Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
HCV - Hints
Enviado por
SakshamDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
HCV - Hints
Enviado por
SakshamDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
OFFICE AT 606 R. K.
MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9835508812
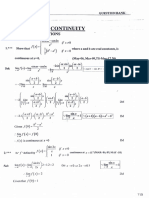
Centre of Mass,
Linear Momentum Collision
9.1. m1 =1k9, m2 =2kg, mg =3kg 16x 0 + 1x (- 0.96x 10-10 sin 52')
x1 -0 x2 =7 x3 =1 + 1 x 0.96 10-10 sin 52o
2 " =0
1+1+16
mtlt+m2l 2+mgl3
Jcm-
m1+m2+mg
16x 0 + 2x O.96, 10-10 cos 52o
1+1+16
2x 0.96r, 10-10 cos 52o
= 6.4x 10-12 m
18
lt =o lz =o y3
The position of centre of mass is
n r, _ (m1x1 + m2x2 + m3x3)
m1 +m2 +mg '
_(mtyt+mzyz+msys)
m1+m2+mg
9.3. Let '0' (0, 0) be the origin of the system
( (1x0)+(2x1)+(3x1l2) Each brick is of mass 'M and.length 'L'
=[.
7+2+3 ' Each brick is displaced with respect to one in contact
(1x0) +(2x0)+3x(J3/2) .L
,, -10
bv-
l+2+3
The X coordinate of the centre of mass
mL ml(t_+- r)l+ml(t_+_3r\l+ml(L
_+_3r\
2
-+ \2 L0) \Z 10) tZ 10)
|
9.2. (t
+ml _+_sL__r,\l+ ml _+_r\l+ ml/r\
_
(L
\2 10 to) tz 10)
|
x.,n \2)
zmL
10
LLLLL3LLLL
-+_+_+_+_+_+_+_+_
22105210252
LL
+-+_
m1 = 16 kg, Xl =yl =0 Xcm = 102
m2 =1k9, x2 = - 0.96 x 10-10 sin 52o m,
xg = 0.96, 10-ro sin 52o m,
m3 =1kg, !z = - 0.96 x 10-10 cos 52o
!3 = - 0.96 x 10-10 cos 52o
m1x1 +m2x2+mgxg
''u-u -
rft1 +m2*mg
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9835508812
zL-+sL*zL 2?L
C.M. is at I3 from the centre of bigger disc away from
-'2'"10'-5- centre of the hole.
9.4. Let the centre of the bigger disc be the origin 9.6. Let m be the mass per unit area
2R = Radius ofbigger disc Mass of the square plate = b\ = 6'2^
R = Radius of smaller disc Mass of the circular disc = Mr'4=nd'
^
mr=pRxTxp Let the centre of the circular disc be the origin of the
n2=m(2R)2 xTxP system
where T = Thickness of the two disces
xt=d h =0
x2=0 !2=0
P = Density of the two disces
Position of centre of mass
Position of the centre of mass
a2ma+x@,2/4)mxo o+o')
_(^r*, + m2x2 m1!1 + m2!2
-{. ,,r.*
=lm'mr+m2)
(
mt+m,
Il=R h=O ={ - o'* ,ol=f 4d,,ol
12 =0 !z=o [d2m it x/$' ) \r 4' )
+ +
( *2rpn*o o The new centre of mass
# risht to the centre of
i, (n+4)
)
tr"4'rt *m'-m1
+^ 1 circular disc.
=[#ffi,')=(+,, 9.7. mr = 1.0 kg Vr = (- 1.5 cos 37'i 1.5 sin 31"-i)
mz =l.2kg Vz =O.4j
ms = 1.5 kg V3 = - 1.0 cos 37" ? + 1.0 sin 37" j
m+ = 0.50 kg Y+ = 3.0 ?
ms = 1.0 kg vs = 2.0cos 37o 7 - z.o sin 37' J
t,'cm l7l1v1 * m2v2 mgV3 + m4r4 + m5v5
+
-
m1 +m2 */l?3 *m4+m5
et {5 fro- Oe centre of bigger disc towards the centre
of smaller dis". - (.
1.of-1.s, 1 ? - r.s'
s il + 7.2x o.4i
:s')
Irt 0'be the origin of the system
* Ls( -!) s -)
R = radius of the smaller disc
2R = radius of the bigger disc
I s'*s])
= O.2ANs at 45o below the direction towards right.
The smaller disc is cut out from the bigger disc
Two masses m1 and m2 are placed on the X-axis
From the figure
mr = 10 kg, mz =20k9
m1 =pR2Tp, xl =R, /l =0 The first mass is displaced by distance of 2 cm
fr2 =tc(la2)fp, x2 =O, !2 =0 tn1x1 + tn2x2 70x 2x 20x2
Position of C.M.
"cm -
m1 +m2 30
(r- *2rpn+om2 o+o ')
| + ,_2O+20x2
* 30
l.- nn'rp + x (?R)2 Tp'
^r ^, ) 20+2Ox2=Q
_ *2fen. ol ! = 2O=-2Oxz
=(
I snn2ro '-";= 3
- =
x2=-7
=)
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Gollision Ph.: 0651 -9.3
2562523,
9835508812
.'. Second mass should be displaced by a distance 1 cm
towards left so as to kept the position of centre of mass
unchanged.
9.9. Two mass e anh m2 are kept in a vertical line
ml = 10 kg, mz =30k9 lrni -n'll
The first block is raised through a height of 7 cm.
The centre of mass is raised by 1 cm. n(nz2 -
n?)
2
Lrl
. r _mtlt * tn2 * yz _10x7 + 30 + lz a (R? + R1R2 + R221
m1+m2 40
3n (R1 + R2)
_74+30xy2 9.\2. m1 = 60 kg, mz = 40kg, mg =50k9
40
LetA be the origin of the system.
Initially Mr. Verma and Mr. Mathus are at extreme
position of the boat.
+ 70+30y2=49
30Y2 = - 39
Distance of the centre of mass
60x0+40x2+50x4 280
150
=-150
= !2=-7 When they come to the midpoint 8 boat the CM lies at
The 30 kg body should be displaced 1 cm. 2 m from'A'.
Downward in order to raise the centre of mass Shiftin CM =2-7.87 =0.13mright.
through 1 cm.
9.13. Let the bob fall at'A'the mass of bob = m.
9.1O. As there is gravity free, after the ice melts, it would
tend to acquire a spherical shape. But, there is no mass of ca;tt = M
external force acting no the system. So, the centre of Initially their centre of mass will be at a distance (from
mass of t}te system would not move. P)
lvd^ mxL+Mx0 m f
9.11. Jr'cm = M+m M+m M
or dm=
i
Mnrdr
- M
- Rl)
rClr
When, the bob falls in the slot the CM is
at a distance 'O'from P. Q P
d
n(Rzz -Rr2) (Rz' mL
IL
Shiftin CM=O-
-2 M +m
R2
( zr\ M rdr
?
mL
i.;i - --::::-
@7 -^h n
Jy'cm = J = towards left
R1
., mL
= ---r- towards nsht
M +m
But there is no external force in horizontal direction.
So the cart displaces a distance -d- 16*6rds right.
M
= +m
9.14. Initially the monkey and balloon are at rest
So, the C.M. is at ?'
