Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Typical Double Bus Schemes in HV & Ehv Substations
Enviado por
javedsmg1Descrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Typical Double Bus Schemes in HV & Ehv Substations
Enviado por
javedsmg1Direitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
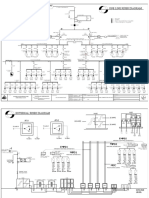
TYPICAL PRIMARY PLANT BUSBAR LAYOUT DESIGNS FOR HV & EHV SUBSTATIONS
These schemes are adopted based on ease of operation & maintenance, availability & reliability of
system.
DOUBLE BUS SCHEMES
Double bus bar schemes have advantage over Single Busbar schemes as it is possible to shift the
Feeder bays from one bus to another in case of a bus fault or for taking maintenance outage of a
Busbar or for expansion/addition of Feeder bays.
Three types of Double Busbar schemes are in practice commonly which is:
Single-CB Double bus scheme (Feeder bay is connected to a particular bus by means of two
Bus Isolators). This scheme has two bus Isolators per Feeder bay which have fault making
and load switching capability. CBs are used for fault breaking duty. Total loss of Substation is
prevented by means of selective switching of Bus Isolators for individual feeder bays. During
a bus fault only those feeder bays which are connected to faulted bus are tripped leaving
other feeder bays in service. After that it is possible to switch the tripped Feeder bays to un-
faulted bus. This results in brief interruption of Feeder bays on a bus fault. Such schemes will
have Bus Coupler & or Bus section CBs to minimize the impact of bus faults on number of
feeder bays. Bus couplers also are required to prevent two buses operated in ‘Electrical’
isolation (split bus) and Substation has one ‘system’ of voltage & frequency. This scheme is
used in HV & EHV Substations.
Double-CB Double bus scheme (Feeder bay is connected to a particular bus by means of two
Bus CBs). This scheme has two CBs per Feeder bay which have fault making and breaking
capability. During a bus fault only those CBs which are connected to faulted bus are tripped
leaving other CBs in service. This results in no interruption of Feeder bays on a bus fault. Bus
coupler CBs may or may not be provided in these schemes as it is common practice to close
both CBs for each feeder bay (thereby reducing the external fault current flow through CB to
one half) which results in less CB maintenance. This scheme is used in HV & EHV Substations
with critical feeder bays.
Two main and a Transfer bus scheme (this is modification of above indicated Double busbar
schemes with an additional transfer bus). This scheme will have additional bus with
additional CB(s) & by-pass isolators. This scheme allows faster restoration of system in case
of emergency by means of minimum protection and allows maintenance of Feeder bay CBs.
This is particularly used in major Power Plant Switchyards.
In all cases, in HV & EHV systems it is required to have both buses tied together electrically.
Você também pode gostar
- Bab 3Documento84 páginasBab 3SudheerKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Questions To Client On SAP HCMDocumento19 páginasQuestions To Client On SAP HCMeurofighterAinda não há avaliações
- Generator Protection Applicatin Guide Basler ElectricDocumento28 páginasGenerator Protection Applicatin Guide Basler ElectricSaravanan NatarajanAinda não há avaliações
- 56.vocal Warmup Log For Belt Your FaceDocumento5 páginas56.vocal Warmup Log For Belt Your FaceAlinutza AlinaAinda não há avaliações
- (PDF) Books Toxic Parents Epub Popular Download - by Susan ForwardDocumento1 página(PDF) Books Toxic Parents Epub Popular Download - by Susan Forwardmartagonzalezbordonaba0% (3)
- Interview Questions On GeneraotrDocumento3 páginasInterview Questions On GeneraotrsrinivasaphanikiranAinda não há avaliações
- LT Panel - 63A Qty-03 NosDocumento1 páginaLT Panel - 63A Qty-03 NosajayAinda não há avaliações
- Flyer Ovb VBF 36kv 31.5ka 12 10 2017Documento2 páginasFlyer Ovb VBF 36kv 31.5ka 12 10 2017Robert MihayoAinda não há avaliações
- Optimum PV PlantDocumento18 páginasOptimum PV PlantVIJKRISH33Ainda não há avaliações
