Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Table 1-4
Enviado por
merii0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
4 visualizações1 páginaThis document compares quantitative and qualitative research methods across several categories. Quantitative research aims to classify and measure attributes numerically to explain observations, using predetermined designs and instruments like questionnaires to collect numerical data. Qualitative research develops detailed descriptions of attributes with an emergent design, uses the researcher as the instrument to collect data like words and pictures, and provides rich but less generalizable meanings with greater researcher subjectivity and immersion.
Descrição original:
Título original
Table 1-4.docx
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document compares quantitative and qualitative research methods across several categories. Quantitative research aims to classify and measure attributes numerically to explain observations, using predetermined designs and instruments like questionnaires to collect numerical data. Qualitative research develops detailed descriptions of attributes with an emergent design, uses the researcher as the instrument to collect data like words and pictures, and provides rich but less generalizable meanings with greater researcher subjectivity and immersion.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
4 visualizações1 páginaTable 1-4
Enviado por
meriiThis document compares quantitative and qualitative research methods across several categories. Quantitative research aims to classify and measure attributes numerically to explain observations, using predetermined designs and instruments like questionnaires to collect numerical data. Qualitative research develops detailed descriptions of attributes with an emergent design, uses the researcher as the instrument to collect data like words and pictures, and provides rich but less generalizable meanings with greater researcher subjectivity and immersion.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 1
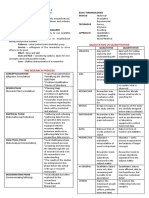
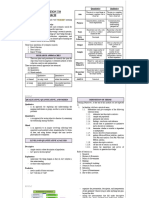
Table 1-4.
Comparison of Quantitative & Qualitative Research
CATEGORY QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Aim To classify the attributes of the subject of To develop a complete or detailed
study, count them, and construct statistical description of the attributes of the subject
models in an attempt to explain what is of the study.
observed.
Design All aspects of the study are carefully The design emerges as the study unfolds.
designed before the data are collected
Data-gathering Researcher uses tools, such as Researcher is the data gathering instrument.
Instrument questionnaires or instrument to collect
numerical data.
Types of data Data are in the form of numbers and Data are in the form of words, pictures or
statistics. objects.
Degree of Partiality Relatively objective as it seeks precise Relatively subjective since the individual’s
measurement and analysis of target interpretation of events is important,
concepts. especially when using participant
observation, in-depth interviews, and the
like.
Use of data Quantitative data is more efficient, able to Qualitative data is richer in meaning, but
test hypotheses, but may miss contextual time consuming, and less able to be
detail. generalized.
Researcher’s Researcher tends to remain objectively Researcher tends to become subjectively
participation separated from the subject matter. immersed in the subject matter.
Você também pode gostar
- How to Research Qualitatively: Tips for Scientific WorkingNo EverandHow to Research Qualitatively: Tips for Scientific WorkingAinda não há avaliações
- Acctg ResearchDocumento38 páginasAcctg ResearchDebbie Grace Latiban LinazaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 3 February 24 2021 Research ApproachesDocumento6 páginasTopic 3 February 24 2021 Research ApproachesCharlton Benedict Bernabe100% (1)
- Qualitative Versus Quantitative Research: Key Points in A Classic DebateDocumento2 páginasQualitative Versus Quantitative Research: Key Points in A Classic DebateGyle Contawe GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- 3.1 METHODOLOGY 3.1.1 Data Analysis The TimeDocumento22 páginas3.1 METHODOLOGY 3.1.1 Data Analysis The TimepsylentkillerAinda não há avaliações
- QualDocumento39 páginasQualaigerim kazhigaliyevaAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Quantitative: DefinationDocumento3 páginasQualitative Quantitative: DefinationMargo ShaezAinda não há avaliações
- Week 2Documento65 páginasWeek 2theresita raval100% (1)
