Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
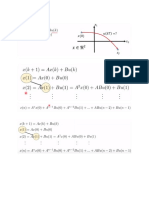
INEL 6085 Analysis and Design of Power Semiconduct
Enviado por
FERDINADDescrição original:
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
INEL 6085 Analysis and Design of Power Semiconduct
Enviado por
FERDINADDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
University of Puerto Rico
Mayagüez Campus
College of Engineering
Electrical and Computer Engineering
Master of Science in Electrical Engineering
1. General Information:
Alpha-numeric codification: INEL 6085
Course Title: Analysis and Design of Power Semiconduct
Number of credits: 3
Contact Period: 3 hours of lecture per week
Contact Period:
Course coordinator`s name:
2. Course Description
English: Analysis and design of single-phase and three-phase controlled rectifiers, dual converters, A.C. voltage
controllers, PWM converters for power supplies, four quadrant choppers, voltage and current source inverters
with modulations techniques, A.C to A.C. converters.
Spanish: Análisis y diseño de rectificadores monofásicos y trifásicos, convertidores duales, controladores de
tensión A.C., convertidores PWM para fuentes de potencia, procesadores de cuatro cuadrantes, inversores de
tensión y de corriente con técnicas de modulación, convertidores de A.C. a A.C.
3. Pre/Co-Requisites
No need requirements
4. Course Objectives:
The student will be able to use analytical an simulation tools to analyze and design power conversion circuits
for applications in different industrial fields.
5.Instructional Strategies:
Conference
Discussion
6. Minimum or Required Resources Available:
Mathematical and circuit simulation software such as SABER, PSpice, and MATLAB
7. Course time frame and thematic outline:
Outline Contact Hours
Common dc-dc PWM converter configurations, analysis, design, basic, modeling and
8.0
control.
Transformer isolated dc-dc PWM converter configurations, analysis, design, basic
10.0
modeling and control, power supply applications.
Inverter basic concepts, configurations, modulation techniques, voltage and harmonic
8.0
control
Analysis, basic modeling and design of single-phase and three phase voltage source
10.0
and current source inverters
Single-phase and three-phase PWM ciclo-converter basic concepts, analysis and 8.0
dOenseigenxam 1.0
8. Grading System:
Quantifiable (letters)
9. Evaluation Strategies:
Quantity Percent
Exams 1 25.00
Projects 3 75.00
10. Bibliography: text book, title, author and year and other supplement materials
1. D. Hart, Power Electronics, McGraw-Hill,1rst Ed., 2010
2. H.J. Sira-Ramirez, R. Silva-Ortigoza, Control Design Techniquesin Power Electronics Devices,
Springer-Verlag New York, LLC, 2006
Classical text books still among the best in the subject:
3. J. Kassakian, M. Schlecht and G. Verghese, Principles of Power Electronics, Prentice H., 1991.
4. Mohan, N., Undeland, T., and Robbins, W. Power Electronics-Converters, Applications and Design: John
Wiley& Sons Inc., 2003.
5. Erickson, R., and Maksimovic, D. Fundamentals of Power Electronics: Springer, 2001.
6. M.H. Rashind, Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices and Applications, Prentice Hall, 2003
11. According to Law 51
Students will identify themselves with the Institution and the instructor of the course for purposes of
assessment (exams) accommodations. For more information please call the
Student with Disabilities Office which is part of the Dean of Students office (Chemistry Building, room 019)
at (787)265-3862 or (787)832-4040 extensions 3250 or 3258.