When the monkey descends through a distance L the
c.m. will shift
mxLrMx0
60kg 40kg 50kg r0 -
M +m
=M*L
+m
from P
F-4m--+
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Gollision
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9.4 9835508812
through a dislxnsg
il-
So, the balloon descends
" -(M+m) '
-
9.15. Let the mass of the two particles be ntlt tnz
respectively
m1 =1kg, m=4kg
According to question
(1)*'"' =(l)^"" 1.67 xlA-27 xVp =1.4* L0-26 a 6.4xLO-27
q u22
= ZO.4 x LO-27
m2
-=- utZ
v2W
-
vr lrz
-=
t-
+ tty W
;;= I ^,
Now,
,rllvl m1 W - 1
^ru= ^r l^, 2
+ I?11V1 _r .o
-L.-
m2v2
9.16. As uranium 238 nucleus emits, o-particle with a speed
of 1.4x 107 m/sec
(b) The electron and antineutrino are ejected
perpendicular to each other
Let v2 be the speed of the residual nucleus thorium
Total momentum of electron and antineutrino
234.
ltl1v1 = ltl2V2 = + (6.4)2 * LO-27 kg-m/s
^16$2
3 4x 1.4x 107 = 234x v2 vtp-- 15.4x 10-27 kg.m/sec
'1
4x l.4x 107 kg
7.6TxtO-27
Va =-
' 234 VP =9'2m/s
=2.4x 105 m/sec 9.19. Mass of rrlsr =M
9.17. rft1v1 = ttl21t2 Initial velocitY = g
+ 50x1.8=gylQ24xv2 Mass of bag= m
Irt the man throws the bag towards left with a
= 15 x 1o-24 m/sec
', = ## velocity v
So, there is no external force in the horizontal
= 1.5 x 10-23 m/sec direction.
So, the earth will recoil at a speed of The momentum will be conserved
1.5 x 10-23 m,/sec Lct he goes right with a velocitY
lnlt =W
9.18. Mass of proton L.67 x to-27 kg + V =(mv/M)
Iret"Vo" be the velocitY of Proton + v =(W/m) "'(i)
Given, momentum of electron Irt the total time he will take to reach ground
=1.4x to-26 kg m,/sec W =u
={7
and momentum of antineutrino
=6.4x10-27 kg m/sec I,et the total time he will take to reach the height
(a) The electron and the antineutrino are ejected in . E@-6
the same direction
As the total momentum is conserved the proton
!="= { ,
Then the time of his flYing
should be ejected in the opposite direction.
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9.5
9835508812
=tl -t2
2Ir 2(H -h)
=f!).o, e -[- ! e)
=
g I
I
^P
I
\r/ 1. r---
"o, i
=,Pdr-.1n-nl -[rJ-"""
=[ft.).o, e
Yg
within this time he reaches the ground in the pond 9.22. ?s the block is exploded only due to its internal
energy. So, net, external force during this process is 0.
covering a horizontal distance
:) So the centre of mass will not ghange. Let the body
x=Vxt while exploded was at t}re origin of the co-ordinate
V=! system. If the two bodies of equal mass is moving at a
t speed of 10 m/s in + x and + y axis direction
Mx
l)=--=-X
M Ji respectively, then their resultant will move with
mt m Jl tJu -,[u7t velocity
As there is no external force in horizontal dlrection, fio'-;10t+ 21o.10 cos 90' =loJi m/s 45o
the x-coordinate of CM will remain at that position
Q=
Mx(x)*fl+x1 If the centre of mass o
which have equal mass "r
r#t:fffffiffi:
then wo will move in the
M +m
opposite direction (i.e. 135-with respect + x-axis) of
+ *, M
=i_, the resultant at the same velocity lN2 m/s
9.23. Since the spaceship is removed from any material
.'. The bag will reach the bottom at a distanc" fgl . object and totally isolated from surrounding, the mass
\ml loss by astornauts couldn't slip away from the
towards left of the line it falls. spaceship. So the total mass of the spaceship remain
9.20. Mass = 50 g = 0.05 kg unchanged and also its velocity.
9.24.d=1cxr, v =20 m/s,
v = (2cos 45o) ? - Z rir, +S" j u = O, p = 900 kg,/m3 = 0.9 gmlcm3
1/L = -2 cos 45o I i - Z tit +S' volume =l,1] nr' =1 n (0.5)3 = 0.5238 crn3
1.3,,l 3
(a) Change in momentu* = #, - ri,
mass = vp = 0.5238 x 0.9 = 0.4774258 gn
= o.o5 (2 cos 45o i - z rir, 4s j)
mass of 2000 halistoe = 2000 x 0.4774
=947.857
- 0.05 (- 2 cos 45" i - z sin +5' j) rate of change of momentum per unit area
=947.857 x 2000
= 0.1 cos 45" j -0.1 sin 45" ? + 0.1 cos 45'? = 19 N/m2
+ 0.1 sin 45'l
= 0.2 cos 45.1
Magnitude =92 =9'394 = o'14 kg m/sec
^lz 2 Ulst
G) The change in magnitude of the momentum of the
ball <l-
Total force exerted = 19 x 100 = 1900 N
1i z I -l 7, I= 2x 0.5- 2x 0.5 = 0 9.25. Aball of mass m is droped onto a floor from a ceftain
9.21. height let'h'
v1 = Jffi, Yl =0
Pir,.id"n
"
=[*)*"?-[*)sinei 1'2=-'{Z4hand 12 =0
Rate of change of velocity :
. _n* 2Jzsh
PReflected = -[*)cos e? -[1)'r, e ; t
The change in momenr.rm will be only in the x-axis
v =.124h, s=h, u=0
direction i.e., = Jffi =gt
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Gentre of Mass, Linear Momentum Gollision
Ranchi -1
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9.6 9835508812
L
W
t-
v =( *u )towards rigtrt
+ m)
-
\l g \M
Case-II
Total time =2 ^W When the man on the right jumps, the velocity of it
\lg with respect to the car is u.
mx 2
p =---=!:--
^[?.s.h
=mg O =tnu -W2
^ l2h
- z-l- ,,2 mu
\l g =r=T
9.26. Arailroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails (V is the change in velocity of the platform -when
when a man of mass m starts moving on the car iUtfot itself ii taken as reference assuming the car
towards the engine. The car recoils with a speed v to be at rest)
backward on the rails. .'. So, net velocity towards left (i'e' the velocity of the
Let the mass is movingwith a velocityxwith respect to car with resPect to the earth)
the engine. mu
The velocity of the mass with respect to earth is M - (M+m)
=fru
(x - v) towards right. + m?u-Ymu
Vcm = 0 (InitiallY at rest) -mMu
M(M+m)
-0--MY+m(x-v) *2u
:+ Mv=m(x-v) =M(M*^)
mx--Mv +mv
= m which is started with
+ * =(*
*
^], =[, * tr)'
I m / \ m)
- '- - A small block of mass
g.2g.
velocity V on the horizontal part of the bigger block of
floor'
a
mass M Placed on a horizontal
g.27.A gun is mounted on a railroad car. The mass of t}re m is started with a
Since the small body of mass
.ui ttt. gun, the shells and the operator is 50 mwhere velocity V in the horizontal direction, so the total
m is the mass of one shell. The muzzle velocity of the
shells is 200 m,/s.
initial momentum at the initial position in the
horizontal bigger block in the horizontal direction'
Initial V.- = 0
From L.C.K. m.
O=49mxV+mx200 mv+MxO=(m+M)V
+ y =_z9l! ws
49 v= fru
m+M
200
fi mzstowards left
9.3O. Mass of the bugghi = 200 kg Va = 10 km'/hour
Mass of the boY = 2.5 Lt
When another shell is fired, then the velocity of the
car, with resPect to the Platform is and VBoy =4kny'hour
If we take the boy a bugghi as a system then total
+ v =209 m/stowards left
49 momentum before the process of sining will remain
constant after the process of sitting
When another shell is fired, then the velocity of the car
m6V6 + mboy Yboy = (m6 + m6sy ) V
with resPect to the Platform is,
+ 200x 10 + 25x 4=(200 + 25) x V
+ Y, =*49 m/stowards left
+ v =2]9-'! =4 =9'3 m/sec
225 3
verocitv earth is
"'ltre Mass of the ball q = 0.5 k8,
: ;:?TtT:T,
\.+s 49)
9.31.
