Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Intramuscular and Intravenous Opioid Pain Relieving Drugs in Labour
Enviado por
Farhana Kanakan0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
9 visualizações2 páginasThere
Título original
DR PICO(1)
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThere
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
9 visualizações2 páginasIntramuscular and Intravenous Opioid Pain Relieving Drugs in Labour
Enviado por
Farhana KanakanThere
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
Notre Dame University
College of Health Sciences
Cotabato City
1st Semester
SY 2018-2019
DELIVERY ROOM
Cotabato Regional and Medical Center (CRMC)
Intramuscular and Intravenous Opioid Pain Relieving Drugs in Labour
Submitted by:
Kanakan, Farhana K.
Group A2
Submitted to:
Prof. Jeory B. Gutigulao, RN
Date of Submission:
August 8, 2018
Intramuscular and Intravenous Opioid Pain Relieving Drugs in Labour
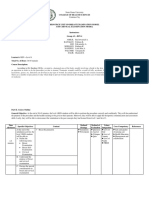
Objective Problem Intervention Comparison Outcome References
A. To assess the We set out to We included randomised We included 70 studies that compared an Though most evidence is Smith LA, Burns E,
effectiveness, determine the controlled trials examining opioid with placebo or no treatment, of low- or very-low Cuthbert A (2018,
safety and effectiveness, side the use of intramuscular or another opioid administered quality, for healthy June 5). Parenteral
acceptability to effects and intravenous opioids intramuscularly or intravenously or women with an opioids for
women of acceptability to (including compared with TENS applied to the uncomplicated pregnancy maternal pain
different types, women of different patient-controlled analgesia) back. Sixty-one studies involving more who are giving birth at management in
doses and modes opioids (pain killers), for women in labour. than 8000 women contributed data to the 37 to 42 weeks, labour. Cochrane
the doses used and review and these studies reported on 34 parenteral opioids appear
of administration Database of
how they are given Cluster-randomised trials different comparisons; for many to provide some relief
of parenteral Systemic Reviews
during labour. We were also eligible for comparisons and outcomes only one from pain in labour but
opioid analgesia were also concerned inclusion, although none study contributed data. All of the studies are associated with 2018, Issue 6. Art.
in labour. about the effects of the were identified. We did not were conducted in hospital settings, on drowsiness, nausea, and No.: CD007396.
B. To assess the opioids on the baby in include quasi-randomised healthy women with uncomplicated vomiting in the woman. DOI:
effects of opioids terms of its safety, trials. We looked pregnancies at 37 to 42 weeks' gestation. Effects on the newborn 10.1002/14651858.
in labour on the alertness at birth and at studies comparing an We excluded studies focusing on women are unclear. Maternal CD007396.pub3
baby in terms of early feeding. opioid with another opioid, with preeclampsia satisfaction with opioid
safety, condition placebo, no treatment, other or pre-existing conditions or with a analgesia was largely
at birth and early Uterine contractions nonpharmacological compromised fetus unreported.
feeding. cause pain during interventions (transcutaneous
labour, particularly as electrical nerve stimulation
they reach their peak. (TENS)) or inhaled
analgesia.