- Research in Daily Life 2: Week 3Documento10 páginasResearch in Daily Life 2: Week 3Abegail PanangAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Research Woksheet 2Documento4 páginasPractical Research Woksheet 2Cedryk PapaAinda não há avaliações
- Research DesignDocumento45 páginasResearch Designsubashik100% (2)
- Research MethodologyDocumento31 páginasResearch MethodologySHANNEL ANN VILLUGAAinda não há avaliações
- Research Basic ConceptsDocumento22 páginasResearch Basic ConceptsRodAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Research & Quantitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQualitative Research & Quantitative ResearchChamali WeerasingheAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Versus Quantitative Research: Key Points in A Classic DebateDocumento6 páginasQualitative Versus Quantitative Research: Key Points in A Classic DebateKumarSriAmanAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1.1 What Is Quantitative ResearchDocumento5 páginasLesson 1.1 What Is Quantitative ResearchClyde EmmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- BM 33 RP Note 8Documento8 páginasBM 33 RP Note 8anFasAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Research 2 Humss 4Documento13 páginasPractical Research 2 Humss 4Oliver CarsolemAinda não há avaliações
- PR2 Exam Final ReviewerDocumento2 páginasPR2 Exam Final ReviewerMaksen LimAinda não há avaliações
- DLP LC1Documento18 páginasDLP LC1Carl AvilaAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Research I: 1 Semester - Module 3Documento13 páginasPractical Research I: 1 Semester - Module 3Reymart C. OmapasAinda não há avaliações
- RESEARCHSDocumento2 páginasRESEARCHSbequillokharelkeit2324Ainda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQuantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchKwennie Ann Pardo Rufino-GallegoAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitativevs Qualitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQuantitativevs Qualitative ResearchShahid khanAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitativevs Qualitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQuantitativevs Qualitative ResearchviperAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitativevs Qualitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQuantitativevs Qualitative ResearchNesanAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQuantitative vs. Qualitative ResearchAnn MasteralAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQuantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchMark Cañete PunongbayanAinda não há avaliações
- Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Stat - Andy FieldDocumento2 páginasDiscovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Stat - Andy Fieldfebty kuswantiAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative VS QuantitativeDocumento2 páginasQualitative VS Quantitativemayonaissedelight smoothieAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchDocumento2 páginasQuantitative Vs Qualitative ResearchJen-jen Corpuz CarpioAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 3.0 Midterm Comm 18Documento3 páginasLesson 3.0 Midterm Comm 18api-3718467Ainda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Research DesignDocumento53 páginasQualitative Research DesignDarwin B. Dela TorreAinda não há avaliações
- Research & StatisticsDocumento12 páginasResearch & StatisticsLeigh FerrerAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Vs QuantitativeDocumento3 páginasQualitative Vs QuantitativePrincess Anne RoldaAinda não há avaliações
- Busitat 1Documento8 páginasBusitat 1MARITHEA LAURA CHAN HUFANOAinda não há avaliações
- Research ReviewerDocumento8 páginasResearch Reviewerela kikayAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Qualitative Research: David Cababaro BuenoDocumento106 páginasPractical Qualitative Research: David Cababaro BuenoCesar Ian RoaAinda não há avaliações
- Division Enhancement On Senior High School Inquiries Investigation and ImmersionDocumento63 páginasDivision Enhancement On Senior High School Inquiries Investigation and ImmersionAshley Jade Hanna FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Different Research Methodology PDFDocumento19 páginasDifferent Research Methodology PDFCyndy Villapando100% (1)
- TVL LAS Practical Research 1 1Documento4 páginasTVL LAS Practical Research 1 1Erika Joyce ValenzuelaAinda não há avaliações
- Part II: Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchDocumento3 páginasPart II: Quantitative and Qualitative Researchjan campoAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Data Collection - Presentation MaterialDocumento15 páginasQualitative Data Collection - Presentation MaterialJudielyn SuaseAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Research I WK1Documento4 páginasPractical Research I WK1Shyla PicazoAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 - Nature of Inquiry & ResearchDocumento17 páginasLesson 1 - Nature of Inquiry & ResearchAlbern BarbacAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Versus Quantitative ResearchDocumento18 páginasQualitative Versus Quantitative ResearchShreyansh PriyamAinda não há avaliações
