Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Expt .No. 9Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Enviado por
FazilDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Expt .No. 9Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Enviado por
FazilDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
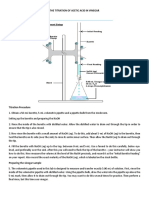
LIQUID – LIQUID EXTRACTION
AIM
To determine the % recovery of Acetic acid from a solution of Water – Acetic acid mixture
using Ethyl acetate as solvent by
1. Single stage
2. Three stage cross current extraction and to determine the stage efficiencies.
INTRODUCTION
Liquid extraction, sometimes called solvent extraction, is the separation of the constituents of
a liquid solution by contact with another insoluble liquid. When a solution of water-acetic
acid is agitated with ethyl acetate some of acetic acid will dissolve in the ester and only little
ester mixes with the aqueous phase. Since at equilibrium the densities of the aqueous and
organic layers are different, they form two layers on settling and can be decanted from each
other.
The solution which is to be extracted is called feed, and the liquid with which the feed is
contacted is the solvent. The solvent rich product is called the extract, and residual liquid
from which solute has been removed is the raffinate. Here acetic acid is the solute(C), water
is the carrier solvent(A) and ethyl acetate is the extracting solvent (B)
PROCEDURE
Single Stage
1. Prepare a feed solution by mixing 50 mL of water and 5mL of acetic acid. Add 75 mL
of ethyl acetate as the extracting solvent to it.
2. Stopper the flask, keep it in a flask shaker and shake for about 1 hr.
3. Separate the contents of flask using separating funnel.
4. Take about 25 mL of the organic layer and determine its refractive index or determine
the density of the layer using specific gravity bottle.
5. Obtain the mass fraction of acetic acid in the organic layer using a calibration chart or
by applying any basic stoichiometric concepts.
6. Similarly determine the mass fraction of acetic acid in the aqueous layer by titrating
against NaOH.
Multistage (Three stage) Cross current Operation
1. Prepare a feed solution by mixing 50 mL of water and 5mL of acetic acid.
2. Add 25 mL of ethyl acetate as the extracting solvent to it.
3. Stopper the flask and agitate the contents using a shaker for about 20 minutes.
4. After 20 min. separate the two layers using separating funnel and add 25 mL of Ethyl
acetate to the aqueous layer.
5. Agitate the contents for another 20 minutes.
6. Again separate the two layers and add another add 25 mL of Ethyl acetate to the
aqueous layer and agitate for 20 minutes.
7. After third agitation, separate the layers and determine the mass fraction of acetic acid
in extract and raffinate.
8. Both single and multistage can be carried out at a time by adding required quantities
into 4 flasks, shaking one flask for 60 minutes continuously while removing the other
3 flasks after 20 min.
OBSERVATION
Sp. Gravity of water =
Sp. Gravity of acetic acid =
Sp. Gravity of ethyl acetate =
STANDARDISATION OF HCl
Weight of Na2CO3 taken in 100 cc volumetric flask =
Volume of Na2CO3 Titre value of HCl , ml
solution
Tit 1 Tit 2 Tit 3
ml
STANDARDISATION OF NaOH
Weight of oxalic acid taken in 100 cc volumetric flask =
Volume of oxalic Titre value of NaOH, ml
acid solution
Tit 1 Tit 2 Tit 3
ml
Single Stage
Volume of Extract =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle alone =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle with extract =
Sp. Gravity of Extract =
Volume of NaOH used for titration =
Multistage
Stage 1
Volume of Extract =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle alone =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle with extract =
Sp. Gravity of Extract =
Stage 2
Volume of Extract =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle alone =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle with extract =
