Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
IJSO Part-8
Enviado por
SadguruDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
IJSO Part-8
Enviado por
SadguruDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MOMENTUM So the magnitude of the resultant force acting on a
body is equal to the product of mass of the body and
Definition : the acceleration produced. Direction of the force is
Momentum of a particle may be defined as the quantity same as that of the acceleration.
of motion possessed by it and it is measured by the
product of mass of the particle and its velocity.
UNITS OF FORCE
Momentum is a vector quantity and it is represented
by p (a) In C.G.S. System :
F = ma gm × cm/s2 = Dyne
p mv
Definition of one dyne :
Unit of momentum :
If m = 1 gm, a = 1 cm/s2, then F = 1 dyne.
(In C.G.S. system) p = mv gram × cm/s = dyne × s
When a force is applied on a body of mass 1 gram and
(In M.K.S. system) p = mv kg × m/s = Newton × s
the acceleration produced in the body is 1 cm/s2, then
the force acting on the body will be one dyne.
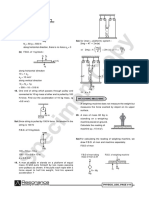
4. A ball of mass 100 gm. is moving with a velocity of
15 m/s. Calculate the momentum associated with the (b) In S.I. System :
ball.
F = ma kg × m/s2 = Newton
Sol .
Definition of one Newton :
100
Mass of the ball = 100 gm. = kg. If m = 1 kg and a = 1 m/s2 then by, F = ma
1000
F = 1 × 1 = 1 kg × m/s2 = 1 N.
= 0.1 kg.
Velocity of the ball = 15 m/s If a force is applied on a body of mass 1 kg and
So, momentum = mass of the ball × velocity of acceleration produced in the body is 1 m/s2, then the
the ball force acting on the body will be one Newton.
= 0.1 kg. × 15 m/s
(c) Kilogram Force (kgf) :
= 1.5 kg. m/s
Kilogram force (kgf) or Kilogram weight (kg. wt.) is force
NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION with which a mass of 1 kg is attracted by the
earth towards its centre.
1kgwt = 1kgf = 9.8 N
The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly
proportional to the applied unbalanced forces i.e. Rate (d) Gram Force (gf) :
of change of momentum Force applied Gram force or gram weight is the force with which a
mass of 1 gram is attracted by the earth towards
Let a body is moving with initial velocity u and after applying its centre.
a force F on it, its velocity becomes v in time t. 1gwt = 1gf = 981 dyne
Initial momentum of the body p1 = mu
Final momentum of the body p2 = mv Abou both the units are called gravitational unit of force.
Change in momentum in time t is mv – mu Relation between Newton and dyne.
We know :
mv – mu
So rate of change of momentum = 1 N = 1kg × 1ms-2
t or 1 N = 1000 g × 100 cms-2
or 1 N = 105 g cms-2 = 105 dyne
mv – mu 1 N = 105 dyne
But according to Newton’s second law, F
t
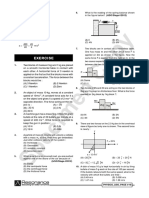
5. A force of 20N acting on a mass m1 produces an
m( v – u) v–u
or F Here, = a (acceleration) acceleration of 4 ms–2. The same force is applied on
t t mass m2 then the acceleration produced is 0.5 ms–2.
So Fma What acceleration would the same force produce, when
both masses are tied together ?
or F = kma (Here k is proportionality constant.
