Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
High-Pass CR Circuit: 3.4.1 Solution
Enviado por
Rafael FeitosaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
High-Pass CR Circuit: 3.4.1 Solution
Enviado por
Rafael FeitosaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
book Mobk059 March 9, 2007 10:21
TRANSIENT CIRCUITS AND LAPLACE TRANSFORMS 25
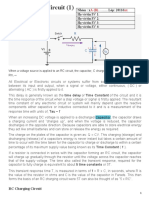
FIGURE 3.3: High-pass CR circuit
a component that is not connected to the ground reference point, such as the voltage across the
capacitor. Select the PSpice/Markers/ Voltage Differential to place two consecutive markers,
where one marker has a plus symbol and the other has a negative symbol (or use the icons from
the top marker icon toolbar).
Apply the Laplace transform and obtain expressions for the capacitor and resistor voltages.
We may obtain current or voltage expressions in time using the inverse Laplace transform table
given in the appendix. After simulation, compare your calculations to the simulation results for
currents and voltages evaluated at certain times. The Sw tClose switch part from the eval.olb
library is closed at time t = 0 s (Assume the capacitor is initially uncharged). Evaluate the
capacitor voltage at t = 5 s, where V 1 = 10 V, R1 = 2 , C = 1 F. Capacitance entered in
PSpice as 1 F (no space between the number and the unit) is interpreted as 1 Femto farads—a
much smaller capacitor, so leave out the F symbol.
3.4.1 Solution
The first switch, sw tClose, closes at a certain time (Note: the sw tOpen switch opens at a
specified time). DLclick the sw tClose part to set the following parameters:
Time to close = TCLOSE = 0 s,
Transient time = TTRAN = 1 us,
Switch resistance when closed = RCLOSED = 0.01 , and
Switch resistance when opened = ROPEN = 1 Meg
Other mechanical switches are available in the discrete.olb library. The voltage across the
capacitor increases exponentially because the current into the capacitor accumulates charge on
the capacitor plates. The capacitor current, however, decreases exponentially with time because
the capacitor voltage that is building up with time opposes the source voltage. The circuit time
constant, τ = CR, is the time it takes for the capacitor voltage to charge up to 63 % of the applied
step voltage. The time constant is also found by extrapolating the initial slope of the capacitor
voltage with a straight line until it intersects a line drawn across from the final capacitor voltage
to the y-axis. The time constant τ is then measured by dropping a perpendicular line from
Você também pode gostar
- Alternating Current CircuitsDocumento8 páginasAlternating Current CircuitsShafiq HafizullahAinda não há avaliações
- The RC Circuit: TheoryDocumento4 páginasThe RC Circuit: TheoryCanh LuongtienAinda não há avaliações
- Capacitance in A RC CircuitDocumento5 páginasCapacitance in A RC CircuitkanchankonwarAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5 - Time Constant of RC CircuitsDocumento4 páginasLab 5 - Time Constant of RC CircuitshamzaAinda não há avaliações
- Charging and DischargingDocumento38 páginasCharging and DischargingUmar M UmarAinda não há avaliações
- Capacitance Is The Ability of A Body To Store An Electrical ChargeDocumento6 páginasCapacitance Is The Ability of A Body To Store An Electrical Chargeankita071291Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab 01 Exponential FuntionDocumento9 páginasLab 01 Exponential FuntionfarhanAinda não há avaliações
- PHYS 2426 Lab 7 - The RC Circuit - ManualDocumento6 páginasPHYS 2426 Lab 7 - The RC Circuit - Manualwhatis you nameAinda não há avaliações
- RC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitDocumento12 páginasRC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitKrishanu ModakAinda não há avaliações
- AP Physics C - RC CircuitsDocumento20 páginasAP Physics C - RC CircuitsnalinigeeAinda não há avaliações
- Capacitance and Uses of CapacitorsDocumento6 páginasCapacitance and Uses of CapacitorsyogocAinda não há avaliações
- LabReport 3 FinaleDocumento16 páginasLabReport 3 FinaleChiara CalvoAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment Physic RC CircuitDocumento7 páginasExperiment Physic RC CircuitLia XeraAinda não há avaliações
