Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Grammar View A Unit PDF
Enviado por
camioliveroTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Grammar View A Unit PDF
Enviado por
camioliveroDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
UNIT
2
SIMPLE PAST VERSUS
PAST CONTINUOUS
USE
SIMPLE PAST PAST CONTINUOUS
The simple past is used The past continuous is used
to express to express
• an action that started and • an action that was in progress
finished at a specific time at a specific time in the past;
in the past; Christine was updating her Facebook
I e-mailed my professor before page at 7:17 p.m.
class. Christine and Caroline were
We talked about the assignment chatting from 7:30 p.m. to 9:00 p.m.
after class. • simultaneous actions
• chronological actions in the past;
© PEARSON LONGMAN • REPRODUCTION PROHIBITED
in the past. Christine was updating her Facebook
First, I e-mailed my professor; page and listening to music.
then, I went to the mall. We were updating our Facebook
I saw my professor at the mall pages while chatting to one another.
and tried to hide. • a background action.
It was raining that night.
They were texting on their cellphones.
The simple past and past continuous are used together to express
an interrupted action in the past. The simple past expresses the
interruption, whereas the past continuous expresses the action that
was interrupted.
While Christine was updating her Facebook page, she received a text from Stephan.
When Christine received a text from Stephan, she was updating her Facebook page.
6 FIELDS OF VISION: GRAMMAR GUIDE
133847_part1_u1-7.indd 6 7/18/11 11:17 AM
Expressions
• Simple past: ago (a month ago, two weeks ago), before, earlier, in 2005, last (last night,
last Tuesday), yesterday
• Past continuous: as, at 7:17 p.m., at noon/midnight, at the same time as, when, while
FORM
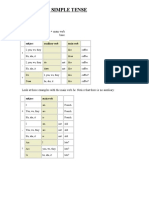
SIMPLE PAST PAST CONTINUOUS
AFFIRMATIVE
Regular verbs not ending in e, Past tense of auxiliary to be
add -ed. (was/were) + present participle
Regular verbs ending in e, add (base form of verb + -ing)
-d. Stephan was teaching at the CEGEP
The professor e-mailed me about in 2010.
missing class. Stephan and Christine were teaching
The students liked their last at the CEGEP in 2010.
assignment.
NEGATIVE
Auxiliary did + not + base form Past tense of auxiliary to be (was/
of verb were) + not + present participle
© PEARSON LONGMAN • REPRODUCTION PROHIBITED
I did not reply to my friend’s e-mail. (base form of verb + -ing)
I didn’t think it was necessary to reply. Stephan was not teaching at the CEGEP
yesterday.
Stephan and Christine weren’t teaching
at the CEGEP yesterday.
INTERROGATIVE
Auxiliary did + subject + base Past tense of auxiliary to be
form of verb (was/were) + subject + present
(Remember not to conjugate participle (base form of verb +
the main verb.) -ing)
Did your professor see you at the mall? Was Stephan teaching at the CEGEP
in 2009?
Did you talk for a long time?
Were you studying there at the time?
UNIT 2 • Simple Past versus Past Continuous 7
133847_part1_u1-7.indd 7 7/18/11 11:17 AM
FYI
• When is used with the past tense to indicate an interruption in the past continuous.
Example: I was walking in the mall when I bumped into my professor.
• While or when is used with the past continuous to indicate simultaneous actions.
Example: You were sleeping while/when I was working.
• In past tense negative questions, not is commonly contracted with the auxiliary did.
Example: Didn’t you go? (Rather than the more formal Did you not go?)
Exceptions
• The verb to be does not require the auxiliary did in the negative and interrogative forms
of the simple past. Examples: It wasn’t necessary to reply to the e-mail. Were you at the
mall yesterday?
• Non-action verbs cannot be used in the past continuous. Instead, they are used
in the simple past. (Refer to Appendix A, on page 135, for a list of non-action verbs.)
• If the verb ends with the letter y preceded by a consonant, remove the y and add -ied
to the base form of the verb in the simple past. Example: I applied to several colleges.
• Many verbs have an irregular past form. (Refer to Appendix B, on page 137, for a list
of irregular verbs.) Examples: Jason spoke to his professor after class. They met in
the library.
