Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Passive Voice Transformation of The Sentence, The Person or Thing That Is The Centre of The Action Is Placed As Subject
Enviado por
bea_xTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Passive Voice Transformation of The Sentence, The Person or Thing That Is The Centre of The Action Is Placed As Subject
Enviado por
bea_xDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Prof Marisa Fidalgo
PASSIVE VOICE NOTES
A. General
- Passive voice= transformation of the sentence, the person or thing that is the centre
of the action is placed as subject.
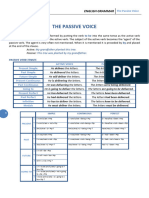
Active Passive
Subject agent ( by)
Object subject
Active Verb passive verb ( to be ( active tense) + past participle ( active verb)
EX: ACTIVE: She gave presents in her office
S V Direct obj place adverbial
PASSIVE: Presents were given in the office by her
S V place adv agent
- Used when:
- The active subject is unknown or not very important, impersonal sentences
Ex: He was killed yesterday ( we don’t know the killer)
It is thought that he was the author / he was thought to be the author
( se pensaba que era el autor)
- The active subject is self-evident from the context
Ex: Peter………. He was sent there by the Government
- For modesty, to avoid mentioning the subject
Ex: As it has been stated before ( as I have stated before…)
- When the object is more important than the subject
Ex: My father was sent to Mexico / Gifts were bought
B. Passive Verb ( auxiliary + past participle)
- Auxiliaries: Be ( the most common) My brother was brought some books
Get ( getting into a state or situation) I got dressed
Get / have ( causative) I got/ had my hair cut
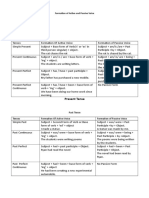
- Tenses
Active Passive
Present Simple give/gives am/is/are given
Present continuous is/are giving is/are being given
Present perfect has/have given has/have been given
Past Simple gave was/were given
Past continuous was/were giving was/were being given
Past perfect had given had been given
Future Simple will give will be given
Going to future am/is/ are going to give am/is/ are going to be given
Simple conditional would give would be given
Infinitive to give to be given
Modal verbs can give can be given
Prof Marisa Fidalgo
C. TYPES OF PASSIVE
1. AGENTIVE passive ( with direct object/ complement)
( the agent is avoided when it’s a pronoun,” people” or an indefinite pronoun)
EX: They sent a present A present was sent yesterday
Her mother kissed her She was kissed by her mother
2. Passive with TWO OBJECTS/ COMPLEMENTS
The indirect object is used as subject if people interest more than things or if it is longer.
EX: They gave her two presents She was given two presents ( preferred)
I. Obj D. Obj Two presents were given to her
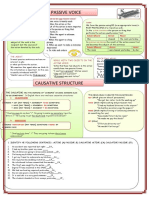
3. CAUSATIVE USE
It is used when you ask, require someone to do something for you. You “get” a benefit.
We use GET or HAVE as the auxiliary + object+ past participle. There’s no agent here.
Ex: Someone fixes my car for me ( I got a benefit ( my car fixed) from other people’s work)
I get/ have my car fixed ( me arreglaron el coche)
Beneficiary auxiliary object past participle
ex: The hairdresser is cutting my sister’s hair my sister is getting/having her hair cut
Someone will repair his watch he will get/have his watch repaired
4. NON- AGENTIVE passive: impersonal sentences without agent, with reporting verbs
Used with verbs like: believe, report, consider, know, think, suppose, say, expect etc.
EX: We are supposed to return next week ( se supone que volveremos la semana que viene)
She was thought to know about it ( se pensaba que ella lo sabía)
You can use a bare infinitive or a perfect one ( to have+ past participle) if you refer to a past
situation
Ex: My mother was expected to have arrived sooner ( se esperaba que mi madre
hubiese llegado antes)
5. Passive with THAT CLAUSE or INFINITIVE as complement / object
a) That clause
- Place “it” as subject + passive verb + that clause
- Place the subject of the ‘that clause’ as the subject + passive verb + infinitive of the verb
in the ‘that clause’ ( bare or perfect infinitive)
EX: They wanted that she made the cake.