' VelocitY of the ball = 5 m/s
Mass of the another'ball = m2 = 1 kg
g.z&.TWo persons eactr of mass m are standing at the two
Let it's velocitY = Y1 rVs
extremes of a railroad car of mass M resting on a
smooth track. Using law of conservation of momentum
Case-I 0'5x5+1'xv1 =6
Let the velocity of the railroad care with respect to the
Y' =-2'5
earth is V when the jumP of left man' .'. Velocity of second ball is 2'5 m/s opposite of the
O =-n1u + (M + m)V direction of motion of I'st ball'
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Gollisidn Ph.: 0651 - 9.7
2562523,
9835508812
9.32. Mass of the rnan m1 = 60 kg
,..'
Speed of the man - v1
10 m/s = =(;)
Mass of the skater
Let its velocity = v
mz = 4A kg
= ,'=!2
60x10+0=100xy
vl =6m/s
-J'|
o=
Loss in x.n. [1') 60 x (10)2 - ] x 100 x 36 = tzoorJ 9.36. (a) Mass of block = 2 kg and speed = 2 m/ s
\2) 2 Mass of 2nd block = 2 kg
9.33. Using law of conservation of momentum Let final velocity of 2nd block = v
+ tTt2u} = m1v (t) + tn2v1
m1u1 Using law of conservation of momentum
where ? = speed of 2nd particle during collision. 2x Z=(2+ 2) _v
+ m1u1 + llllU2 = m1U1 + m1 + Y=lm,/s
(*)(vr -ur ) + m2vl Loss in K.E. in elastic collision
m2u2 =(;). 2x22 -(i),, +2)x(t)2
m2 =Itffl(v1
_u1)+vi
= m2 \Lt )
=4-2=2J
vl =tt2-^' t, (vr
-ur) o) Actual lor, =
Md*l* lott
= 1J
m2 Lt 2
9.94. Mass of the bullet = m and speed = v
Mass of the ball = M
(;), , , (z)2 -(;), , vt2 -(i)" *; =l
ml = fractional mass from the ball
= 4-Qr2 +v221=1
Using law of conservation of momentum . (1 + e2)*4 ='
my + 0-(ml * m)v7 + (M - mt)v1
-4 '- 2
vl = final velocity of the bullet + 2(7 + =g
where fractional = e12
mass
1009 1009
yl= mv-(M-m)v1
^+^L
9.35. Mass of 1st ball = m and speed = v L+e2
3
Massof 2nd ball = m 2
1
Let final velocities of 1st and 2nd ball are v1 and v2 e2
respectively 2
Using law of conservation of momentum -J2
-_ 1
m (v1 + v2) = tnv ...(i)
+ V1 *V2 =V ...(ii)
9.37. Final K.E. =0.2J
Also !1 -v2 =sv InitiatK.E.=1rr,'*0
2'
Given that final K.E. = I ir,i i"l X.E.
4 =1r0.1"u2
z
+
7':'7't31,
*-lTlVo- =-X-lTlV'
-fflVt- = 0.05 u2
2'2042
3t l?lv1 * lW2 =1nY
:+ vy2 + v22 =-1)- where v1 and v2 a;te final velocities of 1st and 2nd
4
block respectively.
(\ +vz)2 + (\ -vz)2 3.>
:) v1 *v2-u ...(1)
= =-V-
2 4 (\-vz)+e(u1 -u2)=0
(l + e2) v2 eu =vz -14 tu2 =0, ur --uI ...(2)
=2 u2 =
24 Adding equations (L) and equation (2),
ht2 =(7 + e)u
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
9.8 Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9835508812
Case-III. When B throws the ball, then applying
", =(;) + e)
(1
L.C.L,M.
!! =t! -lO + el = ++"(?!\=-4x5+4oxv
\44)
u, =L(1 - e)
= v =7 m/ s (towards right)
Case-fV. When A catches the ball, then applying
Given, ! *L =O.2 L.C.L.M.:
^u,'
220 ^u,2 +
v12 + v22
-4x5+(-0.5)x40=44v
=4
+
44=9
=40
u m/stowards left.
:)
lo*"t'e8 -4 11
(c) Case-V. When A throws the ball, then applying
= " -uS L.C.L.M.:
++,[]9)=4x5+4oxy
For maximum value of u, denominator should be
= (1il
minimum,
= u =9402
=2 m/s (towards left)
e=0
u2 =B Case-VI. When B recieves the ball,
Then applying L.C.L.M. :
u =2 J2 m/s.
For minimum value of u, denominator should be
+ 40x1+4x5=44xy
maximum, + , =9 m,/stowards right.
€=L ,44
Case-V[. When B throws the ball,
u2 =B
Then applying L.C.L.M.
u =2m/s
9.38. + v = 44" f!9) m/ s towards left.
\44)
Case-VI[. When A catches the ball, the applying
L.C.L.M.
-4xs.40fll
\2)
=-44v
v = -!44=i'19)m/stowards
\11i
left
Similarly after 5 round trips
The velocity of A will U.[T)u"a velocity of B will be
t. 11/
Two friend A and B (each 40 kg) are sifting on a 5 m,/s.
friaion less platform some distance d a part A rolls a
ball of rnass 4 kg on the platform towards B, which I (d) Since after 6 round trip, the velocity ofa is $11 f. e.,
catches. ThenB rolls the balls towardsA andA catches
it. The ball keeps on moving back and forth betweenA
and B. The ball has a fixed velocity 5 m,/s.
(a) Case-I. Total momentum of the man A and ball
will remain constant.
0=4x5_40xv
y = 0.5 m/ s towrads left
=
(b) Case-II. WhenB catches the ball, the momentum > 5 m/s. So it can't catch the ball. So it can only roll the
between the B and the ball will remain constant. ball six time.
+ 4x5=44v (e) Let the ball and the bodyA at the initial position bc
at origin.
"
=(#)^'" xc
40x0+4x0+40xd
40+40+4
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9.9
9835508812
10
=- 6l M aVa + Msva =(Me+Mp)V
27 2x7 =4xV
.'@- :) v =(])-z*.. ...(ii)
Putting in equation (i)
g.gg.u =.l2gh veloci$ on the ground when ball
=
approach the ground
t-2xl.1)=uo*'
\4)
:+ u=^12x9.8x2
v = velocity of ball when it separates from the
l,1) = ro *,
12)
ground ,>1,
x- =-m3
2mlsec 100
*=[1)m=0.1m = 10 cm.
\ 10i
y =eU 9.42. Mass of bullet m = 0.02 kg
v=JWh2=18*9.8*1.5 Initial velocity of bullet Vr = 500 m,/sec.
Mass of block, M=10k9
Vr -_{tr.93.15
t-:=-
v5
Initial velocity of block =lJz = O
9'8x 2 2
Final velociry of bullet = 100 m,/sec = y
"l2x
g.40.K.E. of Nucleus =[f')rr, Let the final velo:city of block when the bullet emerges
\2) out, if block = yz
E2
=[1), (E/mc2\=
'
\2) zmc2
Energy ernitted by Gamma photon = E
E'
Decrease in internal energy = E * =
2mc2
9.41. Mass of each block Me =2kg
Initial velocity of the Ist block, y = 1 m,/sec Using conservation of energy
Vo =1mlsec
mv1 *Mu2=mv+Mvl
Va - U m,/sec + 0.02 x 500 = 0.02 x 100 + 10 x v2
Spring constant of the spring = 100 N/m y1 = 0.8 m/sec.
