Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Measuring Gas and Vapor Concentrations
Enviado por
ameenallyDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Measuring Gas and Vapor Concentrations
Enviado por
ameenallyDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
The metal that donates electrons (classically
Zn) is the negative terminal (anode), acts as a
reducing agent but itself undergoes oxidation,
Standard electrode potentials (tendency to gain or
and erodes due to releasing Zn²⁺ cations to
accept electrons) between 2 dissimilar metals creates
balance the electron donation
an electromotive force (potential for electron transfer)
Zn(s) → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
when they are joined. This potential is activated when
they are in a circuit with an ion solution that facilitates
this transfer in the form of redox reactions
The metal that accepts electrons (classically Cu)
Anode → Oxidation ½ Reaction → Erosion
is the positive terminal (cathode), acts as an
Cathode → Reduction ½ Reaction → Deposition
oxidizing agent but itself undergoes reduction,
(Memory: Consonants and vowels go together)
and deposition occurs to cations (already in
solution beforehand) accepting the electrons
Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu(s)
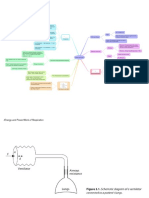
Electrochemical cell dependent on O₂ for reaction
to take place → current generated ∝ [O₂] present
R½R @ Gold mesh Cathode: O₂ + 4e⁻ + 2H₂O → 4OH⁻ Connected in line with tubing
Electrochemical cells
O½R @ Pb Anode: Pb + 2OH⁻ → PbO + 2e⁻ + H₂O
Gives readings in real time with no lag
Thermistor corrects for temperature variation
Main stream
Advantages Advantages: Lightweight, minimal dead space
Reliable, accurate, light weight
Disadvantages: Dead space may make a
Galvanic fuel cell difference in neonates, cannot be used for O₂
30 second reaction time
Life span limited to erosion of Pb Anode Disadvantages A sample line connects the O₂ analyzer to the
tubing in series, with a water trap and a fan
Respiratory gas mointoring
extracting flow at 150-200mL/min
N₂O can cause artifact and damage cell
Side stream Advantage: Allows the bulky O₂ analyzer to
Measuring at 37 °C is called α-stat. At patient work without taking up space on the circuit
temp is called pH-stat
Disadvantage: Tubing can cause gas mixing,
Bubbles cause blood gases to equilibrate with lag or occlude
General
air
Polyatomic gases such as CO₂ absorb IR
Membranes in the analyzer must prevent better than elementary gases such as O₂
contamination with patient proteins
Different gases absorb different wavelengths of
Very similar to galvanic cell except that a 0.6V IR. Collision broadening effect is when the
current is applied across the electrodes (Silver/ peak wavelength of IR that a gas absorbs is
Silver Chloride Cathode and Platinum Anode) widened and/or shifted when gases mix, due to
interactive forces between the molecules
In the presence of O₂, R½R takes place at the
platinum cathode, forming OH⁻ which produces a Measuring PaO₂: The Clark electrode IR emitter (heated wire)
current ∝ [O₂] present: O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
IR absorption spectroscopy for gases Filter: Selects the λ that the gas in question is
2 Silver/Silver Chloride electrodes are used - one known to absorb
as a reference in a KCl solution, the other in a
buffer solution with a glass window to allow H⁺ in
A window which must be a material that does not
Electrodes used in ABG analysis
absorb IR, such as sapphire. Glass absorbs IR
Design
The H⁺ ions entering the glass will only be in
excess of the buffer [H⁺] = the reference [H⁺]
Photodetector notes the IR emitted VS the IR
Measuring pH: The Sanz electrode received → absorbed electromagnetic
Hence the potential difference across the radiation ∝ [gases] present acc to Beer's Law
electrodes ∝ influx [H⁺] ∝ current generated Measuring Gas and Vapor Concentrations
Measured by capnometer and illustrated on a
Similar to the Sanz electrode except that an capnograph/capnogram ([CO₂] VS time)