Direct comple = that clause
1. It was wanted that she made the cake ( se quería que hiciera el pastel)
They wanted that she made the cake.
2. She was wanted to have made the cake
( se quería que hiciera el pastel)
b) Infinitive
- Place “it” as subject + passive verb+ infinitive
They desired to have success
It was desired to have success (se deseaba tener éxito)
Você também pode gostar
- Passive VoiceDocumento22 páginasPassive VoiceMañanaMatutinaAinda não há avaliações
- Active To Passive Voice ConversionDocumento2 páginasActive To Passive Voice ConversionRoshan UpadhyayAinda não há avaliações
- Passive VoiceDocumento16 páginasPassive VoiceJuan SpainAinda não há avaliações
- The Infinitive Without ToDocumento5 páginasThe Infinitive Without ToHằng HàAinda não há avaliações
- Passive Active VoiceDocumento3 páginasPassive Active VoiceAbdennour BelarbiAinda não há avaliações
- Active Passive VoiceDocumento14 páginasActive Passive VoiceAbhieey Choi Soo HyunAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice TeorieDocumento3 páginasThe Passive Voice TeorieValentin MarinAinda não há avaliações
- Active Dan Passive VoiceDocumento5 páginasActive Dan Passive VoiceDella MitasariAinda não há avaliações
- GRAMMAR 1 UNIT 6 Passive-Voice-And-causative-structureDocumento2 páginasGRAMMAR 1 UNIT 6 Passive-Voice-And-causative-structureDavid Isaac Ruiz Chacon100% (2)
- Active & PassiveDocumento5 páginasActive & PassiveUmama MustafaAinda não há avaliações
- Passive VoiceDocumento6 páginasPassive VoiceJonathan AbnerioAinda não há avaliações
- A Book Was Read by Them The Portrait Is Painted by The PainterDocumento28 páginasA Book Was Read by Them The Portrait Is Painted by The PainterAsadas 12Ainda não há avaliações
- Srtucture Passive Voice: Dosen Pengampu: Dara Ftri MarzukiDocumento11 páginasSrtucture Passive Voice: Dosen Pengampu: Dara Ftri MarzukiFahruz zahraAinda não há avaliações
- E1 - The Passive Voice - CDocumento13 páginasE1 - The Passive Voice - CDarcy DeeaAinda não há avaliações
- M7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Documento25 páginasM7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Aline TriciaAinda não há avaliações
- Passivization Elt3Documento5 páginasPassivization Elt3Kerwin Gener GomezAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT V. Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasUNIT V. Passive VoiceCESAR MIERAinda não há avaliações
- E1 - The Passive Voice - CDocumento13 páginasE1 - The Passive Voice - CDarcy DeeaAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice SummaryDocumento5 páginasThe Passive Voice SummaryJavier LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Tiempo Verbal Estructura Ejemplo: Present Simple Present Continuous Future (Will) Future (Going TO) Past SimpleDocumento3 páginasTiempo Verbal Estructura Ejemplo: Present Simple Present Continuous Future (Will) Future (Going TO) Past SimpleFrancisco MatheusAinda não há avaliações
- Bab IDocumento12 páginasBab IEko ServoAinda não há avaliações
- Passive VoiceDocumento3 páginasPassive VoiceAli ChahinAinda não há avaliações
- Formation of Active and Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasFormation of Active and Passive VoiceHavewala VirafAinda não há avaliações
- Past Continuous: Affirmative: Subject + Negative: Subject + / + Interrogative: + Subject + ... ? + +subject + ... ?Documento2 páginasPast Continuous: Affirmative: Subject + Negative: Subject + / + Interrogative: + Subject + ... ? + +subject + ... ?ANCA POPOVICIAinda não há avaliações
- Active & Passive ShowwDocumento43 páginasActive & Passive ShowwLis LisAinda não há avaliações
- Passive Voice ExplanationDocumento5 páginasPassive Voice ExplanationCristina Paniello VimeAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice1Documento10 páginasThe Passive Voice1Ania KadelaAinda não há avaliações
