Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
What Is T1 and E1? Difference Between T1 and E1 Explained
Enviado por
amirDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
What Is T1 and E1? Difference Between T1 and E1 Explained
Enviado por
amirDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
What is T1 and E1?
Difference between T1 and E1
explained
What is T1 and E1?
T1 is a digital carrier signal that transmits the DS – 1 signal. It has a data rate of
about 1.544 megabits / second. It contains twenty four digital channels and hence
requires a device that has digital connection. This digital connection is called as the
CSU / DSU – Customer Switching Unit or Digital Switching Unit. The scalability of
the T1 is up to 200 and above users. It also provides some services similar to the
internet provider. Most of the computer uses a T1 connection. This technology
makes your modem to have higher speeds and it is an affordable technology.
E1 is similar to the T1. T1 is the North American term whereas the E1 is the
European term for the transmission (digital). The data rate of E1 is about 2 mega bits
per second. It has 32 channels at the speed of 64 Kbps. It is important to know that 2
channels among the 32 are already reserved. One channel is used for signaling
while the other channel is used for controlling. The difference between T1 and E1
lies in the number of channels here. The speed remains the same. There may be
inter – connection between the E1 and T1 lines. This is interconnected because it is
used for international purpose.
Differences in the physical delivery:
Here are we are going to discuss the differences in the physical delivery.
Data Rate: The main difference is the data rate. T1 has a data rate of 1.544 mbps
and E1 has a data rate of 2.048 mbps.
Copper Delivery: In the T1 signal there is a copper delivery among 4 wires. It is
grouped into two pairs. One pair is the RX (1+2) and another is TX (4+5). The RX is
the data that is from the network and the TX is to the network. In the E1, there are
two types of physical delivery; balanced physical delivery and unbalance physical
delivery. The balanced physical delivery has 4 copper wires. It is similar to that of T1.
Whereas in the unbalanced physical delivery there is a coax connector which has
one cable for RX and one cable for TX.
Services: T1 has a specific type of service. It has repeaters for every six thousand
feet, a pulse or waveform shape and a jitter. The E1 has 32 timeslots. This can be
said as DS. Each DS is about 8 bits wide.
Differences in the Framing Format:
Let us discuss the differences in the framing format.
Framing: In T1, there are two types of framing formats. One is D4 (twelve bits group)
– used in aligning the equipment which is used for framing and another is ESF
(twenty four bits group) – used in aligning the frames as well as in the maintenance
of the channel which is facilitated by the data link. In E1, there are two framing
formats. One is a called the double frame – it uses the DS0 and another is the
multiframe which is the independent form.
Difference Between E1 and T1
Posted on July 29, 2011 by Andrew
2
E1 vs T1
E1 and T1 are digital telecommunication carrier standards, initially developed in
different continents to carry voice conversations simultaneously using time division
multiplexing. Both the standards use transmit and receive paths separately to achieve
full duplex communication. E1 is the European hierarchy, which was called as
CEPT30+2 (European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications
Administrations) prior to 1988, while T1 is used as North American standard. Structure
and the frames of the E1 and T1 carriers have significant differences.
What is E1?
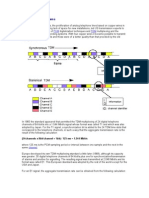
E1 consists of 32 channels, which can be used to carry simultaneous voice calls, and
each channel is called as a Time Slot (TS). As per the ITU-T recommendations, 2 time
slots are reserved for signalling and synchronization. Therefore, E1 can carry 30 voice
calls or data communications simultaneously. Each Time Slot of E1 has a bandwidth
of 64 Kbps, which leads to 2048 Kbps total speed for an E1 carrier. Time division
multiplexing is used to separate the channels from each other. In general E1 time slots
are designed to send Pulse Code Modulated (PCM) voice signals, which have a
sampling frequency of 8000 samples per second. Due to this reason, each E1 frame
is designed to send 1 sample from each channel and the size of E1 frame is limited to
125 µs (1s/8000). So, within this 125µs frame interval, 32 samples should be sent,
which has 8 bits in each sample. Therefore, the total number of bits that should be
transferred in a single frame is 256 bits. Two types of physical delivery methods are
available as per the E1 standard, which is called as balanced physical delivery and
unbalanced physical delivery. Balanced physical delivery is the most popular method,
which uses 4 copper wires grouped as two pairs for transmit and receive paths.