12. Contribution of Course to meeting the requirements of Criterion 5:
Specific goals for the course
ABET Student
# Course Outcomes
Outcomes
Person (s) who prepared this description and date of preparation:
Você também pode gostar
- Analog Electronics: Circuits, Systems and Signal ProcessingNo EverandAnalog Electronics: Circuits, Systems and Signal ProcessingAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Electronic Engineering, Analog CMOS IC DesignDocumento3 páginasBasic Electronic Engineering, Analog CMOS IC DesignAchint VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Computer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABNo EverandComputer Methods in Power Systems Analysis with MATLABAinda não há avaliações
- Bahria University, Islamabad Campus: Department of Electrical EngineeringDocumento2 páginasBahria University, Islamabad Campus: Department of Electrical EngineeringSolar OngridAinda não há avaliações
- Course Plan and Evaluation Plan: Analog Electronics (3-1-0) 4Documento2 páginasCourse Plan and Evaluation Plan: Analog Electronics (3-1-0) 4Tarun VenkatAinda não há avaliações
- 4el01: Power Electronics CREDITS - 3 (LTP: 3,0,0)Documento2 páginas4el01: Power Electronics CREDITS - 3 (LTP: 3,0,0)Keval ShahAinda não há avaliações
- ET301 Linear Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsDocumento41 páginasET301 Linear Integrated Circuits and ApplicationsChaitanya P V KAinda não há avaliações
- Sy 58Documento35 páginasSy 58Dev SinghAinda não há avaliações
- EE 218 Instrumentation and Measurement: B. Sc. Program Status Report 2016Documento3 páginasEE 218 Instrumentation and Measurement: B. Sc. Program Status Report 2016koko wawaAinda não há avaliações
- Cse Aiml 2020 SyllabusDocumento72 páginasCse Aiml 2020 SyllabusSrijeeta SenAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University Instrumentation & Control EngineeringDocumento3 páginasGujarat Technological University Instrumentation & Control Engineeringgecg ICAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus BTech 1st Year Batch 2018-25Documento19 páginasSyllabus BTech 1st Year Batch 2018-25HimanshuAinda não há avaliações
- 6 - Syllabus For B.tech Joined 2018 OnwardsDocumento49 páginas6 - Syllabus For B.tech Joined 2018 OnwardsShubham AgarwalAinda não há avaliações
- Power Electronics SyllabusDocumento4 páginasPower Electronics Syllabussmithprajapati.el21Ainda não há avaliações
- S.E. (Electronics) Semister Iv Electronic and Electrical Measuring Instruments and MachineDocumento3 páginasS.E. (Electronics) Semister Iv Electronic and Electrical Measuring Instruments and MachineGajendra RajputAinda não há avaliações
- EE809 Course PlanDocumento2 páginasEE809 Course PlanAbhay JangirAinda não há avaliações
- ECSE 2010 CircuitsDocumento3 páginasECSE 2010 CircuitsRodelia SansanoAinda não há avaliações
- I - Sem - Syllabus - EE IoT - 2022-23Documento8 páginasI - Sem - Syllabus - EE IoT - 2022-23Sourabh KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus 5th SemDocumento21 páginasSyllabus 5th SemAmit SahuAinda não há avaliações
- 7th Sem SyllabusDocumento14 páginas7th Sem SyllabusS D ManjunathAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 SemesterDocumento4 páginasElectrical Machines & Measurement B.E. 4 Semestersameerpatel15770Ainda não há avaliações
- Syllabus For Preassessment Test B.E. Cse, Ece, Eee (Batch 2011) & Mca (Batch 2012)Documento2 páginasSyllabus For Preassessment Test B.E. Cse, Ece, Eee (Batch 2011) & Mca (Batch 2012)Nikita AggarwalAinda não há avaliações
- UG APE SyllabusDocumento2 páginasUG APE Syllabusdivya k sAinda não há avaliações
- EEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.3 - 53 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and Systems - LTP - 4 - V1.3Documento2 páginasEEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.3 - 53 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and Systems - LTP - 4 - V1.3devmewada2505Ainda não há avaliações
- 16eps21 CWDocumento2 páginas16eps21 CWShruthi BaglodiAinda não há avaliações
- Vtu PHD Coursework Syllabus MechanicalDocumento5 páginasVtu PHD Coursework Syllabus Mechanicalafaocsazx100% (2)
- EEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.1 - 1 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and SystemsDocumento2 páginasEEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.1 - 1 - EEE1001 - Electric Circuits and SystemsParinay SethAinda não há avaliações
- EEE3004 SlbsDocumento3 páginasEEE3004 SlbsBiselary FinahAinda não há avaliações
- Amity, Analog Electronics-2 (B.tech 4th Sem-Ece)Documento1 páginaAmity, Analog Electronics-2 (B.tech 4th Sem-Ece)deepak173Ainda não há avaliações
- Ae 2 PDFDocumento4 páginasAe 2 PDFAydin Mhysa AbetAinda não há avaliações
- Ee404 Industrial Instrumentation and AutomationDocumento3 páginasEe404 Industrial Instrumentation and AutomationArya RahulAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento3 páginasGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Darshit KotadiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Lecturer, Electrical Engineering, Government Polytechnic, Maharashtra Polytechnic Teachers' Services, Group-ADocumento2 páginasLecturer, Electrical Engineering, Government Polytechnic, Maharashtra Polytechnic Teachers' Services, Group-ARhutuja AmbatkarAinda não há avaliações
- 2130902Documento3 páginas2130902Rushabh PatelAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Power Electronic Converters: Hours Per Week: L T P C Total Hours: L T PDocumento2 páginasAnalysis of Power Electronic Converters: Hours Per Week: L T P C Total Hours: L T PGoriparthi SambasievaraavAinda não há avaliações
- EPCE 6237 Course OutlineDocumento4 páginasEPCE 6237 Course OutlineMerera TaresaAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University: 1 of 4 W.E.F. AY 2018-19Documento4 páginasGujarat Technological University: 1 of 4 W.E.F. AY 2018-19Kuldeep SinhAinda não há avaliações
- EC209 Analog ElectronicsDocumento2 páginasEC209 Analog ElectronicsBonifus Parambaloth Leenus0% (1)
- EC209 Analog Electronics PDFDocumento2 páginasEC209 Analog Electronics PDFgmAinda não há avaliações
- 8695 - 4 EE1 Power Course Syllabi PDFDocumento48 páginas8695 - 4 EE1 Power Course Syllabi PDFAlvin AngAinda não há avaliações
- EEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.2 - 18 - Electric Circuits and SystemsDocumento2 páginasEEE1001 - ELECTRIC-CIRCUITS-AND-SYSTEMS - LTP - 1.2 - 18 - Electric Circuits and Systemssatendrasinghparihar340Ainda não há avaliações
- Ee001 Power Generation Systems: L T P CDocumento32 páginasEe001 Power Generation Systems: L T P CPARTH DAVEAinda não há avaliações
- Engineering Study Abroad Handbook 2023 2024Documento114 páginasEngineering Study Abroad Handbook 2023 2024BRAHMJOT SINGH100% (1)
- SyllabusDocumento7 páginasSyllabuskarlapuditharunAinda não há avaliações
- SCHEME - E Fourth Semester - IE, IS, IU, IC - PDFDocumento40 páginasSCHEME - E Fourth Semester - IE, IS, IU, IC - PDFonkarsdatar0% (1)
- EMTPCourse Australia December2015Documento6 páginasEMTPCourse Australia December2015Brian Zuñagua FloresAinda não há avaliações
- CS207 Electronic Devices & CircuitsDocumento3 páginasCS207 Electronic Devices & Circuitsnisanth123Ainda não há avaliações
- 0 Power Electronics - Lecture Plan - 2021-22Documento1 página0 Power Electronics - Lecture Plan - 2021-22OmkarAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento3 páginasGujarat Technological UniversityHardik MehtaAinda não há avaliações
- Rutgers University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Abet Course Syllabus COURSE: 14:332:460Documento3 páginasRutgers University, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Abet Course Syllabus COURSE: 14:332:460Shreyasee MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- 29 ML839 Power ElectronicsDocumento2 páginas29 ML839 Power Electronicsjimmy jimenez barriosAinda não há avaliações
- Wave Shaping and Swiching CircuitsDocumento3 páginasWave Shaping and Swiching Circuitskaran007_mAinda não há avaliações
- Buet Eee Ug Obe 2023 02 20Documento22 páginasBuet Eee Ug Obe 2023 02 20XubayerAinda não há avaliações
- New SyllabusDocumento4 páginasNew SyllabusBB MukherjeeAinda não há avaliações