Sol. For mass m1: F = 20N, a = 4 ms–2
If 1N force is applied on a body of mass 1 kg and the
F 20
acceleration produced in the body is 1 m/s 2, then then m1 = = = 5 kg
1 = k × 1 × 1 or k = 1 a 4
For mass m2 : F = 20N, a = 0.5 ms–2
Hence, F = ma
PHYSICS_IJSO_PAGE #77
Você também pode gostar
- IJSO Part-2Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-2SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- 2858 Topper 21 110 2 4 322 2541 Newton S Laws of Motion Up201508051951 1438784483 8881Documento4 páginas2858 Topper 21 110 2 4 322 2541 Newton S Laws of Motion Up201508051951 1438784483 8881Ilaiya Maha LakshmiAinda não há avaliações
- 2.4 MOMENTUM-IMPULSe PDFDocumento71 páginas2.4 MOMENTUM-IMPULSe PDFsanad boshehAinda não há avaliações
- Impulse and MomentumDocumento8 páginasImpulse and MomentumAlethea LangAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresNo EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Classical MechanicsDocumento5 páginasClassical MechanicsFarjana KabirAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureNo EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureAinda não há avaliações
- DynamicsDocumento8 páginasDynamicsLaud FumhandaAinda não há avaliações
- Momentum, Impulse and Energy: Pre-Reading: KJF 9.1 and 9.2Documento27 páginasMomentum, Impulse and Energy: Pre-Reading: KJF 9.1 and 9.2lady jazzmineAinda não há avaliações
- 1 Force Stress IDocumento13 páginas1 Force Stress Iaravind grandhiAinda não há avaliações
- Mass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Documento11 páginasMass and Inertia: Dynamics 1Joe West100% (2)
- ForceDocumento26 páginasForceShinji100% (1)
- PHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawDocumento52 páginasPHYSICS Newtons-1st-LawLago, Azel Chin L.Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter3 Forces and MotionDocumento77 páginasChapter3 Forces and Motionyue yueAinda não há avaliações
- Impulse MomentumDocumento19 páginasImpulse MomentumAhmed Raza100% (1)
- Momentum and CollisionsDocumento27 páginasMomentum and CollisionseltytanAinda não há avaliações
- Science Force Summary NoteDocumento4 páginasScience Force Summary NotedenyAinda não há avaliações
- 2.3 Momentum Impulse HonDocumento33 páginas2.3 Momentum Impulse HonHuanjun FengAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture # 1: "Engineering Mechanics"Documento18 páginasLecture # 1: "Engineering Mechanics"Razaq Khan MandokhailAinda não há avaliações
- 3.4 Newton's 2nd and 3rd LawDocumento18 páginas3.4 Newton's 2nd and 3rd LawIDKAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Laws and Gravitation ExplainedDocumento5 páginasNewton's Laws and Gravitation ExplainedMohammad Fuad HasanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1.1Documento6 páginasUnit 1.1LGG MATRICULATIONAinda não há avaliações
- LAWS OF MOTION - NOTES Grade 11Documento47 páginasLAWS OF MOTION - NOTES Grade 11Zian100% (1)
- Momentum Student NotesDocumento17 páginasMomentum Student NotesabdulfcAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics 1Documento113 páginasThermodynamics 1Lloyd MontemayorAinda não há avaliações
- Module 3 Impulse Momentum BelloDocumento13 páginasModule 3 Impulse Momentum BelloDanny Riel BarachinaAinda não há avaliações
- Force Equals Mass Times AccelerationDocumento1 páginaForce Equals Mass Times AccelerationDen EsicAinda não há avaliações
- Laws of Motion 3EDocumento13 páginasLaws of Motion 3EAditya VijayAinda não há avaliações
- ProblemSet 2 SolutionsDocumento6 páginasProblemSet 2 SolutionsnormanAinda não há avaliações
- What Is ForceDocumento2 páginasWhat Is ForceGreatestEver EvergreatestAinda não há avaliações
- Dunman High School Physics: Forces and MomentumDocumento29 páginasDunman High School Physics: Forces and MomentumWee Chee LimAinda não há avaliações
- 6.NLM TheoryDocumento24 páginas6.NLM Theoryujjwal pathakAinda não há avaliações
- Newton's Laws of MotionsDocumento40 páginasNewton's Laws of MotionsJay MatoorahAinda não há avaliações
- Physics CHP 3 (C)Documento15 páginasPhysics CHP 3 (C)Omkar PawarAinda não há avaliações
- IGCSE Physics - MomentumDocumento3 páginasIGCSE Physics - MomentumSamira YasserAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamics PDFDocumento35 páginasDynamics PDFLukeman IssahAinda não há avaliações
- DAY FOUR LAWS OF MOTION REVISIONDocumento14 páginasDAY FOUR LAWS OF MOTION REVISIONRaj KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Laws of Motion-01Documento34 páginasLaws of Motion-01wixirepAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Lesson Plan 08 - Impulse and Momentum PDFDocumento6 páginasPhysics Lesson Plan 08 - Impulse and Momentum PDFKim MacarasigAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Note About ForceDocumento6 páginasLesson Note About Forcemark joseph cometaAinda não há avaliações
- THERMO 1 (Intro Elements Units Common Properties)Documento3 páginasTHERMO 1 (Intro Elements Units Common Properties)Beaw GtAinda não há avaliações
- Forces and MotionDocumento23 páginasForces and MotionIza Natasha AzaharAinda não há avaliações
- Further Mechanics 1:: Momentum and ImpulseDocumento18 páginasFurther Mechanics 1:: Momentum and ImpulsednaielAinda não há avaliações
- PHY083 Ch3 DynamicsDocumento44 páginasPHY083 Ch3 Dynamicshaziqkhairul59Ainda não há avaliações
- Thermo 5th Chap01P001 PDFDocumento33 páginasThermo 5th Chap01P001 PDFHasan ÖzdemAinda não há avaliações
- Statics Notes: Chap1 Page 1 of 7Documento7 páginasStatics Notes: Chap1 Page 1 of 7Hussain Mohammad ImranAinda não há avaliações
- UPCh 10Documento49 páginasUPCh 10Abdullah KarimAinda não há avaliações