What is T1?
T1 is the North American digital communication carrier standard that consists of 24
channels, which has 64Kbps bandwidth each. Initially each 64Kbps channel is
designed to transfer pulse code modulated voice signals. As per the North American
standard PCM with µ-Law is used with T1 carrier. Duration of the T1 time frame is
decided based on the sampling frequency of PCM, because within one second each
channel of T1 frame should transfer 8000 samples. In other words, 1 sample within
125µS (1s/8000 samples). As per the ANSI specification, each T1 consists of 24
channels, which are multiplexed into 125µS time frame. Other than these channels,
T1 frame consists of a Framing bit, which denotes the end of the frame, is also used
for signalling. Altogether, T1 frame consists of 193 bits (24 samples x 8 bits per sample
+ 1 frame bit) that need to be transferred within 125µS. Therefore, data rate of T1
carrier is 1.544 Mbps (193 bits/125µS). Physical transmission of T1 channels are done
using 4 copper wires grouped into two pairs.
What is the difference between E1 and T1?
E1 and T1 are digital telecommunication carrier standards; in other words, multi-
channel telecommunication systems, which are time multiplexed into a single carrier
to transmit and receive. Both standards use two pairs of wires for transmit and
receive paths to achieve full duplex communication. Initially, both methods are
developed in order to send voice channels over copper wires simultaneously, which
leads to less transmission cost.
- Data rate of E1 is 2048kbps as per the recommendations of ITU-T, while the data
rate of T1 is 1.544Mbps as per the ANSI recommendations.
- E1 comprises of 32 simultaneous channels, while T1 consists of 24 simultaneous
channels, which has 64kbps data rate in each channel.
- Since both systems initially designed to transmit PCM voice, frame rate of both
carriers are designed as 8000 frames per second to support 8kHz sampling rate of
PCM.
- Even though both E1 and T1 have same 125µS frame interval, E1 transmit 256
bits, while T1 transmit 193 bits within the same period.
- In general E1 uses European standard of PCM called A-law while T1 uses North
American standard of PCM known as µ-Law as voice channel modulation method.
- Both E1 and T1 carrier methods are initially developed to transmit and receive
pulse code modulated voice signals over time multiplexed copper wires.
- Key difference of E1 and T1 is the number of channels, which can be transmitted
simultaneously over the given physical medium.
Você também pode gostar
- E1 VS. T1: Phil LomboyDocumento17 páginasE1 VS. T1: Phil LomboyKara Nicole SabayoAinda não há avaliações
- T1 & E1 LinesDocumento49 páginasT1 & E1 LinesChandraSekhar100% (1)
- The E1 in TelecommunicationsDocumento2 páginasThe E1 in TelecommunicationsEric Gitonga100% (5)
- 2p 2p 2p 2p 2pDocumento4 páginas2p 2p 2p 2p 2pAbid AliAinda não há avaliações
- T1 Carrier System: ENGR 475 - Telecommunications Harding University Jonathan WhiteDocumento20 páginasT1 Carrier System: ENGR 475 - Telecommunications Harding University Jonathan WhiteNitin PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- E1 CarrierDocumento3 páginasE1 CarrierEngr Gohar MumtazAinda não há avaliações
- What Is T1 and E1Documento3 páginasWhat Is T1 and E1shipu_ctg100% (1)
- Dedicated LinesDocumento2 páginasDedicated LinesAnkit VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Pulse Code ModulationDocumento2 páginasPulse Code ModulationGabs EscotoAinda não há avaliações
- E1 InterfacesDocumento21 páginasE1 InterfacesPalash SarkarAinda não há avaliações
- Time Division MultiplexingDocumento6 páginasTime Division MultiplexingJohn AlexisAinda não há avaliações