Você também pode gostar
- Assessment of Pain Management in Anaesthesia Practice among Nurse AnaesthetistsNo EverandAssessment of Pain Management in Anaesthesia Practice among Nurse AnaesthetistsAinda não há avaliações
- Hypno 1Documento7 páginasHypno 1Eka AfriliaAinda não há avaliações
- How Does Stress, Depression and Anxiety Affect Patients Undergoing Treatment?Documento5 páginasHow Does Stress, Depression and Anxiety Affect Patients Undergoing Treatment?Mayrá LobatoAinda não há avaliações
- Interventions For The Prevention of Pain Associated With The Placement of Intrauterine Contraceptives: An Updated ReviewDocumento14 páginasInterventions For The Prevention of Pain Associated With The Placement of Intrauterine Contraceptives: An Updated ReviewLeonardo Daniel MendesAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Birth Ball On Labor Pain Relief A Systematic ReviewDocumento8 páginasEffect of Birth Ball On Labor Pain Relief A Systematic Reviewgina hardiatiAinda não há avaliações
- Poster Session II: The Rate of Cesarean Delivery After Successful External Cephalic VersionDocumento1 páginaPoster Session II: The Rate of Cesarean Delivery After Successful External Cephalic VersionJonathan WibisanaAinda não há avaliações
- Bai 2017Documento4 páginasBai 2017kurnia fitriAinda não há avaliações
- Jama Krebs 2018 Oi 180013Documento11 páginasJama Krebs 2018 Oi 180013Yeison UrregoAinda não há avaliações
- Anesthesia Research ChildbirthDocumento7 páginasAnesthesia Research ChildbirthPutri Ramadiana SariAinda não há avaliações
- Apu Cunt UraDocumento22 páginasApu Cunt UraAlekhine Cubas MarinaAinda não há avaliações
- RIZZO Et Al 2018 Hipnose e Dor CrônicaDocumento9 páginasRIZZO Et Al 2018 Hipnose e Dor CrônicaBOUGLEUX BOMJARDIM DA SILVA CARMOAinda não há avaliações
- Research About HypnobirthingDocumento4 páginasResearch About HypnobirthingMarsaidAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Remifentanyl For Pain LaborDocumento11 páginasJurnal Remifentanyl For Pain LaborAshadi CahyadiAinda não há avaliações
- 2022_lingyu_Acupuncture for the Treatment of Diarrhea-Predominant_ecaDocumento11 páginas2022_lingyu_Acupuncture for the Treatment of Diarrhea-Predominant_ecaesmargarAinda não há avaliações
- Literature Review: Effect of Benson's Relaxation Therapy (BRT) On Post Caesarean Section Pain and StressDocumento6 páginasLiterature Review: Effect of Benson's Relaxation Therapy (BRT) On Post Caesarean Section Pain and StressLaelannie MagpayoAinda não há avaliações
- Jurnal Sistem ReproduksiDocumento5 páginasJurnal Sistem ReproduksiYuri Auliya ArrahimAinda não há avaliações
- Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice: Semiha Ayd In Özkan, Gülay Rath FischDocumento6 páginasComplementary Therapies in Clinical Practice: Semiha Ayd In Özkan, Gülay Rath FischAlek OkeAinda não há avaliações
- Artikel 1 Pandita 2018Documento5 páginasArtikel 1 Pandita 2018Eline DebaereAinda não há avaliações
- Analgesia For Labour: An Evidence-Based Insight For The ObstetricianDocumento9 páginasAnalgesia For Labour: An Evidence-Based Insight For The ObstetricianDiana NeculceaAinda não há avaliações
- 4 +uso+da+bola+sui C ADocumento10 páginas4 +uso+da+bola+sui C AJuliana MariaAinda não há avaliações
- Nop2 8 2345Documento9 páginasNop2 8 2345api-600421611Ainda não há avaliações
- The Clinical Implementation of Pain Neuroscience Education: A Survey StudyDocumento13 páginasThe Clinical Implementation of Pain Neuroscience Education: A Survey Studycookiepower54321Ainda não há avaliações
- Practice Bullet In: Obstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaDocumento17 páginasPractice Bullet In: Obstetric Analgesia and AnesthesiaKatherine ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Pengaruh Hypnotherapy Terhadap Intensitas Nyeri Pada Ibu Bersalin Normal Di Rsud Wangaya Kota DenpasarDocumento5 páginasPengaruh Hypnotherapy Terhadap Intensitas Nyeri Pada Ibu Bersalin Normal Di Rsud Wangaya Kota DenpasarMagenda BismaAinda não há avaliações
- Research Article: Kasturba Gandhi Nursing CollegeDocumento5 páginasResearch Article: Kasturba Gandhi Nursing CollegesanthiyasandyAinda não há avaliações
- Original Article September-December, 2016/vol 36/issue 3: Singh RK, Simalti AK, Singh DDocumento5 páginasOriginal Article September-December, 2016/vol 36/issue 3: Singh RK, Simalti AK, Singh DAnjaliAinda não há avaliações
