Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
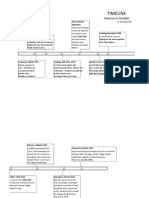
Date Belligerents Causes Important Events Consequences
Enviado por
RocbeaDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Date Belligerents Causes Important Events Consequences
Enviado por
RocbeaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
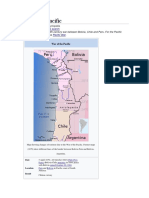
WAR OF THE PACIFIC
DATE BELLIGERENTS CAUSES IMPORTANT EVENTS CONSEQUENCES
It lasted Bolivia and Peru National borders in the On February 14, 1879 when Victory for Chile.
from vs. region had never been Bolivian authorities attempted to Chile got a significant
1879 to Chile definitively established. confiscate property of a Chilean amount of resource-rich
The discovery of valuable mining company, Chilean armed
1884. territory from Peru and
guano and nitrate deposits forces occupied the port city of
Bolivia.
in the disputed territories. Antofagasta.
Popular belief attributes
The guano and nitrate's On 1 March 1879 Bolivia declared
much of the Bolivia's
value as fertilizer and war on Chile and called on Peru
saltpeter's role in explosives, to activate their alliance.
problems to its
especially for Europeans. The Battle of Topáter, on March landlocked condition.
The region in conflict was 23, 1879.
populated mostly by On Oct. 20, 1883, Peru and Chile
Chileans. signed the Treaty of Ancón, by
The Bolivian government of which Tarapacá province was
President Hilarión Daza ceded to the latter.
decreed a backdated 1874 In 1884, Bolivia signed a truce,
tax of 10 centavos on Chilean the Treaty of Valparaiso, whereby
companies for the Bolivia accepted the military
exploitation of guano and occupation of the entire Bolivian
saltpeter. coast.
In 1904, Chile and Bolivia signed
the "Treaty of Peace and
Friendship" establishing definite
boundaries.
ACRE WAR
DATE BELLIGERE CAUSES IMPORTANT EVENTS CONSEQUENCES
NTS
Betwee Bolivia The Acre Region On January 2, 1899, Bolivia set The conflict
n 1899 vs. was rich in up a customs office in Puerto ended with the
and Brazil rubber and gold. Alonso , which upset the Brazilian
1903. From the end of Brazilian settlers; Bolivians victory and the
the 19th century were forced to leave the region. subsequent
until the middle Spaniard Luis Gálvez Treaty of
of the 20th Rodríguez de Arias proclaimed Petrópolis,
century, rubber the Republic of Acre on July which ceded
14, 1899. Acre to Brazil.
trees were crucial
Bolivia responded by sending a
to the automobile Bolivia gave up
force of 500 men.
and transport A Brazilian war flotilla reached Acre in
industry. Puerto Alonso, arrested Galvez exchange for
Acre aroused and dissolved the Republic of Brazilian
little interest for Acre. territory from
its inaccessibility ______________________________ the State of
and apparent lack In November 1900 there was Mato Grosso,
another rebellion in order to
of commercial the payment of
take Acre from Bolivia and
value. create an independent republic. 2 million and
The Acre Carvalho Rodrigo became the promise to
population was president of the newly declared construct the
composed of a Republic of Acre. Madeira-
small number of On June 11, 1901 Bolivia Mamoré
Indians without signed a lease with a Bolivian Railroad.
national identity Trading based in Jersey City,
New Jersey. (the company had
and a handful of
some very influential
Brazilians and shareholders: king of Belgium
Bolivians. and the president of the United
In the late 19th States)
century about Bolivia had given the company
18,000 almost total control over the
Acre province to protect its
adventurers and
sovereignty. Under the
settlers, most agreement, the group of U.S.
from Brazil, went and British capitalists would
to Acre to exploit assume total control over the
the rubber trees. region, occupying and
exploiting it for 30 years.
Brazil and Peru, which also
claimed the territory, strongly
disapproved of the lease act.
José Plácido de Castro came to
Amazon and led a second
uprising.
After many battles the
governments of Brazil and
Bolivia signed a preliminary
treaty on March 21, 1903.
