Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CX-5 Textbook 4A 2012 PDF
Enviado por
Do KietTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
CX-5 Textbook 4A 2012 PDF
Enviado por
Do KietDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
February 2012
TN-CX5-1203
Mazda Motor Corporation
Technical Service Training Gr.
Intentionally blank
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
SKYACTIV technology
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY is a blanket term for Mazda’s innovative new-generation
technologies that are being developed under the company’s long-term vision for
technology development, Sustainable Zoom-Zoom.
All the technologies that are developed based on the Building Block Strategy will fall
under the SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY umbrella.
Building Block Strategy
Mazda is prioritizing improvement of the base technologies that are responsible for
the core performance of our cars while adopting a Building Block Strategy of gradually
introducing electric devices such as regenerative braking, hybrid, and other systems.
It is forecast that ICE (Internal Combustion Engines) will still account for a high
percentage of automobile powertrains even as far ahead as 2020.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Reference
SKYACTIV technologies are introduced into the market in phases.
In 2015, 80% or more of global production will be SKYACTIV
After 2015, the second generation of SKYACTIV will adopt lean burn
Reference
If driving performance is to be improved, it usually sacrifices fuel economy. This
means that Driving performance and Fuel economy bear a trade-off relation.
Engineers in the field of R&D always have a dilemma to overcome.
Mazda’s engineers have been tackling many challenges to innovate new
technologies that can balance the two challenges at a higher level.
The most popular word used among those Mazda engineers is “Breakthrough”. It is
spread among all Mazda employees to succeed Mazda’s building block strategy
with SKYACTIV technology.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
SKYACTIVE-G
Principle of thermal efficiency improvement in internal combustion engines
In an internal combustion engine, a significant amount of power generated by the
combustion is lost due to exhaust, cooling, pumping, and mechanical friction losses.
Thermal efficiency improvement in internal combustion engines is nothing, but to
reduce these losses. As indicated in the diagram below, there are six factors that can
be controlled to reduce these losses.
Technologies of SKYACTIV-G
SKYACTIVE-G is a new-generation highly-efficient direct-injection gasoline engine
that achieves the world's highest gasoline engine compression ratio without abnormal
combustion.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Features of SKYACTIV-G
High compression ratio is obtained by a 4-2-1 exhaust system, cavity pistons,
multi-hole injectors and other innovations enable the high compression ratio
Due to high compression combustion, fuel efficiency and torque is increased by
15 % with regard to the existent engines
Drivability at low- to mid-engine speeds is improved due to increased engine
torque
Merits and issues of high compression ratio
Increasing the compression ratio considerably improves thermal efficiency.
Theoretically, the thermal efficiency will improve by roughly 9% if the compression
ratio is raised from 10:1 to 15:1. But, it is impossible to put it into practice. One of the
obstacles is the ignition timing retard to prevent pre-ignition and knocking from
occurring.
Knocking is abnormal combustion in which the air-fuel mixture ignites prematurely due
to exposure to high temperature and pressure, creating an unwanted high-frequency
noise. When the compression ratio is increased, the temperature at compression top
dead center (TDC) also rises. Knocking is more likely to occur when the temperature
rises.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
In order to lower the temperature at compression TDC, it is effective to reduce the
amount of hot exhaust gas which remains in the combustion chamber.
For example, with a compression ratio of 10:1, a residual gas temperature of 750°C,
and an intake air temperature of 25°C, if 10% of the exhaust gas remains, the
temperature inside the cylinder before compression increases by roughly 70°C, and
the temperature at compression TDC is calculated to increase by roughly 160°C.
750°C
160°C
70°C
25°C
These calculations are summarized in the graph below, and as indicated, if the
amount of residual gas is reduced from 8% to 4%, the calculated temperature at
compression TDC remains the same even when the compression ratio is increased
from 11: 1 to 14: 1.
Combustion improvement
Combustion duration is shortened to improve resistance to knocking. The faster the
combustion velocity, the shorter amount of time the unburned air-fuel mixture is
exposed to high temperatures. This allows for normal combustion to complete before
knocking occurs.
Homogeneous mixture is formed due to improved fuel spray characteristics by means
of intensifying air flow, increasing injection pressure, and using multi-hole injectors.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Stable combustion is produced even when the ignition timing after engine-start is
considerably retarded. This is made possible by a piston cavity and optimizing fuel
injection in order to formulate a stratified air-fuel mixture around the spark plug.
Furthermore, the piston cavity resolved the issue of the initial flame coming in contact
with the piston head and generating a cooling loss.
Light weight piston and connecting rod contribute to reduce inertia and friction losses.
4-2-1 exhaust system
4-2-1 exhaust system is employed to reduce the amount of exhaust gas in the
combustion chamber.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
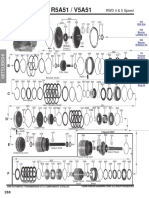
SKYACTIV-DRIVE
Combines all the advantages of conventional automatic transmissions,
continuously variable transmissions, and dual clutch transmissions
A dramatically widened lock-up range improves torque transfer efficiency and
realizes a direct driving feel that is equivalent to a manual transmission
A 4-to-7 percent improvement in fuel economy compared to the current
transmission
CX-5 is equipped with SKYACTIV-Drive*. It is a high performance transaxle, designed
as a result of pursuant to the ideal transaxles defined by evaluating advantages and
disadvantages of STEP-AT, CVT, and DCT.
* The SKYACTIV-Drive is named as FW6A-EL (2WD) and FW6AX-EL (4WD).
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
SKYACTIV-Drive Development concept
Transaxles’ development is very important not only for improving fuel economy, but for
the vehicle driving performance. Auto-manufactures have been using a variety of
automatic transaxles and selecting ones according to the market’s preference. There
is no such thing that one automatic transaxle can meet every needs from every
markets.
Type Features
Helped by creep phenomenon, easy to start up; because of torque
converter clutch, fuel economy is comparable with manual transaxles.
STEP-AT
However, due to its characteristics, there is loss of power transmission
when start up.
Little shift shock and good fuel economy at lower speed. It is well
accepted in the markets such as Japan, where drivers need to stop
CVT
and start the vehicle within short distance. This is not well accepted in
Europe where vehicles are driven highways.
Basic feature is very manual transaxle/transmission, which a pair of
clutch transmits the power in turn within a very short period of time.