1
© PEARSON LONGMAN • REPRODUCTION PROHIBITED
EXERCISE
Fill in the blanks with the form of the verb given in parentheses.
1. Last year, Étienne (go, simple past) to Collège
de Maisonneuve in Montréal. He (study, past cont.)
to be an Intervention and Corrections officer.
Étienne (enjoy, simple past, neg.)
his internship because he (take, past cont.)
both the metro and a bus to get there. He (hope, past cont.)
to be placed closer to his home.
…
8 FIELDS OF VISION: GRAMMAR GUIDE
133847_part1_u1-7.indd 8 7/18/11 11:17 AM
2. Christine and Stephan (work, past cont.)
on their resumés when Caroline (call, simple
past) .
3. (find, simple past, interr.) you
the job you (look, past cont.) for?
4. Étienne (apply, simple past) for a job at the
Laval Detention Centre.
5. (call, past cont., interr.) Caroline
from her cellphone?
EXERCISE 2
Last night, someone uploaded a video to the Internet of Professor
Blake dancing with a lampshade on his head. Principal Frey wants
to know who is responsible.
Complete the conversion using the appropriate tense: simple past
or past continuous.
© PEARSON LONGMAN • REPRODUCTION PROHIBITED
Principal Frey: Samuel, what (do) you
at 8:47 last night?
Samuel: I (study) for my math
quiz at the library, but I (see)
Marie-Claude there, and she (have)
a really strange look on her face.
Marie-Claude: Impossible! I (go, neg.) to
the library last night. In fact, I (leave, neg.)
the house after 6:00 p.m.
…
UNIT 2 • Simple Past versus Past Continuous 9
133847_part1_u1-7.indd 9 7/18/11 11:17 AM
Pierre: Then, why (answer, neg., interr.)
you the phone when I (call)
? I (try) to reach
you all night!
Marie-Claude: I (want, neg.) to
answer it. I (sleep) .
The mystery continues!
COMMUNICATIVE ACTIVITY Mystery Video
■ Form a group of four (or five) students. Create a skit to continue
the dialogue in Exercise 2. Decide among yourselves who will
assume the roles of Principal Frey, Samuel, Marie-Claude and
Pierre. (If you have an extra group member, this student can
play Professor Blake.) Use the simple past and past continuous
in your dialogue.
■ Once your skit is complete, perform it in front of another group
of students or the class, but do not reveal who uploaded the
© PEARSON LONGMAN • REPRODUCTION PROHIBITED
video of Professor Blake. Have your audience ask questions
in the simple past and past continuous to try and guess who is
responsible.
■ Here are a few things you will need to know before you begin:
1. Marie-Claude was not at home last night.
2. Principal Frey does not like Professor Blake.
3. Samuel didn’t really see Marie-Claude at the library last night.
4. Pierre was at the library last night.
10 FIELDS OF VISION: GRAMMAR GUIDE
133847_part1_u1-7.indd 10 7/18/11 11:17 AM
Você também pode gostar
- Verbs!: Verb Forms Review of TensesDocumento49 páginasVerbs!: Verb Forms Review of TensesConnie Alexa D100% (8)
- HAG Script For Easy Reading PDFDocumento6 páginasHAG Script For Easy Reading PDFcamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- HAG Script For Easy Reading PDFDocumento6 páginasHAG Script For Easy Reading PDFcamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- Indirect Speech For Exclamatory and Imperative SentencesDocumento8 páginasIndirect Speech For Exclamatory and Imperative SentencesRizwan BashirAinda não há avaliações
- Tenses For SpeakingDocumento34 páginasTenses For Speakingdsekulic_1100% (1)
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocumento21 páginasPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousJhoab Jchs Chacon100% (2)
- Iex 3e Intermediate Tests U6Documento5 páginasIex 3e Intermediate Tests U6Martyna CegiełkaAinda não há avaliações
- Past SimpleDocumento52 páginasPast SimpleMaria Rada100% (1)