=+
The blockA strikes the spring with a velocity lm,/sec After moving a distance 0.02 m it stops.
After the collision, it's velocity decreases continuously + change in K.E. = work done
and at a instant the whole system. (Block A + the
compound spring + Block B) rnove together with a = ,-(;)x 1ox (0.8)2 =M x 1ox 1ox 0.2
cotrrmon velocity. \
Let that velocity be V, + M =0.16
Using conservation of energy, 9.43. The projected velocity = 11
The angle of projection = 0
(l)"^'^'.(i)"*; When the projectile hits the ground for the 1st time
The velocity would be the same i.e.u. here the
.(l)*,u, .(*)*,
=(*)* component of velocity parallel to ground.
^u, u cos 0 should remain constant.
(;)., (1)2 +,=(;).(;).,, .(i)x2 x 1oo But the vertical component of the projeaile
undergoes.
(when x = maximum compression of spring).
+ y=eusino
+ l-2v2=50x2 ...(i) Now for the 2nd projectile rnotion.
As there is no external force in the horizontal u = velocity of projection = l,i1u cos 0)2 + (eu sin 0)2
direction, the momentum should be conserved.
and Angle of projeaion
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
9.10 Ph.:Collision
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum 0651 - 2562523,
9835508812
= cr = t3n-1 (eu sin 0/u cos 0) = tan-1 (e tan 0) So, I =vo sin t[?) + ]s sin r[?)
tanct=etan0 ...(2)
gxz sec2 av8 sin r?
y=xtanc[tan -t
c,
Because, ...(3) -
2] g
Here, y = 0, tan u, = e tan 0, sec2 a =1+ e2 tan 0 Hence the plane will hit again at a distance
I=8hsin0
and u2 =n2 cos2 o + sin2 o
"2u2 9.45. h=5m
Putting the above values in the equatiol (3).
0=45o
gr2 (1 * 12 tan2 g)
xetan0=
ztz (cos2 o + e2 sin2 o) -" =(g)
[+J
2*u2 tano (cos2 o + e2 sin2 e1 Here the velocity with which it would strike
X=
g (1 + e2 tan2 g) =v-Jzg"5=10m/sec.
After collision, let it make an angle p with horizontal'
2eu2 tan 0. cos2 e
The horizontal component of velocity 10 cos 45" will
I remain unchanged and velocity in the perpendicular
eu2 sin 20 direction to the plane after wilisine
g rr=ex10sin45o
it will fall ata (9) ,. to x 7/Ji
+ So, from the starting point O, =
\.4/
distance
= (3.75) Ji m/sec.
Similarly, vz = SJi m/sec
u=^p', *rl
= ^l7eJ25 = 8.03 m,/sec
Angle of reflection from the wall
g= tan-1 (s.7s Jb/sJ,
= tan-r [9) = rr"
sin 20 (4i
_ u2 sin 20 * eu2. sin 20 _u2 (1 + e)
ggs ) Angle ofprojection o = 90
- (e + 9)
g.44.The ball strikes the inclined plane at origin with 90-(45+37o)=$o
velocityvs = JzdE.As the ball elastically rebounds. It Let the distance where it falls =L
recalls with same velocityvg, at the same angle 0 from x=Lcos0
the normal or y-axis. Let the ball suikes the incline Angle of Projection (cr) = - Bo
second time at any point P, which is at a distance I --2 sec-
^^^2
8x- cl
from the origin along the incline. From the equation v
!=rayt*!*yi
0=vo cos0t -]S.ore12
where t is the same time of motion of ball in air which
moving from origin to P.
As r*0 so - zvs
g
Now from the equation
x =voxf *f,*rr'
+ -L sin 4 =L cos0x tan 8'-*
r=vosinet+]gsino12 2
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Goltision Ph.: 0651 -9.{
2562523,
1
9835508812
L2 cos2 45" sec2 8o Velocity of the bullet with which it strikes
u2 u = 300 m,/sec
Let the bullet emerges-out with velocity V and the
+ - sin 45o = cos 45o. tan 8o 1o cos2 4.5o sec2 8o velocity of block v1
(8.83)2
As per law of conservation of momentum
(i)
...
mu =Mv2 * l\v ...(i)
Solving t}te above equation, we get
Again applying work-energy principle for the block
I=18.5m
9.46. Mass of block M = 2OO g = 0.20 kg <- xl---l
M',[^,1^ l^m*
Block of the particle = m =720 gm = 0.12
In the equilibrium condition, the spring is stretched by
a distance x = 1.00 cm.
= 0.01 M
after the collision,
+ A.2xg=K.x , -f+l M x (v1)2 = - M.s.h.(where h = 0.2 m)
+ 2=Kx0.01 \2)
:+ k = 200 N/M :) (4)2 =24h
The velocity with which the particle m will suike M is
given by u
\ =,lW = JN" LO =2m/sec.
Substituting the value of v1 in equation (i), we get
=18* i0" 045 0.02x300=0.5x2+0.2xv
=Ji=3mlsec + v=6-l= 5 =250mlsec.
So, after the collision, the velocity of the parricle and 0.02 0.02
the block is 9.49. Mass of the two block are mt . m2" Initially the spring
l./
0.12x
=-.
3 =_9 m,/SeC is stretched by x9 spring constant K. For the block to
0,32 8 come to rest again. Let the distance travelled by m1
Let the spring be stretched through an extra deflection and m2 be x1 and x2 towards right and left
of6 respectively. As no external force acts in horizontal
direction.
, -(;) x 0.32, (#) = 0.32x ro x o -(]), zoo
tr\X1 = tTl2X2 ...(1)
Again, t}te energy would be conserved in the spring.
x (5 + 0.1)2 - (i)>< 2oo x (0.01)2
= (;)-, ,.' =(;)k (x1 + xz - xo)2
Solving the above equation, we can get
6 = 0.045 = 4.5 crn xo =xl +x2 -xg
9.47. Mass of bullet=25 g = 0.25 kg x1 * x2 =2)cg ...(2)
Mass of pendulum = 5 kg x1 =Zxg - x2
The vertical displacement h = 10 cm = 0.L m
( 2m, )
Let it strike the pendulum with a velocity u
Similarly xr =l-lxo
+m2)
\m1
Let the final velocity be v + mt (2xo - x2) = m2x2
+ mv =(M + m)v
= 2m1xg - mtxZ =tn2X2
= v= (M fl u=o'25 *u- u
x2 =J
2m,
xo
+ m) 5.025 207 m1 * fi12
Using conservation of energy : \t\ + m2v2
9.5O. (a) Velocity of centre of mass =
.-(;)(M + m) .u2 =(M + m). s .h m1+m2
Here vt =O Y2 =vo
+ u2
=2xL0x0.1 =2 _mtx0+mZxv} =_Wg_
QOD2 n\.+mZ m1 +fi2
u = 2O7 * Ji = 280 m/sec (b) The spring will attain maximum elongation when
= both velocity of two blocks will attain are velocity of
9.48. Mass of bullet m =20 gm = 0.02 kg
centre of mass.
Mass of wooden block M = 500 gm = 0.5 kg
x -+ maximum elongation of spring.
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Ph.:Collision
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum 0651 - 2562523,
9.12 9835508812
Change in kinetic energy = potential energy strored in Due to { and F2 block of mass m1 and m2 will
spring. experience different acceleration and experience an
inertia force.