DCT Therefore, it has better fuel economy and good direct feel. However, it
tends to develop shift shock when shifting to or from 1st or 2nd gear.
Besides, it is big and heavy, and costly.
The basic structure of SKYACTIV-Drive is popular one; mainly consists of torque
converter and STEP-AT. But, it employs many new technologies such as multiple-disc
torque converter clutch, which makes it possible to widen lock-up range; all ranges
from 1st gear to 6th gear. This design contributes to highly improve efficiency and direct
feel, resulting in taking advantages of other types of automatic transaxles. In another
word, SKYACTIV-Drive eliminated the weakness of STEP-AT. It is believed that
SKYACTIV-Drive is to be accepted by the customers in a variety of markets
SKYACTIV-Drive is developed to make it possible to meet fuel economy, direct feel,
and shift quality by taking only advantages from different types of automatic
transaxles.
Simply, it was developed based on STEP-AT, which has relatively well balanced and
little disadvantages, by uncompromising KAIZEN against.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Market preference
Japan Europe North America
Good fuel at low speed X X
economy at high speed X X
Easy start up (Launch feel) X X
Easy start up on hill (Creep) X X
Direct feel X
Smooth shifting (Shifting quality) X
SKYACTIV-Drive is aimed to meet all preferences of all markets.
New features
Items to be improved New features
- Widened lock-up range
Fuel economy - High efficient gear train
- Reduced clutch resistance
Start-up - Small size torque converter
- Improved clutch response
Direct feel
- Improved solenoid valve response
- Improved parts accuracy
Smooth shifting
- Employed direct linear solenoid valves
Widened lock-up range
The graph below shows lock-up ranges of FS5A-EL and SKYACTIV-Drive*: the black
colored curves indicate FS5A-EL and the pink colored curves indicate lock-up range
of SKYACTIV-Drive.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
* The type of the SKYACTIV-Drive and the vehicle were not known for this test.
Obviously, the lock-up range for the SKYACTIV-Drive is widened. In this test mode, it
is observed that 49% of driving time for FS5A-EL is in the lock-up range, while
SKYACTIV-Drive is 82%.
Reference
Japanese test modes for measuring fuel consumption
JC08: It is a Japanese test mode to measure mileages which vehicle is driven with
one liter of fuel (km/liter).
10-15 mode: This is another test mode effective in 1991. As this mode does not
reflect today’s vehicle driving condition, JC08 mode was established.
JC08 mode 10-15 mode
Average vehicle speed 24.4km/h 22.7km/h
Maximum vehicle speed 81.6km/h 70km/h
Time for test mode completion 1204 sec 660 sec
Total mileage 8.172km 4.165km
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 10
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Reference
Gear positions that lock-up control is applicable are shown in the table below.
Lock-up control is applicable to all 6 speeds for FW6A-EL (SKYACTIV-Drive).
Deceleration Slip
Type of ATX/AT Gear Lock-up
Lock-up
GF4A-EL 4 4GR NA
FN4A-EL 4 4GR (3GR, 4GR for some models) Available
RC4A-EL 4 3GR, 4GR NA
FS5A-EL 5 4GR, 5GR Available
SJ6A-EL 6 5GR, 6GR Available
AW6A-EL 6 4GR, 5GR, 6GR Available
FW6A-EL 6 1GR, 2GR, 3GR, 4GR, 5GR, 6GR Available
FW6A-EL (Normal mode)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 11
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
SKYACTIV-MT
The development concept was to create a “light and compact MT with improved shift
feel and better fuel economy”. The goal was to achieve an MX-5-like sporty and brisk
shift feel.
By pursuing the ideal structure of manual transmissions, 16% at maximum of weight
reduction was achieved. Furthermore, internal friction losses were significantly
reduced to achieve a 1% improvement in fuel economy.
Light in weight and compact size
Quick and crisp shift feel like that of a sport car
Light and compact MT
Since the structure of an MT is relatively simple, completely new ideas and logical
thinking are required to achieve further weight reduction and higher efficiency.
The triple-shafted gear train with a common gear for 2nd and 3rd was selected from
approximately 30 different configurations due to its potential to achieve lightness, light
shift effort, high efficiency, and a wide gear ratio. Based on this selection, the lightest
structural specifications were selected from over 10,000 alternatives. By reviewing the
function of each component, commoditization of the 1st and reverse gears was newly
employed.
This enabled the length of the secondary shaft to be reduced by 20%. A common 1st
and reverse gear made possible the removal of the reverse idle shaft. As a result, by
reexamining gear configurations, the number of components decreased and the gear
train weight was reduced by roughly 3 kg.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 12
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Quick and crisp shift feel
To achieve lighter shift effort with a short shift lever stroke, the lever ratio must be
increased. However, an increased lever ratio reduces the internal stroke. To achieve
precise synchronizer and torque transmission even with a short internal stroke, a
small module* spline is used.
Shift effort: F Shift lever stroke: 45 mm
Lever ratio: a/b
Shift lever a
Internal stroke: L
Cable
b
Small module Internal stroke: L
* Module: Size of a tooth on the gear or spline.
Also, the shift effort gradually reduces through the stroke, providing reassuring
resistance as the lever is first pushed, then getting lighter so it feels as if the shift lever
is automatically moving into gear. With the current shift lever, shift effort in the select
direction (right-left direction) increases with the movement of the shift lever, but with
the new shift lever, a constant shift effort is achieved. Binding is minimized when
shifting diagonally.
Select direction
Shift effort
gradually
reduces
Diagonal shifting
Minimized
Binding Binding
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 13
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
SKYACTIV-Chassis
Key points
Suspension and steering functions have been thoroughly revised to provide
driving pleasure of the oneness of car and driver
Driving quality has been greatly improved by improved comfortableness and
stability & safety
The weight of entire chassis is reduced, which is lighter by 14% than the existent
model (Mazda6).
Technical aims and concept
Feeling of oneness with vehicle
Responsive Hard
1. Combination of 2. Balance of ride
agility at low-to-mid comfort with agility at
speeds and stability at Trade-off Trade-off low-to-mid speeds
high speeds
Unresponsive Soft
Stability & safety Comfortableness
Trade-off
Weight reduction
3. Achievement of both
weight reduction and
high rigidity
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 14
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Yaw-gain is increased at low-to-mid vehicle speeds to improve agility (responsive),
and decreased at high vehicle speeds to improve stability (not over-responsive).