- Week 8 Activity: Collisions: Name: - Grade 12 STEM Sec.Documento4 páginasWeek 8 Activity: Collisions: Name: - Grade 12 STEM Sec.J-heart Basabas MalpalAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - 3 Laws of MotionDocumento27 páginasUnit - 3 Laws of Motiondevli falduAinda não há avaliações
- Review Topic 1Documento14 páginasReview Topic 1AlteaAlAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 8 Learning Module (Week 1)Documento45 páginasGrade 8 Learning Module (Week 1)Mai Jane Gonzales BaezAinda não há avaliações
- 6engineering Mechanics 1st Yr LMDocumento11 páginas6engineering Mechanics 1st Yr LMAkash Kumar Bhoi4004Ainda não há avaliações
- Laws of MotionDocumento27 páginasLaws of MotionT.MuruganAinda não há avaliações
- Physics AestheticDocumento7 páginasPhysics Aestheticsafrin irfaanaAinda não há avaliações
- Dynamic 1Documento13 páginasDynamic 1SharonAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Thermo IDocumento124 páginasManual Thermo IJay-ar MohammadsaidAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Level2 Solution Class 4 Set 1Documento3 páginasImo Level2 Solution Class 4 Set 1SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-12Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-12SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-7Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-7SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-3Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-3SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-6Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-6SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-10Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-10SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-9Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-9SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-10Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-10SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-11Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-11SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-5Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-5SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-4Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-4SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-B Answer Keys Class-8Documento1 páginaImo Set-B Answer Keys Class-8SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-12Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-12SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-11Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-11SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-6Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-6SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-8Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-8SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-7Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-7SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-9Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-9SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Imo Set-A Answer Keys Class-3Documento1 páginaImo Set-A Answer Keys Class-3SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-21Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-21SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-20Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-20SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-18Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-18SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-14Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-14SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-17Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-17SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-19Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-19SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunDocumento1 páginaPrinciple of Conservation of Linear Momentum: (A) Recoil of GunSadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-16Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-16SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-15Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-15SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- IJSO Part-13Documento1 páginaIJSO Part-13SadguruAinda não há avaliações
- (B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairDocumento1 página(B) The Working of A Rocke T:: N' and MG Are Not Action - Reaction Pair. Since PairSadguruAinda não há avaliações
- Finite Element Analysis Notes and Question BankDocumento375 páginasFinite Element Analysis Notes and Question Bankfgh fghfghfAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 22 - ElectromagnetismDocumento5 páginasTopic 22 - ElectromagnetismMauriceAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-Two Part 1Documento26 páginasChapter-Two Part 1Wiz Nati XvAinda não há avaliações
- Circular Slab Design OptimizationDocumento4 páginasCircular Slab Design OptimizationAbiyotAinda não há avaliações
- MOM I - Module 37Documento6 páginasMOM I - Module 37Muhammad HabibAinda não há avaliações
- Final Project ReportDocumento47 páginasFinal Project ReportShashank Dubey100% (1)
- Fundamentals of AcousticsDocumento180 páginasFundamentals of Acousticscastro100% (7)
- Marketing Information T 588 N T 589 N: European Power-Semiconductor and Electronics CompanyDocumento7 páginasMarketing Information T 588 N T 589 N: European Power-Semiconductor and Electronics CompanysebastianAinda não há avaliações
- Castigliano's Theorem for Beam Deflection AnalysisDocumento6 páginasCastigliano's Theorem for Beam Deflection AnalysisMaxpein Del ValleAinda não há avaliações