- DE UNIT 3 Timing Circuit and OscillatorsDocumento29 páginasDE UNIT 3 Timing Circuit and Oscillatorsjosephryanbeloria45Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Documento11 páginasLab 06 RC, RL, and RLC Transients-2Ece KayaAinda não há avaliações
- Transfer FunctionDocumento15 páginasTransfer FunctionVarli ArsolAinda não há avaliações
- 242 Lab-1Documento6 páginas242 Lab-1George PaceAinda não há avaliações
- CSE250 Lab Exp 8 Simulation TransientDocumento10 páginasCSE250 Lab Exp 8 Simulation TransientArefin MahinAinda não há avaliações
- The RC Circuit: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocumento8 páginasThe RC Circuit: Pre-Lab QuestionsMd. Sazidul Haque SazzadAinda não há avaliações
- RC Circuits and The Oscilloscope: ObjectiveDocumento13 páginasRC Circuits and The Oscilloscope: Objectiveআব্দুল্লাহ আল ইমরানAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 6 - RC CircuitsDocumento9 páginasLab 6 - RC Circuitsmalik awaisAinda não há avaliações
- Capacitors: The Impedance of A CapacitorDocumento4 páginasCapacitors: The Impedance of A Capacitornavinchopra1986Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab 01-Transient Response of A Series RC CircuitDocumento4 páginasLab 01-Transient Response of A Series RC CircuitAly HuzmurAinda não há avaliações
- Circuit Theory LabDocumento9 páginasCircuit Theory LabSoorya Priya Gopala KrishnaAinda não há avaliações
- 21 RccirDocumento7 páginas21 Rcciracademic19Ainda não há avaliações
- The Study of DC Transients in RC CircuitDocumento2 páginasThe Study of DC Transients in RC CircuitNur Muhammad Alif RamliAinda não há avaliações
- RC Charging CircuitDocumento6 páginasRC Charging CircuitNguyen Tran Quoc TuanAinda não há avaliações
- Time Constant RCDocumento9 páginasTime Constant RCHassan M Khan0% (1)
- RC Charging CircuitDocumento43 páginasRC Charging Circuitleonard1971Ainda não há avaliações
- Capacitive Reactance Lab1Documento9 páginasCapacitive Reactance Lab1Hazel HinaiAinda não há avaliações
- Eee Lab Report 07Documento11 páginasEee Lab Report 07Sayeed MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- The Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesDocumento9 páginasThe Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesyashsviAinda não há avaliações
- The Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesDocumento9 páginasThe Time Constant of An RC Circuit: 1 ObjectivesSGSAinda não há avaliações
- RC CircuitDocumento3 páginasRC CircuitShlôkä JõshïAinda não há avaliações
- The RC Series CircuitDocumento7 páginasThe RC Series CircuitRhea DaisonAinda não há avaliações
- CapacitorsDocumento5 páginasCapacitorsluis casasAinda não há avaliações
- RC CircuitDocumento5 páginasRC CircuitSatish BunnyyAinda não há avaliações
- ALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"Documento39 páginasALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"api-19788618Ainda não há avaliações
- Capacitors in Series and Parallel and The Time Constant RC: 1 Purpose of Experiment 10Documento0 páginaCapacitors in Series and Parallel and The Time Constant RC: 1 Purpose of Experiment 10Jaiprasad ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5Documento3 páginasLab 5willstamp2003Ainda não há avaliações
- Lecture 10: Passive Circuit Elements: Capacitors and RC CircuitsDocumento8 páginasLecture 10: Passive Circuit Elements: Capacitors and RC CircuitsHuzaifa RehanAinda não há avaliações
- P Iv P I ( - Ir)Documento19 páginasP Iv P I ( - Ir)John Angelo ManaloAinda não há avaliações
- Lab No. # 11 Transient Response Analysis of Series RC CircuitDocumento6 páginasLab No. # 11 Transient Response Analysis of Series RC CircuitWaqas AmeenAinda não há avaliações
- CaoacitanceDocumento6 páginasCaoacitanceHassan KenjrawyAinda não há avaliações
- Capacitor PDFDocumento5 páginasCapacitor PDFsathyakalyanAinda não há avaliações
- RC CircuitsDocumento35 páginasRC CircuitsRufat SafaraliyevAinda não há avaliações
- 241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceDocumento14 páginas241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceWsma AmswAinda não há avaliações
