Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Biology Autumn Revision Cells
Enviado por
api-439720777Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Biology Autumn Revision Cells
Enviado por
api-439720777Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Biology Autumn revision
Cells
● Some organisms are unicellular (with no transport systems)
● Others are multicellular (often containing sophisticated transport systems
● Cells are tiny, they can often only be seen with a light microscope
● When they are created the are divided by mitosis
● Stem cells are cells that can transfer into any different function (there are two types:
embryonic and adult – one can transfer into anything, the other can only go into multiple
certain examples
● Bone marrow transplants can help you regenerate
● Examples of specialized cells
o Red blood cells carry vital nutrients around the body
o Nerve cells carry electrical impulses from one organ to another
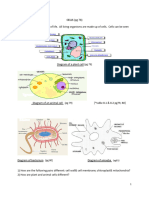
Animal cells have:
- A nucleus to store DNA and control the activity of the cell
-A partially permeable oily layer to control what enters and exits the cell (membrane)
-A cytoplasm which is the site of many chemical reactions
-Some mitochondrion to host aerobic respiration
-Ribosomes for protein photosynthesis
Plant cell have:
- A nucleus to store DNA and control the activity of the cell
-A partially permeable oily layer to control what enters and exits the cell (membrane)
-A cytoplasm which is the site of many chemical reactions
-Some mitochondrion to host aerobic respiration
-Ribosomes for protein photosynthesis
-Cell walls for protection and structure
-A vacuole to contain cell sap and uphold the structure
-Chloroplasts for photosynthesis
Organisation
organelles → cells → tissues → organs → organ systems → organism
● The _____ is a group of specialized ______ working together to fill a specific purpose
Movement of substances into & out of cells
Active transport
Active transport uses respirational energy to move proteins from a low to a high concentration of
said protein.
Osmosis
Osmosis is exclusively the movement of only water through a selectively permeable membrane from
a low to a high (therefore a high to a low water concentration) concentration of particles. Osmosis
is a type of diffusion.
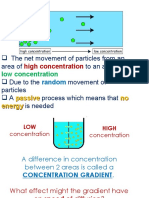
Diffusion
Diffusion is movement from a high to a low concentration of a substance. Diffusion is a passive
process - NO ENERGY INPUT (all particles above absolute 0 have kinetic energy) REQUIRED. Diffusion
is when liquids and gasses spread out (from a high to a low concentration)
Diffusion can be sped up by:
● Surface area to volume ratio
● Amount of kinetic energy (temperature)
● Distance the substance has to diffuse
● Concentration gradient (how large the difference in concentration is)
Solute, Solvent and solution
● Solute – The substance of the solution which the solvent dissolved in
● Solvent - The substance that dissolves in another solution
● Solution - A molecular mixture of 2 or more substances
These are the main differences between arteries and veins.