The time lag of the increase of lateral-G with respect to yaw rate is reduced to
improve stability.
Yaw gain (deg/sec/deg)
Existent models
Improved agility
SKYACTIV-Chassis Improved stability
Vehicle speed (km/h)
Reference
Yaw-gain: the degree of yaw rate change with respect to the angle of steering
(deg./sec/deg.). The higher the yaw-gain, the more the vehicle tends to turn easily.
Lateral-G: the acceleration applying in lateral direction of the vehicle that increase
or decrease in response to turning movement of the vehicle
Yaw rate: the degree of change of turning angle per second that occurs due to
yawing (deg./sec)
Turning motion of the vehicle
Yawing
Lateral-G: generated in
response to turning
Gravity center of movement of the vehicle
the vehicle
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 15
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Rear cornering power is increased to reduce yaw-gain at high vehicle speeds,
ensuring stability. A high-geared steering gear is employed to increase yaw-gain at
low-to-mid vehicle speeds.
Yaw gain
Steering
Rear cornering power
angle
Front cornering power
(Employed technology)
The geometry of the rear suspension links is optimized to effectively use
compliance steer in order to increase cornering power in rear tires without sacrifice
of the lateral rigidity.
Existing model CX-5
The link damper leaning forward absorbs not only up-and-down vibrations, but also
forward-and-backward ones.
The timing of the weight transfer in rear tires is advanced by reducing the
hysteresis characteristics of the suspension cross mount bushing.
Input from the road Bushing
Reaction force
Bushing
Input from the road
Reaction force
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 16
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
(Continued)
Existent models
SKYACTIV-Chassis
Load (N)
Hysteresis
Displacement (mm)
A high-geared steering gear ratio is employed to increase yaw-gain at low-to-mid
vehicle speeds.
Caster angle and caster trail are increased to ensure the proper amount of required
steering effort that varies according to the vehicle speed, while the stability of
straight-ahead driving is improved.
Increased caster angle
Increased caster trail
Caster angle in comparison
CX-5 CX-7 CX-9
3°04′ (2WD)
Caster angle 6°29’ 2°57’
3°05′ (4WD)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 17
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
The installation position of the rear trailing link was moved upward so that the
longitudinal impact from the road is more easily absorbed in the vertical movement
of the rear trailing link. This reduces the longitudinal force input to the rear trailing
link bush, improving the ride comfort.
Existent models CX-5
Recession angle Recession angle
Bush
Rear trailing longitudinal
link bushing impact shock
Rear trailing
Bush
link bushing
longitudinal
impact shock
Direction of travel Direction of travel
The front cross-member mount was changed from the conventional rubber mount
type to rigid mount type (rubber mount eliminated). Rigid mounting suspension
directly transmits the force generated from the tire.
Welding flanges were removed from the front and rear cross-members to enhance
the coupling rigidity of the welded sections.
Rigid mount
Welding flange
No welding
flange
Existent models
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 18
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
On the front cross-member, cross section of the center member was increased and
the longitudinal offset of the front lower arm attachment position was reduced.
The longitudinal span of the rear cross-member was extended and the longitudinal
offset of the rear lateral link attachment position was reduced.
Front Rear
Front: b/n front lower arm attachment position and front cross-member
Rear: Rear cross-member longitudinal span
Front cross-member width
(Existent model)
For both front and rear suspensions, coupling rigidity of the welded area is
improved by disusing welded flange (flangeless).
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 19
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
SKYACTIVE-Chassis (Brake)
Aiming to improve all the three items below under any conditions:
Oneness with the vehicle (controllability)
Stability & Safety (Brake effectiveness)
Comfortableness (Brake Noise and Vibration)
Oneness with the vehicle
Controllability
Target
Existent
Thermal control
Stable & Safe Comfortableness
Effectiveness Brake NV
Weight reduction
For these aims, SKYACTIVE-Chassis combines the following:
Weight reduction with cooling capability (thermal control)
1) By efficiently directing air to cool down the brake
2) Improving cooling performance of brake disc rotor
Brake effectiveness with brake noise and vibration
1) By identifying the structure generating the least vibration energy
2) By establishing the brake structure design for suppressing noise
Structural change in brake caliper
Mazda defined the contributing factors based on the analysis in brake temperature,
effectiveness, and noise. Then, the contributing factors were used for CAE analysis,
natural vibration analysis, and on-vehicle parameter verification to identify optimal
structure design.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 20
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Reference
As part of contribution of SKYACTIV-Chassis, a greater anti-lift force than that of
existent models is produced.
Existent model CX-5
A<B
49 mm
B
A Anti-lift force Anti-lift force
Brake force Brake force
SKYACTIV-BODY
The highest level of collision safety performance
Pedestrian protective bonnet
Realized a light-weight body, while it ensures the world highest level of collision
safety performance. (Weight of the white body is reduced by 8 % as compared
with existent models.)
Chassis dynamics
By improved aerodynamics, the Coefficient of drag (Cd) of 0.335 is realized by, in a
well-balanced way, minimizing trailing vortexes, which are generated upward or
downward in the rearward of the vehicle. This improvement contributes to better fuel
economy.
Body framework & rigidity
(1) Straight frame: Body framework is straightforwardly and continuously stretched
without cutting-off
(2) Rigidity of mounting portions: Rigidity at suspension and engine mounting portions
are enhanced
(3) Multi-load path: An ideal framework with the view to collision, chassis dynamic
stability, and NVH is realized
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 21
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
Existent model
CX-5
For various type of collision possibly happening in the market, an outstanding frontal
collision safety is realized by efficiently absorbing collisional energy for frontal
collisions that minimizes cabin deformation
A high efficient multi-load path structure, which a frontal impact is dispersed and
absorbed in the engine compartment
Upper Path: - A structure for impact absorption by utilizing the apron portion
Mid Path (main): - A high collisional energy absorption and weight reduction are
realized by adopting cruciform section
- Designed a load-dispersive load path that can stably absorb
collisional energy by steady deformation
Lower Path: - In addition to body related parts, an extension for impact
absorption is equipped with the front suspension cross member
(1) At a collision, the engine and suspension cross-member is to be separated from
the body in order to provide crushable space in the engine room.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 22
Mazda CX-5
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY
TN-CX5-1203
(2) High-tensile steel sheet is used for the load-dispersion load path structure of the
cabin site and for the portions where the restricting deformation of the front floor
pan is vital.
