Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Animal Nutrition: in The Digestive Tract, Food Comes in Via Through Gut & Comes Out As Feces
Enviado por
Jordan ChizickTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Animal Nutrition: in The Digestive Tract, Food Comes in Via Through Gut & Comes Out As Feces
Enviado por
Jordan ChizickDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
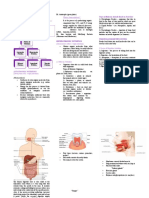
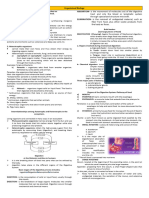
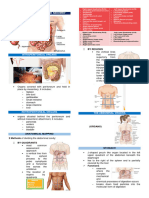
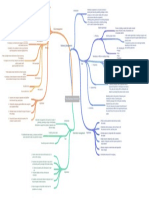
Food Processing 1) Ingestion
Act of eating
What it involves: An increase surface area such as the villi in the Animal Form & Function
small intestine The 4 Mechanisms
Exchange Surfaces
Significance: This is a way for cells for cells to get ride of their
waste & gain nutrients DEF: They are mostly aquatic animals that strain small organisms
or food particles from the surrounding medium
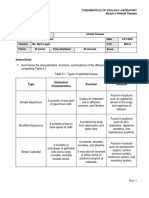
Levels of organization Filter feeders
Cells need: H2O, minerals, oxygen,glucose,fats, proteins...ect
EX: Attached to a humpback whale's upper jaw are comblike
EX: The respiratory system fueling the circulatory system: plates (baleen) which remove small invertebrates & fish from large
volumes of H2O or mud
It's a type of suspension feeding which also includes removing
suspended food particles from the surrounding medium by the
trapping of mechanisms
DEF: Animals that live in or on their food source
EX: Leaf minor caterpillar is eating through the soft tissue of an
EX: In the digestive tract, food comes in via through gut & comes
Animal Nutrition Substrate feeders oak leaf & leaves a trail of feces on its wake
out as feces
EX: Maggots (fly larvae) burrow into animal carcasses
EX: In the Excretory system, the byproduct of cellular respiration DEF: Suck nutrient rich fluid from a living host
in released
Fluid feeders EX: A mosquito that pierced the skin of its human host with
The big picture of exchange surfaces: needlelike mouthparts in order to consume blood
EX of this being a benefit: humminbirds & bees move pollen
between flowers as the fluid-feed on nectar
DEF: Animals that eat large pieces of food
Bulk feeders
Adaptations: claws, pincers, venomous fangs, tentacles, & teeth
Bulk feeders include: Most animals & humans
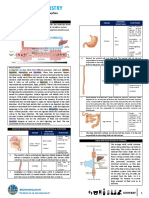
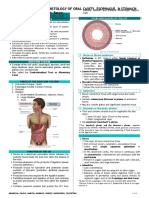
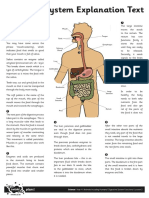
Digestive EX: A rock python that cannot chew it's food into small pieces
Components: Mouth, phyarynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, consumes it's prey whole & spends two weeks or longer digesting
liver, pancreas, anus it's meal
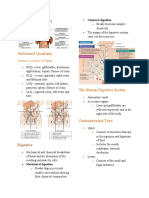
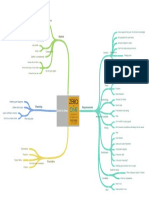
The 11 organ systems in mammals
DEF: A widening of superficial blood vessels Function: Food processing (ingestion, digestion, absorption, DEF: Food is broken into small enough molecules for the bodies
Vasodilation elimination) absorption
Consequence of vasodilation: Blood flow in skin increases
Components: Heart, blood vessels, blood, spleen
The mechanical digestion of chewing comes first
EX: In endotherms, vasodilation usually warms the skin & Circulatory Adaptions Circulatory
increases the transfer of body heat to the environment by Function: Internal distribution of materials 2) Digestion Chemical digestion is last Function: Ingestion & mechanical digestion begins here