+ l^ruo' - |wr
+ ml(r$' 1*' = Net force * ,,'
mz =: :" - _r2_\
my+m2
= ^ru&,(t- l= pz
\ mt+mz) -mr\+mz\-mt\+Fzmt
.=lp;l "
I 1t/2
=mzF\
+ mtFz
m1+m2
ff\+m2
9.51. If both blocks are pulled by some force, they suddenly (F, -F1)
move some acceleration and instantaneously stop at Similarly Net forcc ofi m2 - - m2 x
same position where the elongation of spring is - = Fz ----
ml+mz
maximum. m1F2+nZFZ-m2F2+m2\
m1+m2
-mt.F2+TZFZ
m1+m2
:> Let x1,x2 -> extension by block m1 andm2 .'.If rq displaced by a distance x1 and x2 by m2 the
Total work done = Fx1 + Fx2 ...(1) maximum extension of the spring is x1 + xr.
Increase the potential energy of spring .'. Work done by the blocks = €il€rBY stored in the
spring.
=(;)" (x1+ x2)2 ...(2)
+ mz'\ ++trl2
mtFz, + mtF2
(xr) *mz\ * *,
m1 m1 + m2
Equating (1) and (2) /r \
F (x1 + rr, =(1) K (x1 + x2)2 =l* l.
\z,t
1x1 + x2)2
2 m2\ + m1F2
+ (x1 + x2) =(zF/k) -Ir -rfe =-#
k m1+m2
Since the net extemal force on the n'vo blocks is zero
thus same force act on opposite direction. 9.53. Mass of the man (M = 50 kg
fn1X1 = rll2X2 ...(3) ^)
Mass of the pillow (Mo) = 5 kB
and x1 + x2 =?.F/k When the pillow is pushed by the man, the pillow will
rb go down while the man goes up. It becomes the
'' X2 = ----:- X1 external force on the system which is zero'
;m2 of mass is zero
= Acceleration of centremass
,l t, * Velocity of centre of is constant
MmxV^=MOxVo ...( 1)
t' *t + x1 =7-F/k Given the velocity of pillow is 80 ftls which is relative
Substituting
m2 of pillow with resPect to man
ry)=zrtt Vplm =Vo -?Vm)
*r(t * mz) =VP + Vm
\ Vo =VP/w-V^
11 =
?.Fmo -
' k(mr +*z) Putting in equation (1)
---:2-
2.Fm.
M^'V* =Mpx(VPlm-V^)
- 3 50xV- =5x(8-V^)
9.5.2. Acceleration of mass m1
^2
-Fz
F1'
=m1+m2
k@l;Gj
= ,* =i
=O.727 ft/s
Similarly acceleration of mass m2 =
Fz -\. .'. Absolute velocity of pillow = 8 - A.727
m1+m2 =7.2ft./sec.
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision Ranchi -1
Ph.: 0651 9.13
- 2562523,
9835508812
t 8- 1.1 sec. + u =.!r.s gh
v =7.2 =
.'. Time taken to reach the floor =
So the block will travel with a velocity greater than
As the'mass of wall > > >then pillow.
Jrs sh
The velocity of block before the collision = velocity f.e., man must awake.
after the collision. 9.55. Mass of block = 4909m
+ Time of ascent = 1.11 sec Mass of buller = 10 gm
Total time taken = 1.11 + 1.11 Since the bullet embedded inside the block, it is an
= 2.22 sec plastic collision
9.54. Let the velocity of A =ul Initial velocity of bullet \ = 5OJ7 m/s
Let the final velocity when reaching at B become Velocity of the block is v2 = g
collision = vr Let final velocity of both = y
(*)^:(i)* '=m,h Here
10x 10-3 +490x10-3 x 0=(4q0+10)
+ v12
"5OJ7
-u12 =24h = 10-3 x Ve
= u, =.,{z4h * u! ...(1) vt = J7 m/s
When the blockB reached at the upper man's head the When the block loses the contact at'D't}te component
velocity of B is just zero. For B, block mg will act on it.
(vil2 :
(i), ,*, (o)2 -
[;) "
2m x v2 = msh
m
r
mg sin o
+ v =.,l2Bh =+ (Vil2 =gr sin 0 ...(1)
Before collision velociry of u4 = y, Putting work energy principle
uB =0
Aftercollisionvelocity of vn - V(say) (;)- *(vil2 -[;), mx(v1)2
vs =JW
Since it is an elastic collision the momentum arid
K .......... be conserved
trlx y1 + 2m x 0 = rl x v + 2m * "lZgh
+ tt1 -v =2,1W -- mg (O.2 + 0.2 sin 0)
,- (;) x nt x Y1z.
[;)
, 2m x (o)2 (i),' ". '-(;) * d7)2
g (0.2 + 0.2 sin 0)
=(i), mu2 +(l)" ,^ d-z gn)2 =
3.s - ft) x 9.8 x 0.2 x sin o
=) ,12 -r2 =2* JW " JNE ...(2)
\2)
Dividing (1) by (2), = 9.8 x 0.2 (1 + sin 0)
(vr + v) (vr - v) _2x JW J2sh
I ,it e =(1)
(v1 + v)
\2)
2x,!?ah 0=30o
+ yl*v=J2gh =
Angle of projection = 90o - 30o = 60o
Adding (1) and (3),
2v1 =grl2U1,
Time of reaching the ground = -E
\lg
,=(i)m _@
-! ef
But u, =^lz.gh;u, =0.247 sec
Distance uavelled in horizontal direction
=G)w s=Ycos0xf
=#rsinecos0xt
?4h + u2 =(20)wot = 0.196 m
Total distance = (0.2 - 0.2 cos 30") + 0.196
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
9.14 Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9835508812
'= 0.22 m a small element at a distance'/ from
9.57. Let us consider
9.56. (a) Let the velociry of m reaching at lower end = vl ttre flour of length 'dy'
From work energy principle so, a* =Y dt
L
(i).,,,, -(;)" m(012 =,'g1 So, the velocity with which the element will strike the
+ \=Jw floor is,
v = J2Bi
Similarly velocity of heavy block will bev2 = ,!2g1,
So, the momentum transfered to the floor is,
1t1. =1/2 =u (SaY)
lct find velocity of m and 2m are v1 and v2 14 =(dm), ={L . dx JW
respectively
[because the element comes to rest]
According to law of conservation of momentum
So, the force exefted on the floor change in
= mxu -2mu =mv1 + 2mv2 ...(1)
momentum is given bY,
+ v1 *2v2=-11
Again, vt - v2 = [(u - v)] ...(2) \=#=T #t*
=-2!
Subsracdng, Because, , = (#) = J2si (for the chain element)
3v2 =tl
_@ 11 =+.rJ-wt2 =f .a*=ry
'z -i -17
9.58.q =10m/s
Substituting in equation (2) V2 = O,r\t r'2 ) velocity of A and B after collision
+ vL -v2 - -Zl
uu ==--i..il:
(a) If the collision is perfectly elastic
mV1 +mVr=tnv1 +tTw2
3 10+0=v1+v2
\3i v1 + v2 =lO ...(1)
-5 Again v1 +v2=-(u1 -u2)
-u
3
= _ (10.0)
-5x JN = - 10 ...(2)
3
Substracting (2) from (1)
J@ bz =20
Y2 =lO m/s
(b) Putting the work .rlr", principle =
The deceleration ofB
(i). - "
(o)2 -(i), 2mx (v2)2 Putting work energY PrinciPle
/r\ .^-, (t\
lalxmx(0)" 2-
--mxaxh
-l:lx mxLlo
=_?,tnxgxh \z) \2)
lh -+ height reached by heavY balll
-(i),.
=) h =r!.]
Ig]
= (10)2
100,,
=-Fs x h
= h =-2x1x10 =5m
simirarry,(i)',, (0)2 -[i)' mvt2 - mx g x h2
(b) If the collision is perfectly in elastic
(height reached by small ball)
tTtxUl*mxU2=(m+m)xv
=(1)'!f; s'nz = mx 10+ mx 0 =2mxv
,llo 0.25L = ,=flg)=5m,/s
'9 =- \2 )
The two block will together attacking to each other
some h3 is more than 2L, the velocity at highest point
Putting work energY PrinciPle
will not be zero.