intermediary chamber allows CO₂ to combine
with H₂O to form carbonic acid and then H⁺:
EtCO₂ is calculated from the graph (max value)
H₂O + CO₂ H₂CO₃ H⁺ + HCO₃⁻
Capnography Upstroke = expiration, Downstoke = inspiration
The H⁺ then enters an electrode with a buffer
and a window, which creates a potential Measuring PaCO₂: The Severinghaus
difference between that electrode an a electrode
S-shape due to lag from mixing of gases
Shape
reference electrode, as in the Sanz electrode
Plateu continues to rise to to continued
Adaptation of the above principles, diffusion of CO₂ out of the alveoli in expiration
maintaining the reference electrode but
Measuring the concentration of other ions
changing the measuring electrode to be
sensitive to the ion being measured The electronegativity of O₂ causes the electron
cloud to generate a magnetic field (a property
unique to O₂ to the exclusion of other gases of
The sample is mixed with a carrier gas and air) which can be exploited to measure [O₂]
moved through a column. This is called the
Mobile Phase. The column contains a liquid to
which each component of the sample is variably A beam shines a light onto a mirror which is
attracted (this is called the Stationary Phase) deflected onto a gauge. The mirror is attached
which determines the unique speed with which to 2 N₂ spheres which move the mirror as they
each component moves up the column respond diamagnetically when exposed to the
paramagnetism of O₂
Gas chromatography
The position of the detection peak
shows the time taken to travel through Advantage: Very accurate
the column which is unique to each
The analyzer at the end of the column
compound, allowing identification Null-deflection PMOA
excludes the carrier gas and then outputs
Paramagmetic Oxygen analysers Disadvantage: 10 second lag, prone to
detection peaks
interference from vibration, high flow and
The height of each detection peak shows the water vapour
concentration of each substance
Chamber draws in the sample gas as well as a
Atoms are bombarded with electrons to strip reference gas (air)
their electrons, then a current is passed through,
then a magnetic field. Their deflection is
proportional to their mass → charge mass ratio A pulse of 100Hz generates a magnetic field
→ unique to each atom → allows identification attracting the O₂ molecules from both to either
side of a double-sided pressure transducer
Other gas monitoring techniques
Mass spectrometry
Advantages: Highly accurate and can
measure all gases Pulse field PMOA The difference in partial pressures on either
side of the transducer will give the sample [O₂]
relative to the known reference [O₂]
Disadvantages: Machine is large, easily
damaged, and gases cannot be returned to
patient due to ionization
Photons are usually bounces off atoms with
the atom and photon retaining their original
energy (Elastic scattering)
Rarely, a photon will raise the energy level of
the electrons and the photon itself will emerge
with a different energy than before (Inelastic or Raman spectroscopy
Raman Scattering)
RS uses an Argon laser and its deflection is
measured at right angles - previously used to
CO₂ and N₂O, cheap, simple, portable, low
maintenance, but IR is now much cheaper
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Respiratory gas mointoring
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../IR absorption spectroscopy for...
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../IR absorption spectroscopy for.../Design
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Paramagmetic Oxygen analysers/Null-deflection PMOA
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Paramagmetic Oxygen analysers/Pulse field PMOA
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Electrodes used in ABG analysi.../Measuring PaO₂: The Clark elec...
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Electrodes used in ABG analysi.../Measuring pH: The Sanz electro...
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Electrodes used in ABG analysi.../Measuring PaCO₂: The Severingh...