- What's The Difference Between E1 and T1Documento2 páginasWhat's The Difference Between E1 and T1Anshuman GhughutiyalAinda não há avaliações
- Capacity and ModulasiDocumento20 páginasCapacity and ModulasiRizka Nurhasanah0% (1)
- E1 Frame StructuretDocumento3 páginasE1 Frame Structuretabhilash152Ainda não há avaliações
- What Is E1 / T1 ?: Common CharacteristicsDocumento1 páginaWhat Is E1 / T1 ?: Common CharacteristicsManish YadavAinda não há avaliações
- Time Division Multiplexing Time Division Multiplexing: EE4367 Telecom. Switching & TransmissionDocumento7 páginasTime Division Multiplexing Time Division Multiplexing: EE4367 Telecom. Switching & TransmissionSridhar JayaramanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2 Data Communications Lecture 2.3Documento25 páginasChapter 2 Data Communications Lecture 2.3Deepak SutharAinda não há avaliações
- Sonet/Sdh: Channel 1 Channel 1Documento7 páginasSonet/Sdh: Channel 1 Channel 1rthrbyAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation On T1 Telephone Hierarchy: PresentersDocumento15 páginasPresentation On T1 Telephone Hierarchy: PresentersNischalcha SexyAinda não há avaliações
- E1 T1 TutorialDocumento16 páginasE1 T1 Tutorialমোহাম্মাদ নাবিল নূর50% (2)
- All You Wanted To Know About T1 But Were Afraid To AskDocumento20 páginasAll You Wanted To Know About T1 But Were Afraid To AskF4ARAinda não há avaliações
- Hand Outs of SDH Basics (1) IntroductionDocumento32 páginasHand Outs of SDH Basics (1) IntroductionKarthikeyan PandianAinda não há avaliações
- 06 Multiple Access TechniqueDocumento23 páginas06 Multiple Access TechniqueBijoy SahaAinda não há avaliações
- What Is E1 / T1: Common CharacteristicsDocumento1 páginaWhat Is E1 / T1: Common CharacteristicsVarun SoniAinda não há avaliações
- E1 T1Documento33 páginasE1 T1stroker05Ainda não há avaliações
- Twisted Pair Volt Mbit/s Full Duplex Bits Sampled: Citation NeededDocumento1 páginaTwisted Pair Volt Mbit/s Full Duplex Bits Sampled: Citation NeededsandeeeprAinda não há avaliações
- European Digital Carrier SystemDocumento2 páginasEuropean Digital Carrier SystemXyAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of Transmission: 2.1 Multiplexing TechniquesDocumento12 páginasOverview of Transmission: 2.1 Multiplexing Techniquesjokerxyz2009Ainda não há avaliações
- E1 Structure and Traffic MappingDocumento15 páginasE1 Structure and Traffic MappingJeandelaSagesseAinda não há avaliações
- Digital Communication Chapter 11Documento5 páginasDigital Communication Chapter 11MIsh GomezAinda não há avaliações
- PSTN and ISDNDocumento29 páginasPSTN and ISDNleangsimAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1 - Telecommunication OverviewDocumento34 páginasLecture 1 - Telecommunication OverviewsadeeqhardoAinda não há avaliações
- Clase 2. Servicios WAN - Parte 1 PDFDocumento71 páginasClase 2. Servicios WAN - Parte 1 PDFCarmita PinduisacaAinda não há avaliações
- Superior University Lahore, Pakistan: The Data Communication & Networking - Spring 2019Documento12 páginasSuperior University Lahore, Pakistan: The Data Communication & Networking - Spring 2019Aqib HameedAinda não há avaliações
- Speed DetilsDocumento1 páginaSpeed Detilstush1210Ainda não há avaliações
- Multiple XingDocumento30 páginasMultiple XingSadia Afrin NibhaAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter I Data TransmissionDocumento13 páginasChapter I Data TransmissionMohamedLashabAinda não há avaliações
- 3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Documento34 páginas3 MULTIPLEXING Part1Brian Edward HarrisAinda não há avaliações
- Erian Putra Assyakur BM 2A Evaluasi Week-11Documento3 páginasErian Putra Assyakur BM 2A Evaluasi Week-11Erian Putra AssyakurAinda não há avaliações