- Calculate SCCRDocumento17 páginasCalculate SCCRsimonAinda não há avaliações
- Power TransfPower-Transformer-Testing-Procedures Ormer Testing Procedures REFDocumento3 páginasPower TransfPower-Transformer-Testing-Procedures Ormer Testing Procedures REFwas00266Ainda não há avaliações
- Circuit Breaker SizingDocumento4 páginasCircuit Breaker Sizingjavedsmg1Ainda não há avaliações
- MCCB Cable SizesDocumento1 páginaMCCB Cable SizesMohamed AdelAinda não há avaliações
- Contract No.4400008460: Halfmoon To Dhahiyah BSPDocumento1 páginaContract No.4400008460: Halfmoon To Dhahiyah BSPProject m707Ainda não há avaliações
- Molded Case Circuit Breakers PDFDocumento7 páginasMolded Case Circuit Breakers PDFMohamedAhmedFawzyAinda não há avaliações
- One and Half Breaker Bus SystemDocumento3 páginasOne and Half Breaker Bus SystemkarthikAinda não há avaliações
- 12kV Air Insulated Metal Clad Switchgear PanelDocumento2 páginas12kV Air Insulated Metal Clad Switchgear PanelHarmanPreetAinda não há avaliações
- Calculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabDocumento6 páginasCalculation of Induction Motor Starting Parameters Using MatlabДејан ПејовскиAinda não há avaliações
- Fill Factor in Organic Solar CellsDocumento11 páginasFill Factor in Organic Solar CellsjonasgoAinda não há avaliações
- Busbar SchemeDocumento26 páginasBusbar Schemeanirooddha_patelAinda não há avaliações
- Functional Capacity Evaluation: Occupational Therapy's Role inDocumento2 páginasFunctional Capacity Evaluation: Occupational Therapy's Role inramesh babu100% (1)
- EE9AL EE5D Celestial Mendoza PDF File 2Documento3 páginasEE9AL EE5D Celestial Mendoza PDF File 2jenixson tamondongAinda não há avaliações
- Mepe 3 3W, 11kV: Project Title: Site Name: Bago StationDocumento2 páginasMepe 3 3W, 11kV: Project Title: Site Name: Bago StationAung Thein OoAinda não há avaliações
- Fire Safety: Good Servant But A Bad MasterDocumento143 páginasFire Safety: Good Servant But A Bad MasterernmrajaAinda não há avaliações
- Safelink CB: Gas Insulated Ring Main UnitDocumento2 páginasSafelink CB: Gas Insulated Ring Main UnitABCDAinda não há avaliações
- Arc Resistance CalculationDocumento6 páginasArc Resistance CalculationS Naved MasoodAinda não há avaliações
- MetalClad Outdoor VCBEnglish PDFDocumento2 páginasMetalClad Outdoor VCBEnglish PDFdip461Ainda não há avaliações
- Fundamentals of Substation Equipment and Control SystemsDocumento4 páginasFundamentals of Substation Equipment and Control Systemsbutt_sonAinda não há avaliações
- PV-Plant-Information-SystemDesign EN 01Documento2 páginasPV-Plant-Information-SystemDesign EN 01anmn123Ainda não há avaliações
- SKM Product BrochureDocumento48 páginasSKM Product BrochureyalmanzaAinda não há avaliações
- HV Winding Phase Overcurrent ProtectionDocumento5 páginasHV Winding Phase Overcurrent Protection386Ainda não há avaliações
- The Design Basics of Motor Protection Circuit BreakerDocumento15 páginasThe Design Basics of Motor Protection Circuit BreakerKI OHAinda não há avaliações
- Morita Therapy For Depression and AnxietyDocumento13 páginasMorita Therapy For Depression and AnxietyPedro GuimarãesAinda não há avaliações
- 15 Busbar ProtectionDocumento21 páginas15 Busbar ProtectionSristick100% (8)
- Design of Protection Schemes in Networks With Future Electric Energy Delivery PDFDocumento132 páginasDesign of Protection Schemes in Networks With Future Electric Energy Delivery PDFsahli medAinda não há avaliações
- SR 750 Commissioning Course Rev 2Documento105 páginasSR 750 Commissioning Course Rev 2Suresh K KrishnasamyAinda não há avaliações
- ABB Technical Application Papers - Vol. 2 MVLV Transformer SubstationsDocumento42 páginasABB Technical Application Papers - Vol. 2 MVLV Transformer SubstationsASM_213Ainda não há avaliações
- Resistance GroundingDocumento4 páginasResistance Groundingjawad_13Ainda não há avaliações
- Resistencia ArcoDocumento11 páginasResistencia ArcoLuis BriceñoAinda não há avaliações
- Indoor Catalogue 1-12 PageDocumento12 páginasIndoor Catalogue 1-12 PageSantoshAinda não há avaliações
- Over Current Tripping Time Calculation (Idmt) : Type of Curve StandardDocumento2 páginasOver Current Tripping Time Calculation (Idmt) : Type of Curve StandardmaheshAinda não há avaliações