Sp. Gravity of Extract =
Stage 3
Volume of Extract =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle alone =
Wt of sp.gravity bottle with extract =
Sp. Gravity of Extract =
Volume of NaOH used for titration =
Você também pode gostar
- Chemistry Practical Basics, Calibration, Titration and StanderdisationDocumento22 páginasChemistry Practical Basics, Calibration, Titration and StanderdisationPritam SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- What To Do Following A Workplace AccidentDocumento5 páginasWhat To Do Following A Workplace AccidentMona DeldarAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Physical Pharmaceutics 2012Documento33 páginasPractical Physical Pharmaceutics 2012sam100% (2)
- Intoduction To WeldingDocumento334 páginasIntoduction To WeldingAsad Bin Ala QatariAinda não há avaliações
- Legg Calve Perthes Disease: SynonymsDocumento35 páginasLegg Calve Perthes Disease: SynonymsAsad ChaudharyAinda não há avaliações
- SA 8000 Audit Check List VeeraDocumento6 páginasSA 8000 Audit Check List Veeranallasivam v92% (12)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesNo EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesAinda não há avaliações
- Derivative Investment!Documento24 páginasDerivative Investment!Asif Riaz100% (2)
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresNo EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Aspirin TabletsDocumento5 páginasAnalysis of Aspirin TabletsDorien Villafranco60% (5)
- DR Hoon Park III - Indigenous Microorganism (IMO)Documento33 páginasDR Hoon Park III - Indigenous Microorganism (IMO)neofrieda79100% (1)
- (Lab Report Operation Unit) Experiment 3: Separation of An Ordinary Binary Mixture Consisting of Acetic Acid and Water by Using Simple Batch Distillation Technique.Documento8 páginas(Lab Report Operation Unit) Experiment 3: Separation of An Ordinary Binary Mixture Consisting of Acetic Acid and Water by Using Simple Batch Distillation Technique.Fazsroul100% (9)
- Salt of Fatty AcidDocumento9 páginasSalt of Fatty AcidFermi Dio AlfatyAinda não há avaliações
- VI Sem Mass Transfer Lab ManualDocumento53 páginasVI Sem Mass Transfer Lab Manualoctoviancletus80% (10)
- Exp 2 Analysis of Unknown Acetic Acid Solution As245 Applied ChemistryDocumento10 páginasExp 2 Analysis of Unknown Acetic Acid Solution As245 Applied ChemistryNaz HelmiAinda não há avaliações
- Of Periodontal & Peri-Implant Diseases: ClassificationDocumento24 páginasOf Periodontal & Peri-Implant Diseases: ClassificationruchaAinda não há avaliações
- SA01 GENXXX SDIN BSDS 0001 B04 A - Instrumentation Design Basis Sazeh CommentedDocumento31 páginasSA01 GENXXX SDIN BSDS 0001 B04 A - Instrumentation Design Basis Sazeh Commentedamini_mohiAinda não há avaliações
- Exp - 2, Extraction Lab - 97-2003Documento16 páginasExp - 2, Extraction Lab - 97-2003venu11chemistAinda não há avaliações
- Calculate Distribution Coefficient: I. AimDocumento2 páginasCalculate Distribution Coefficient: I. Aimmishrajitesh2004Ainda não há avaliações
- Adsorption of Acetic Acid in Activated Carbon: Experiment No. 1Documento10 páginasAdsorption of Acetic Acid in Activated Carbon: Experiment No. 1Ronald TysonAinda não há avaliações
- Study On AntacidDocumento6 páginasStudy On Antacidsalucr7777777Ainda não há avaliações
- Manual Lab CMT450 - Unit OperationDocumento17 páginasManual Lab CMT450 - Unit OperationNur Hafikah MustaphaAinda não há avaliações
- ExtractionDocumento4 páginasExtractionPuty Prianti Novira0% (1)
- CHM 152 Formal Lab 3Documento3 páginasCHM 152 Formal Lab 3jazminAinda não há avaliações
- Vol Expt 2 ChemistryDocumento4 páginasVol Expt 2 ChemistryVrisanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5 Practical 3 - Calculating KCDocumento3 páginasUnit 5 Practical 3 - Calculating KCMuaaz IqbalAinda não há avaliações
- Mass Transfer Lab ManualDocumento53 páginasMass Transfer Lab Manualshaliq28Ainda não há avaliações
- Ops 2 Lab ReportDocumento11 páginasOps 2 Lab ReportMaridil IsidroAinda não há avaliações