Existent model CX-5
e
a b c d
Existent model
CX-5
0 20 40 60 80 100
Steel a 270 MPa
b 340/440 MPa
c 590 MPa
High-tensile steel
d 780/980 MPa
e 1,500 MPa or higher
Bonnet pedestrian protection
(1) A sufficient space between the bonnet and engine is provided for absorbing
collisional energy
(2) The vertical plate on the front side of the striker lane installed in the forward end
has been eliminated. Instead, the stiffener's shape is optimized to be squashy at a
collision.
Impact energy is absorbed
Impact to the engine
within this range
room is reduced
Shroud upper member
Bumper & crash-can
Suspension cross
member crash-can
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 23
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Contents
00 GENERAL INFORMATION
01G ENGINE SKYACTIV-G
01D Engine SKYACTIV-D
02 SUSPENSION
03 DRIVELINE/AXLE
04 BRAKES
05 TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE
06 STEERING
07 HVAC
08 RESTRAINTS
09 BODY & ACCESSORIES
10 Multiplex communication system
11 I-stop
12 Personalization features
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Mazda CX-5
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Item CX-5 CX-7 CX-9
L5
SKYACTIV-G 2.0
Engine L3-Turbo MZI-3.7
SKYACTIV-D 2.2
MZR-CD 2.2
6EAT 6EAT
T/M 6EAT
6MT 6MT
Length (mm) 4,540 4,695 5,099
Width (mm) 1,840 1,870 1,936
Height (mm) 1,705 1,645 1,728
Wheel base (mm) 2,700 2,750 2,857
Tread: FR (mm) 1,585 1,615 1,654
Tread: RR (mm) 1,585/1590 1,610 1,644
215 (2WD) 215 (2WD)
Clearance 206/208
210 (4WD) 210 (4WD)
Weight (kg) 1,440 – 1,610 1,660 – 1,760 1,939 – 1,974
225/65R17 245/60R18
Tire size 235/60R18
225/55R19 245/50R20
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Item CX-5
Engine SKYACTIV-G 2.0 SKYACTIV-D 2.2
6EAT (FW6A-EL/FW6AX-EL) 6EAT (GW6A-EL/GW6AX-EL)
T/M
6MT (C66M-R/C66MX-R) 6MT (D66M-R/D66MX-R)
Length 4,540 mm
Width 1,840 mm
Height 1,705 mm
Wheel base 2,700 mm
Tread: FR 1,585 mm
Tread: RR 1,585 mm /1590 mm
Clearance 210 mm
Weight (kg) 1,440 - kg
Tire size 225/65R1, 225/55R19
SKYACTIV technology
SKYACTIV TECHNOLOGY is a blanket term for Mazda’s innovative new-generation
technologies that are being developed under the company’s long-term vision for
technology development, Sustainable Zoom-Zoom.
Major components of SKYACTIV technology
SKYACTIV-G SKYACTIV-D SKYACTIV-MT SKYACTIV-Drive
SKYACTIV-Chassis SKYACTIV-Body
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Vehicle identification Number (VIN)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
The VIN marking position is located on the floor on the front passenger-side. If the VIN
plate is adhered to the dashboard, it is located in the position shown in the figure.
Item Specification
API: SG/SH/SJ/SL/SM/SN or
ILSAC: GF-2/GF-3/GF-4/GF-5
SKYACTIV-G
SAE: 10W-30, 10W-40, 10W-50,
Engine oil
5W-20, 5W-30, 5W-40, 0W-20, 0W-30
ACEA: C3/C1 or JASO: DL-1
SKYACTIV-D
SAE: 0W-30, 5W-30
SKYACTIV-G PE01 14 302
Engine oil filter
SKYACTIV-D SH01 14 302
MTX – Gear oil API: GL-4, SAE: 75W-80
ATX – ATF ATF-FZ
Rear differential oil API: GL-5, SAE: 80W-90
Transfer oil API: GL-5, SAE: 80W-90
PE01 18 110 (NGK)
Spark plug SKYACTIV-G
PE02 18 110 (DENSO)
55D23L (Panasonic, GS Yuasa)
SKYACTIV-G 75D23L (GS Yuasa)
Battery
Q-85 (Panasonic)*
SKYACTIV-D T-110 (GS Yuasa)*
* With i-stop system
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Scheduled maintenance table (for General)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Required procedure after negative battery cable disconnection/connection
Required procedure
Conditions after
disconnecting Before
System name After connecting Remark
the negative disconnecting
battery cable negative battery
negative battery
cable
cable
Power window Reset to initial Perform the
system setting and power window
auto-function is - system initial -
disabled. setting.
Sunroof system Reset to initial Perform the
setting and sunroof system
function is - initial setting. -
disabled.
Clock and audio Clock display Verify the setting Set the verified
and audio content. content before
system memory disconnecting -
are reset. negative battery
cable.
Tire pressure The tire pressure Perform the tire
monitoring Monitoring pressure
system (TPMS) system detection - monitoring -
accuracy system
decreases. initialization.
i-stop system Specified Verify PID Perform battery Only vehicles
information “BATT_SOC” condition initial with i-stop
in the PCM value and record. setting (i-stop
cleared and the *1 setting). *2
i-stop does not
operate normally.
*1: For vehicles with i-stop, if the negative battery cable is disconnected and re-connected, battery
condition initial setting (i-stop setting) must be performed.