- Active Dan Passive VoiceDocumento5 páginasActive Dan Passive VoiceDella Mitasari100% (2)
- The Passive Voice: My Grandfather Planted This Tree. This Tree Was Planted by My GrandfatherDocumento4 páginasThe Passive Voice: My Grandfather Planted This Tree. This Tree Was Planted by My Grandfatherlmora_270918Ainda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice PPT Eso 4 - Unit 4Documento11 páginasThe Passive Voice PPT Eso 4 - Unit 4freddy CaisapantaAinda não há avaliações
- Voice Change (Active To Passive)Documento10 páginasVoice Change (Active To Passive)Limon HassanAinda não há avaliações
- GRAMMAR 1 UNIT 6 Passive-Voice-And-Causative-StructureDocumento2 páginasGRAMMAR 1 UNIT 6 Passive-Voice-And-Causative-StructureAlexandra ParedesAinda não há avaliações
- Active Passive Voice Class 7Documento4 páginasActive Passive Voice Class 7sakshigoel2023Ainda não há avaliações
- Passive Voice - PresentationDocumento18 páginasPassive Voice - PresentationVanina Guadalajara QuelaliAinda não há avaliações
- Makalah Passive VoiceDocumento13 páginasMakalah Passive VoiceSolehudin100% (1)
- Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasPassive Voicecamila.lopespatraoAinda não há avaliações
- La Voz Pasiva 2Documento6 páginasLa Voz Pasiva 2Ines Rodri MorenoAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice AnswerDocumento5 páginasThe Passive Voice AnswerGiulia Danzi100% (1)
- English Assignment Nadya SyaviraDocumento6 páginasEnglish Assignment Nadya Syaviranadya syaviraAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice1Documento10 páginasThe Passive Voice1N ChannelAinda não há avaliações
- Passive VoiceDocumento6 páginasPassive VoiceAriana CordovaAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice1Documento10 páginasThe Passive Voice1Orsolya Loószné BernáthAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice1Documento10 páginasThe Passive Voice1Kta MarchesiAinda não há avaliações
- English Grammar - Passive VoiceDocumento10 páginasEnglish Grammar - Passive VoiceMenon HariAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice (UNIT 6) PDFDocumento9 páginasThe Passive Voice (UNIT 6) PDFMaria Eugenia GONZALES FONSECAAinda não há avaliações
- Passive Voice and Causative Structure 17969Documento2 páginasPassive Voice and Causative Structure 17969Darmesta I Ketut67% (3)
- Passive Voice: The Causative: Have/get Something DoneDocumento2 páginasPassive Voice: The Causative: Have/get Something DoneCorina Mitrulescu0% (1)
- PASSIVE VOICE-EnglishDocumento3 páginasPASSIVE VOICE-EnglishNatalijaAinda não há avaliações
- English Language Notes - Standard Vii Active and Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasEnglish Language Notes - Standard Vii Active and Passive VoiceSteveAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice ANSWER KEYSDocumento10 páginasThe Passive Voice ANSWER KEYSMuhammad Mubin Maqba38% (24)
- 3.4 Passive Voice Exercise KeyDocumento10 páginas3.4 Passive Voice Exercise KeyOnline Group100% (1)
- A2 - Passive VoiceDocumento10 páginasA2 - Passive VoiceNguyễn Ngọc LanAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice1Documento10 páginasThe Passive Voice1Adriana Li LooAinda não há avaliações
- Active N Passive NewDocumento6 páginasActive N Passive Newsangay.dekiAinda não há avaliações
- English 101Documento9 páginasEnglish 101soraindyAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar Active and Passive FormDocumento4 páginasGrammar Active and Passive FormZenZaadAinda não há avaliações
- Passive Voice: Example: My Bike Was Stolen. The Snack Had Been EatenDocumento20 páginasPassive Voice: Example: My Bike Was Stolen. The Snack Had Been EatenTan Kiet DangAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive VoiceDocumento5 páginasThe Passive VoiceJatuporn KammoonAinda não há avaliações
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3No EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3Ainda não há avaliações