- Layout and SLDDocumento30 páginasLayout and SLDmeraatAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Protection Related - CT - EN - AP - D11Documento78 páginasElectrical Protection Related - CT - EN - AP - D11javedsmg1100% (1)
- Medium Voltage Application Guide en IECDocumento224 páginasMedium Voltage Application Guide en IECJag Jagdish0% (1)
- Protection of Microgrid Through Coordinated Directional Over-Current RelaysDocumento6 páginasProtection of Microgrid Through Coordinated Directional Over-Current RelaysChristos ApostolopoulosAinda não há avaliações
- Section E Volume 07 HV TransformersDocumento26 páginasSection E Volume 07 HV TransformersRigoberto UrrutiaAinda não há avaliações
- Street LightDocumento49 páginasStreet LightnarendrabisoyiAinda não há avaliações
- One-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis)Documento13 páginasOne-Line Diagram - OLV1 (Load Flow Analysis)Yogesh MittalAinda não há avaliações
- Medium Voltage CableDocumento7 páginasMedium Voltage Cableakheel201Ainda não há avaliações
- 112ampacity PDFDocumento12 páginas112ampacity PDFCarlos Lino Rojas AgüeroAinda não há avaliações
- ETAP User Guide 7.1Documento8 páginasETAP User Guide 7.1hesse21Ainda não há avaliações
- 228 Power System ProtectionDocumento2 páginas228 Power System ProtectionRamesh Prajapat100% (1)
- VD4 enDocumento13 páginasVD4 enmaruf048Ainda não há avaliações
- Tutorials 360 enDocumento49 páginasTutorials 360 enJosé MariñoAinda não há avaliações
- 14 Voltage Regulation and Per Unit SystemDocumento13 páginas14 Voltage Regulation and Per Unit SystemAlfredo Brumnić FredoAinda não há avaliações
- Protection PDFDocumento32 páginasProtection PDFZulyadain Ishak100% (1)
- Insulation Test SystemDocumento12 páginasInsulation Test SystemYi Fang YueAinda não há avaliações
- TDA2009ADocumento12 páginasTDA2009AnamsongdayAinda não há avaliações
- Hisense Single Split Unit 2018-2019Documento6 páginasHisense Single Split Unit 2018-2019Tuấn NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Summation CTDocumento13 páginasSummation CTjakes87100% (1)
- Medium Voltage Cable Training 02242023010240Documento36 páginasMedium Voltage Cable Training 02242023010240NOELGREGORIOAinda não há avaliações
- Power System Voltage StabilityDocumento31 páginasPower System Voltage StabilityVenkatesh PeruthambiAinda não há avaliações
- Equipment Damage Curves CapacitorsDocumento2 páginasEquipment Damage Curves CapacitorsrobertoseniorAinda não há avaliações
- Design Bus BarDocumento7 páginasDesign Bus BarFarhad UllahAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Double Bus-Bar Basic SystemDocumento6 páginasDesign of Double Bus-Bar Basic SystemAli ImtiazAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Bus System & Substation LayoutDocumento8 páginasElectrical Bus System & Substation LayoutRajeshRaman100% (1)
- Edoc-Electrical Substation Bus Schemes ExplainedDocumento8 páginasEdoc-Electrical Substation Bus Schemes ExplainedEl Comedor BenedictAinda não há avaliações
- Bus Bar ArrangementDocumento4 páginasBus Bar ArrangementAgha AsimAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Bus Bar ArrangementsDocumento6 páginasTypes of Bus Bar Arrangementsمحمد مصطفيAinda não há avaliações
- Bus ArrangementDocumento9 páginasBus ArrangementharimadhavareddyAinda não há avaliações
- Substation Bus Bar Configuration: Electrical Maintenance TeamDocumento18 páginasSubstation Bus Bar Configuration: Electrical Maintenance TeamFaisalAinda não há avaliações
- Network Protection & Automation Guide - NPAG 2011 AlstomDocumento508 páginasNetwork Protection & Automation Guide - NPAG 2011 Alstomhenry100% (1)
- Overhead Transmission Line Distance Protection - Mutual CompensationDocumento53 páginasOverhead Transmission Line Distance Protection - Mutual Compensationjavedsmg1100% (6)
- Distance Relay FundamentalsDocumento20 páginasDistance Relay FundamentalsSyed Muhammad Munavvar HussainAinda não há avaliações
- Resistance To Internal Faults: Martin Schaak Olaf Bischur Thomas StommelDocumento20 páginasResistance To Internal Faults: Martin Schaak Olaf Bischur Thomas Stommeljavedsmg1Ainda não há avaliações