Você também pode gostar
- The Pacific WarDocumento2 páginasThe Pacific WarVicky VargasAinda não há avaliações
- War of The Pacific WikiDocumento38 páginasWar of The Pacific WikiHernanAinda não há avaliações
- PeruchileDocumento20 páginasPeruchileapi-643527847Ainda não há avaliações
- Intro Ducci OnDocumento4 páginasIntro Ducci Oncielo balderramaAinda não há avaliações
- The War of the Pacific (1879-1883) - Chile vs. Bolivia and PeruNo EverandThe War of the Pacific (1879-1883) - Chile vs. Bolivia and PeruAinda não há avaliações
- Eduardo AbaroaDocumento1 páginaEduardo AbaroaCamila GutiérrezAinda não há avaliações
- Cavite MutinyDocumento21 páginasCavite MutinyMariel EstipularAinda não há avaliações
- The War in The Pacific Coast of South America 1879 - 81Documento83 páginasThe War in The Pacific Coast of South America 1879 - 81BibliomaniachilenaAinda não há avaliações
- 19th Century Philippines As Rizal's Context: Agrarian Relations and The Friar LandsDocumento38 páginas19th Century Philippines As Rizal's Context: Agrarian Relations and The Friar LandsVince Martin OrozcoAinda não há avaliações
- British Borneo: Sketches of Brunai, Sarawak, Labuan, and North BorneoNo EverandBritish Borneo: Sketches of Brunai, Sarawak, Labuan, and North BorneoAinda não há avaliações
- Copia de Puerto RicoDocumento12 páginasCopia de Puerto Riconicole.marchant.tsengAinda não há avaliações
- BACOOR CaviteDocumento1 páginaBACOOR CaviteGwen AgnesAinda não há avaliações
- South America Conflict1Documento1 páginaSouth America Conflict1Toronto StarAinda não há avaliações
- Agrarian ReformDocumento3 páginasAgrarian ReformFher CariagaAinda não há avaliações
- 16history6 Spain and The Portuguese EmpiresDocumento2 páginas16history6 Spain and The Portuguese EmpiresSzántó ErikaAinda não há avaliações
- Timeline of Land Dispossession and Segregation in South Africa 1800-1899Documento14 páginasTimeline of Land Dispossession and Segregation in South Africa 1800-1899AndrewAinda não há avaliações
- The Ibaloy Ibaloi People of The Philippines History, Culture, Customs and Tradition Philippine Indigenous PeopleDocumento52 páginasThe Ibaloy Ibaloi People of The Philippines History, Culture, Customs and Tradition Philippine Indigenous PeopleNhyjy Jones AwalAinda não há avaliações
- 5.1 Emilio ContinuationDocumento71 páginas5.1 Emilio ContinuationDianne Rose LopezAinda não há avaliações
- BS TransDocumento5 páginasBS TransAmanda Joy TuizaAinda não há avaliações
- Disputas Entre Y: Possidetis de 1810 (En El Caso de Maynas)Documento17 páginasDisputas Entre Y: Possidetis de 1810 (En El Caso de Maynas)Huber Callata TapiaAinda não há avaliações
- Age of Discovery1Documento17 páginasAge of Discovery1AlexfunnyAinda não há avaliações
- The Chaco WarDocumento4 páginasThe Chaco WaralcanturAinda não há avaliações
- Chap 8 - The Beginning of Filipino NationalismDocumento4 páginasChap 8 - The Beginning of Filipino NationalismPark Min YeonAinda não há avaliações
- Republic of Bolivia V Indemnity Mutual Marine Assurance Co 1909Documento11 páginasRepublic of Bolivia V Indemnity Mutual Marine Assurance Co 1909darthfafaloAinda não há avaliações
- Oxford JournalsDocumento11 páginasOxford JournalsPaulina ValenciaAinda não há avaliações
- History of Cavite CityDocumento4 páginasHistory of Cavite CitydeenaAinda não há avaliações
- The War of The PacificDocumento1 páginaThe War of The PacificAlejandro Nuñez AlvarezAinda não há avaliações
- Readings in Philippine History Compilation of LessonsDocumento8 páginasReadings in Philippine History Compilation of LessonsAngelyn Grace TanAinda não há avaliações
- 1969 Geoffrey Smith El Rol de Balmaceda en La GDPDocumento15 páginas1969 Geoffrey Smith El Rol de Balmaceda en La GDPJulio AbantoAinda não há avaliações