*2: Because the “BATT_SOC” value before disconnecting the negative battery cable is required for
the battery condition initial setting (i-stop setting), record the “BATT_SOC” value before
disconnecting the negative battery cable.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
00 – General
TN-CX5-1203
Availability for your
Category Major features
market
SKYACTIV-G 2.0 All markets
01 ENGINE
SKYACTIV-D 2.2
SKYACTIV-Chassis All markets
02 SUSPENSION
TPMS All markets
03 DRIVELINE/AXLE 4WD
SCBS
04 BRAKES
Secondary Collision Reduction
FW6A-EL/FW6AX-EL
6AT
TRANSMISSION/ GW6A-EL/GW6AX-EL
05
TRANSAXLE C66M-R/C66MX-R
6MT
D66M-R/D66MX-R
06 STEERING EPS All markets
Electric water pump
07 HVAC HFO1234yf
PTC heater
08 RESTRAINTS Side airbag
SYACTIV-Body All markets
Main beam control
BODY & LDWS
09
ACCESSORIES RVM
Auto-dimming mirror
Push button start All markets
Multiplex
communication SSU, FBCM, RBCM All markets
10
system
11 i-stop
Please check the availability of the major features for your market.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
SKYACTIV-G 2.0
Item Specification
Engine type SKYACTIV-G 2.0
Type Gasoline, 4-cycle
In-line 4 cylinders,
Cylinder arrangement and number
transverse-mounted
Combustion chamber Pent roof
Displacement (L) 1.997
Bore x Stroke (mm) 83.5 x 91.2
13.0
Compression ratio
14.0
978 {9.97, 142} [300]
Compression pressure (kPa {kgf/cm2, psi} [rpm])
885 {9.02, 128} [300]
Max power [net] (kW/rpm) 113/6,200 (Reference)
Max torque [net] (Nm/rpm) 194/4,100 (Reference)
Open BTDC (º) -32 – 42
IN
Close ABDC (º) 110 – 36
Valve timing
Open BBDC (º) 54 – 11
EX
Close ATDC (º) 7 – 50
IN (mm) 0 (HLA)
Valve clearance [cold]
EX (mm) 0 (HLA)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 1
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
OUTLINE New features
Improved the fuel economy by:
Reducing loss by mechanical resistance
Reducing pumping loss
Reducing fuel consumption at idling)
Adopting a piston with cavity
Long stroke
L-jetronic*1 and D-jetronic*2 type detectors have been adopted for intake air
amount detection, improving the accuracy of the intake air amount measurement.
- MAF sensor adopted
- MAP sensor adopted
- IAT sensor No.1 and No.2 adopted
1
* : Measures the intake air amount directly using the MAF sensor. (L: Luft=Air)
*2: Measures the intake air pressure introduced into the cylinder using the MAP
sensor and calculates the intake air amount indirectly. (D: Druck=Pressure)
Valve timing control has been adopted on both sides of the intake and exhaust,
improving fuel economy and emission performance.
Intake side: Electric variable valve timing control
- Intake CMP sensor adopted
- Electric variable valve timing motor/driver adopted
- Electric variable valve timing relay adopted
Exhaust side: Hydraulic variable valve timing control
- Exhaust CMP sensor adopted
Engine oil control has been adopted reducing engine load.
- Engine oil solenoid valve adopted
Fuel pump control has been adopted improving startability and safety.
- Fuel pump control module adopted
With the adoption of the ion sensor, which detects pre-ignition, engine reliability
has been improved.
With the adoption of LIN communication, wire harness is simplified
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 2
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Mechanical
Mechanical resistance is substantially reduced.
Piston-Crank Reduced crank journal diameter
Improved piston skirt rigidity
Reduced piston ring expansion force
Low tension piston ring
Cam Mirror-like surface finishing
Valves Adopted roller follower HLA (Hydraulic Lash Adjuster)
Reduced valve spring loads
Timing chain Adopted a high rigidity straight chain guide
Reduced timing chain tensile force
Cooling Reduced resistance in the engine coolant flow
High efficient molded plastic water pump impeller
FEAD* Lowered tension drive belt
Lubrication Oil pump discharge pressure control by dual-stage switching
Reduced resistance of the oil passages
Decreased hydraulic pressure demanded by hydraulic devices
* FEAD: Front End Auxiliary Drive
Pumping loss is reduced.
Variable Valve Timing Intake: electrically-driven, Exhaust hydraulic-driven.
Retarded intake valve closed timing
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 3
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Engine exploded diagram
1 Engine 8 Hydraulic lash adjuster (HLA)
2 Drive belt auto tensioner 9 Cylinder head gasket
3 Drive belt 10 Rear oil seal
4 OCV 11 Timing chain
5 Plug hole plate 12 Front oil seal
6 Hydraulic variable valve timing 13 Electric variable valve timing
actuator motor/driver
7 Electric variable valve timing
actuator
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 4
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Cylinder head
Cylinder head bolt
HLA
Exhaust
Intake
Exhaust Intake
Cylinder block
Upper cylinder block
Lower cylinder block
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 5
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Piston
The piston head conducts heat away from the combustion flame, interfering flame
propagation. The cavity on the piston head helps to grow combustion flame.
Initial
flame
With cavity Without cavity
Cavity Piston center
Top ring
Second
ring
Oil ring
Offset
Spacer Side rail
Graphite coat
Piston pin center
Technical tip Positioning the piston end gap/Piston
Left: Position the mark on the piston head in the intake side.
Right: It is required only for the oil ring (Side rails and spacer). It is not required for
the top and second piston rings to be aligned.
Exhaust
Piston pin axis
Lower side rail
Mark Spacer
Intake Upper side rail
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 6
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Crankshaft
The plate for CKP sensor is bolted to the crankshaft. The gap between CKP sensor
and the plate is not required.
Counter weight
Key groove
Plate for CKP sensor signal detection
Technical tip Installing plate for CKP sensor signal detection
Position the wide gap as shown in the image below; tighten the bolts in the following
order: A – B – C.
Wide gap
Crankshaft
B
C
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 7
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Connecting rod
Reference
The connecting rod for SKYACTIV-G is designed to reduce the stress concentration
due to bending moment, contributing to reducing thickness (W) and weight of the
connecting rod.
Tensile load by inertia
Thick
Thin
Bending
moment
Item SKYACTIV-G 2.0 LF
Distance between small and big ends (mm) 155.2 160.3
Thickness (mm) 21.0 21.8
Weight (g) 461 524
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 8
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Valve mechanism
Rocker
Chain guide No. 1 HLA arm
Exhaust camshaft
Timing Intake camshaft
chain
Valve
Needle roller bearing
Needle
roller
Tensioner
arm
Chain
guide
Timing No. 2
chain
tensioner
Rocker arm
Crank
shaft Valve
sprocket HLA
HLA: Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
Oil discharge hole
Plunger Plunger
Body
Oil discharge hole
Body (B) Reserve chamber
Check ball cage
Check ball spring
Plunger spring
(A) High pressure chamber
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 9
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
A B
Air bubble
Chamber A
Baffle
Engine oil
Chamber B Chamber B
A: The plunger is lifted to contact the valve rocker arm to adjust the clearance to
ZERO. If valve clearance is going to exist, the plunger moves up to adjust the valve
clearance to zero. Then, the pressure inside Chamber B lowers, making the check
ball move down to open oil passage, allowing the oil into Chamber B.