- 2 Multiple Stage LLE-FinalDocumento6 páginas2 Multiple Stage LLE-FinalRAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-Lab 8Documento1 páginaPre-Lab 8SaulS.DiazAinda não há avaliações
- Practical 27 EsterificationDocumento2 páginasPractical 27 EsterificationDavid LuAinda não há avaliações
- Lab DiscussionDocumento7 páginasLab DiscussionZeinab A. ElBhnsawiAinda não há avaliações
- Titration Part 1Documento5 páginasTitration Part 1takomolyentinAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 2 Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar Sample ObjectivesDocumento5 páginasExperiment 2 Analysis of An Unknown Vinegar Sample ObjectivesVirginia DukeAinda não há avaliações
- Exp 3 Lab ReportDocumento3 páginasExp 3 Lab ReportAlyssa OrtegaAinda não há avaliações
- Determine An Equilibrium ConstantDocumento13 páginasDetermine An Equilibrium ConstantMeMeMelol100% (2)
- Imp Page 4 Naoh TitrationDocumento12 páginasImp Page 4 Naoh TitrationkavitakudtarkarAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 10 Titration v2Documento14 páginasExperiment 10 Titration v2Renu ReenuAinda não há avaliações
- Kinetics of Ester Hydrolysis NewDocumento3 páginasKinetics of Ester Hydrolysis Newbits_who_am_iAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Exp No.4Documento4 páginasLab Exp No.4Jennefer TonizaAinda não há avaliações
- Chem Lab 2 For The Ib DiplomaDocumento3 páginasChem Lab 2 For The Ib DiplomaZoravar Sher Singh KalsiaAinda não há avaliações
- CHM256 - Laboratory ManualDocumento27 páginasCHM256 - Laboratory ManualSyahshaiAinda não há avaliações
- SameerDocumento8 páginasSameerAryaman LegendAinda não há avaliações
- MTO-II - Lab Manual - GECBDocumento9 páginasMTO-II - Lab Manual - GECBKinnari PatelAinda não há avaliações
- USP-FCC Sugar Beet FiberDocumento3 páginasUSP-FCC Sugar Beet FiberMAXAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Ac 5Documento13 páginasLab Ac 5Najmi NasirAinda não há avaliações
- CMT267 - Liquid - Liquid ExtractionDocumento10 páginasCMT267 - Liquid - Liquid ExtractionNUR AINUL MARDHIAH FAZLISYAMAinda não há avaliações
- Mass Transfer Lab ManuAL - 2Documento18 páginasMass Transfer Lab ManuAL - 2VigneshParthasarathy0% (1)
- Octyl AcetateDocumento6 páginasOctyl AcetateKristine BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Teacher Resource Bank: GCE Chemistry PSA14: A2 Physical Chemistry - Determine An Equilibrium ContstantDocumento8 páginasTeacher Resource Bank: GCE Chemistry PSA14: A2 Physical Chemistry - Determine An Equilibrium ContstantDzumani YamikaniAinda não há avaliações
- Chemistry Practical: Class 11Documento14 páginasChemistry Practical: Class 11Priyansh GandhiAinda não há avaliações
- 〈89.2〉 COLLAGENASE IIDocumento5 páginas〈89.2〉 COLLAGENASE IIehsan050628Ainda não há avaliações
- Group 4 PSY 214 TitrationDocumento8 páginasGroup 4 PSY 214 TitrationMari Angelo ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- The Titration of Acetic Acid in VinegarDocumento3 páginasThe Titration of Acetic Acid in VinegarGladies AlvarAinda não há avaliações
- CH31CH-33056. Separation Organic Compound MixtureDocumento4 páginasCH31CH-33056. Separation Organic Compound MixtureBisma YameenAinda não há avaliações
- EM202257CON1014CHMDocumento8 páginasEM202257CON1014CHMhoney arguellesAinda não há avaliações
- Practical Physical Pharmaceutics 2012 PDFDocumento33 páginasPractical Physical Pharmaceutics 2012 PDFdrugdrug100% (5)
- Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) in Ready-To-Feed Milk-Based Infant FormulaDocumento2 páginasVitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) in Ready-To-Feed Milk-Based Infant FormulaAhmed GwealyAinda não há avaliações
- Percentage Ascorbic AcidDocumento2 páginasPercentage Ascorbic AcidVinodAinda não há avaliações
- 4.liquid2 Extraction FullDocumento17 páginas4.liquid2 Extraction FullMuhammad Zaidi MisniAinda não há avaliações