- Katutubo: Memory of Dances by Philippine Center For I Nvestigative JournalismDocumento4 páginasKatutubo: Memory of Dances by Philippine Center For I Nvestigative JournalismAulineu BangtanAinda não há avaliações
- Agrarian Relations and Friar Lands: Monique - Red Shaina - Orange Joshua - Blue Angelica - GreenDocumento15 páginasAgrarian Relations and Friar Lands: Monique - Red Shaina - Orange Joshua - Blue Angelica - GreenAngelica NavarroAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Agrarian Reform Policy PowerpointDocumento55 páginasPhilippine Agrarian Reform Policy PowerpointDeity Ann Reuterez100% (23)
- Bakaassi HistoryDocumento843 páginasBakaassi HistoryyooooAinda não há avaliações
- Group 6 Batch 2 BSTM101 TP Pre FinalDocumento66 páginasGroup 6 Batch 2 BSTM101 TP Pre FinalAngelica MotayAinda não há avaliações
- History of Cuba: Cuba Libre! Cuban History from Christopher Columbus to Fidel CastroNo EverandHistory of Cuba: Cuba Libre! Cuban History from Christopher Columbus to Fidel CastroAinda não há avaliações
- History of CaviteDocumento4 páginasHistory of CaviteMixsz LlhAdyAinda não há avaliações
- Timeline of CubaDocumento1 páginaTimeline of Cubaapi-453354340Ainda não há avaliações
- Cuba: Cuba Libre! 3 Manuscripts in 1 Book, Including: History of Cuba, Cuba Travel Guide and Havana Travel GuideNo EverandCuba: Cuba Libre! 3 Manuscripts in 1 Book, Including: History of Cuba, Cuba Travel Guide and Havana Travel GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostico Creoles en La CostaDocumento53 páginasDiagnostico Creoles en La CostaMarieliz RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Displacement of Indigenous Peoples and Land Conflicts in Baguio City: Legal Calamities Descended From Civil Reservation Case No. 1Documento25 páginasDisplacement of Indigenous Peoples and Land Conflicts in Baguio City: Legal Calamities Descended From Civil Reservation Case No. 1Cheryl L. Daytec-Yangot100% (3)
- Ipra Law For Pamb by VMBDocumento24 páginasIpra Law For Pamb by VMBVictor MarcAinda não há avaliações
- Cuba: Cuba Libre! 4 Manuscripts in 1 Book, Including: History of Cuba, History of Havana, Cuba Travel Guide and Havana Travel GuideNo EverandCuba: Cuba Libre! 4 Manuscripts in 1 Book, Including: History of Cuba, History of Havana, Cuba Travel Guide and Havana Travel GuideAinda não há avaliações
- Cuba. From Independence To RevolutionDocumento5 páginasCuba. From Independence To RevolutionTaaboAinda não há avaliações
- US Colonial PolicyDocumento38 páginasUS Colonial PolicyLeyn MarallagAinda não há avaliações
- Chaco War: Anglo Dutch Resource GrabDocumento3 páginasChaco War: Anglo Dutch Resource GrabJim McIntosh100% (1)
- The Wars of Independence - Brazilian IndepenceDocumento7 páginasThe Wars of Independence - Brazilian IndepenceVictoria Goulart NaderAinda não há avaliações
- Republic of Chile - Perú v. ChileDocumento18 páginasRepublic of Chile - Perú v. ChileNiccaPAinda não há avaliações
- Slavery and Emancipation in BZ by ISCR NICH PDFDocumento6 páginasSlavery and Emancipation in BZ by ISCR NICH PDFKeyana BelisleAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 2: Agrarian Reform and Legislation in The PhilippinesDocumento53 páginasActivity 2: Agrarian Reform and Legislation in The PhilippinesIan John MasotesAinda não há avaliações
- Tagalogs Bacoor Bay: History of CaviteDocumento5 páginasTagalogs Bacoor Bay: History of CaviteJP NielesAinda não há avaliações
- Metis: TimelineDocumento1 páginaMetis: Timelinee33498138Ainda não há avaliações
- Agrarian Reform FinalsDocumento5 páginasAgrarian Reform FinalsVernadel ApolloAinda não há avaliações
- Berlin Treaty Evolution of State AmalgamationpdfDocumento7 páginasBerlin Treaty Evolution of State AmalgamationpdfAbdullahi ChuwachuwaAinda não há avaliações