Chamber B is filled with engine oil for the plunger to resist the force while the valve is
open.
B: Air bubbles in the engine oil will be separated by the baffle and brought up to
release from the lubricant hole for the rocker arm. If air bubbles intrude into Chamber
B, HLA cannot work properly. This HLA was thoroughly tested for the reliability on
this issue.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 10
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Variable valve timing
Intake: Electric Variable Valve Timing actuator (New)
Exhaust: Hydraulic Variable Valve Timing actuator
Exhaust CMP sensor
OCV
Intake CMP sensor
Hydraulic Variable Valve
Timing Actuator
Electric Variable Valve
Timing Actuator
Electric Variable Valve
CKP sensor Timing Moto/Driver
Intake camshaft position and Exhaust camshaft position are independently detected
and input to the PCM.
Electrical Variable Valve Timing Actuator reduces the speed of the electric motor to
drive the camshaft and varies phase angle difference.
Electric Variable Valve Timing driver drives the built-in electric motor based on the
signal from the PCM.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 11
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Electric Variable Valve Timing Actuator
Electric Variable Valve Timing Moto
Cover
Bearing (Large gear)
Planetary gear
(Small gear)
Eccentric shaft Camshaft gear
Sprocket gear
Intake camshaft
Intake camshaft sprocket
Reference
Advantages of Electric Variable Valve Timing
- Not affected by fluidity of engine oil, which varies depending on the temperature
- No need to equip the actuator with hydraulic chambers, enabling a greater variable
angle
- Electric devices have better responsiveness than Hydraulic devices do
- Directly controlled by the PCM, improving reliability
Electric Hydraulic
Retard Variable angle Retard
Variable angle
Advanced Advanced
C: Hydraulic chamber
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 12
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Electric Variable Valve Timing Motor
Electric variable valve timing motor
Motor shaft
Eccentric shaft
Valve timing control by zone
Mid- /High-load (Low speed)
High-load (Low- /Mid- speed)
High-load (High- speed)
Engine load
Mid-load
Low
load
Engine speed
Idling
Start
(Cold) Appropriate valve timing is determined to ensure effective pressure, which
overcomes the starting resistance, contributing to improved startability.
(Hot) Appropriate valve timing is determined to lower effective pressure, which
prevents abnormal combustion at start from occurring, contributing to improved
startability.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 13
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Idling
Valve overlap is reduced to avoid the exhaust gases back into the Intake manifold
through the combustion chamber. Stabling combustion even before warming-up by
appropriate valve timing contributes to lower fuel consumption.
TDC BDC TDC BDC
Exhaust
Valve lift
Intake Exhaust Intake
Crankshaft angle
BDC
Low load
By retarded intake valve and exhaust valve closing timings, pumping loss is reduced
to improve fuel economy.
Mid-load (Hot)
By retarded intake valve and exhaust valve closing timings, pumping loss is reduced
to improve fuel economy.
TDC BDC TDC BDC
Exhaust
Valve lift
Intake Exhaust Intake
Crankshaft angle
BDC
Mid-load (Cold)
Effective pressure is increased by advanced intake valve closing timing. By reducing
valve overlap, combustion is made stable.
TDC
BDC TDC BDC
Exhaust
Valve lift
Intake
Exhaust
Intake
BDC Crankshaft angle
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 14
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
High-load, Low/Mid-speed
Intake valve closing timing is advanced to prevent intake air from returning back into
the Intake manifold through the combustion chamber. Exhaust valve closing timing is
retarded to scavenge residual exhaust gases in the combustion chamber, contributing
improving volumetric efficiency, which ensures sufficient engine torque for
low/mid-speed range.
TDC BDC TDC BDC
Exhaust Intake
Valve lift
Exhaust Intake
Crankshaft angle
BDC
High-load, High-speed
Intake valve closing timing is retarded to improve inertia charging effect to generate
more sufficient engine power.
TDC BDC TDC BDC
Exhaust
Valve lift
Intake Exhaust Intake
Crankshaft angle
BDC
Miller cycle engine
The Miller cycle engine is a high-efficiency engine which realizes high fuel economy
performance by obtaining a high-expansion ratio. By retarding the intake air valve
close timing substantially, a high-expansion ratio without increasing its effective
compression ratio is made possible.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 15
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Electric variable valve timing control
The PCM determines the optimum intake valve timing according to the engine
operation conditions, and sends the motor drive signals to the electric variable valve
timing driver. With the adoption of the electric drive system, variable intake valve
timing can be controlled without any influence from the engine conditions, thus the
fuel economy has been improved and pumping loss has been decreased.
Based on the coordination with the hydraulic variable valve timing control and by
increasing the amount of overlap during high engine loads, nitrogen oxide (NOx)
occurring largely at high temperatures is reduced by re-circulating exhaust gas into
the combustion chamber which reduces combustion temperature.
Intake valve timing determination
The PCM determines the optimum (1) target intake valve timing, and controls the
output duty ratio to the electric variable valve timing driver so that the (2) actual intake
valve timing approaches close to the target intake valve timing.
(1) Target valve timing
The target intake valve timing is determined according to the engine speed, charging
efficiency, and engine coolant temperature.
(2) Actual valve timing
The actual intake valve timing is calculated by adding a correction, which is based on
the electric variable valve timing actuator signal value, to the value calculated by
subtracting the (3) cam maximum retard learning value from the (4) standard intake
valve timing.
(3) Cam maximum retard learning value
The cam maximum retard learning value is determined by the maximum retard
indication output from the PCM and the standard intake valve timing when the
standard intake valve timing is stabilized.
(4) Standard valve timing
The standard intake valve timing is calculated based on the signals from the
crankshaft position and camshaft position sensors.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 16
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
System wiring diagram
Main relay
Electric variable valve
Electric timing motor/driver
variable valve
timing relay
Speed
1 sensor
Driver
2
PCM Motor
3
1: Driver signals
2: Motor speed signals
3. Motor rotational direction signals
4. Diagnosis signal
Output duty ratio determination
The PCM divides the electric variable valve timing motor drive range modes according
to the engine operation conditions, and determines the output duty ratio to the electric
variable valve timing actuator in each mode.