- Participles AcsDocumento7 páginasParticiples AcsAngel Gavani YusonAinda não há avaliações
- Athenaze VocabDocumento17 páginasAthenaze VocabEric Schwartz100% (1)
- Irregular and Regular Verbs ListDocumento20 páginasIrregular and Regular Verbs ListAbrahamAinda não há avaliações
- B2 Course: Unit 63 - Passive Vs Active VoiceDocumento4 páginasB2 Course: Unit 63 - Passive Vs Active VoiceEugeniaAinda não há avaliações
- LEC II B CursuriDocumento28 páginasLEC II B CursuriDianaMaria100% (1)
- Modal VerbsDocumento5 páginasModal VerbsCarlos Paz ChanganaAinda não há avaliações
- Classified Irregular VerbsDocumento4 páginasClassified Irregular VerbsMarta JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- Gramatica LB EnglezeDocumento85 páginasGramatica LB Englezemitiloi100% (1)
- Classification of Verbs: ObjectivesDocumento5 páginasClassification of Verbs: ObjectivesLovely Grace CajegasAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 10. Exercises Grammar Practice For Upper Intermediate StudentsDocumento12 páginasLecture 10. Exercises Grammar Practice For Upper Intermediate StudentsFoxAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs in EnglishDocumento2 páginasModal Verbs in EnglishgotmyvampAinda não há avaliações
- Finite+ ClausesDocumento72 páginasFinite+ ClausesSonia MiminAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Lengkap Regular Verb Beserta Artinya IrregularDocumento30 páginasDaftar Lengkap Regular Verb Beserta Artinya Irregularrina100% (1)
- Modal AuxiliariesDocumento7 páginasModal AuxiliariesShinta Ari HerdianaAinda não há avaliações
- 004 List of Irregular Verbs - Infinitive - Past - Participle - TranslationDocumento5 páginas004 List of Irregular Verbs - Infinitive - Past - Participle - TranslationPaulo RicardoAinda não há avaliações
- French - Grammar - Tense - Booklet and Y12 Summer Task PDFDocumento13 páginasFrench - Grammar - Tense - Booklet and Y12 Summer Task PDFAnonymous LVibFVAinda não há avaliações
- The Infinitive and Ing - FormDocumento4 páginasThe Infinitive and Ing - Formdanijela_vuković_3Ainda não há avaliações
- Recognising and Verbs: IntransitiveDocumento25 páginasRecognising and Verbs: IntransitiveLaura Hadeith EissaAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech PDFDocumento3 páginasReported Speech PDFTeresa Peteiro CereijoAinda não há avaliações
- Verbos Irregulares Del Idioma InglésDocumento5 páginasVerbos Irregulares Del Idioma InglésgabrielsolerAinda não há avaliações
- Greek Verbs Chart-NewDocumento1 páginaGreek Verbs Chart-NewChristosAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Lengkap Regular Verb Beserta ArtinyaDocumento20 páginasDaftar Lengkap Regular Verb Beserta ArtinyaYossy Ramadhanti100% (2)
- Main Verb (V1) Past Form (V2) Participle (V3) MeaningDocumento31 páginasMain Verb (V1) Past Form (V2) Participle (V3) MeaningMariani Sinaga100% (1)
- This Is My WorkDocumento3 páginasThis Is My WorkwestlifexAinda não há avaliações
- Active and Passive VoiceDocumento3 páginasActive and Passive VoiceChristieUmang100% (1)
- Passive Voice Kelompok 5.1Documento19 páginasPassive Voice Kelompok 5.1Su FitaAinda não há avaliações
- Irregular Verbs Past TenseDocumento13 páginasIrregular Verbs Past TenseJose Luis Peñafort MartinezAinda não há avaliações
- ActivityDocumento1 páginaActivityRamz Latsiv YohgatAinda não há avaliações
- ENGLISH 5 Q1 W4 Compose Clear and Coherent Sentences Using Appropriate Grammatical Structures Modals by Sir Rei MarasiganDocumento16 páginasENGLISH 5 Q1 W4 Compose Clear and Coherent Sentences Using Appropriate Grammatical Structures Modals by Sir Rei Marasiganliezl heranaAinda não há avaliações
- Daftar Kata Kerja Beraturan (Regular Verbs) : Kata Dasar Past Participle ArtinyaDocumento13 páginasDaftar Kata Kerja Beraturan (Regular Verbs) : Kata Dasar Past Participle ArtinyaRizky Meilandi Saputra 9.5Ainda não há avaliações