- Stoichiometry - Determination of Percent by Mass of NaHCO3 in Alka Seltzer TabletsDocumento6 páginasStoichiometry - Determination of Percent by Mass of NaHCO3 in Alka Seltzer Tabletsgabbal009Ainda não há avaliações
- Liquid-Liquid Extraction (Effect of Phase Ratio)Documento21 páginasLiquid-Liquid Extraction (Effect of Phase Ratio)Jimit PAinda não há avaliações
- Methodology (Flow Chart) A. Single ExtractionDocumento1 páginaMethodology (Flow Chart) A. Single ExtractionAnonymous Xn4W85CAinda não há avaliações
- SALTISE Chem Protocol Colligative Properties v2Documento9 páginasSALTISE Chem Protocol Colligative Properties v2Khaeru NisaAinda não há avaliações
- Amal Jyothi College of Engineering Koovapally P.O., Kanjirapally Department of Chemical EngineeringDocumento69 páginasAmal Jyothi College of Engineering Koovapally P.O., Kanjirapally Department of Chemical EngineeringElsyAinda não há avaliações
- Acid Neutralizing Capacity of An AntacidDocumento4 páginasAcid Neutralizing Capacity of An AntacidibdpAinda não há avaliações
- Soumyarup ChemistryyyyyyyyDocumento5 páginasSoumyarup ChemistryyyyyyyySoumyarup BasuAinda não há avaliações
- Shizhong Liang, Xueming Liu, Feng Chen, Zijian Chan, (2004) .Documento4 páginasShizhong Liang, Xueming Liu, Feng Chen, Zijian Chan, (2004) .Kiệt LêAinda não há avaliações
- Social Style InventoryDocumento12 páginasSocial Style InventoryMaheshwari JaniAinda não há avaliações
- Vaccination Schedule in Dogs and CatsDocumento3 páginasVaccination Schedule in Dogs and CatsAKASH ANANDAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 03Documento35 páginasChapter 03david jenil nabuaAinda não há avaliações
- FennelDocumento2 páginasFennelAlesam44bAinda não há avaliações
- Faraz Chem ProjectDocumento13 páginasFaraz Chem ProjectFaraz AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- Emission Estimation Technique Manual: For Mining and Processing of Non-Metallic MineralsDocumento84 páginasEmission Estimation Technique Manual: For Mining and Processing of Non-Metallic MineralsAbdelaziem mahmoud abdelaalAinda não há avaliações
- Beckhoff Service Tool - USB StickDocumento7 páginasBeckhoff Service Tool - USB StickGustavo VélizAinda não há avaliações
- Essay 31 - Permissive ParentingDocumento2 páginasEssay 31 - Permissive Parentingqbich37Ainda não há avaliações
- Debunking The Evergreening Patents MythDocumento3 páginasDebunking The Evergreening Patents Mythjns198Ainda não há avaliações
- Free Higher Education Application Form 1st Semester, SY 2021-2022Documento1 páginaFree Higher Education Application Form 1st Semester, SY 2021-2022Wheng NaragAinda não há avaliações
- Measurement of Bioreactor K ADocumento18 páginasMeasurement of Bioreactor K AAtif MehfoozAinda não há avaliações
- 7 Fuel Failure in Water Reactors - Causes and MitigationDocumento165 páginas7 Fuel Failure in Water Reactors - Causes and MitigationLauri RubertiAinda não há avaliações
- Calao Deliquente Diadi River SystemDocumento15 páginasCalao Deliquente Diadi River SystemJason MalamugAinda não há avaliações
- Schematic Diagram For Pharmaceutical Water System 1652323261Documento1 páginaSchematic Diagram For Pharmaceutical Water System 1652323261Ankit SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Onuaguluchi1996 1Documento10 páginasOnuaguluchi1996 1IkaSugihartatikAinda não há avaliações
- Datasheet MEC MPS200 v1 2018Documento4 páginasDatasheet MEC MPS200 v1 2018Cepi Sindang KamulanAinda não há avaliações
- Практичне 25. Щодений раціонDocumento3 páginasПрактичне 25. Щодений раціонAnnaAnnaAinda não há avaliações
- Carolyn Green Release FinalDocumento3 páginasCarolyn Green Release FinalAlex MilesAinda não há avaliações
- Bitumen BasicsDocumento25 páginasBitumen BasicsMILON KUMAR HOREAinda não há avaliações
- Varioklav Steam Sterilizer 75 S - 135 S Technical SpecificationsDocumento10 páginasVarioklav Steam Sterilizer 75 S - 135 S Technical Specificationssagor sagorAinda não há avaliações
- ECC83/12AX7: Quick Reference DataDocumento4 páginasECC83/12AX7: Quick Reference DataLuisAinda não há avaliações