Mode Description Control conditions
Feedback mode Determine duty cycle ratio based Except when neither of
on the monitored gap between Electricity cut-off mode
target valve timing and actual or Phase-locked mode is
valve timing not executed
Energize cut mode Hold the intake valve timing in the When a malfunction in
most retarded position to stable Eclectic Variable Valve
engine speed Timing driver is detected
Phase holding mode Hold the phase of Eclectic After the engine has
Variable Valve Timing actuator in stopped
the middle after the engine has
stopped
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 17
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Variable valve timing related Fail-safe
Hydraulic variable valve timing
P0014:00 Exhaust CMP timing Performs the exhaust variable valve timing
over-advanced control with a maximum cam retard request.
P0015:00 Exhaust CMP timing Performs the exhaust variable valve timing
over-retarded control with a maximum cam retard request.
P2090:00 OCV circuit low input Performs the exhaust variable valve timing
control with a maximum cam retard request.
P2091:00 OCV circuit high input Performs the exhaust variable valve timing
control with a maximum cam retard request.
Electric variable valve timing
P0011:00 Intake CMP timing Stops activation of the electric variable valve
over-advanced timing driver.
P0012:00 Intake CMP timing Stops activation of the electric variable valve
over-retarded timing driver.
P1380:00 Electric variable valve Stops activation of the electric variable valve
timing control circuit timing driver.
problem
Drive belt
A hydraulic auto-tensioner reduces belt tension force by improved tensioner
performance in absorbing tension force variation.
Hydraulic auto-tensioner
Drive belt auto-tensioner pulley
Water pump belt
Water pump pulley
Generator
pulley
Drive belt
AC compressor pulley
Crankshaft pulley
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 18
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Lubrication system
Pressure loss is reduced by optimizing the oil passage.
With the adoption of the chain drive type oil pump, oil pump drive force has been
reduced.
With the adoption of the oil shower pipe, sliding resistance has been reduced.
With the adoption of the engine oil solenoid valve, oil pump discharge pressure
can be controlled (hydraulic 2-step control).
With oil cooler
Oil cooler
Oil filter body
Oil
filter
Oil filter
Oil filter body
Item Specification
Type of lubrication Full-flow filtered and pressure fed
Oil pressure (reference) (kPa) [rpm] 110 – 175 [1,500]
Relief pressure (kPa) [rpm] 300 – 430 [4,500]
Oil pump
Type Trochoid gear
Type Full-flow
Oil filter
Bypass pressure (kPa) 78 – 118
Engine oil Total (Dry engine) 4.9
(reference) Oil replacement 4
(L) Oil and oil filter replacement 4.2
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 19
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Exploded diagram
Oil shower pipe
Oil jet valve
Engine oil solenoid
valve
Oil pump chain tensioner
Oil pump chain
Oil strainer
Oil pan Oil pump
Oil pump driven
Oil filter sprocket
Oil pan drain plug
Item Description
Oil gallery Reduced pressure loss in the oil gallery; Pressure loss can be reduced
by shortening the length of oil gallery in the cylinder block. The
structure of the cylinder block was totally changed and oil gallery was
shortened by positioning the oil filter behind the drive shaft.
Hydraulic Lowered required pressure for hydraulic devices. If devices can work
device with lower pressure, oil pump can be downsized. Required oil
pressure was reduced by 10% by adjusting crankshaft metals,
Variable Valve Timing, and HLA.
Discharge 1. Feedback control: The maximum oil pressure required for driving
condition is determined based on the oil pressure in the main gallery.
2. The engine oil pressure is regulated based on the ECT, RPM, and
volumetric efficiency.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 20
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Engine oil flow
Oil pump
Pilot valve
Outer rotor
Inner rotor
Bypass valve
Relief valve
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 21
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Engine oil control
The PCM reduces the load and friction resistance applied to the engine by controlling
the appropriate engine oil amount according to the engine operation conditions.
The engine oil amount switches in two steps.
When hydraulic pressure is not needed, the oil pump discharge amount is reduced by
the operation of the engine oil solenoid valve. In addition, if the engine oil solenoid
valve is malfunctioning, priority is given to protecting the engine by maximizing the oil
pump discharge amount.
Spring
Engine oil Coil
solenoid
valve Plunger
Oil pressure switch
Valve
Ball
Return spring
The PCM switches the engine oil pressure which lubricates the engine in two steps by
driving the engine oil solenoid valve according to the engine operation conditions.
HI
Engine oil
Oil pressure
Without Engine oil control
solenoid valve
OFF
LO ON
LO Engine speed HI
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 22
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
The PCM controls the operational voltage energized to the engine oil solenoid
according to the duty signal.
After opening the engine oil solenoid valve at the output duty ratio of 100%, load
applied to the parts is reduced by lowering the duty value to the output duty value at
which the open valve condition can be maintained.
The output duty value for maintaining the opening value changes according to the
battery voltage.
Engine oil solenoid valve: ON
ON
Control signal
OFF
Engine oil solenoid valve: OFF
100
Output duty
0
Output voltage
0
Engine oil solenoid valve operation conditions
The PCM operates the engine oil solenoid valve when any of the following conditions
is met:
Condition Description
Engine speed 4,000rpm or High oil pressure for crankshaft journal and pins is
higher required when in Mid/High speed zone
Ensure the pressure of engine oil being injected from
Low speed/High load
the oil jets to the pistons to avoid temperature rise
Cool down the engine and lubricate the rotational
ECT is at 98ºC or higher
parts for improving reliability
Open circuit, solenoid valve
When a malfunction is detected, engine oil pressure
is adjusted to HI, improving reliability
Other system malfunctions
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 23
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Engine oil flow when setting low oil pressure
Engine oil solenoid valve: ON
To engine
Bypass valve
a b
Pilot valve
From oil strainer
Relief valve
a. When the engine oil solenoid valve is turned ON, oil pressure is applied to the
upper part of the pilot valve. Because almost the same value of the oil pressure is
applied to the upper and lower parts of the pilot valve, the pilot valve is kept pressed
down by the spring force.
b. Oil pressure is applied to the upper part of the relief valve.
c. When the oil pressure exceeds the relief valve opening pressure, the relief valve is
pressed down to open the passage; and therefore, the engine oil flows.
d. When the oil pressure is less than the relief valve opening pressure, the relief valve
closes its passage. As a result, the engine oil flow stops (oil pressure increase).