- M.tech (PE) Syllabus2014Documento52 páginasM.tech (PE) Syllabus2014shashi_2384Ainda não há avaliações
- 27 ML839 Power ElectronicsDocumento2 páginas27 ML839 Power Electronicsjimmy jimenez barriosAinda não há avaliações
- Electrical Machines OBE, Clo Plo.Documento4 páginasElectrical Machines OBE, Clo Plo.Awais KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Gujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject NameDocumento3 páginasGujarat Technological University: Semester - III Subject NamePratham MaskeAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Instrumentation For Engineers (AET-454)Documento3 páginasSyllabus Instrumentation For Engineers (AET-454)rajeevAinda não há avaliações
- Are TransmittedDocumento2 páginasAre TransmittedFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Preference For A Par Ticular Response Connections Associa Tions ResponseDocumento2 páginasPreference For A Par Ticular Response Connections Associa Tions ResponseFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Basic (CPRC - PELb74)Documento10 páginasBasic (CPRC - PELb74)FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model For Information Storage and Organization in The BrainDocumento2 páginasThe Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model For Information Storage and Organization in The BrainFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Quiz 1-10 INEL 4115Documento10 páginasQuiz 1-10 INEL 4115FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- ReferenceDocumento2 páginasReferenceFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 6. Transportation and Transshipment ProblemsDocumento32 páginasLecture 6. Transportation and Transshipment ProblemsFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- JBCDocumento2 páginasJBCFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Thesis Proposal - Linda MogeDocumento29 páginasThesis Proposal - Linda MogeFERDINAD100% (1)
- Proj Proposal LozanDocumento4 páginasProj Proposal LozanFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- HMW2Documento2 páginasHMW2FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- HMW3Documento41 páginasHMW3FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Proj Proposal LozanDocumento4 páginasProj Proposal LozanFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- HMW3Documento40 páginasHMW3FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- SMS of Fernando Vega in EnglishDocumento5 páginasSMS of Fernando Vega in EnglishFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Data Tesis2Documento89 páginasData Tesis2FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Consumo de Edificios Con Metros 2014-2018 - Fer2Documento13 páginasConsumo de Edificios Con Metros 2014-2018 - Fer2FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Statistical Process Control For MonitoringDocumento10 páginasStatistical Process Control For MonitoringFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- DIgSILENT RUM11 PDFDocumento1 páginaDIgSILENT RUM11 PDFFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Methodology Sostenibilidad Fernando2Documento14 páginasMethodology Sostenibilidad Fernando2FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Consumo de Edificios Con Metros 2014-2018Documento14 páginasConsumo de Edificios Con Metros 2014-2018FERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- DIgSILENT RUM11 PDFDocumento1 páginaDIgSILENT RUM11 PDFFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Alternate Transactions Articles TemplateDocumento9 páginasAlternate Transactions Articles TemplateFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Master Solved - DssDocumento1 páginaMaster Solved - DssFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Diagramas ElectricosDocumento1 páginaDiagramas ElectricosFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Problem JustificationDocumento3 páginasProblem JustificationFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Curricula Vitae (CVS) Versus Resumes - The Writing CenterDocumento4 páginasCurricula Vitae (CVS) Versus Resumes - The Writing CenterFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Cable Tupe OPEN DSS Roger DunganDocumento1 páginaCable Tupe OPEN DSS Roger DunganFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- Examen Parcial LaboratorioDocumento4 páginasExamen Parcial LaboratorioFERDINADAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 páginas6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Spesifikasi Cisco 1841 RouterDocumento4 páginasSpesifikasi Cisco 1841 RouterDwi Soca Baskara0% (1)
