Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
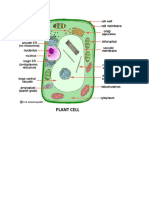
Organelle Location Description Function: Cell Wall
Enviado por
Poonam RanieTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Organelle Location Description Function: Cell Wall
Enviado por
Poonam RanieDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
ORGANELLE LOCATION DESCRIPTION FUNCTION
cell wall plant, fungi and bacteria but *outer layer *support (grow tall)
not animal *rigid, strong, stiff *protection
*made of cellulose *allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass into and out of cell
cell membrane both plant/animal *plant - inside cell wall *animal *support
All cells - outer layer; cholesterol *protection
*selectively permeable *controls movement of materials in/out of
cell *barrier between cell and its environment
*maintains homeostasis
Nucleus both plant/animal *large, oval generally *controls cell activities
nucleus is absent in . *key organelle which has the genetic material and is
prokaryotic cells involved in multiplication of cell, growth and
maintenance of cell.
nucleolus All cells except prokaryotes * Make ribosomes, contains building blocks or
*Found inside cell’s nucleus mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
* may have more than one
*disappears during cell division
nuclear membrane both plant/animal *surrounds nucleus *Controls movement of materials in/out of nucleus
*selectively permeable
Centrioles Animal cells *paired structures near the nucleus *stparate chromosome pairs during mitosis
*made of cylinder of microtubule pairs
Cytoplasm both plant/animal *clear, thick, jellylike material *supports /protects cell organelles
All cells (sytosol)
* organelles found inside cell
membrane
*contains cytoskelon fibers
endoplasmic both plant/animal *network of tubes or membranes *carries materials through cell
reticulum (E.R.)
Smooth No ribosomes
Rough Attached ribosome Synthesis of fats/lipids
Ribosomes synthesis proteins for export
ribosome both plant/animal *small bodies free or attached to E.R. *synthesizes proteins
*made of rRNA and protein
Mitochondria both plant/animal *bean-shaped *breaks down sugar molecules into energy
*inner membranes *site of aerobic cellular respiration
Double membrane outer smooth inner
folded into cristae
Golgi/golgi bodies / both plant/animal except These are the vacuoles or sac like * to modify and package proteins for
golgi apparatus Prokaryotes structures. They occupy a considerable export *have cis and trans face
amount of cytoplasm.
*stacks of flattened sacs
vacuole plant - few/large *fluid-filled sacs * Vacuoles are pouches in the cell that store materials such
animal - small as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates, waste products
and toxic waste..
*store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts
of food)
Vesicles A lot of small bubble sacs in These are small-sized sac like *These help in storage and release of substances as required
animals, large sac in the structures. They are of different by the cell. For example lysosomes help in cell digestion when
middle of plant cells types lysosomes, peroxisomes. cell dies. Vacuoles function is to store water.
lysosome plant - uncommon *breaks down larger food molecules into smaller
animal - common *small, round, with a membrane molecules *digests old cell parts
chloroplast plant, not animal *green, oval usually containing *uses energy from sun to make food for the
chlorophyll (green pigment) plant (photosynthesis)
Cilia Animal cells and protozoa Have a 9-2 arrangement Movement of cell
of microtubules
*short but numerous
flagellum Bacteria cells and protozoan *Have a 9-2 arrangement of Movement
Sex cells microtubules
*long but few in number
Micro-tubules = All cells *micro-tubules provide structural * the cell has a fixed structure and does not collapse
cytoskeleton strength. * form the cyto-skeleton
* These are filamentous extensions *moves organelles within the cell
in cytoplasm.
Você também pode gostar
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Bio, Plant & Animal CellsDocumento6 páginasBio, Plant & Animal CellssparklyhinataAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 páginasCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsborneAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 páginasCell Organelles WorksheetJohn OsborneAinda não há avaliações
- Lego Harry Potter: Years 1-4: Contents: 1. Cheat Codes 2. Character List 3. Hogwarts Locations 4. Character LocationsDocumento25 páginasLego Harry Potter: Years 1-4: Contents: 1. Cheat Codes 2. Character List 3. Hogwarts Locations 4. Character LocationsMegan Friggles Pendleton100% (1)
- Children's Educational Stories and Test ReviewerDocumento18 páginasChildren's Educational Stories and Test ReviewerDina Dumlao88% (25)
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocumento8 páginasCell Organelles Worksheet53777730% (2)
- Laws of Articulation - PPTX FinalDocumento119 páginasLaws of Articulation - PPTX FinalParmod Gulia100% (1)