Artery Vein
Carries blood away from the heart Carries blood towards the heart
Carries oxygenated blood (except pulmonary Carries deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary
artery) vein)
Arteries do not have/need valves Veins require valves
Under relatively high pressure Under relatively low pressure
Thicker walls Thinner walls
Smaller lumen Larger lumen
Multiple cells thick One cell thick for faster diffusion
Cannot fit between cells Can fir between cells
Você também pode gostar
- Bio Notes Chapter 1-8Documento36 páginasBio Notes Chapter 1-8Zhi En LeeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Two ThreeDocumento50 páginasChapter Two Threerue pattinsonAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Membrane Lab 3Documento23 páginasCell Membrane Lab 3Hama JamalAinda não há avaliações
- Cells Structure and Their Functions: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNDocumento60 páginasCells Structure and Their Functions: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNFeah DaydayAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 15Documento69 páginasChapter 15sashitharan2010Ainda não há avaliações
- Combined Powerpoints On Cells 2017Documento66 páginasCombined Powerpoints On Cells 2017api-242405009Ainda não há avaliações
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology Revision NotesDocumento5 páginasEdexcel IGCSE Biology Revision Notesjanna50% (2)
- Notes Cell MembraneDocumento3 páginasNotes Cell MembraneSandeep BhargavaAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Cells PDFDocumento51 páginasBiology Cells PDFTanaka ChirawuAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Animal Systems TestDocumento14 páginasBiology Animal Systems TestAnam FAinda não há avaliações
- Transport in AnimalsDocumento32 páginasTransport in AnimalsAshwika RajanAinda não há avaliações
- TransportDocumento176 páginasTransportbiologi88Ainda não há avaliações
- Cellular TransportDocumento41 páginasCellular TransportFaithlyn Riche YocorAinda não há avaliações
- The Cell and Cellular Transport RevisedDocumento38 páginasThe Cell and Cellular Transport RevisedSavanha Del MundoAinda não há avaliações
- Histology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsDocumento48 páginasHistology: Cytology, The Study of The Structure and Function of CellsZmeu CristinaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell ConstituentsDocumento8 páginasCell ConstituentsSanaa SamkoAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Transport PowerpointDocumento32 páginasCell Transport PowerpointtanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer2 0Documento14 páginasReviewer2 0BJ Bernardo IlAinda não há avaliações
- Cell n2Documento73 páginasCell n2ketyleenbAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 10 Academic Biology NotesDocumento9 páginasGrade 10 Academic Biology NotesJason FokAinda não há avaliações
- Intro To PhysiologyDocumento86 páginasIntro To PhysiologyMelissa LouiseAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Documento4 páginasGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqAinda não há avaliações
- G) CELLSDocumento4 páginasG) CELLSamarashah182Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell Membrane TransportDocumento75 páginasCell Membrane Transportvinay chaudhary100% (1)
- Cell Transport ReviewerDocumento9 páginasCell Transport ReviewerNa LuAinda não há avaliações
- General Science Reviewer For LET 2022Documento117 páginasGeneral Science Reviewer For LET 2022Elaine May Cabunoc GalvezAinda não há avaliações
- Ultimate Biology Revision Notes For O-LevelDocumento63 páginasUltimate Biology Revision Notes For O-Leveltanmay.g1474Ainda não há avaliações
- Biology Notes: Topic 1BDocumento13 páginasBiology Notes: Topic 1Blaiba amirAinda não há avaliações
- Cell 1Documento48 páginasCell 1Pavel GaladiucAinda não há avaliações
- CH 7.3 Cell TransportDocumento19 páginasCH 7.3 Cell TransportRoen Grace Lapuz CalivosoAinda não há avaliações
- Cellular Transport PowerpointDocumento50 páginasCellular Transport PowerpointPortia EgkenAinda não há avaliações