- Caitlin M P Jones Opioid Analgesia For Acute Low BackDocumento9 páginasCaitlin M P Jones Opioid Analgesia For Acute Low BacktsyrahmaniAinda não há avaliações
- The Effect of GB21 Acupressure On PainDocumento5 páginasThe Effect of GB21 Acupressure On PainSiti AisahAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Review: Single-Dose Intrathecal Analgesia To Control Labour PainDocumento6 páginasClinical Review: Single-Dose Intrathecal Analgesia To Control Labour PainCindy Apriliana NingsihAinda não há avaliações
- Medicina 55 00424Documento9 páginasMedicina 55 00424rahma suci ladyaAinda não há avaliações
- Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice: Faranak Safdari Dehcheshmeh, Hossein Ra FieiDocumento4 páginasComplementary Therapies in Clinical Practice: Faranak Safdari Dehcheshmeh, Hossein Ra Fieielsa ismirandaAinda não há avaliações
- A Comparison of Intramuscular Diamorphine and Intramuscular Pethidine For Labour Analgesia: A Two-Centre Randomised Blinded Controlled TrialDocumento10 páginasA Comparison of Intramuscular Diamorphine and Intramuscular Pethidine For Labour Analgesia: A Two-Centre Randomised Blinded Controlled TrialWinda ResmythaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S266657782100040X MainDocumento8 páginas1 s2.0 S266657782100040X MainmudrikabakriAinda não há avaliações
- Prevention and Management of Procedural Pain in The Neonate An U 2016Documento13 páginasPrevention and Management of Procedural Pain in The Neonate An U 2016Indra WijayaAinda não há avaliações
- 1 PDFDocumento8 páginas1 PDFIvan Leonardo Cepeda LealAinda não há avaliações
- Potentized Estrogen in Homeopathic Treatment of Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainDocumento8 páginasPotentized Estrogen in Homeopathic Treatment of Endometriosis-Associated Pelvic PainDiego RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- TecnicasDocumento11 páginasTecnicasMonse SantillánAinda não há avaliações
- Anderson 2019Documento27 páginasAnderson 2019Muhammad SawalAinda não há avaliações
- OSTEOPATIA Hensel2015Documento9 páginasOSTEOPATIA Hensel2015ManuelGarciaMouriñoAinda não há avaliações
- Lilly.C.D (Sr. Teena Davis) : Vice Principal, St. James College of Nursing, Chalakudy PO Near Rever Bank. KeralaDocumento11 páginasLilly.C.D (Sr. Teena Davis) : Vice Principal, St. James College of Nursing, Chalakudy PO Near Rever Bank. KeralaVruxika SolankiAinda não há avaliações
- Non-Steroidal Anti-In Ammatory Drugs For Spinal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocumento11 páginasNon-Steroidal Anti-In Ammatory Drugs For Spinal Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysistanyasisAinda não há avaliações
- Effect of Acupressure Therapy Point HT 6 and LI 4 On Post Cesarean Sectio's PainDocumento4 páginasEffect of Acupressure Therapy Point HT 6 and LI 4 On Post Cesarean Sectio's PainbelaAinda não há avaliações
- 2554 10028 1 PB PDFDocumento4 páginas2554 10028 1 PB PDFbelaAinda não há avaliações
- International Journal of Obstetric AnesthesiaDocumento6 páginasInternational Journal of Obstetric Anesthesiaanita pratiwiAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal Pain Assessment EvidenceDocumento4 páginasNeonatal Pain Assessment EvidenceDewi MaharaniAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical GuidelinesDocumento34 páginasClinical GuidelinesAlberto PachecoAinda não há avaliações
- Mind-Body Practice As A Primer To Maintain Psychological Health Among Pregnant Women - YOGESTA-a Randomized Controlled TrialDocumento11 páginasMind-Body Practice As A Primer To Maintain Psychological Health Among Pregnant Women - YOGESTA-a Randomized Controlled TrialAlief NovitasariAinda não há avaliações
- IndomethacinDocumento5 páginasIndomethacinDian NovitasariAinda não há avaliações
- Owais 2018Documento57 páginasOwais 2018Guillermo MoranteAinda não há avaliações
- Aromatherapy and Music Therapy To Improve Pain and AnxietyDocumento6 páginasAromatherapy and Music Therapy To Improve Pain and AnxietyFiorel Loves EveryoneAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0378378214000140 MainDocumento5 páginas1 s2.0 S0378378214000140 MainPablo GonzálezAinda não há avaliações
- Literacy-Adapted Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Versus Education For Chronic Pain at Low-Income ClinicsDocumento15 páginasLiteracy-Adapted Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Versus Education For Chronic Pain at Low-Income ClinicsJay JalaliAinda não há avaliações