- History of Cuba: Cuba Libre! 2 Manuscripts in 1 Book, Including: History of Cuba and History of HavanaNo EverandHistory of Cuba: Cuba Libre! 2 Manuscripts in 1 Book, Including: History of Cuba and History of HavanaAinda não há avaliações
- Geographical Scenario of The Abya Yala or American ContinentDocumento5 páginasGeographical Scenario of The Abya Yala or American ContinentRocbeaAinda não há avaliações
- Geographical Scenario of The Abya Yala or American ContinentDocumento5 páginasGeographical Scenario of The Abya Yala or American ContinentRocbeaAinda não há avaliações
- THE ORIGIN OF HUMAN BEINGS LessonDocumento6 páginasTHE ORIGIN OF HUMAN BEINGS LessonRocbeaAinda não há avaliações
- National Identity WorksheetDocumento3 páginasNational Identity WorksheetRocbeaAinda não há avaliações
- Christmas Work-Revision 2nd BachDocumento11 páginasChristmas Work-Revision 2nd BachDragan SamardzicAinda não há avaliações
- Homework! Present Simple vs. Past SimpleDocumento4 páginasHomework! Present Simple vs. Past SimpleGabriela Ionela100% (1)
- Plantilla - Jornadas Aocphilips 24-09Documento72 páginasPlantilla - Jornadas Aocphilips 24-09Gustavo Umpire CabelloAinda não há avaliações
- Secret of The Andes 01 Origin of White Brotherhood of 7 RaysDocumento9 páginasSecret of The Andes 01 Origin of White Brotherhood of 7 RaysEvolucion del SerAinda não há avaliações
- Au G 47 Continents of The World Powerpoint - Ver - 9Documento10 páginasAu G 47 Continents of The World Powerpoint - Ver - 9Denisa BolboacaAinda não há avaliações
- Annona SquamosaDocumento10 páginasAnnona SquamosaAlarm GuardiansAinda não há avaliações
- MEDINA en El Bicentenario. Consideraciones en Torno Al Paradigma de F-X GuerraDocumento325 páginasMEDINA en El Bicentenario. Consideraciones en Torno Al Paradigma de F-X GuerraCarlos Eduardo Valencia VillaAinda não há avaliações
- Avance III - P.I. at FebreroDocumento28 páginasAvance III - P.I. at Febreroapuesta totalAinda não há avaliações
- World Flags - Flag Quiz GameDocumento1 páginaWorld Flags - Flag Quiz GameAva FarrellAinda não há avaliações
- Presentacion Charla Guido VildozoDocumento19 páginasPresentacion Charla Guido VildozoNatalia Nolasco TorresAinda não há avaliações
- LAFER, Celso, 2000. Brazilian International Identity and Foreign Policy PDFDocumento21 páginasLAFER, Celso, 2000. Brazilian International Identity and Foreign Policy PDFBruno PasquarelliAinda não há avaliações
- Yds Okuma Ceviri Kelime 3Documento22 páginasYds Okuma Ceviri Kelime 3nt100% (4)
- World Tourism GeographyDocumento29 páginasWorld Tourism GeographyJOHN CARLO SENDONAinda não há avaliações
- The Andes 6Documento5 páginasThe Andes 6mickAinda não há avaliações
- 126 29 2 2024Documento9 páginas126 29 2 2024rodrigo jacomeAinda não há avaliações
- Places and Landscapes in The Changing WorldDocumento5 páginasPlaces and Landscapes in The Changing WorldRaffy Jade Salazar100% (1)
- World GeographyDocumento49 páginasWorld GeographyAbhinandan Sawant100% (1)
- Colombia in EnglishDocumento26 páginasColombia in EnglishkellyAinda não há avaliações
- Port Schedules-20150123-122832 PDFDocumento6 páginasPort Schedules-20150123-122832 PDFmarceloestimuloAinda não há avaliações
- Mycological Contributions of Rolf SingerDocumento144 páginasMycological Contributions of Rolf SingerAmaterasuAinda não há avaliações
- Argentina Facts For KidsDocumento5 páginasArgentina Facts For Kidsexfireex1Ainda não há avaliações
- Pizarro Timeline 1Documento2 páginasPizarro Timeline 1api-391396721Ainda não há avaliações
- Latin America S International Relations and Their Domestic Consequences War and Peace, Dependency and Autonomy, Integration... (Jorge I. Domínguez (Editor) ) (Z-Library) PDFDocumento464 páginasLatin America S International Relations and Their Domestic Consequences War and Peace, Dependency and Autonomy, Integration... (Jorge I. Domínguez (Editor) ) (Z-Library) PDFCouscous SaucisseAinda não há avaliações