- IC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsDocumento11 páginasIC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsKaran YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Dctoac: DT T DV C T IDocumento6 páginasDctoac: DT T DV C T IMichael LeinerAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 5Documento21 páginasLab 5Sindbad HooAinda não há avaliações
- Time Delay CircuitDocumento16 páginasTime Delay CircuitJBS SPOBIAinda não há avaliações
- RC ChargingDocumento6 páginasRC ChargingkaushalAinda não há avaliações
- RC RL RLC 3.0 PDFDocumento13 páginasRC RL RLC 3.0 PDFlp_blackoutAinda não há avaliações
- Astable MultivibratorDocumento146 páginasAstable Multivibratorsantovaron123Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab 5 - Phys2150 - Muskaan, RyanDocumento4 páginasLab 5 - Phys2150 - Muskaan, Ryanmusy1233Ainda não há avaliações
- Lab5 2Documento21 páginasLab5 2Sindbad HooAinda não há avaliações
- Abu Hashim1999Documento9 páginasAbu Hashim1999Rafael FeitosaAinda não há avaliações
- Energy Efficiency and Power Quality in Low IncomeDocumento6 páginasEnergy Efficiency and Power Quality in Low IncomeRafael FeitosaAinda não há avaliações
- Kaw Ann 1996Documento7 páginasKaw Ann 1996Rafael FeitosaAinda não há avaliações
- ProteusDocumento3 páginasProteusRafael FeitosaAinda não há avaliações
- Is There A Paper On The OpenDSS Solution Method - OpenDSSWikiDocumento2 páginasIs There A Paper On The OpenDSS Solution Method - OpenDSSWikiRafael FeitosaAinda não há avaliações
- How Do I Register The COM Server DLL On Windows 7 - OpenDSSWikiDocumento1 páginaHow Do I Register The COM Server DLL On Windows 7 - OpenDSSWikiRafael FeitosaAinda não há avaliações
- Can I Do Unbalanced Power Flow?Documento2 páginasCan I Do Unbalanced Power Flow?Rafael FeitosaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Concept of GeneratorsDocumento120 páginasBasic Concept of GeneratorszakalyAinda não há avaliações
- Conceptual Physics Equation SheetDocumento2 páginasConceptual Physics Equation SheetjeremytimmonsAinda não há avaliações
- Class 11Th Physics Yt - Padhai Ak Mazza Magic HandbookDocumento492 páginasClass 11Th Physics Yt - Padhai Ak Mazza Magic Handbookaarohibhatt285Ainda não há avaliações
- CHEM1001 Worksheet 4: Moles and Stoichiometry Model 1: Balancing Chemical EquationsDocumento4 páginasCHEM1001 Worksheet 4: Moles and Stoichiometry Model 1: Balancing Chemical EquationsEllah Mae CaguladaAinda não há avaliações
- PHYSICS-08 13th (Z) CLASS TESTDocumento3 páginasPHYSICS-08 13th (Z) CLASS TESTRaju SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Design A ThermosDocumento4 páginasDesign A Thermosapi-491143171Ainda não há avaliações
- Why Are Q and Q Used To Symbolize Heat?: Chemistry For EveryoneDocumento1 páginaWhy Are Q and Q Used To Symbolize Heat?: Chemistry For EveryoneEzephusAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 Theory of MachinesDocumento21 páginasChapter 1 Theory of Machinesmunim matinAinda não há avaliações
- Fem Analysis of Jack-Up Spudcane Penetration PDFDocumento10 páginasFem Analysis of Jack-Up Spudcane Penetration PDFSơn Nguyễn-LêAinda não há avaliações
- Conclusion 6&7Documento1 páginaConclusion 6&7David AquinoAinda não há avaliações
- Reinforcement Bond Capacity: Jewell, R. A. (1990) - Gcotechnique 40, No. 3,51Q8Documento6 páginasReinforcement Bond Capacity: Jewell, R. A. (1990) - Gcotechnique 40, No. 3,51Q8Saleh HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Equilibrium: The Concept of EquilibriumDocumento20 páginasChemical Equilibrium: The Concept of Equilibriumshashank shriAinda não há avaliações
- Heat 3: Class-VIII Physics Question BankDocumento28 páginasHeat 3: Class-VIII Physics Question BankSayantan ChakrabortyAinda não há avaliações
- CE363 Lab Book Eng Prop of Soils Bowles PDFDocumento249 páginasCE363 Lab Book Eng Prop of Soils Bowles PDFFurkan YılmazAinda não há avaliações
- LyophilizationDocumento64 páginasLyophilizationmeghanadl100% (1)
- Arshad 2020Documento13 páginasArshad 2020ramesh tAinda não há avaliações
- FG29 fm1Documento12 páginasFG29 fm1yassinebouazziAinda não há avaliações
- General CatalogDocumento20 páginasGeneral CatalogFlorin Petri100% (1)
- Neet Full Mock TestDocumento31 páginasNeet Full Mock Testdhanan dhanan100% (2)