- Synchronous Optical NetworkDocumento5 páginasSynchronous Optical Networkdeepaknath2200Ainda não há avaliações
- 02 channels-VP PDFDocumento27 páginas02 channels-VP PDFSilicon DaltonAinda não há avaliações
- Modeling of An ADSL Transceiver Data Transmission Subsystem: Elmustafa ErwaDocumento9 páginasModeling of An ADSL Transceiver Data Transmission Subsystem: Elmustafa ErwaIrving Peña BalderasAinda não há avaliações
- Theory and Application of G.SHDSL - BisDocumento5 páginasTheory and Application of G.SHDSL - Biss_meherAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Wide Area NetworksDocumento10 páginasUnderstanding Wide Area NetworksBryan Malla VLOGSAinda não há avaliações
- DS TDM Packet NetworkDocumento4 páginasDS TDM Packet NetworkprejpprAinda não há avaliações
- PCM PriniciplesDocumento36 páginasPCM PriniciplesbhagAinda não há avaliações
- P5 P6 The Principles of Signal TheoryDocumento12 páginasP5 P6 The Principles of Signal Theoryraytopman50% (2)
- Basics of Communication SystemsDocumento55 páginasBasics of Communication SystemsMarielle Lucas GabrielAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Three Introduction To Digital Telecom Transmission and ApplicationsDocumento80 páginasChapter Three Introduction To Digital Telecom Transmission and ApplicationsTibebu Xibe TeAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplexing: AKE OrestDocumento17 páginasMultiplexing: AKE OrestAnjaliAinda não há avaliações
- NETW 310: Wired, Optical and Wireless CommunicationsDocumento10 páginasNETW 310: Wired, Optical and Wireless CommunicationsMarvel RamliAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3 - Transmission MediaDocumento36 páginasChapter 3 - Transmission MediaDiorella PaguioAinda não há avaliações
- T1 and E1 PCM SystemsDocumento10 páginasT1 and E1 PCM SystemsPrafull BAinda não há avaliações
- ChannelDocumento16 páginasChannelaungsoe02Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter (2) : Introducing To Time-Division Multiplexing MultiplexingDocumento55 páginasChapter (2) : Introducing To Time-Division Multiplexing MultiplexingIbrahim ElghawilAinda não há avaliações
- Optical Fiber BasicDocumento48 páginasOptical Fiber BasicAntariksha Singh100% (1)
- Tutorial Sheet 2 (Computer Networks) - 2Documento2 páginasTutorial Sheet 2 (Computer Networks) - 2Areej AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- OQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsNo EverandOQAM/FBMC for Future Wireless Communications: Principles, Technologies and ApplicationsNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (3)
- Level Abrev. Full Name: UMTS ChannelsDocumento3 páginasLevel Abrev. Full Name: UMTS ChannelsamirAinda não há avaliações
- 05 6275 Hspa E01 KH MoDocumento136 páginas05 6275 Hspa E01 KH MoamirAinda não há avaliações
- 01 - 6541 - E01 - Interworking GSM To WCDMA PDFDocumento70 páginas01 - 6541 - E01 - Interworking GSM To WCDMA PDFamir100% (1)
- KPI & CounterDocumento16 páginasKPI & CounteramirAinda não há avaliações
- Stamp JSPTP, Arnumber7841787, Isnumber7841475Documento6 páginasStamp JSPTP, Arnumber7841787, Isnumber7841475amirAinda não há avaliações
- GSM and WCDMA Networks Interworking v5Documento34 páginasGSM and WCDMA Networks Interworking v5amirAinda não há avaliações
- GSM and WCDMA Networks Interworking v5Documento34 páginasGSM and WCDMA Networks Interworking v5amirAinda não há avaliações
- Opt ParametersDocumento7 páginasOpt ParametersamirAinda não há avaliações
- QoS Trends For April 2012Documento6 páginasQoS Trends For April 2012amirAinda não há avaliações
- WCDMA RF Optimization: Site Optimization AspectsDocumento15 páginasWCDMA RF Optimization: Site Optimization AspectsamirAinda não há avaliações