And the'm'will rise by a distance 2I. [1']' ,* , (0)2 -f\2)
1.) . 2m x (v)2 = 2mx[r8 x s
\2)
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Gollision Ph.: 06519.15
- 2562523,
9835508812
+ (5)2 a2=
frdx mg sm q, cos 0
...( 1)
0.1x10x2 =s M +m M +m
+ S=12.5m So, the absolute (Resultant) acceleration of 'm' on the
9.59. Let velocity of 2 kg block on reaching the 4 kg block block "M' along the direction of the incline will be
before collision = ur c=gsinc[-a2 coscr,
Given, V2 =0 (velocityof 4kgblock) =g sin cr -
mg sin o cos2 o
M +m
(i)- " *' -[;) mx (t)2=-m x ps x s . lru*r-r.os2
+ pr=@ "
=gslnC[l-
L M+m ']
= = 0.6 m,/sec . lm+msin2al
a=.gslnc[t-l
+ ut = 0.6 m,/sec " L M+m l ...(2)
Since it is a perfectly elastic collision
kt v1, v2 + velocity of 2 kg and 4 kg block after lct, the time taken by block'm'to reach the bottom
collision end by't'
m1 x u1 + m2u2 = tnlVl * tn2v2 Now, s =ur *[1.]"r'
\2)
= 2x O.6 + 4.0 = Zv1 + 4v2
:3 h
2v1 + 4v2 =1.)
= -;- -=(!\o,,
Again, vl -v2=+(ut-u2) ...(1) srn o \2)
=+(0.6-0)=-0.6 I ._ 4fr-
'-!"tin"
Substracting (2) from (1)
3v2 =1'2 "'(2) So, the velocity of the bigger block after time f will be
:) vz =0.4m/s Vm =U * a2t
vl =-0.6+0.4=-O.2m/s
.'. Putting work energy principle for 1st 2 kg block -mSsincrcosa @
M.^ ilrtir"
when come to rest
x (o)2 .(;), 2x (0.2)2 - lz^'s'lrsin2 cr "or' o1"'
(;),, = 2x1o x s1 -t-
|
L Cu+m)2asincr l
x 2x 0.2x 0.2 = 2x 0.2x 10 x 51 Now substituting the value of 'a' from equation (2),
= f+l
\2) we get
+ Sl =lcrn
Iz^'r2hsir2 o . .or2,, (M +m) 1"'
Puning work energy principle for 4 kg block =[*
'u * rf ,in o 'g ti' o (M.,- - tin,o)]
(;), -, (o)2 -(i)' 4x (0.4)2
=-4x
0.2x 10x 52 or u* =l
- ^'rn "" Y , )"'
:+ 2xO.4x 0.4= 4x0.2x 10x 52
Lf, * m) (M + sin2 m a;.1
+ 52 =4cm 9.61. The mass'm'is given a velocity ?'over the larger mass
M
Distance between 2 kg and 4 kg block = Sr + 52
(a) When the smaller block is travelling on the
=1+4=5crn vertical paft, let the velocity of the bigger block be v1
9.60. The block 'm' will slide down the inclined plane of towards left.
mass M with acceleration o1 = g sin o (relative) to the
From law of conservation of momentum (in the
inclined plane.
horizontal direction)
The honzontal component of a1 will be
mv=(M+m)v1
dx = g sin o cos cr, for which the block M will
accelerate towards left. Let the acceleration be a2.
= u7=L
According to the concept of centre of mass, (in the
M+m
horizontal direction external force is zero), (b) When the smaller block breaks off, left its
frex =(M + m) a2 resultant velocity is v2
From law of a conservation of energy
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
9.16 Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision
Ranchi -1
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
9835508812
in its
G)^* =(l)*"'
.(l)^",' + mgh
So, t}te time for which the smaller block was
flight is grven by,
:) u22 =y2 -A-ur' -rnn ...(1)
m
f -- c 1
= u22 =u21,-4 . ^o ^l-Wn
L m (M+m)")
= u, = l[(^' * t't^ *-^')] - run1"' +"osnf
L + m)'
tita J
.r
r -*' 8L -ztu
=zl=_-zlMv2
(M+m) l
(c) Now, the vertical component of the velocity v2 of
mass'm'is given by So, the distance travelled by the bigger block during
this time is
ur' =u22 -ut2
S =y1T
(M2 +Mm+m2) , nr 2 2 (M : m) sh)1/2
(M + m)'
^212
(M + m)2 =M+m8"- lMvz -
(M*d1/2
f = ^, I
- W fMu2 - 2(M + m) ghTr/2
L"'" M.^)
I(M + m'frz
+ !y-zM2
+Mm+^2 -^2 v2 - ?.gh 9.62.Givenh<<<R
-u"-zgh- =
(M +m)
Gmass=6x1024kg
+ ur' = -!t- -wn ...(2) mb =3x 1024 kg
Let V, -+ Velocity of earth
To find the maximum height (from the ground),
V6 + Velocity of the block
Let us assume the body rise to a high 'h' over and
The two blocla are attracted by gravitational force of
above'h' atffaction. The gravitation potential enerry stored
Now, (i)^"; =msht will be the K.E. of two blocks
+ hr=t
GM,m6+n
*.[;J # =(1)^,"",,
2g
.(i)*o "'o'
So, Total height =h + ht =h,u *'!^' Again as the an internal force acts
Mu'
=h * -h ...(4) M"V, =M6V6
(M + m) ?.9
+ =Mbvb
v."M" ...(2)
[From equation (3) and (a)]
u_ Mv2 Putting in equation (1)
(d)
2e(M+m)
Because the smaller mass has also got a horizontal
Gm" x *,1#, rh] =(;), *, -W
component of velocity 'lr' at the time it break off from
.M (which has a velocity vr), the block'm'will again . (1). M6 x v]
land on the block'M (bigger one)
Let us find out the time of flight of block 'm' after
breaks off.
it =(i)' M6 x v62
W.), u6,,62
During the upward motion (BC)
+ GM,
2R + ?h -2R -h
0=yv -8t (2R+h)(R-h)
- tt=;=;l#^ *'] ...(s) =(;)""'[i;#.';
[From equation (2)]
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
OFFICE AT 606 R. K. MALIK' S RANCHI CENTRE :
6TH FLOOR , NEWTON CLASSES 606, 6th Floor,
Hariom Tower,
HARIOM TOWER JEE ( MAIN & ADV.), MEDICAL + BOARD Circular Road,
Ranchi -1
Ph.: 0651 - 2562523,
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum Collision 9835508812
9.17
=w]=(;) ",;"(1) :+ v12 sin2 o. + v22 sin2 p +
Zvf 2 cos o cos B
cos o cos p
+ sn =vrz
" *(2\
\z)
+ sinosin0=cosocosp
+ cos0,. cosp-sin o cos0=0
+ vu =28h :+ cos(o+9)=0=cos90o
3 + a + p=99"
9.63. Since it is not a head on collision the tr /o bodies move
9.64. Let the mass of both the particle and the spherical
in different dimensions body be 'm', the particle velocity !, has two
Let v1, v2 + velocities of the bodies vector collision components y cos o normal to the sphere and y sin a
Since, the collision is elastic. Applyrng law of tangential to the spheres.
conservation of momentum on X = direction After the collision, they will exchange their velocities.
mpt + 171 X sr = mv1 COs o + mv2 COS p So, t}re spherical body will have a velocity v cos q, and
+ v1 cos d * v2 cos p - u1 ...(1) the particle will not have anycomponent of velocityin
this direction.