- EF3e Preint Progresstest 1 6a PDFDocumento5 páginasEF3e Preint Progresstest 1 6a PDFcamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- EF3e Preint Progresstest 1 6a PDFDocumento5 páginasEF3e Preint Progresstest 1 6a PDFcamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- EF3e Preint Progresstest 1 6a PDFDocumento5 páginasEF3e Preint Progresstest 1 6a PDFcamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive Voice (UNIT 6) PDFDocumento9 páginasThe Passive Voice (UNIT 6) PDFMaria Eugenia GONZALES FONSECAAinda não há avaliações
- Engl111 Week 5Documento58 páginasEngl111 Week 5Beverly A PanganibanAinda não há avaliações
- КТП 10 Aspect английский язык for KazakhstanDocumento17 páginasКТП 10 Aspect английский язык for KazakhstanМатасова Лидия50% (2)
- Grammar CardsDocumento9 páginasGrammar CardsJuan Diego MerchanAinda não há avaliações
- Past Simple + Present Perfect SummaryDocumento1 páginaPast Simple + Present Perfect SummaryKagome HigurashiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 7 Past Tense Dan Present PerfectDocumento12 páginasChapter 7 Past Tense Dan Present PerfectDewi Miranda SaputriAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Verb TensesDocumento36 páginas12 Verb Tensesmariaanagb23Ainda não há avaliações
- Obisnuite, Repetate.: Present SimpleDocumento2 páginasObisnuite, Repetate.: Present SimpleAnda AdaAinda não há avaliações
- Past TensesDocumento22 páginasPast TensesLuigi Franco Mula (WigiFranco)Ainda não há avaliações
- Engl111 Week 6Documento56 páginasEngl111 Week 6Allen DomingoAinda não há avaliações
- English Learners All Tenses With ExamplesDocumento3 páginasEnglish Learners All Tenses With ExamplesJudy Ann Jude AdornaAinda não há avaliações
- Present Perfect: Have (Present Tense), Plus The Past Participle of TheDocumento3 páginasPresent Perfect: Have (Present Tense), Plus The Past Participle of TheIvonne HernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Mind Map Present PerfectDocumento3 páginasMind Map Present PerfectIvonne HernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar BookletDocumento40 páginasGrammar BookletSALDAÑA NAVARRETE ANDREAAinda não há avaliações
- Tenses of Verb Pre-DemoDocumento31 páginasTenses of Verb Pre-DemoMaridel DiamsayAinda não há avaliações
- Monografia de Ingles Recuperacion 2022Documento20 páginasMonografia de Ingles Recuperacion 2022Miguel Rodriguez SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- TensesDocumento8 páginasTensesសាយ ពិសិដ្ឋAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of The Present Perfect TenseDocumento10 páginasDefinition of The Present Perfect Tenseluis manuelAinda não há avaliações
- Week 1 English Iii Session 2 Unit 2: Express YourselfDocumento48 páginasWeek 1 English Iii Session 2 Unit 2: Express YourselfCarlosCristobalAinda não há avaliações
- TeoriaDocumento4 páginasTeoriaAyluAinda não há avaliações
- Past Simplevs Past Cont.Documento13 páginasPast Simplevs Past Cont.dandreamerAinda não há avaliações
- Seance 02 PDFDocumento4 páginasSeance 02 PDFdeux icAinda não há avaliações
- Inglês - Resumo 3Documento2 páginasInglês - Resumo 3FraGerCanAinda não há avaliações
- Present Tenses Review: Present Simple Tense and Present Continuous Tense - English GraDocumento4 páginasPresent Tenses Review: Present Simple Tense and Present Continuous Tense - English GrajohanaAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Tenses: Present - Past - Future: Grammar UnderstandingDocumento13 páginasSimple Tenses: Present - Past - Future: Grammar UnderstandingPratidinaDeboraAinda não há avaliações
- Narrative Tenses: English 7 M. en Ed. María Del Rosario Alonso EspinozaDocumento15 páginasNarrative Tenses: English 7 M. en Ed. María Del Rosario Alonso EspinozaMaría del Rosario AlonsoAinda não há avaliações
- Present Perfect and Past Simple With Other Time PDFDocumento13 páginasPresent Perfect and Past Simple With Other Time PDFcatherineAinda não há avaliações
- Upper Intermediate - Unit 1 - A Life of LearningDocumento61 páginasUpper Intermediate - Unit 1 - A Life of LearningSmart AcademyAinda não há avaliações
- Past TensesDocumento16 páginasPast TensesKesAinda não há avaliações