radiation, conduction, and convection
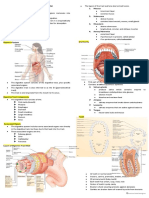
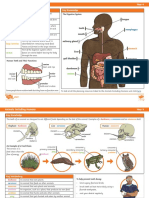
1) Mouth Function: Connects to the stomach & once food enters,
World EX: Ibuprofen Components: Lungs, trachea, other breathing tubes peristaltic contractions of smooth muscles move each bolus to the
Respiratory stomach
Function: Gas exchange (uptake of O2; disposal of CO2)
DEF: Reduces blood flow & heat transfer by decreasing the DEF of peristaltic: Altering waves of contraction & relaxation in
diameter of superficial vessels the smooth muscles lining the canal
Vasoconstriction Components: Bone marrow, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, **Organs & process of the digestive system
EX: Ectotherms control heat exchange by regulating blood flow 2) Esophagus DEF of bolus: The saliva mixed with chewed food that the
lymph vessels
Immune & Lymphatic tongue makes
EX: When the marine iguana swims in the cold ocean, the core of Function: Body defense (Fighting infections & cancers)
the iguana's body is warm to conserve heat Function: Stores food & begins digestion of proteins
3) Stomach The stomach secrets: A digestive fluid called gastric juice that
Components: Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
mixes w / the food through a churning action
Excretory
Function: Disposal of metabolic waste; regulation of osmotic
balance of blood Function: 90% of the foods absorption and digestion occurs in
the small intestines
4) Small intestine
Two Types of Body Temperatures Components: Pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, other
hormone secreting glands Function: Absorb H2O from the remaining indigestible food & get
DEF: An animal whose body temp varies w/environment Variable - Poikilotherm Endocrine ride of the waste from the body
Function: Coordination of body activities 5) Large intestine
EX: Largemouth bass which is a conformer is a poikilotherm
DEF: The hydrolysis of food inside vacuoles
Components: Ovaries, testes, & associated areas
Misconception between the two cleared: There is no fixed Variation in body temperature Intracellular Digestion
relationship between the source of heat & stability of body 1) Begins after a cell engulfs solid food by phagocytosis or
Function: Reproduction Reproductive pinocytosis
temperature PROCESS
2) New formed food vacuoles fuse w / lysosomes, organelles
DEF: The body temp remains constant regardless of environmet Components: Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory organs containing hydrolytic enzymes
Constant - Homeotherm 3) Now that the food is protected inside an enclosed membrane,
EX: The river otter which which is a regulator is a homeotherm Function: Coordination of body activities, detection of stimuli & Nervous digestion can take place
formation of responses to them
DEF of Thermoregulation: A process by which animals maintain Thermoregulation
their normal temperature EX: of animals that digest food this way aresponges
Components: Skin & it's derivatives
DEF: Organisms are warmed mostly by heat generated Integumentary
Function: Protection against mechanical injury, infection, Difference the two: Intra - happens within the cell. Extra happens
metabolism Endothermic dehydration; thermoregulation outside the cell.