- The Effectiveness of Complementary ManualDocumento10 páginasThe Effectiveness of Complementary ManualAli DptAinda não há avaliações
- NSAIDs For Postpartum Perineal PainDocumento2 páginasNSAIDs For Postpartum Perineal PainYohanna Lawanda da CostaAinda não há avaliações
- 0006 0323 1 PBDocumento6 páginas0006 0323 1 PBSiti Yuli setyaningsihAinda não há avaliações
- Patient-Controlled Epidural Analgesia For Labor.: International Anesthesiology Clinics February 2007Documento9 páginasPatient-Controlled Epidural Analgesia For Labor.: International Anesthesiology Clinics February 2007k3 rschAinda não há avaliações
- Sonnykalangi,+9 +ok+ (5) +Ravenska+Salawati+318-323+doiDocumento6 páginasSonnykalangi,+9 +ok+ (5) +Ravenska+Salawati+318-323+doiFifi AlyaniAinda não há avaliações
- How Does Pain Lead To Disabilitylee2015Documento10 páginasHow Does Pain Lead To Disabilitylee2015VictorAinda não há avaliações
- The Effectiveness of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions Upon Pregnancy-Related Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocumento11 páginasThe Effectiveness of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions Upon Pregnancy-Related Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisYenie YenAinda não há avaliações
- NICU Pain Management: Anesthesia, Analgesia, and AssessmentDocumento19 páginasNICU Pain Management: Anesthesia, Analgesia, and AssessmentPaulHerreraAinda não há avaliações
- InvitationDocumento1 páginaInvitationFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Notre Dame University SSG Program Evaluation Highlights Academic and Community OutreachDocumento2 páginasNotre Dame University SSG Program Evaluation Highlights Academic and Community OutreachFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Text 3Documento2 páginasText 3Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- 1Documento4 páginas1Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Text 2Documento1 páginaText 2Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- College of Health SciencesDocumento12 páginasCollege of Health SciencesFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Text 4Documento1 páginaText 4Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Text 2Documento2 páginasText 2Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- History of SterilizationDocumento14 páginasHistory of Sterilizationrahulbafnae100% (7)
- ConsultationDocumento3 páginasConsultationFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Mental Health Programs in Selected Barangays of Cotabato CityDocumento17 páginasMental Health Programs in Selected Barangays of Cotabato CityFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- 1)Documento2 páginas1)Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- DrugDocumento2 páginasDrugFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Elective 2 - Function of An ICU NurseDocumento3 páginasElective 2 - Function of An ICU NurseFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Front PageDocumento3 páginas1 Front PageFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- 1Documento4 páginas1Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- A Seminar On Understanding Data Privacy Act (2012) and Nursing RolesDocumento3 páginasA Seminar On Understanding Data Privacy Act (2012) and Nursing RolesFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Elective Dos: For Enumeration PortionDocumento3 páginasElective Dos: For Enumeration PortionFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- A Seminar On Understanding Data Privacy Act (2012) and Nursing RolesDocumento3 páginasA Seminar On Understanding Data Privacy Act (2012) and Nursing RolesFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- A Seminar On Understanding Data Privacy Act (2012) and Nursing RolesDocumento3 páginasA Seminar On Understanding Data Privacy Act (2012) and Nursing RolesFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- TextDocumento3 páginasTextFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd SpeakerDocumento28 páginas3rd SpeakerFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- NCM 207 Review NotesDocumento19 páginasNCM 207 Review NotesFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- Reso 13Documento4 páginasReso 13Farhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- TextDocumento3 páginasTextFarhana KanakanAinda não há avaliações