- Electrical Protection Application Get 8402Documento15 páginasElectrical Protection Application Get 8402javedsmg1Ainda não há avaliações
- ABB Publication 1MRK509015-BEN C en High Impedance Differential Relay RADHADocumento5 páginasABB Publication 1MRK509015-BEN C en High Impedance Differential Relay RADHAjavedsmg1Ainda não há avaliações
- Universal Arc Resistance Model "Zagreb" For Emtp: CiredDocumento4 páginasUniversal Arc Resistance Model "Zagreb" For Emtp: Ciredjavedsmg1Ainda não há avaliações
- Arc Resistance Calculator HelpDocumento3 páginasArc Resistance Calculator Helpjavedsmg1Ainda não há avaliações
- Cable LimiterDocumento6 páginasCable Limiterjavedsmg1Ainda não há avaliações
- Group 13Documento4 páginasGroup 13Surisetti Jyothsna LathaAinda não há avaliações
- Rekapan Belanja JKNDocumento5 páginasRekapan Belanja JKNAPOTEK PUSKESMAS MALEBERAinda não há avaliações
- .. - Bcsbi - .Documento2 páginas.. - Bcsbi - .Varun GopalAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1 Animal CareDocumento8 páginasLesson 1 Animal CareLexi PetersonAinda não há avaliações
- Voca-Book (This Must Be The Place)Documento13 páginasVoca-Book (This Must Be The Place)Анастасия ВознесенскаяAinda não há avaliações
- CITEC Genesis & GenXDocumento45 páginasCITEC Genesis & GenXPutra LangitAinda não há avaliações
- WWW - Devicemanuals.eu: GardenaDocumento6 páginasWWW - Devicemanuals.eu: GardenapotoculAinda não há avaliações
- Implementing Self-Administration of Insulin in Hospital: A Journey of Discovery and Innovation. Part 1: Culture and StorageDocumento4 páginasImplementing Self-Administration of Insulin in Hospital: A Journey of Discovery and Innovation. Part 1: Culture and Storagesunrise755Ainda não há avaliações
- Dolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Documento5 páginasDolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Alejandro RuizAinda não há avaliações
- Profile of RespondentsDocumento36 páginasProfile of RespondentsPratibha SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- All India Quota Medical Seats (MBBS) With AIPMT 2015 Score PDFDocumento5 páginasAll India Quota Medical Seats (MBBS) With AIPMT 2015 Score PDFjuhiAinda não há avaliações
- WB Food Processing IndustryDocumento13 páginasWB Food Processing IndustryRakesh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The Man Booker PrizeDocumento2 páginasThe Man Booker PrizeChu Hòa Bình100% (1)
- Primary Tooth Pulp Therapy - Dr. Elizabeth BerryDocumento52 páginasPrimary Tooth Pulp Therapy - Dr. Elizabeth BerryMihaela TuculinaAinda não há avaliações
- ANNEX I of Machinery Directive 2006 - 42 - EC - Summary - Machinery Directive 2006 - 42 - CE - Functional Safety & ATEX Directive 2014 - 34 - EUDocumento6 páginasANNEX I of Machinery Directive 2006 - 42 - EC - Summary - Machinery Directive 2006 - 42 - CE - Functional Safety & ATEX Directive 2014 - 34 - EUAnandababuAinda não há avaliações
- Review Factors Contributing To Medication Errors: A Literature ReviewDocumento9 páginasReview Factors Contributing To Medication Errors: A Literature Reviewsoul_0602Ainda não há avaliações
- Lenovo TAB 2 A8-50: Hardware Maintenance ManualDocumento69 páginasLenovo TAB 2 A8-50: Hardware Maintenance ManualGeorge KakoutAinda não há avaliações
- 45relay Rm4ua PDFDocumento1 página45relay Rm4ua PDFtamky SubstationAinda não há avaliações
- Dosage Calculations, CH 10 ProblemsDocumento1 páginaDosage Calculations, CH 10 ProblemsJacqueline GreerAinda não há avaliações
- WEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE - Cell Structures and Functions - UY-OCODocumento4 páginasWEEK 3 LAB EXERCISE - Cell Structures and Functions - UY-OCOBianca LouiseAinda não há avaliações
- Raffles Hotel Jakarta Pricelist 2020Documento2 páginasRaffles Hotel Jakarta Pricelist 2020kielachela aaAinda não há avaliações
- Ens TecDocumento28 páginasEns TecBorja CanalsAinda não há avaliações
- Green Partnership of The Future: DieselfactsDocumento12 páginasGreen Partnership of The Future: DieselfactsKamal WanniarachchiAinda não há avaliações
- DS Flow SwitchesDocumento51 páginasDS Flow SwitchesAnonymous Xnaj1g8Y3100% (1)