Benefits: They can maintain stable body temperatures
Components: Skeleton, bones, tendons, ligaments, cartilage DEF: The breaking down of food on the outside of the cell either
Benefits: In cold weather, they warm themselves mechanically or with acid
Skeletal Extracellular Digestion
Function: Body support, protection of internal organs, movement
Benefit: Enables animals to consume much more food that can
Benefits: In hot weather, they cool themselves be ingested by phagocytosis
Components: Skeletal muscles
EX of organisms: Some fish, many insects, humans, a few EX: Humans use this when we eat - 1) Our teeth grind the food 2)
Function: Locomotion & other movement Muscular
reptiles, birds, & other mammals Enzymes & acid in the stomach liquefy it 3) additional enzymes in
DEF: Organisms gain most of their heat from external sources the stomach break it down into parts our cells can use
Benefits: They can adjust their temperature by behavioral means Ectothermic EX: Fungi - 1) Suck the life out of the substrate they grow on; for
instance, mold on strawberries secreting chemicals that break
down the strawberry, the fungal cells then absorb the released
Benefits: They can consume less food b/c less energy is needed
nutrients. If the strawberries sat long enough, they would be
liquefied
EX of organisms: Amphibians, most invertebrates, many
honavian reptiles & fishes EX: Hydra or sea anemone - 1) The gastrovascular cavity fills the
center of the animal w/1 opening for both food & waste. 2) When
prey swim into the opening, gland cells of the gastrodermis
(tissue layer that lines the cavity) then secrete digestive enzymes
that break the soft tissues of the prey into small pieces. 3) Other
gastrodermis cells engulf food particles, & most of the hydrolysis
of macromolecules occurs intracellularly as in sponges
The cell takes up small molecules such as amino acid & simple
sugars
3) Absorption
Undigested particles pass out of the digestive system
4) Elimination
Urine Function: Filters waste
The benefit of testing: Give many clues to health such as whats
The major difference between urine & feces going on in the blood
Function: Removes waste from the body
Feces
The benefit of testing: Give clues to what the person ate and
show parasites
Você também pode gostar
- Alimentary System WritingDocumento2 páginasAlimentary System WritingIsis Marian Rodriguez JaramilloAinda não há avaliações
- Success Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 1 5158No EverandSuccess Topical Guidebook For GCE O Level Biology 1 5158Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 4 Basic Principles of Animal Form and FunctionDocumento44 páginasChapter 4 Basic Principles of Animal Form and FunctionPrince VillacrusisAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocumento112 páginasBasic Principles of Animal Form and Function: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionRauven Jean Erodias FadriquelaAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function: BiologyDocumento106 páginasBasic Principles of Animal Form and Function: BiologyEriko DarmawanAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Dog and CatDocumento7 páginasAnatomy and Physiology of The Dog and CatJosé Moreira Lima NetoAinda não há avaliações
- Pamilya Naghihiwalay: Epekto Nito Sa Mga AnakDocumento5 páginasPamilya Naghihiwalay: Epekto Nito Sa Mga AnakCute AkoAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 3Documento6 páginasActivity 3Jefferson SociasAinda não há avaliações
- Fishwan Ekskresi (Fix)Documento78 páginasFishwan Ekskresi (Fix)maya cindiatiAinda não há avaliações
- 6 Digestion and AbsorptionDocumento8 páginas6 Digestion and AbsorptionAlexandra DalisayAinda não há avaliações
- ClassificationDocumento5 páginasClassificationtrishaAinda não há avaliações
- General Histology FinalDocumento60 páginasGeneral Histology FinalDr P N N ReddyAinda não há avaliações
- Nutrition: General Biology 2Documento5 páginasNutrition: General Biology 2Thea DegraciaAinda não há avaliações
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocumento1 páginaCharacteristics of Living OrganismsCharlotte FranklinAinda não há avaliações
- Anaphylec Digestive System Finals GelaDocumento20 páginasAnaphylec Digestive System Finals GelaPutri Oskieah MuhammadAinda não há avaliações
- BiologyDocumento7 páginasBiologyorla earnshawAinda não há avaliações
- Biología ExamenDocumento6 páginasBiología ExamenluciaarecesdiazAinda não há avaliações