- Nature of Inquiry and Research: Some Research Ethics PrinciplesDocumento11 páginasNature of Inquiry and Research: Some Research Ethics PrinciplesAlexander QuemadaAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research MethodsDocumento7 páginasQuantitative and Qualitative Research MethodsAbdul Rehman ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- Learning Activity Sheets - SedanoDocumento61 páginasLearning Activity Sheets - SedanoKristine ColicoAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Research 1 Q1 M4Documento20 páginasPractical Research 1 Q1 M4dv vargasAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative Vs Qualitative MethodsDocumento32 páginasQuantitative Vs Qualitative MethodsJoop Vinke100% (1)
- Module 1 - III (Final) PDFDocumento8 páginasModule 1 - III (Final) PDFLyka Bactong DICES MNKAinda não há avaliações
- G11 Practical Research Lesson 3Documento7 páginasG11 Practical Research Lesson 3Jay Mark Cartera TumalaAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Qualitative ResearchDocumento106 páginasPractical Qualitative ResearchQi KeiAinda não há avaliações
- Qualitative Vs Quantitative ResearchDocumento6 páginasQualitative Vs Quantitative ResearchJelly Mae PeñaAinda não há avaliações
- Research NotesDocumento7 páginasResearch NotesRaiza Eve GaniaAinda não há avaliações
- PracticalQualitativeResearch PDFDocumento106 páginasPracticalQualitativeResearch PDFRyan SaladagaAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 2 Research DesignDocumento49 páginasTopic 2 Research DesignNOOR ARFARINA BINTI NASIR (BP)Ainda não há avaliações
- Methods of ResearchDocumento6 páginasMethods of ResearchRonald DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Quantitative and Qualitative Research: Grade 9Documento12 páginasQuantitative and Qualitative Research: Grade 9Rosalyn RayosAinda não há avaliações
- Value-Added TaxDocumento30 páginasValue-Added TaxmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Quiao Vs QuiaoDocumento21 páginasQuiao Vs QuiaomeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Cover BclteDocumento3 páginasCover BcltemeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Case Summary - DOMA Case - US V WindsorDocumento3 páginasCase Summary - DOMA Case - US V WindsormeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Government Service Insurance System Vs MonteclarosDocumento17 páginasGovernment Service Insurance System Vs MonteclarosmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Aquino v. Delizo PDFDocumento4 páginasAquino v. Delizo PDFmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Almario Vs Executive SecretaryDocumento34 páginasAlmario Vs Executive SecretarymeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Classification of TermsDocumento3 páginasClassification of TermsmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Facts About TurmericDocumento1 página10 Facts About TurmericmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Due ProcessDocumento112 páginasDue ProcessmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Use CaseDocumento4 páginasUse CasemeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Nego Digest P.3Documento20 páginasNego Digest P.3meriiAinda não há avaliações
- Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalanceDocumento29 páginasFluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base BalancemeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Gorrospe Dissected (Experimental)Documento9 páginasGorrospe Dissected (Experimental)meriiAinda não há avaliações
- Reading Skills and TechniquesDocumento25 páginasReading Skills and Techniquesmerii100% (2)
- 280 HoursDocumento1 página280 HoursmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Plaintiffs-Appellants vs. vs. Defendants-Appellees Tomas Trinidad James PajeresDocumento8 páginasPlaintiffs-Appellants vs. vs. Defendants-Appellees Tomas Trinidad James PajeresmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Authorization LetterDocumento15 páginasAuthorization LettermeriiAinda não há avaliações
- Hort. 305 Turmeric Cultivation and Processing-6Documento9 páginasHort. 305 Turmeric Cultivation and Processing-6meriiAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 1: Test For Glucose: Materials and EquipmentsDocumento1 páginaExperiment 1: Test For Glucose: Materials and EquipmentsmeriiAinda não há avaliações
- SubsequentDocumento1 páginaSubsequentmeriiAinda não há avaliações