- Directions in Ferrohydrodynamics (Invited) PDFDocumento7 páginasDirections in Ferrohydrodynamics (Invited) PDFivan celyAinda não há avaliações
- CHE-221: Fluid Mechanics-I: Dr. Zaib JahanDocumento10 páginasCHE-221: Fluid Mechanics-I: Dr. Zaib JahanBilal JuttAinda não há avaliações
- 2020 - Sept25 - ME 004ADocumento15 páginas2020 - Sept25 - ME 004ADaniel ManivoughAinda não há avaliações
- Aet 2022 23 IDocumento1 páginaAet 2022 23 IRam RajAinda não há avaliações
- PE326Documento12 páginasPE326Ramy MaamounAinda não há avaliações
- GeoTech ProblemsDocumento25 páginasGeoTech Problemsev xvAinda não há avaliações
- Power in AC Circuit Lab ReportDocumento8 páginasPower in AC Circuit Lab ReportJEJUNG67% (3)
- Science - 2ND SummativeDocumento2 páginasScience - 2ND SummativeericksonAinda não há avaliações
- Kinematics DPP 2Documento2 páginasKinematics DPP 2Shahil AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- CapacitanceDocumento45 páginasCapacitanceraghu ramAinda não há avaliações
- Bulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersNo EverandBulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Pilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CNo EverandPilot's Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (2024): FAA-H-8083-25CAinda não há avaliações
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionNo EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (3)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedNo EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Basic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesNo EverandBasic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Cyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsNo EverandCyber-Physical Systems: Foundations, Principles and ApplicationsHoubing H. SongAinda não há avaliações
- Post Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&ANo EverandPost Weld Heat Treatment PWHT: Standards, Procedures, Applications, and Interview Q&AAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsNo EverandGas Turbines: A Handbook of Air, Land and Sea ApplicationsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (9)
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionNo EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (10)
- Corrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsNo EverandCorrosion and Materials in Hydrocarbon Production: A Compendium of Operational and Engineering AspectsAinda não há avaliações
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisNo EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Safety Theory and Control Technology of High-Speed Train OperationNo EverandSafety Theory and Control Technology of High-Speed Train OperationNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)
- Machinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionNo EverandMachinery's Handbook Pocket Companion: Quick Access to Basic Data & More from the 31st EditionAinda não há avaliações
- Laminar Flow Forced Convection in Ducts: A Source Book for Compact Heat Exchanger Analytical DataNo EverandLaminar Flow Forced Convection in Ducts: A Source Book for Compact Heat Exchanger Analytical DataAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeNo EverandElectrical (Generator and Electrical Plant): Modern Power Station PracticeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (9)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseNo EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (51)
- The Galactic Federation: Discovering the Unknown Can Be Stranger Than FictionNo EverandThe Galactic Federation: Discovering the Unknown Can Be Stranger Than FictionAinda não há avaliações
- Airplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)No EverandAirplane Flying Handbook: FAA-H-8083-3C (2024)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (12)
- Mechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringNo EverandMechanical Vibrations and Condition MonitoringNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- 1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideNo Everand1,001 Questions & Answers for the CWI Exam: Welding Metallurgy and Visual Inspection Study GuideNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (7)