- Human Teeth vs. Animal Teeth PPT (Student Version)Documento22 páginasHuman Teeth vs. Animal Teeth PPT (Student Version)Allison LeCoq75% (8)
- Zoology 100 Notes 2Documento27 páginasZoology 100 Notes 2Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroAinda não há avaliações
- Organelle location and function chartDocumento2 páginasOrganelle location and function chartAnisa Dyah100% (1)
- ORGANELLE Table PDFDocumento2 páginasORGANELLE Table PDFDebjit BanerjeeAinda não há avaliações
- Plant CellDocumento5 páginasPlant CellWilma BundangAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Wall: Organelle Location Description FunctionDocumento2 páginasCell Wall: Organelle Location Description FunctionXime OchoaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Summaries: Human and Social Biology UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and The Environment SituationsDocumento7 páginasLesson Summaries: Human and Social Biology UNIT 1 - Living Organisms and The Environment SituationsAbigaleAinda não há avaliações
- Cells and OrgannellesDocumento5 páginasCells and OrgannellesLionela EkAinda não há avaliações
- Organelle TableDocumento2 páginasOrganelle Tablejamkulit29Ainda não há avaliações
- The Beginning of CellDocumento4 páginasThe Beginning of CellTrishia Lynn MaldiaAinda não há avaliações
- BIO1 The CellDocumento52 páginasBIO1 The CellSeth MotaAinda não há avaliações
- Organelle Location Description Function: Cell WallDocumento3 páginasOrganelle Location Description Function: Cell WallDannyAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Organelles Table: Organelle Cell Type Description Function Picture Cell WallDocumento2 páginasCell Organelles Table: Organelle Cell Type Description Function Picture Cell WallDyo MandeAinda não há avaliações
- Biology ReviewerDocumento4 páginasBiology ReviewerLycaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Plants?Documento46 páginasWhat Is Plants?Genelie Abuzo CadayonaAinda não há avaliações
- LETS19 BIO SCI HandoutsDocumento25 páginasLETS19 BIO SCI HandoutstorrAinda não há avaliações
- Scientists That Contribute To The Discovery of The CellDocumento6 páginasScientists That Contribute To The Discovery of The Celljerikbenito46Ainda não há avaliações
- Gen Bio Sem 1 NotesDocumento12 páginasGen Bio Sem 1 NotesFrances Chynna KhoAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Structure Locati ON Descripti ON FunctionDocumento7 páginasCell Structure Locati ON Descripti ON Functionalvin christian pasteleroAinda não há avaliações
- Anph 1001 Chapter 3Documento4 páginasAnph 1001 Chapter 3KaraAinda não há avaliações
- Plant and Animal CellsDocumento39 páginasPlant and Animal CellsDelfin Jr UrbanoAinda não há avaliações
- Plant and Animal CellsDocumento39 páginasPlant and Animal CellsDelfin Jr UrbanoAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Notes 1Documento1 páginaBio Notes 1Irah LokmanAinda não há avaliações
- General Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)Documento37 páginasGeneral Biology Notes For Grade 11 (1st Semester)shieeesh.aAinda não há avaliações
- Sel PDFDocumento32 páginasSel PDFJeje DengiAinda não há avaliações
- Rganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationDocumento26 páginasRganisation of The Organism: 1 Cell Structure and OrganisationGasterAinda não há avaliações
- Notes School RandomDocumento25 páginasNotes School RandomAdriel EnkiAinda não há avaliações
- Micro Chapter 2Documento34 páginasMicro Chapter 2Farrah GwynethAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Parts and Functions 2Documento3 páginasCell Parts and Functions 2Arshelyn Donna NovenoAinda não há avaliações
- Reviewer in Biology 1Documento6 páginasReviewer in Biology 1CameronAinda não há avaliações
- Cells: Simple or Complex CellsDocumento2 páginasCells: Simple or Complex CellsMary Jean BoAinda não há avaliações
- Human Bio Chapter 1Documento9 páginasHuman Bio Chapter 1Areej KurshedAinda não há avaliações
- A Double Membrane Composed of Lipids and Proteins, Present in Plant and Animal CellDocumento2 páginasA Double Membrane Composed of Lipids and Proteins, Present in Plant and Animal CellLerr Real RelleAinda não há avaliações
- Cell - The Unit of Life Mind MapDocumento2 páginasCell - The Unit of Life Mind MapAshwath Kuttuva100% (1)
- Biology Y10 Ch2Documento7 páginasBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolAinda não há avaliações
- The Cell as a SchoolDocumento3 páginasThe Cell as a SchoolRoselie Mae GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Biological Science: 20 BranchesDocumento25 páginasBiological Science: 20 BranchesJustine PamaAinda não há avaliações
- L2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgDocumento65 páginasL2 - Prokaryotic Eukaryotic CellhgfhfgNoriko MatsumotoAinda não há avaliações
- Cells: The Basic Units of LifeDocumento17 páginasCells: The Basic Units of LifeglezamaeAinda não há avaliações
- Biology Form 4Documento9 páginasBiology Form 4Ashlyn OoiAinda não há avaliações
- 3 - CellsDocumento28 páginas3 - CellsKat MicaelAinda não há avaliações
- Cell AnalogyDocumento11 páginasCell AnalogyMikaella Jayne CatanaoanAinda não há avaliações