- English MidtermDocumento31 páginasEnglish MidtermMarianne GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Present Perfect - English Grammar - EFDocumento4 páginasPresent Perfect - English Grammar - EFManuel DalelinoAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Past X Present Perfect Grammar Guides 124605Documento13 páginasSimple Past X Present Perfect Grammar Guides 124605Ruben MatthewsAinda não há avaliações
- Past Continuous TenseDocumento26 páginasPast Continuous Tenseverosaavedra.fotoAinda não há avaliações
- VerbalTenses TheoryDocumento3 páginasVerbalTenses Theorymeriem semmaa chihiAinda não há avaliações
- Present PerfectDocumento14 páginasPresent PerfectEspinosa Alfaro María FernandaAinda não há avaliações
- Final Remedial Grammar Tenses ConcordDocumento28 páginasFinal Remedial Grammar Tenses ConcordIzzy Dale Cagas SilangaAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar Unit 3Documento1 páginaGrammar Unit 3evaAinda não há avaliações
- Active Voice: Object (Recipient)Documento8 páginasActive Voice: Object (Recipient)Andrea MendezAinda não há avaliações
- Past ContinuousDocumento11 páginasPast ContinuousDavenia SaldañaAinda não há avaliações
- Verb TensesDocumento20 páginasVerb Tensesvpetrovaa23Ainda não há avaliações
- BCN Languages Grammar File: Past PerfectDocumento2 páginasBCN Languages Grammar File: Past PerfectPiro LagrandeAinda não há avaliações
- Presentación Notebook Papel Aesthetic Llamativo Amarillo RosaDocumento16 páginasPresentación Notebook Papel Aesthetic Llamativo Amarillo RosaMishell VillarrealAinda não há avaliações
- Inglês - Present and Past PerfectDocumento15 páginasInglês - Present and Past PerfectHoneylandAinda não há avaliações
- CURRENT-English Verb TensesDocumento5 páginasCURRENT-English Verb TensesMauriceAinda não há avaliações
- Past Perfect WorksheetDocumento11 páginasPast Perfect Worksheetflorencia.benitezAinda não há avaliações
- EPR MODULE 2 Lesson 1 TENSES OF VERBSDocumento7 páginasEPR MODULE 2 Lesson 1 TENSES OF VERBShithisisklAinda não há avaliações
- 12 Verb TensesDocumento36 páginas12 Verb Tensesモーラーリー いたちAinda não há avaliações
- 1.2 GRAMMAR - Tenses (5 Exercises)Documento7 páginas1.2 GRAMMAR - Tenses (5 Exercises)Bryan Erok Sanchz LeonAinda não há avaliações
- Wider World 4 Grammar Presentation 1 4Documento6 páginasWider World 4 Grammar Presentation 1 4veronika rugunAinda não há avaliações
- B1 - Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocumento9 páginasB1 - Past Simple and Past Continuousalvanialler98Ainda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary and Grammar CompendiumDocumento45 páginasVocabulary and Grammar CompendiumAlexia AntuanetAinda não há avaliações
- PerfectDocumento14 páginasPerfectCold CanberAinda não há avaliações
- Bahasa Inggris Materi Presentasi Simple Present Past TenseDocumento14 páginasBahasa Inggris Materi Presentasi Simple Present Past TenseAnnisa Nur Al-IslamiAinda não há avaliações
- Colorful Playful Creative Portfolio PresentationDocumento22 páginasColorful Playful Creative Portfolio Presentationkjm4r2cbhtAinda não há avaliações
- LLM No. 2Documento13 páginasLLM No. 2Rowena AroyAinda não há avaliações
- Untitled Document 2Documento3 páginasUntitled Document 2Charls BuenaflorAinda não há avaliações
- English Verb TensesDocumento13 páginasEnglish Verb TensesJane_Doe3050% (2)
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocumento5 páginasPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousSorana PaleuAinda não há avaliações
- Health ProblemsDocumento19 páginasHealth ProblemscamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- Have YouDocumento13 páginasHave YoucamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- Should Need To Have ToDocumento11 páginasShould Need To Have TocamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- Since or ForDocumento12 páginasSince or ForcamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- About AdjectivesDocumento11 páginasAbout Adjectivescamiolivero100% (1)
- Grammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocumento15 páginasGrammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuouscamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar-EXTRA NI 3 Answer KeyDocumento3 páginasGrammar-EXTRA NI 3 Answer KeyJohn HamiltonAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar View A Unit PDFDocumento5 páginasGrammar View A Unit PDFcamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocumento1 páginaGrammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuouscarminaAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocumento3 páginasGrammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuouscamioliveroAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar-EXTRA NI 3 Answer KeyDocumento3 páginasGrammar-EXTRA NI 3 Answer KeyJohn HamiltonAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuousDocumento1 páginaGrammar EXTRA NI 3 Unit 1 Past Simple and Past ContinuouscarminaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan For 5th GradeDocumento179 páginasLesson Plan For 5th GradeariefAinda não há avaliações
- 40past TensesDocumento27 páginas40past TensesGiorgino WatersAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Unit 01b PDFDocumento2 páginasAdvanced Unit 01b PDFVictor de RiveraAinda não há avaliações
- Ten SsesDocumento9 páginasTen SsesHibatul MatematikaAinda não há avaliações
- PREPARED English Enhancement 1 MODULE 3 PDF FIle 2022 2023Documento34 páginasPREPARED English Enhancement 1 MODULE 3 PDF FIle 2022 2023Jeahn Mica DugadugaAinda não há avaliações
- 2023 Cua Mod 1Documento5 páginas2023 Cua Mod 1akjarnubAinda não há avaliações
- English Grammatik Mit Present PerfectDocumento3 páginasEnglish Grammatik Mit Present Perfectmalaika lahyaniAinda não há avaliações
- Daylight Exam MaterialsDocumento72 páginasDaylight Exam Materialsmurats33Ainda não há avaliações
- Квал тест английскийDocumento117 páginasКвал тест английскийArujan BekmoldanovaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1BActive Passive VoiceDocumento27 páginasLecture 1BActive Passive Voice摩羯座Ainda não há avaliações
- Past TensesDocumento7 páginasPast TensesVincent NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 4 Past Progressive Tense ADocumento2 páginasGrade 4 Past Progressive Tense ASalika PramayudhaAinda não há avaliações
- Verb Tenses and Other Forms MapDocumento1 páginaVerb Tenses and Other Forms MapBrenda Emilia Medina CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Conjugare To EATDocumento2 páginasConjugare To EATcrisAinda não há avaliações
- ملخص شامل لدروس BacDocumento6 páginasملخص شامل لدروس Bacعبد العزيز تقية100% (3)
- Tenses PDFDocumento4 páginasTenses PDFNurohmah SariAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-3 TensesDocumento20 páginasChapter-3 TensesManoj Kumar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Present Simple and Present ProgressiveDocumento7 páginasPresent Simple and Present ProgressiveAYOUB ESSALHIAinda não há avaliações
- OXFORDgrammar PDFDocumento110 páginasOXFORDgrammar PDFJwnwns NwnsnaAinda não há avaliações
- Weekly Worksheet 3 Part1 CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources Dire 126637Documento8 páginasWeekly Worksheet 3 Part1 CLT Communicative Language Teaching Resources Dire 126637Marinela AnghelAinda não há avaliações
- Pt. 3.1 EE 1 23 24Documento36 páginasPt. 3.1 EE 1 23 24hiimleoAinda não há avaliações
- 16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocumento5 páginas16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisIka Yuniati WinataAinda não há avaliações
- General Review of Verb TensesDocumento2 páginasGeneral Review of Verb TensesMai RodasAinda não há avaliações
- SUMSEM-2021-22 ENG2000 LO VL2021220700597 Reference Material I 02-06-2022 Active and Passive VoiceDocumento22 páginasSUMSEM-2021-22 ENG2000 LO VL2021220700597 Reference Material I 02-06-2022 Active and Passive VoiceDeadshotAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive VoiceDocumento16 páginasThe Passive VoiceNguyễn Hải NhiAinda não há avaliações