- The CEO's Plain English Guide ToDocumento36 páginasThe CEO's Plain English Guide ToadinankaleemAinda não há avaliações
- Sierra Wireless AirLink Fastrack Xtend User Guide Rev001Documento124 páginasSierra Wireless AirLink Fastrack Xtend User Guide Rev001mataAinda não há avaliações
- Manual UPS RT 5 10kVA en UsDocumento48 páginasManual UPS RT 5 10kVA en UsJesus GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Transfer Fundtion of DC GeneratorDocumento5 páginasTransfer Fundtion of DC GeneratorMohammad Haris MAinda não há avaliações
- De110e2 PDFDocumento4 páginasDe110e2 PDFSureshkumar Kulanthai Velu100% (1)
- Altimatic Iiic Service ManualDocumento239 páginasAltimatic Iiic Service ManualDRAGONFLYDF63% (8)
- PhysicsDocumento10 páginasPhysicssatvikvishnoi0805Ainda não há avaliações
- Install Windows 7 From USB PDFDocumento2 páginasInstall Windows 7 From USB PDFemonwreAinda não há avaliações
- TMS320LF/LC240xA DSP Controllers Reference Guide: System and PeripheralsDocumento531 páginasTMS320LF/LC240xA DSP Controllers Reference Guide: System and Peripheralssudhaa206Ainda não há avaliações
- Nonlinear Optics and ApplicationsDocumento10 páginasNonlinear Optics and ApplicationsTilahun ArfichoAinda não há avaliações
- 08 - Installation Tbular OpzsDocumento21 páginas08 - Installation Tbular OpzsMohd ShahidAinda não há avaliações
- CBSE X Science Board Paper: (Time Allowed: 2 Hours) (Maximum Marks:60)Documento11 páginasCBSE X Science Board Paper: (Time Allowed: 2 Hours) (Maximum Marks:60)Jince JacobAinda não há avaliações
- Level 3 Repair: 8-1. Block DiagramDocumento61 páginasLevel 3 Repair: 8-1. Block DiagramEdison Andres Ocampo GomezAinda não há avaliações
- Siemens Thermostat RAB20Documento4 páginasSiemens Thermostat RAB20AmarAinda não há avaliações
- Hitachi Samsung Tutorial V 41 MergedDocumento69 páginasHitachi Samsung Tutorial V 41 MergedΓιάννης ΠαναγόπουλοςAinda não há avaliações
- Computer System Architecture - John D CarpinelliDocumento123 páginasComputer System Architecture - John D Carpinellivb_murthyAinda não há avaliações
- Riello Gulliver RS5D Gas Burner Df41c2dc.889Documento16 páginasRiello Gulliver RS5D Gas Burner Df41c2dc.889Virgil CenariuAinda não há avaliações
- USB Fast Charging ModuleDocumento2 páginasUSB Fast Charging ModuleFuture is Now Amazing World VideosAinda não há avaliações
- Session 2 Wiring and Setting - LATAMDocumento58 páginasSession 2 Wiring and Setting - LATAMPaulo Augusto GarayAinda não há avaliações
- C172R Checklist PDFDocumento2 páginasC172R Checklist PDFNirgunaRamkissoonAinda não há avaliações
- How Do Global 4G and 5G Standards Get Created - Demystifying 3GPPDocumento30 páginasHow Do Global 4G and 5G Standards Get Created - Demystifying 3GPPyangchenyuAinda não há avaliações
- IRADC2020 - E020 0360 E020 0391 E020 03b1TP11 PDFDocumento8 páginasIRADC2020 - E020 0360 E020 0391 E020 03b1TP11 PDFsk8globe_01100% (1)
- ACL 395 Resistivity Meter: Operation ManualDocumento13 páginasACL 395 Resistivity Meter: Operation Manualrhap_0925060Ainda não há avaliações
- Sigma Control 2 9 - 9450 - 00use-Tcm8-285058Documento204 páginasSigma Control 2 9 - 9450 - 00use-Tcm8-285058francisseeAinda não há avaliações
- Viewnet Diy PricelistDocumento2 páginasViewnet Diy PricelistmichaelpaulpenangAinda não há avaliações
- Table FanDocumento8 páginasTable Fanpraba1690Ainda não há avaliações
- 2004 Lincoln Navigator Owner's GuideDocumento384 páginas2004 Lincoln Navigator Owner's GuideKristinaAinda não há avaliações
- Motor Cd20Documento152 páginasMotor Cd20Maciej Sobczyński100% (1)
- Conductive Surface Layer On Wind Turbine Blade As PDFDocumento6 páginasConductive Surface Layer On Wind Turbine Blade As PDFMICHEL RAJAinda não há avaliações