- WCDMA Radio Resource Management, Features and Parameters NAK Training Part 1Documento14 páginasWCDMA Radio Resource Management, Features and Parameters NAK Training Part 1amirAinda não há avaliações
- DSPWCDocumento2 páginasDSPWCParamesh WaranAinda não há avaliações
- Zuku Training ManualDocumento21 páginasZuku Training Manualkikwete25% (4)
- Digital Transmission and Line Coding Techs.Documento32 páginasDigital Transmission and Line Coding Techs.mgoyal_28Ainda não há avaliações
- Cable Modemppt NewDocumento24 páginasCable Modemppt NewSwaru PemmarajuAinda não há avaliações
- FH JammerDocumento5 páginasFH JammerkvmuniprasadAinda não há avaliações
- DVB-S2 at Incospec SeminarDocumento54 páginasDVB-S2 at Incospec SeminarpabloAinda não há avaliações
- 200ufrep EC ISRO2020PaperDocumento58 páginas200ufrep EC ISRO2020Paperchetan kapoorAinda não há avaliações
- Chap - 2 - Discrete-Time and Continuous-Time AWGN Channels PDFDocumento11 páginasChap - 2 - Discrete-Time and Continuous-Time AWGN Channels PDFBKZ0Ainda não há avaliações
- Explanation: Energy Spectral DensityDocumento19 páginasExplanation: Energy Spectral DensityVikas MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- DSL Technologies1Documento39 páginasDSL Technologies1Mohammed AatifAinda não há avaliações
- Manual de Operação MSQ900Documento46 páginasManual de Operação MSQ900felipersbragaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Analog and Digital CommunicationsDocumento93 páginasIntroduction To Analog and Digital CommunicationsK R Shenthil KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Efficiency ComparisonDocumento6 páginasEfficiency ComparisonSreeja SujithAinda não há avaliações
- Flamingo 660 Technical SpecificationsDocumento19 páginasFlamingo 660 Technical SpecificationsMeriton EmërllahuAinda não há avaliações
- LBA Guide - 20070813Documento15 páginasLBA Guide - 20070813黃江祥Ainda não há avaliações
- IECEP Questions (2-4-2014)Documento140 páginasIECEP Questions (2-4-2014)Ariel Paulo G. Tabangay0% (1)
- Notes Digital Communication Lecture 1Documento61 páginasNotes Digital Communication Lecture 1Igho Silva0% (1)
- 16 PSKDocumento22 páginas16 PSKhappy girlAinda não há avaliações
- Coherent DetectionDocumento108 páginasCoherent DetectionGhulam ShabbirAinda não há avaliações
- (Chapter 6-10) Tomasi Communications Systems Terms (41-70)Documento30 páginas(Chapter 6-10) Tomasi Communications Systems Terms (41-70)Kyle Ivan CasindacAinda não há avaliações
- PART-B: Simulation Experiments Using MATLAB: Experiment-1Documento11 páginasPART-B: Simulation Experiments Using MATLAB: Experiment-1sindhu-aravinda9Ainda não há avaliações
- Computer Networks UNIT-2 Syllabus: Physical Layer - Fourier Analysis - Bandwidth Limited Signals - The MaximumDocumento39 páginasComputer Networks UNIT-2 Syllabus: Physical Layer - Fourier Analysis - Bandwidth Limited Signals - The MaximumRaju ImandiAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Physical LayerDocumento96 páginasIntroduction To Physical LayerBimal GajeraAinda não há avaliações
- 1492166910cs Btech Ece Even Sem 6 Ec 601 2015 16 ExamvedaDocumento4 páginas1492166910cs Btech Ece Even Sem 6 Ec 601 2015 16 ExamvedaSakil AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- CH 03Documento38 páginasCH 03mas aryAinda não há avaliações
- DCS Module 1Documento46 páginasDCS Module 1Sudarshan GowdaAinda não há avaliações
- 29Documento481 páginas29Zainul AnwarAinda não há avaliações
- PC CardsDocumento11 páginasPC CardsjisskuruvillaAinda não há avaliações
- DMM-2400TM: User's ManualDocumento21 páginasDMM-2400TM: User's ManualHeri PurwantoAinda não há avaliações
- Review26 HC-12 User ManualDocumento10 páginasReview26 HC-12 User ManualSasha PkhidenkoAinda não há avaliações