Puning law of conservation of momentum in y
direction [This collision will be due to the component y cos a in
the normal direction. But, the tangential velocity, of
0=ftyl sillc v2 sin p ...(2) the particle y sin a will be unaffeaed.l
Again (i)*r, * o =[1),.,,2 .(i)^ - *,
",' So, velocity ofthe sphere .o, o - 'r -p2
+ ur2 =vr2 +v22 ...(3) t.
and velocity of the particle = y sin a =
Squaring equation (1) r
v12 + v22 =v12 cos2 o. + v22 cos2 p+ zvf 2
o
FOR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS OF STUDY RESOURCES ,
CHAPTERWISE IMP NOTES ,QUESTION BANK , CONCEPT MAPS , CHAPTERWISE TEST PAPERS ,
NCERT AND OTHER REFRENCE TEXTBOOK SOLUTIONS VISIT NEWTONCLASSES.NET
NEWTONCLASSES.NET
Você também pode gostar
- Ion Beams for Materials AnalysisNo EverandIon Beams for Materials AnalysisR. Curtis BirdAinda não há avaliações
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYAinda não há avaliações
- ComDocumento43 páginasComPranay KishoreAinda não há avaliações
- Matthew 271123 Review PASDocumento6 páginasMatthew 271123 Review PASmsyahrulramdan050199Ainda não há avaliações
- Mole ConceptDocumento185 páginasMole ConceptladenkristenAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTDocumento1 páginaChapter 11, Solution 15.: DV A KT DT DV V DV KT DTLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATAAinda não há avaliações
- Nguyenkhuyen - G.HK2Documento2 páginasNguyenkhuyen - G.HK2Hiếu PhanAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1 Gaussian EliminationDocumento1 páginaAssignment 1 Gaussian EliminationTolga UZUNERAinda não há avaliações
- 2do Trabajo de Analisis EstructuralDocumento7 páginas2do Trabajo de Analisis EstructuralOscar Piero Clemente LlancariAinda não há avaliações
- Solutions Solution - 6bDocumento10 páginasSolutions Solution - 6bapi-26658409Ainda não há avaliações
- 33i Graficki RadDocumento12 páginas33i Graficki RadSead MavricAinda não há avaliações
- Ahmad Ardian Satya Nagar Studio Perancangan Arsitektur 5Documento3 páginasAhmad Ardian Satya Nagar Studio Perancangan Arsitektur 5Ardian Nanda PradapaAinda não há avaliações
- Core Solution P-6Documento10 páginasCore Solution P-6Ahana Singh XI S5Ainda não há avaliações
- ME VibrationDocumento2 páginasME VibrationRichmond OlarteAinda não há avaliações
- HT Cs 22156Documento5 páginasHT Cs 22156Carlos SosaAinda não há avaliações
- GR 9 Maths Eng - MediumDocumento6 páginasGR 9 Maths Eng - MediummlmihjazAinda não há avaliações
- Chegg Esfuerzos PrincipalesDocumento4 páginasChegg Esfuerzos PrincipalesGuillermo DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Report: Rotor On Flexible Supports: 1. Free Body Diagram of The SystemDocumento3 páginasReport: Rotor On Flexible Supports: 1. Free Body Diagram of The SystemGiovanni LabriniAinda não há avaliações
- EsercitazioneDocumento12 páginasEsercitazioneAres D'AbramoAinda não há avaliações
- HW 10 MarchDocumento6 páginasHW 10 MarchEgor SemenovAinda não há avaliações
- 2002 Oct-2019Documento3 páginas2002 Oct-2019Rohith A ThomasAinda não há avaliações
- Vibrations: D. Energy Methods E. Undamped Forced Vibrations F. Damped Free Vibrations G. Damped Forced VibrationsDocumento13 páginasVibrations: D. Energy Methods E. Undamped Forced Vibrations F. Damped Free Vibrations G. Damped Forced VibrationsJitendra ItankarAinda não há avaliações
- Matma Akcja 1Documento8 páginasMatma Akcja 1natlinertAinda não há avaliações
- UPSC Question Paper-II (2022)Documento7 páginasUPSC Question Paper-II (2022)ARYA AROHIAinda não há avaliações
- Mathematics 2022 P2Documento7 páginasMathematics 2022 P2rd1412901995Ainda não há avaliações
- CHP 3 Solutions PDFDocumento31 páginasCHP 3 Solutions PDFTalha NasirAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 12 - ComputationalDocumento12 páginasChapter 12 - ComputationalBen SzapiroAinda não há avaliações
- HarmonicDocumento3 páginasHarmonicREMO MosesAinda não há avaliações
- 1a-System of Particles and Rigid Body Dynamics (1-50)Documento50 páginas1a-System of Particles and Rigid Body Dynamics (1-50)Kartik SurwaseAinda não há avaliações
- ДоклDocumento2 páginasДоклAlexey KaliberdaAinda não há avaliações
- ComplexNumbers Ex2Documento3 páginasComplexNumbers Ex2Ashani RayAinda não há avaliações
- H:K Ne - Aub Interuald: Ftod O5n) +3 (%+8 +Y - )Documento21 páginasH:K Ne - Aub Interuald: Ftod O5n) +3 (%+8 +Y - )Y20me135 V.LokeshAinda não há avaliações
- System of Particles Lec 1Documento5 páginasSystem of Particles Lec 1Purav PillaiAinda não há avaliações
- Taller Electricidad y MagnetismoDocumento1 páginaTaller Electricidad y MagnetismoJuan Barragan CarrascoAinda não há avaliações
- Taller Electricidad y MagnetismoDocumento1 páginaTaller Electricidad y MagnetismoJuan Barragan CarrascoAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrolycs QN and Ans.Documento10 páginasHydrolycs QN and Ans.AyebareAinda não há avaliações
- HCV - HintsDocumento15 páginasHCV - HintsSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- PaprDocumento5 páginasPaprShubham MauryaAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Fin Sist 2°Documento3 páginas2 Fin Sist 2°Shaneth Magali Chambi LimachiAinda não há avaliações
- مهندس برق قدرت تولیدDocumento8 páginasمهندس برق قدرت تولیدMalek KamelAinda não há avaliações
- SPA5304 Physical Dynamics Solution 6: (20 Marks + 5 Bonus)Documento4 páginasSPA5304 Physical Dynamics Solution 6: (20 Marks + 5 Bonus)Roy VeseyAinda não há avaliações
- Relativistic QMDocumento21 páginasRelativistic QMI m mortal Beast ytAinda não há avaliações
- Exam Question Complex AnalysisDocumento3 páginasExam Question Complex AnalysisJaZz SFAinda não há avaliações
- Form 5: Chapter 20 (Motion Along A Straight Line) SPM Practice Fully-Worked SolutionsDocumento4 páginasForm 5: Chapter 20 (Motion Along A Straight Line) SPM Practice Fully-Worked SolutionsTohsi AkiAinda não há avaliações
- 01-Centre of MassDocumento19 páginas01-Centre of MassDeborshi ChakrabartiAinda não há avaliações
- Seance 1Documento23 páginasSeance 1cwcwcwcwcwcwcacAinda não há avaliações
- Governors & Cams SolutionsDocumento1 páginaGovernors & Cams Solutionsraghu.entrepreneurAinda não há avaliações
- Solution 854457Documento8 páginasSolution 854457sujinAinda não há avaliações
- HW5 SolutionDocumento7 páginasHW5 SolutionMuhammad Saqib IrshadAinda não há avaliações
- StoikiometriDocumento6 páginasStoikiometriRafa MufidahAinda não há avaliações
- Mai Nhat Thong - BTVN 03Documento5 páginasMai Nhat Thong - BTVN 03THÔNG MAI NHẬTAinda não há avaliações
- Nov7 PDFDocumento6 páginasNov7 PDFMohamed SayedAinda não há avaliações
- MATH 1150 - Assign #10Documento1 páginaMATH 1150 - Assign #10Anthony BasantaAinda não há avaliações
- Adobe Scan 24 Nov 2023Documento15 páginasAdobe Scan 24 Nov 2023Akshith IsolaAinda não há avaliações
- Tarea 12 CMDocumento4 páginasTarea 12 CMMargarito Robles KingAinda não há avaliações
- MODUL 2 - Balok Diatas Dua PerletakanDocumento11 páginasMODUL 2 - Balok Diatas Dua PerletakanYohanes SiagianAinda não há avaliações
- ′ ′ ′ k+k m m k+k k m k m m g ω k k m (k ω −λ m k E π λT −tDocumento1 página′ ′ ′ k+k m m k+k k m k m m g ω k k m (k ω −λ m k E π λT −tahmadAinda não há avaliações
- Centre of Mass: System of Particles and Rigid Body DynamicsDocumento28 páginasCentre of Mass: System of Particles and Rigid Body DynamicsSarath BabuAinda não há avaliações
- ′ ′ ′ k+k m m k+k k m k m m g ω k k m (k ω −λ m k E π λT −tDocumento1 página′ ′ ′ k+k m m k+k k m k m m g ω k k m (k ω −λ m k E π λT −tahmadAinda não há avaliações