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Electrochemical cells
/Measuring Gas and Vapor Concen.../Electrochemical cells/Galvanic fuel cell
Você também pode gostar
- TOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVDocumento25 páginasTOE For FCA2: Depth: From The ME Ascending Aortic SAX, Advance Probe and Turn Clockwise To Centre The TVameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- FCA 2 Trials MindmapDocumento1 páginaFCA 2 Trials MindmapameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Radiography: S. Moore, E. GardinerDocumento6 páginasRadiography: S. Moore, E. GardinerameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- FATE MindmapDocumento47 páginasFATE MindmapameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Gas SuppliesDocumento5 páginasMedical Gas SuppliesameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Measurement of Gas FlowDocumento15 páginasMeasurement of Gas FlowameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Energy and PowerDocumento5 páginasEnergy and PowerameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Monitors (M&M) PDFDocumento3 páginasSummary of Monitors (M&M) PDFameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Transfer of Electrons Between Atoms With ADocumento1 páginaTransfer of Electrons Between Atoms With AameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Diffusion / Osmosis PhysicsDocumento1 páginaDiffusion / Osmosis PhysicsameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- HumidityDocumento6 páginasHumidityameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Gas Laws PDFDocumento2 páginasGas Laws PDFameenallyAinda não há avaliações
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNo EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNo EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)No EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNo EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNo EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNo EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNo EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNo EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNo EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNo EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNo EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNo EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNo EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNo EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)No EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Nota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (120)
- Task 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureDocumento2 páginasTask 1 Methods in Teaching LiteratureJaepiAinda não há avaliações
- Hapter 2: Theoretical FrameworkDocumento18 páginasHapter 2: Theoretical FrameworkMohamed HamzaAinda não há avaliações
- Marriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveDocumento33 páginasMarriage and Divorce Conflicts in The International PerspectiveAnjani kumarAinda não há avaliações
- HF CharactersDocumento5 páginasHF CharactersAudri DebnathAinda não há avaliações
- Failure of Composite Materials PDFDocumento2 páginasFailure of Composite Materials PDFPatrickAinda não há avaliações
- What Is A Business IdeaDocumento9 páginasWhat Is A Business IdeaJhay CorpuzAinda não há avaliações
- Cyclosporin ARCDocumento9 páginasCyclosporin ARCSean GreenAinda não há avaliações
- Kuo SzuYu 2014 PHD ThesisDocumento261 páginasKuo SzuYu 2014 PHD ThesiskatandeAinda não há avaliações
- Eco 407Documento4 páginasEco 407LUnweiAinda não há avaliações
- Direct RetainerDocumento186 páginasDirect RetainerAngkita KalitaAinda não há avaliações
- Kravitz Et Al (2010)Documento5 páginasKravitz Et Al (2010)hsayAinda não há avaliações
- PREETI and RahulDocumento22 páginasPREETI and Rahulnitinkhandelwal2911Ainda não há avaliações
- Ra 9048 Implementing RulesDocumento9 páginasRa 9048 Implementing RulesToffeeAinda não há avaliações
- USA V Rowland - Opposition To Motion To End Probation EarlyDocumento12 páginasUSA V Rowland - Opposition To Motion To End Probation EarlyFOX 61 WebstaffAinda não há avaliações
- Telesis Events - Construction Contract Essentials - WorkbookDocumento52 páginasTelesis Events - Construction Contract Essentials - WorkbookassmonkeysAinda não há avaliações
- Rule Against Multiplicity and Child PornoDocumento3 páginasRule Against Multiplicity and Child PornoHouston Criminal Lawyer John T. FloydAinda não há avaliações
- How To Manage Asthma: A GuideDocumento44 páginasHow To Manage Asthma: A GuideSrinivas YerriboinaAinda não há avaliações
- Herramientas para Pronosticar en STATADocumento53 páginasHerramientas para Pronosticar en STATAMarcos Polo100% (1)
- Khutbah About The QuranDocumento3 páginasKhutbah About The QurantakwaniaAinda não há avaliações
- FS 1 Activity 3.3Documento6 páginasFS 1 Activity 3.3HYACINTH GALLENEROAinda não há avaliações
- Subculture of Football HooligansDocumento9 páginasSubculture of Football HooligansCristi BerdeaAinda não há avaliações
- How Death Came To The CityDocumento3 páginasHow Death Came To The City789863Ainda não há avaliações
- SakalDocumento33 páginasSakalKaran AsnaniAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 Review QuestionsDocumento2 páginasChapter 8 Review QuestionsSouthernGurl99Ainda não há avaliações
- Universal Prayers IIDocumento3 páginasUniversal Prayers IIJericho AguiatanAinda não há avaliações
- Father Saturnino Urios University Engineering and Technology Program Butuan CityDocumento16 páginasFather Saturnino Urios University Engineering and Technology Program Butuan CityTalal SultanAinda não há avaliações
- Characters: Philadelphia Here I Come! by Brian FrielDocumento4 páginasCharacters: Philadelphia Here I Come! by Brian FrielDominic LenihanAinda não há avaliações
- 17PME328E: Process Planning and Cost EstimationDocumento48 páginas17PME328E: Process Planning and Cost EstimationDeepak MisraAinda não há avaliações
- Literacy Block Lesson PlanDocumento5 páginasLiteracy Block Lesson Planapi-286592038Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 2 4 Ak Sequentiallogicdesign Counters DLBDocumento7 páginas1 2 4 Ak Sequentiallogicdesign Counters DLBapi-290804719100% (1)