- Life Processes-NutritionDocumento9 páginasLife Processes-NutritionAaratrika DasAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System Lecture NotesdocxDocumento11 páginasDigestive System Lecture NotesdocxAdaAinda não há avaliações
- Buccal Mucoadhesive Films: A ReviewDocumento8 páginasBuccal Mucoadhesive Films: A ReviewLidya AmelianaAinda não há avaliações
- Drei Javierto - Quarter 2 Week 3 Activity 3 (GB)Documento4 páginasDrei Javierto - Quarter 2 Week 3 Activity 3 (GB)Andrei Sy JaviertoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 16: Digestive SystemDocumento4 páginasChapter 16: Digestive SystemPrecious Faith RodriguezAinda não há avaliações
- Physiology Spring: Lecture 22 Study Guide: Chapter 16 The Digestive System 1 (P 565 - 597)Documento12 páginasPhysiology Spring: Lecture 22 Study Guide: Chapter 16 The Digestive System 1 (P 565 - 597)Ngọc QuỳnhAinda não há avaliações
- Feeding & Digestion in Birds: A Gut FeelingDocumento3 páginasFeeding & Digestion in Birds: A Gut FeelingAlfi OktafaniAinda não há avaliações
- Tracheal System, Digestive & ExcretionDocumento33 páginasTracheal System, Digestive & ExcretionUmmi Nur AfinniAinda não há avaliações
- BIOLAB (ZOOLOGY) : Animal TissuesDocumento8 páginasBIOLAB (ZOOLOGY) : Animal TissuesChloeLAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Animal Digestive Systems PDFDocumento6 páginasTypes of Animal Digestive Systems PDFBill DaoaroonkietAinda não há avaliações
- 3 Tissues in The Human Body 22864Documento11 páginas3 Tissues in The Human Body 22864Musharaf RehmanAinda não há avaliações
- Digestion EunitDocumento6 páginasDigestion Eunitكسلان اكتب اسميAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 1-Digestive System - Student Version - FinalDocumento111 páginasLecture 1-Digestive System - Student Version - FinalAshley TsoiAinda não há avaliações
- Git Trans-Oral Cavity To StomachDocumento6 páginasGit Trans-Oral Cavity To StomachHanako Sasaki AranillaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy & Physiology Outlines - Finals (Chapter 16: Digestive)Documento15 páginasAnatomy & Physiology Outlines - Finals (Chapter 16: Digestive)Dahrell Lopez BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)Documento5 páginasBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)SUHANEERIYAAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive SystemDocumento5 páginasDigestive SystemKate BambalanAinda não há avaliações
- Trans Chapter 16Documento5 páginasTrans Chapter 16رجمه ديوانAinda não há avaliações
- CH 24 Digestive 2017Documento142 páginasCH 24 Digestive 2017JuliaAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System: Abdominal QuadrantsDocumento4 páginasDigestive System: Abdominal QuadrantsAngel Rose BrillanteAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive System (Week 15)Documento20 páginasDigestive System (Week 15)Krisha Mabel TabijeAinda não há avaliações
- Life ProcessesDocumento6 páginasLife Processespranav .gAinda não há avaliações
- Slide 1: Assessing The AbdomenDocumento18 páginasSlide 1: Assessing The AbdomenKristil ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- BIOL228 Student Study Guide Unit3Documento17 páginasBIOL228 Student Study Guide Unit3mariam sabeehAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocumento66 páginasBasic Principles of Animal Form and Function: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionASEEL AHMADAinda não há avaliações
- Bio - 4.1Documento4 páginasBio - 4.1Alecel May PacardoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 21 DigestionDocumento96 páginasChapter 21 DigestionJwnsbdhdAinda não há avaliações
- Digestive SystemDocumento6 páginasDigestive SystemCXT EnterpriseAinda não há avaliações
- BioCo 2020 SyllabusDocumento2 páginasBioCo 2020 SyllabuschengpeckAinda não há avaliações
- Lab 7 Digestive System AnatomyDocumento35 páginasLab 7 Digestive System AnatomyAva YoungAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 10. Animal Form and Function 1Documento106 páginasLecture 10. Animal Form and Function 1Thu AnhAinda não há avaliações
- BIODocumento12 páginasBIOvinjireh caasiAinda não há avaliações
- NARATopic4 RevisionMatDocumento4 páginasNARATopic4 RevisionMatnaraAinda não há avaliações
- Ncma121 Final ReviewerDocumento48 páginasNcma121 Final Reviewerchloepaxton030Ainda não há avaliações
- 5th STD Term I Science EM - FTB - V22Documento40 páginas5th STD Term I Science EM - FTB - V22Dr. Naresh GohelAinda não há avaliações
- DigestionDocumento59 páginasDigestionFarragut1Ainda não há avaliações