- 2.lecture 2 - Cell Structure and Function of Organelles PDFDocumento73 páginas2.lecture 2 - Cell Structure and Function of Organelles PDFMuhammad Danial HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Movement Into and Out of CellsDocumento12 páginasMovement Into and Out of Cellsf8sdh6xvzyAinda não há avaliações
- Blood Vessels: The Endothelium: Peter Takizawa Department of Cell BiologyDocumento47 páginasBlood Vessels: The Endothelium: Peter Takizawa Department of Cell BiologySwarna RAinda não há avaliações
- LECTURE 2 Cellular and Chemical Organisation GN - ConceptualDocumento74 páginasLECTURE 2 Cellular and Chemical Organisation GN - Conceptualjty4mkp59xAinda não há avaliações
- CELL TRANSPORTPOWEPOINT (Recovered)Documento140 páginasCELL TRANSPORTPOWEPOINT (Recovered)ntakirutimana valensAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Notes For o Level HTMLDocumento91 páginasBiology Notes For o Level HTML123456789Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter-Ii Cells and OsmosisDocumento5 páginasChapter-Ii Cells and OsmosisNIEL RYAN HIZOLEAinda não há avaliações
- Cells Cheat SheetDocumento2 páginasCells Cheat SheetUlka Sutar100% (2)
- Transport MechanismDocumento24 páginasTransport MechanismAnjelica BucasasAinda não há avaliações
- BIOL101 Ch5-2Documento41 páginasBIOL101 Ch5-2marwa haribAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Transport and Plant and Animal Cell Power Point 2013Documento27 páginasCell Transport and Plant and Animal Cell Power Point 2013carloafacturanAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Membrane FunctionsDocumento60 páginasCell Membrane FunctionsKate Clancy NugaoAinda não há avaliações
- The Mammali An Circulator y SystemDocumento21 páginasThe Mammali An Circulator y SystemFern BaldonazaAinda não há avaliações
- Anaphy Cells ReviewerDocumento3 páginasAnaphy Cells ReviewerPlacido Edgar MagaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Cell?Documento6 páginasWhat Is A Cell?Waleed Bin KhalidAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Transport PowerpointDocumento34 páginasCell Transport PowerpointMicaela Joy QuijanoAinda não há avaliações
- A2.2 Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocumento37 páginasA2.2 Eukaryotic Cell Structuretaleenwas2Ainda não há avaliações
- A8) Transport Across The MembraneDocumento105 páginasA8) Transport Across The MembraneTitliMaopussyAinda não há avaliações
- GenBio9 051716Documento35 páginasGenBio9 051716salihuddinalkaizarAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Documento21 páginas02 Cells Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Pablo CostaAinda não há avaliações
- 7.4 Nathan Cellular TransportDocumento7 páginas7.4 Nathan Cellular Transportnancie8Ainda não há avaliações
- Cell TransportDocumento27 páginasCell TransportAnne HidalgoAinda não há avaliações
- C2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismDocumento39 páginasC2-Organisation and Maintenance of The OrganismyourmoAinda não há avaliações
- Cell: Cell Is Called The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocumento6 páginasCell: Cell Is Called The Fundamental Unit of LifeShrinivasan HariprasanthAinda não há avaliações
- High ConcentrationDocumento23 páginasHigh ConcentrationGlprasad NaiduAinda não há avaliações
- Chapt 3Documento7 páginasChapt 3Chelsea MansuetoAinda não há avaliações
- Latin SummerDocumento12 páginasLatin Summerapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- Summer GeographyDocumento4 páginasSummer Geographyapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- BiologyDocumento8 páginasBiologyapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- TP AutumnDocumento5 páginasTP Autumnapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- Physics AutumnDocumento2 páginasPhysics Autumnapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- Latin AutumnDocumento2 páginasLatin Autumnapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- Geography AutumnDocumento6 páginasGeography Autumnapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Autumn TrialDocumento2 páginasChemistry Autumn Trialapi-439720777Ainda não há avaliações
- K - 2 Gambar Histopatologi (Ilmu Penyakit Kulit-Kelamin)Documento14 páginasK - 2 Gambar Histopatologi (Ilmu Penyakit Kulit-Kelamin)Monika AyuningrumAinda não há avaliações
