiitjeemuraliAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry 2.3.5Documento9 páginasChemistry 2.3.5Sean Citherlet100% (1)
- CL 10 Physics MCQ Question Bank Chapter 2Documento3 páginasCL 10 Physics MCQ Question Bank Chapter 2JoshuaAinda não há avaliações
- Cracking Bgcse PhysicsDocumento96 páginasCracking Bgcse Physicstmoatshe96Ainda não há avaliações
- Skylab Experiments. Volume 6 MechanicsDocumento40 páginasSkylab Experiments. Volume 6 MechanicsBob Andrepont100% (2)
- Unit 4 ExercisesDocumento4 páginasUnit 4 Exercises张书Ainda não há avaliações
- Week 4 - Skate Park Phet LabDocumento3 páginasWeek 4 - Skate Park Phet LabSavannah RoseAinda não há avaliações
- El Tanque TorricelliDocumento4 páginasEl Tanque TorricelliMelanie RebourAinda não há avaliações