- Ch. 40 pdf1Documento38 páginasCh. 40 pdf1emilyfalck17Ainda não há avaliações
- Animal BodyDocumento99 páginasAnimal Bodywafaaj419Ainda não há avaliações
- Gen Bio Week 3 ActivityDocumento3 páginasGen Bio Week 3 ActivityJasper BarlisAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 8 - Digestive SystemDocumento96 páginasChapter 8 - Digestive Systemfit3akmal0% (1)
- T SC 2549622 Science Knowledge Organiser Animals Including Humans Year 4 Knowledge Organiser - Ver - 7Documento2 páginasT SC 2549622 Science Knowledge Organiser Animals Including Humans Year 4 Knowledge Organiser - Ver - 7kosoe2004Ainda não há avaliações
- Digestive System Explanation Text and QuestionsDocumento3 páginasDigestive System Explanation Text and QuestionsSyifa IndanaAinda não há avaliações
- Brand Discovery WorkbookDocumento8 páginasBrand Discovery WorkbookJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Branding WorksheetDocumento5 páginasBranding WorksheetJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Web Awareness and Digital CitizenshipDocumento1 páginaWeb Awareness and Digital CitizenshipJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Branding Workbook Extended VersionDocumento25 páginasBranding Workbook Extended VersionJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- The Digital Currency Toolkit For Financial Advisors: The Who, What, and Why of Investing in BitcoinDocumento22 páginasThe Digital Currency Toolkit For Financial Advisors: The Who, What, and Why of Investing in BitcoinJordan Chizick100% (1)
- Longmeadow Studio Brand Strategy WorkbookDocumento12 páginasLongmeadow Studio Brand Strategy WorkbookJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- 62e7f1ed72b473060964becd - SC Brand Strategy Workbook 2022Documento24 páginas62e7f1ed72b473060964becd - SC Brand Strategy Workbook 2022Jordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- WavesDocumento1 páginaWavesJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Specific Pricing Strategy: Marketing Mix - 4PsDocumento1 páginaSpecific Pricing Strategy: Marketing Mix - 4PsJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Light Colour in The AtmosphereDocumento1 páginaLight Colour in The AtmosphereJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Ignores Time Value of Money: Biased Towards LiquidityDocumento1 páginaIgnores Time Value of Money: Biased Towards LiquidityJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Regression - Classification:: When Is CategoricalDocumento1 páginaRegression - Classification:: When Is CategoricalJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Passe Subjunctif: Infinitif PresentDocumento1 páginaPasse Subjunctif: Infinitif PresentJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Key Business FunctionsDocumento1 páginaKey Business FunctionsJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Carbon Compunds and The Macromolecules of LifeDocumento1 páginaCarbon Compunds and The Macromolecules of LifeJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- ManagementDocumento1 páginaManagementJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- King TutDocumento1 páginaKing TutJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- 4 Major Contingency Leadership TheoriesDocumento1 página4 Major Contingency Leadership TheoriesJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- What Are MisconceptionsDocumento1 páginaWhat Are MisconceptionsJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Using The Help: Learning CoggleDocumento1 páginaUsing The Help: Learning CoggleJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- A Startup Is "A Temporary Organisation Designed To Search For A Repeatable and Scalable Business Model."Documento1 páginaA Startup Is "A Temporary Organisation Designed To Search For A Repeatable and Scalable Business Model."Jordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Word of MouthDocumento1 páginaWord of MouthJordan Chizick100% (1)