- Hoffman (2014) Physiological Aspects of Sport Training and Performance PDFDocumento520 páginasHoffman (2014) Physiological Aspects of Sport Training and Performance PDFNicolás Bastarrica75% (4)
- Heart Failure and Liver DiseaseDocumento11 páginasHeart Failure and Liver DiseaseFreddy PanjaitanAinda não há avaliações
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Sistem PenghadamanDocumento133 páginasStruktur Dan Fungsi Sistem PenghadamanStephanie Ming FunAinda não há avaliações
- ANAPHY Lec Session #12 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Documento7 páginasANAPHY Lec Session #12 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaAinda não há avaliações
- MLS 014 - Sas 4Documento5 páginasMLS 014 - Sas 4Ylia MastarsAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan Feb 25, 2024Documento3 páginasAdobe Scan Feb 25, 2024mohitsorengts09Ainda não há avaliações
- Jens Waschke (Editor), Tobias M. Böckers (Editor), Friedrich Paulsen (Editor) - Sobotta Anatomy Textbook - With Latin Nomenclature-Educa Books (2018) PDFDocumento843 páginasJens Waschke (Editor), Tobias M. Böckers (Editor), Friedrich Paulsen (Editor) - Sobotta Anatomy Textbook - With Latin Nomenclature-Educa Books (2018) PDFЙоана Георгиева100% (2)
- Nodal AnatomyDocumento7 páginasNodal Anatomymeet ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- Follicular Proliferative Lesion Arising in Struma Ovarii: Min Jee Park Min A Kim Mi Kyung Shin Hye Sook MinDocumento5 páginasFollicular Proliferative Lesion Arising in Struma Ovarii: Min Jee Park Min A Kim Mi Kyung Shin Hye Sook MinRebecca Agustine KristianAinda não há avaliações
- 5 HypersensitivityDocumento13 páginas5 HypersensitivityPurityAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Organelles Worksheet-PrintDocumento2 páginasCell Organelles Worksheet-PrintmuraliMu0% (1)
- The Human Heart: Presentation By: Zuhaib FayyazDocumento22 páginasThe Human Heart: Presentation By: Zuhaib Fayyazfdrz200887Ainda não há avaliações
- Pathophysiology - Exam 1 ReviewDocumento9 páginasPathophysiology - Exam 1 ReviewWaqas Gill100% (2)
- Untitled PresentationDocumento11 páginasUntitled Presentationapi-421863070Ainda não há avaliações
- A. Strelnikova Breathing Exercises - Unique Method of Treating Chronic DiseasesDocumento121 páginasA. Strelnikova Breathing Exercises - Unique Method of Treating Chronic Diseaseslance wong100% (1)
- Imci Case StudyDocumento60 páginasImci Case StudyVida RoseAinda não há avaliações
- Heart & Hemodynamics NotesDocumento8 páginasHeart & Hemodynamics NotesBrandice BradleyAinda não há avaliações
- 2.1. Cell Structure and Function of OrganellesDocumento66 páginas2.1. Cell Structure and Function of OrganellesNama Saya100% (1)
- DR - Savant ShirsoliDocumento1 páginaDR - Savant Shirsolijitendra karvandeAinda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary of Our Senses PDFDocumento3 páginasVocabulary of Our Senses PDFDavid EcheverriaAinda não há avaliações
- BTEC Sport Level 3 Revision Guide Muscular SystemDocumento19 páginasBTEC Sport Level 3 Revision Guide Muscular Systemkanuku100% (1)
- General Botany Laboratory Exercises 1-3 (First Set)Documento19 páginasGeneral Botany Laboratory Exercises 1-3 (First Set)Kristel Padilla100% (3)
- Laboratory Tests v5 May 15 - 30052017 - 0Documento10 páginasLaboratory Tests v5 May 15 - 30052017 - 0Raghu RaghuAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan LiverDocumento9 páginasLesson Plan LiverSAYMABANUAinda não há avaliações
- GOTICO - 1E - Exercise 3 - Integumentary SystemDocumento5 páginasGOTICO - 1E - Exercise 3 - Integumentary SystemLuke Aaron GoticoAinda não há avaliações
- Drug Delivery - Exam 2 NotesDocumento30 páginasDrug Delivery - Exam 2 NotesfelixAinda não há avaliações
- Rebound Your Way To Lymphatic HealthDocumento7 páginasRebound Your Way To Lymphatic HealthMaxLev10100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan Science and Health Xi Muscular SystemDocumento7 páginasA Detailed Lesson Plan Science and Health Xi Muscular SystemSaminahAinda não há avaliações
- Menstrual CycleDocumento8 páginasMenstrual CycleAlloiBialba100% (1)