- A Quantitative Correlational Study Between Transformational LeadeDocumento177 páginasA Quantitative Correlational Study Between Transformational LeadePrincess Camille RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Equity Theory: The Recent Literature, Methodological Considerations, and New DirectionsDocumento10 páginasEquity Theory: The Recent Literature, Methodological Considerations, and New DirectionsZelia FreriaAinda não há avaliações
- Mastery Test 3rd - 4th QuarterDocumento10 páginasMastery Test 3rd - 4th QuarterlettyAinda não há avaliações
- Bank Products Sales Skill Participant's Manual PDFDocumento64 páginasBank Products Sales Skill Participant's Manual PDFdiriba abebeAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of The Organization: 1.2 Vision and Values VisionDocumento32 páginasOverview of The Organization: 1.2 Vision and Values Visionمحمد عمر صدیقیAinda não há avaliações
- GSPL - Company Profile @bangalore Office-1Documento7 páginasGSPL - Company Profile @bangalore Office-1Eagle BangaloreAinda não há avaliações
- African Feminist Studies Desiree LewisDocumento138 páginasAfrican Feminist Studies Desiree LewisAYY100% (2)
- Ebscoeijer+vol +8+n01+paper+9Documento10 páginasEbscoeijer+vol +8+n01+paper+9Kabiru Mohammad UmarAinda não há avaliações
- Contemporary World Final Quiz 2Documento5 páginasContemporary World Final Quiz 2James Marasigan Ambas100% (1)
- Medicine Brochure RussiaDocumento13 páginasMedicine Brochure Russiapratima unidirectionAinda não há avaliações
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100Documento3 páginasTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100Huba ZehraAinda não há avaliações
- Big Data Analytics Report Jan2013Documento36 páginasBig Data Analytics Report Jan2013Varun BharadwajAinda não há avaliações
- Procedure For The Subject'S ReexaminationDocumento2 páginasProcedure For The Subject'S ReexaminationMa Estrellene OrcalesAinda não há avaliações
- Esci ResultsDocumento23 páginasEsci Resultsapi-304738945Ainda não há avaliações
- Designing A Strategic Information Systems Planning Methodology For Malaysian Institutes of Higher Learning (Isp-Ipta)Documento8 páginasDesigning A Strategic Information Systems Planning Methodology For Malaysian Institutes of Higher Learning (Isp-Ipta)Janet G.Ainda não há avaliações
- LastDocumento35 páginasLastKervin SysingAinda não há avaliações
- The Efficacy of Theoretical and Practical Teaching Approach: A Research Proposal Presented To: Prof. Edwin NebriaDocumento20 páginasThe Efficacy of Theoretical and Practical Teaching Approach: A Research Proposal Presented To: Prof. Edwin NebriaVanesa LataranAinda não há avaliações
- Hydraulics Geotech2Documento19 páginasHydraulics Geotech2Sigue Ramel HinayasAinda não há avaliações
- Federico CosenzDocumento14 páginasFederico Cosenzsergio londoñoAinda não há avaliações
- Resume of Hagokkkk GroupDocumento6 páginasResume of Hagokkkk Groupjune dela cernaAinda não há avaliações
- History of CMU A Brief Historical BackgroundDocumento1 páginaHistory of CMU A Brief Historical BackgroundMariane Rae AndrionAinda não há avaliações
- DWIGHTDocumento115 páginasDWIGHTIan Carlos FajardoAinda não há avaliações
- ACD Guidelines For Product Information File (PIF)Documento7 páginasACD Guidelines For Product Information File (PIF)NukiAdelaAinda não há avaliações
- Theoryand Paradigmin Social ResearchDocumento18 páginasTheoryand Paradigmin Social ResearchZeline ZephyreAinda não há avaliações
- Template JOLLT 2020Documento3 páginasTemplate JOLLT 2020Wahyu HadiAinda não há avaliações
- KEY IDEAS OF ABSTRACTS, PRÉCIS AND SUMMARIESDocumento2 páginasKEY IDEAS OF ABSTRACTS, PRÉCIS AND SUMMARIESGabrielle GeolingoAinda não há avaliações
- Investors Preference in Commodities MarketDocumento7 páginasInvestors Preference in Commodities MarketMuthu9751Ainda não há avaliações
- Sociology: Tension Between Science and Militant Activism?: Sandro SerpaDocumento8 páginasSociology: Tension Between Science and Militant Activism?: Sandro SerpaHamza ButtAinda não há avaliações
- ELTU2020 English For Social Science Students I: Tentative Course Schedule (2021-2022 Term 1) - Mondays and WednesdaysDocumento2 páginasELTU2020 English For Social Science Students I: Tentative Course Schedule (2021-2022 Term 1) - Mondays and Wednesdaysdebate spsltAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Writing: I. The Big PictureDocumento6 páginasAcademic Writing: I. The Big PictureEmman CastroAinda não há avaliações