- DR Travhtatoy: Epuc+LyDocumento6 páginasDR Travhtatoy: Epuc+Lymuhammad adnielAinda não há avaliações
- Waves Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento31 páginasWaves Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- System of Particles and Rotational Dynamics Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento42 páginasSystem of Particles and Rotational Dynamics Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetic Theory Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento22 páginasKinetic Theory Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Thermodynamics Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento22 páginasThermodynamics Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Oscillations Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento33 páginasOscillations Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Laws of Motion Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento41 páginasLaws of Motion Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Work, Energy and Power Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento44 páginasWork, Energy and Power Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento30 páginasMechanical Properties of Fluids Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Gravitation Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento27 páginasGravitation Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Properties of Solids Worksheet (Fully Solved)Documento25 páginasMechanical Properties of Solids Worksheet (Fully Solved)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Organic Compounds Containing NitrogenDocumento35 páginasOrganic Compounds Containing NitrogenSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- The D - and F - Block ElementsDocumento18 páginasThe D - and F - Block ElementsSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Motion in A PlaneDocumento33 páginasMotion in A PlaneSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Physical World and MeasurementDocumento23 páginasPhysical World and MeasurementSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Coordination CompoundsDocumento32 páginasCoordination CompoundsSaksham100% (1)
- The P-Block ElementsDocumento43 páginasThe P-Block ElementsSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of ElementsDocumento13 páginasGeneral Principles and Processes of Isolation of ElementsSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical KineticsDocumento44 páginasChemical KineticsSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocumento38 páginasAlcohols, Phenols and EthersSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocumento30 páginasHaloalkanes and HaloarenesSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Electrostatistics (Practice Questions PDFDocumento32 páginasElectrostatistics (Practice Questions PDFSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Gravitation (Practice Questions)Documento17 páginasGravitation (Practice Questions)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Magnetics (Practice Questions)Documento23 páginasMagnetics (Practice Questions)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Spontaneity of Chemical ReactionsDocumento12 páginasSpontaneity of Chemical ReactionsSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- SolutionsDocumento24 páginasSolutionsSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Rotational Motion (Practice Questions PDFDocumento46 páginasRotational Motion (Practice Questions PDFSakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Simple Harmonic Motion (Practice Questions)Documento29 páginasSimple Harmonic Motion (Practice Questions)SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Colloids: Office.: 606, 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1, PH.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968Documento16 páginasColloids: Office.: 606, 6th Floor, Hariom Tower, Circular Road, Ranchi-1, PH.: 0651-2562523, 9835508812, 8507613968SakshamAinda não há avaliações
- Volare Questions PerformanceDocumento43 páginasVolare Questions Performance734100% (1)
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocumento6 páginasLaws of ThermodynamicszzaanAinda não há avaliações
- Part List of Main SubstationDocumento6 páginasPart List of Main SubstationFatholla SalehiAinda não há avaliações
- AC40B AmprobeDocumento2 páginasAC40B Amprobeboba78Ainda não há avaliações
- Instruction Manual Portable LP400 - LP500 - LP600 - LP700 - LP850 - LP1000Documento41 páginasInstruction Manual Portable LP400 - LP500 - LP600 - LP700 - LP850 - LP1000Carlos U. CallirgosAinda não há avaliações
- Origin of Quantum Physics From Atomic Physics by SN GhoshalDocumento13 páginasOrigin of Quantum Physics From Atomic Physics by SN Ghoshalsanasniraj37Ainda não há avaliações
- Report On Thermal Power PlantDocumento39 páginasReport On Thermal Power PlantRajatAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Physics PDFDocumento91 páginas6 Physics PDFKervDhanKervAinda não há avaliações
- Dimmer CircuitDocumento10 páginasDimmer CircuitMd. Azizul Haque 180235Ainda não há avaliações
- Power Consumption in Agitated VesselDocumento4 páginasPower Consumption in Agitated VesselRoronoaAinda não há avaliações
- Sound WavesDocumento26 páginasSound Wavesthinkiit100% (5)
- Stepmotor CTDocumento16 páginasStepmotor CTPeter SimpsonAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 5Documento10 páginasAssignment 5AthreyaAinda não há avaliações
- Amperes Law of ForceDocumento4 páginasAmperes Law of ForceAli khan7Ainda não há avaliações
- Phys 1011-Chapter 3Documento49 páginasPhys 1011-Chapter 3melaku zegeyeAinda não há avaliações
- List Mov & Pov Ujp PNSDocumento78 páginasList Mov & Pov Ujp PNSBenny NaibahoAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Mark (ED Questions)Documento26 páginas2 Mark (ED Questions)Pradeep ravichanderAinda não há avaliações
- Chiller IQ Checklist - 2021.05Documento2 páginasChiller IQ Checklist - 2021.05Yu-Chih PuAinda não há avaliações
- Work Energy, Pressure, Turning EffectDocumento8 páginasWork Energy, Pressure, Turning EffectShad BegumAinda não há avaliações
- Cable & Wire Sizing CalculationDocumento2 páginasCable & Wire Sizing CalculationVijai PrasathAinda não há avaliações
- 1i Cot Due To DensityDocumento2 páginas1i Cot Due To DensityShankar SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Digsilent Powerfactory: Technical Reference DocumentationDocumento19 páginasDigsilent Powerfactory: Technical Reference DocumentationAlexAinda não há avaliações
- Gemetory & Mensuratin Solve PaperDocumento8 páginasGemetory & Mensuratin Solve PaperABHIMAN BHARTIAinda não há avaliações
- DocxDocumento5 páginasDocxelbronAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5Documento4 páginasLab 5Akay HanafiahAinda não há avaliações
- Zaengl Spectroscopy TheoryDocumento15 páginasZaengl Spectroscopy TheoryArpan PradhanAinda não há avaliações
- Sabic B52-E02Documento20 páginasSabic B52-E02viveik_mudgalAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Standard of Electricity Supply Services of TNB (2nd Edition) 1Documento10 páginasPerformance Standard of Electricity Supply Services of TNB (2nd Edition) 1Mohamad AzliAinda não há avaliações
- A Current-Tripler DC-DC Converter PDFDocumento8 páginasA Current-Tripler DC-DC Converter PDF李漢祥Ainda não há avaliações