- ChangeDocumento1 páginaChangeJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- "Why Some Firms Outperform Others" Resource Possession & Exploitation Resources & CapabilitiesDocumento1 página"Why Some Firms Outperform Others" Resource Possession & Exploitation Resources & CapabilitiesJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Manage Conflicts Better: Do Not Afraid of ChallengesDocumento1 páginaManage Conflicts Better: Do Not Afraid of ChallengesJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Creativity Ability To Adapt Change and Make New Connections Bruce 2011 P 9Documento1 páginaWhat Is Creativity Ability To Adapt Change and Make New Connections Bruce 2011 P 9Jordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- What Is The Process of Taste Sensation and PerceptionDocumento1 páginaWhat Is The Process of Taste Sensation and PerceptionJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- What Are The Most Important Educational PrinciplesDocumento1 páginaWhat Are The Most Important Educational PrinciplesJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- What Is CultureDocumento1 páginaWhat Is CultureJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Zero To OneDocumento1 páginaZero To OneJordan ChizickAinda não há avaliações
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocumento6 páginasExcretory Products and Their Eliminationkanth3012Ainda não há avaliações
- ACE 2007 4A QuestionsDocumento29 páginasACE 2007 4A QuestionsRachana GudipudiAinda não há avaliações
- Greater Glasgow and ClydeDocumento24 páginasGreater Glasgow and ClydeUm ArAinda não há avaliações
- A GENERAL BIOLOGY I 12 Q2M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDocumento18 páginasA GENERAL BIOLOGY I 12 Q2M4 Teacher Copy Final LayoutmariaAinda não há avaliações
- Cards+Against+Paediatric+ECGs+ (v1 0)Documento62 páginasCards+Against+Paediatric+ECGs+ (v1 0)Donna RicottaAinda não há avaliações
- CNS NeurotransmitterDocumento67 páginasCNS NeurotransmitterGreenAinda não há avaliações
- IB Biology Plant ScienceDocumento26 páginasIB Biology Plant Sciencealekzi67% (3)
- NCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialDocumento4 páginasNCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Circulatory System Chapter 8.1 & 8.2 2020Documento61 páginasCirculatory System Chapter 8.1 & 8.2 2020ALEXANDER NYKKO BAYLANAinda não há avaliações
- Coronary Atery Disease-Htn-Thrombo QuestionsDocumento38 páginasCoronary Atery Disease-Htn-Thrombo Questionssrivari sriniAinda não há avaliações
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocumento5 páginasIncreased Intracranial PressureLorelyn Santos CorpuzAinda não há avaliações
- Kuliah 16 Cor PulmonaleDocumento41 páginasKuliah 16 Cor PulmonalecaturwiraAinda não há avaliações
- Respiratory SystemDocumento41 páginasRespiratory Systemshendie cadiatanAinda não há avaliações
- Chest PainDocumento31 páginasChest PainMarwan GamaleldinAinda não há avaliações
- An Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento45 páginasAn Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyMac Paul AlariaoAinda não há avaliações
- Grade 11 Hope 1Documento14 páginasGrade 11 Hope 1Angelica ManabatAinda não há avaliações
- ABG Made EasyDocumento5 páginasABG Made Easyjoanna marie cheongAinda não há avaliações
- Chemical Coordination and Integration: SolutionsDocumento10 páginasChemical Coordination and Integration: SolutionsIhtisham Ul HaqAinda não há avaliações
- Tilt Table Testing For Assesing SyncopeDocumento13 páginasTilt Table Testing For Assesing SyncopeNino SatriaAinda não há avaliações
- Anatomy and Physiology Reviewer PDFDocumento10 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Reviewer PDFArnoldAinda não há avaliações
- Cell Communication Packet 1Documento20 páginasCell Communication Packet 1jade20090106100% (1)
- NCM 1234 - Thorax and LungsDocumento150 páginasNCM 1234 - Thorax and LungsXerxes DejitoAinda não há avaliações
- CH 29Documento39 páginasCH 29Jann Zaniel Allayne RiAinda não há avaliações
- Manual Advance First AidDocumento127 páginasManual Advance First AidLee Khai ChienAinda não há avaliações
- Nand Foundation Academy, Shegaon. 9834274427: Xii - A DivDocumento10 páginasNand Foundation Academy, Shegaon. 9834274427: Xii - A DivSanket PatilAinda não há avaliações
- 12 - Chapter III PDFDocumento65 páginas12 - Chapter III PDFReji RajuAinda não há avaliações
- Science P5 Revision Unit 1Documento7 páginasScience P5 Revision Unit 1starsschooljktAinda não há avaliações
- Group 5 Bahasa Inggris 2Documento12 páginasGroup 5 Bahasa Inggris 2Desri AjengAinda não há avaliações
- CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Part II (Glycolysis)Documento9 páginasCARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Part II (Glycolysis)InshaAinda não há avaliações
- AN Introducti: Submitted By: Jonalyn P. Laurel Bspsych 2-7NsDocumento12 páginasAN Introducti: Submitted By: Jonalyn P. Laurel Bspsych 2-7NsJona LaurelAinda não há avaliações