- Cells: A Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic StructuresDocumento30 páginasCells: A Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic StructuresnoaAinda não há avaliações
- Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocumento8 páginasCell: The Basic Unit of LifePradyun DSAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Final (All Units)Documento32 páginasBio Final (All Units)Gingito LedwimAinda não há avaliações
- Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: A Comparison of Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento10 páginasProkaryotes vs Eukaryotes: A Comparison of Cell Structure and FunctionElla RelfAinda não há avaliações
- Genbio Group 5Documento1 páginaGenbio Group 5lanceandreycafeAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM113 LECTURE COVERS CELLS AND CARBOHYDRATESDocumento10 páginasCHEM113 LECTURE COVERS CELLS AND CARBOHYDRATESJamaica M DanguecanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 - 3Documento32 páginasUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- HS-BIO101 Eukaryotic Cell StructureDocumento14 páginasHS-BIO101 Eukaryotic Cell StructureBSN 1-1Ainda não há avaliações
- CellsDocumento8 páginasCellsAnchal ChadhaAinda não há avaliações
- The Cell and Its BeginningDocumento6 páginasThe Cell and Its BeginningZarc VenturaAinda não há avaliações
- 1590 - Invented Primitive Microscope 1665 - 1665-1676 Cell Theory - Complete Cell TheoryDocumento4 páginas1590 - Invented Primitive Microscope 1665 - 1665-1676 Cell Theory - Complete Cell TheoryjaysparklesAinda não há avaliações
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocumento2 páginasThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functionsraphael100% (1)
- Introduction To EukaryotesDocumento2 páginasIntroduction To EukaryotesJero DaclanAinda não há avaliações
- HandwritingDocumento18 páginasHandwritingNấm NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Veterinary Abattoir DepartmentDocumento37 páginasVeterinary Abattoir DepartmentToyahabi NyunyutabisAinda não há avaliações
- Skrining Tuberkulosis (TB) Paru: Field Epidemiology and Training Program (FETP) Universitas Gadjah MadaDocumento6 páginasSkrining Tuberkulosis (TB) Paru: Field Epidemiology and Training Program (FETP) Universitas Gadjah MadaYulia FondaAinda não há avaliações
- ChordataDocumento28 páginasChordatatinchu guptaAinda não há avaliações
- Punicalagin ToxicityDocumento9 páginasPunicalagin ToxicitySatish Chandra KushwahaAinda não há avaliações
- Actividades Aicle AnimalsDocumento3 páginasActividades Aicle AnimalsMaria Jose VillarrubiaAinda não há avaliações
- Advocacy ProposalDocumento4 páginasAdvocacy ProposalLyannah Rizch BlanqueraAinda não há avaliações
- Animal Farm by George Orwell Chapter 8Documento13 páginasAnimal Farm by George Orwell Chapter 8TioLoloAinda não há avaliações
- Science 6 q2 Lamp v3Documento8 páginasScience 6 q2 Lamp v3marvin susminaAinda não há avaliações
- The Human Digestive SystemDocumento5 páginasThe Human Digestive SystemMarta Pérez MadridAinda não há avaliações
- Vet Marketing Pro Releases "Veterinary Lead Funnel" To Connect Clients With Vet ClinicsDocumento2 páginasVet Marketing Pro Releases "Veterinary Lead Funnel" To Connect Clients With Vet ClinicsPR.comAinda não há avaliações
- BagheeraDocumento5 páginasBagheeraAndreea AftodorAinda não há avaliações
- Comedy and Tragedy in Socrates' Ideal City (CTISICDocumento12 páginasComedy and Tragedy in Socrates' Ideal City (CTISICnickgrokAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2BDocumento4 páginasUnit 2BGiang Nguyen Thi ThuAinda não há avaliações
- Texto Del ArtículoDocumento11 páginasTexto Del ArtículoEvelyn ChocaAinda não há avaliações
- Navya Garg Class 8 Bhabha Science Activity 2Documento7 páginasNavya Garg Class 8 Bhabha Science Activity 2Navya GargAinda não há avaliações
- Zodiac Academy Endocrine MCQDocumento5 páginasZodiac Academy Endocrine MCQMourian AmanAinda não há avaliações
- Humane Stoat and Rodent Trap InstructionsDocumento4 páginasHumane Stoat and Rodent Trap InstructionsGina FelyaAinda não há avaliações
- Nerve and Spinal Cord BiomechanicsDocumento65 páginasNerve and Spinal Cord BiomechanicsZinneRah RahManAinda não há avaliações
- Kuceng KuuuuuDocumento2 páginasKuceng KuuuuuAndira RenandaAinda não há avaliações
- FSSAI Accredited Food Testing LabsDocumento32 páginasFSSAI Accredited Food Testing LabsSoma GhoshAinda não há avaliações
- GST English6 2021 2022Documento13 páginasGST English6 2021 2022Mariz Bernal HumarangAinda não há avaliações
- 2 IcebreakerDocumento1 página2 Icebreakerapi-248961865Ainda não há avaliações
- Corrected Mid-Unit Classification Quiz - Google FormsDocumento6 páginasCorrected Mid-Unit Classification Quiz - Google Formsapi-331307423Ainda não há avaliações
- NEPHROPROTECTIVE PLANTSDocumento24 páginasNEPHROPROTECTIVE PLANTSZaid AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- 02advancedthinkahead1 Extrapractice Module3bDocumento2 páginas02advancedthinkahead1 Extrapractice Module3bVanesa MorenoAinda não há avaliações