- Dynam Ics of Watem Waves: Selected Papers of Michael Longuet-HigginsDocumento663 páginasDynam Ics of Watem Waves: Selected Papers of Michael Longuet-Higginsmfgobbi4515Ainda não há avaliações
- Oscillations, Waves and OpticsDocumento25 páginasOscillations, Waves and OpticsTushar GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- Made By-Samiran Ghosh Class - Xi "A"Documento88 páginasMade By-Samiran Ghosh Class - Xi "A"Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Bolted Connections PDFDocumento56 páginasBolted Connections PDFÃvēđÆñ ŤhåķųřAinda não há avaliações
- Ryu Et Al (2008) Capacity Curves, 14WCEE PDFDocumento8 páginasRyu Et Al (2008) Capacity Curves, 14WCEE PDFsekkeiAinda não há avaliações
- 01 - List of NASTRAN SOL Numbers and DescriptionDocumento1 página01 - List of NASTRAN SOL Numbers and DescriptionffontanaAinda não há avaliações
- (Fundamental) Physics of Elementary Particles FPPv2012 0104Documento598 páginas(Fundamental) Physics of Elementary Particles FPPv2012 0104sollun3Ainda não há avaliações
- TUDelft MBD LectureDocumento8 páginasTUDelft MBD Lecturestarling1001408Ainda não há avaliações
- Calculation ExampleDocumento20 páginasCalculation Examplepavankumar0001Ainda não há avaliações
- Tổng hợp tải trọng Summation phần mềm MIDASDocumento8 páginasTổng hợp tải trọng Summation phần mềm MIDASAnonymous DNb6yWERfBAinda não há avaliações
- Modern Physics PDFDocumento20 páginasModern Physics PDFPrathm MittalAinda não há avaliações
- Aeletters 2023 8 2 2Documento8 páginasAeletters 2023 8 2 2miskoscribdAinda não há avaliações
- L4 - Application of Momentum Integral Theorem and Boundary Layer SeparationDocumento25 páginasL4 - Application of Momentum Integral Theorem and Boundary Layer SeparationKar AbhishekAinda não há avaliações
- Rheology and Soil Mechanics RH Ologie Et M Canique Des Sols Symposium Grenoble April 1-8-1964 Symposium Grenoble 1er 8 Avril 1964Documento518 páginasRheology and Soil Mechanics RH Ologie Et M Canique Des Sols Symposium Grenoble April 1-8-1964 Symposium Grenoble 1er 8 Avril 1964Jasmin AgriAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetoplasmadynamic ThrustersDocumento22 páginasMagnetoplasmadynamic ThrustersAdam BruceAinda não há avaliações
- CE74.12: Hydrodynamics 3 (3-0) Course Objectives:: School of Engineering and Technology, (SET)Documento3 páginasCE74.12: Hydrodynamics 3 (3-0) Course Objectives:: School of Engineering and Technology, (SET)Danna ValdezAinda não há avaliações
- Amplitude - PhaseDocumento6 páginasAmplitude - Phasemuhammad awaisAinda não há avaliações
- Kumar and Kodur 2019 PCI: Kumarpu2@msu - EduDocumento20 páginasKumar and Kodur 2019 PCI: Kumarpu2@msu - Eduhussen miftaAinda não há avaliações
- FilmdropwiseDocumento26 páginasFilmdropwiseahmad pidotAinda não há avaliações
- Som Unit - 1.2.1 Stepped Bar 3 Regions ProblemDocumento2 páginasSom Unit - 1.2.1 Stepped Bar 3 Regions ProblemNagamani ArumugamAinda não há avaliações
- Introducing Gear Ratings and AGMA Conversion Factors For The Steel Spur Gear Design Under Bending FatigueDocumento11 páginasIntroducing Gear Ratings and AGMA Conversion Factors For The Steel Spur Gear Design Under Bending FatiguebakchodbanarasiAinda não há avaliações
- Chakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.No EverandChakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingNo EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (66)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessNo EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (104)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceNo EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (23)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessNo EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (6)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNo EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (69)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindNo EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (1)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingNo EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidNo EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1395)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismNo EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (500)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerNo EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayNo EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (125)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesNo EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2193)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterNo EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (409)
- Wall Pilates: Quick-and-Simple to Lose Weight and Stay Healthy. A 30-Day Journey with + 100 ExercisesNo EverandWall Pilates: Quick-and-Simple to Lose Weight and Stay Healthy. A 30-Day Journey with + 100 ExercisesAinda não há avaliações
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowNo EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (48)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeAinda não há avaliações
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsNo EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (94)
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsNo EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (95)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsNo EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishNo EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (18)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldNo EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (8)