Engine oil pressure is regulated by repeating c and d.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 24
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Engine oil flow when setting high oil pressure
Engine oil solenoid valve: OFF
c To engine
Bypass valve
Pilot valve
Relief valve From oil strainer
a. When the oil pressure exceeds the pilot valve opening pressure, the pilot valve is
pressed up and oil pressure is applied to the upper part of the relief valve.
b. Because the relief valve opening pressure is exceeded by being applied the oil
pressure to the upper part of the relief valve, the relief valve is pressed down to open
the passage and the engine oil flows (oil pressure decrease).
c. When the oil pressure is less than the pilot valve opening pressure, the pilot valve
closes its passage. As a result, the relief valve closes and engine oil flow stops (oil
pressure increase).
The oil pressure is regulated by repeating b and c.
Lubrication system related Fail-safe
P06DA:00 Engine oil solenoid valve Engine oil control is inhibited
circuit problem
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 25
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Cooling system
Passing water resistance is reduced by improvement of the engine coolant
passage shape.
Pump efficiency is improved by changing the water pump impeller to the closed
impeller.
1 Coolant reserve tank 5 Thermostat
2 Cooling fan motor No.2 6 Radiator
3 Cooling fan motor No.1 7 Cooling system cap
4 Water pump
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 26
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Item Specification
Cooling system type Liquid cooled, Electric fan
Total amount of (reference) (L) 8.1
Water pump Type Centrifugal, Belt driven
Type Wax
Temp. open (°C) 80.5 – 83.5
Thermostat
Temp. full-open (°C) 95
Lift at full-open (mm) 8.5 or more
Supplier Visteon
Radiator
Type Colgate (Sealed)
Cooling system cap Pressure, open (kPa) 90 – 110
Supplier BOSCH
Type Electrically-driven
Cooling fan
No. of blade 7
Outer diameter (mm) 390
Water pump
Using plastic mold water pump impeller with shroud (hard-plastic closed impeller),
water pump efficiency is improved.
Water
pump
body Gasket Impeller Shaft
Impeller
Shroud Optimized
vane shape
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 27
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Reference
Coolant flow resistance is reduced by improvement of the engine coolant passage
shape.
A – A’ Non-SKYACTIV
A A’
Technical tip Water inlet pipe stay bolt
Water inlet pipe stay bolt is not reusable. Replace it with new one when removed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 28
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Technical tip Thermostat cover removal/installation
Projection
Thermostat
Jiggle pin
When removing or installing the thermostat cover, lift it upward as shown in the
figure right so as not to damage, or not to interfere the jiggle valve function.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 29
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Intake-air system
A vacuum pump has been employed to ensure supplying stable vacuum to the
power brake unit.
Check valve
Air hose Vacuum pump
Intake manifold
Throttle body
Fresh-air duct
Air cleaner
Acceleration pedal Resonance chamber
Fresh-air duct Throttle body
Air cleaner
Intake manifold
Resonance chamber
To the PCM
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 30
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Intake-air system related Fail-safe
P2101:00 Throttle valve actuator • Stops the idle air control.
circuit • Stops the drive-by-wire control and sets to
range/performance a throttle valve opening angle necessary for
problem minimum driveability.
P2107:00 Throttle valve actuator • Stops the idle air control.
control module processor • Stops the drive-by-wire control and sets to
error a throttle valve opening angle necessary for
minimum driveability.
P2110:00 Throttle valve actuator • Stops the idle air control.
control system-forced • Stops the drive-by-wire control and sets to
limited RPM a throttle valve opening angle necessary for
minimum driveability.
P2112:00 Throttle valve actuator • Stops the idle air control.
control system • Stops the drive-by-wire control and sets to
range/performance a throttle valve opening angle necessary for
problem minimum driveability.
P2119:00 Throttle valve actuator • Restricts the upper limit of the engine
control throttle body speed.
range/performance
problem
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 31
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Fuel system
A multiple hole type fuel injector has been adopted which provides higher fuel
injection accuracy for improved fuel efficiency and output.
Piston movement-compression by the 4-head cam inside the high pressure fuel
pump heightens the fuel pressure, realizing improved fuel efficiency and output.
By switching the fuel pump discharge amount, a lower load on the fuel pump and
lower power consumption have been realized. In addition, stable fuel supply is
assured by operating the fuel pump according to the engine operation conditions,
improving the startability and safety.
Item Specification
Supplier DENSO
Type Multi-hole (6 holes)
Fuel injector
Type of fuel delivery Top feed
Drive type Electronic
High pressure fuel Regulated pressure (MPa) 20
pump Relief pressure (MPa) Approx. 23.5
Regulating pressure (kPa) Approx. 430
Fuel pump type Electric (Variable speed)
56 (2WD)
Fuel tank capacity (L)
58 (4WD)
Fuel type Regular unleaded
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 32
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Overview
High pressure fuel pump
Fuel injectors Quick release
Quick release connector connector
Fuel distributor
Relay and
fuse block
Fuel pump relay
Fuel injector relay
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 33
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Quick release connector Fuel filter (High Fuel filler
pressure) pipe
Fuel tank
Fuel pump Breather
unit hose
Behind the rear
seat (LH)
Fuel pump
control module
Joint hose
Non-return
valve
High pressure
Fuel injector Pressure regulator
fuel pump
Fuel
tank
Fuel filter (High pressure)
2WD
Fuel pump
Fuel filter (Low
control Fuel pump pressure)
module
Pressure regulator
Fuel
Fuel filter (High pressure) tank
To the PCM Jet
4WD pump
Fuel pump
control Fuel filter (Low
module Fuel pump pressure)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 34
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
High pressure fuel pump
1 Quick release connector 5 Seal rubber
2 High pressure fuel pipe 6 O-ring
3 High pressure fuel pump cover 7 Tension collar
4 High pressure fuel pump 8 Rear housing
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 35
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Fuel injector
Fuel injector
Fuel injectors Multi-hole (6 holes)
Fuel injection pattern
Fuel pump control
The PCM determines the optimum fuel pump drive force according to the engine
operation conditions, and sends the fuel pump drive signal to the fuel pump control
module.
CKP sensor DIAG
FPC
Fuel pressure sensor
PCM +B
Ignition switch
FP+
Fuel pump
FP-
Battery GND
Fuel pump
Circuit opening relay
control module
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 36
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Circuit opening relay
The PCM switches the fuel pump relay on/off according to the engine operation
conditions.
Relay ON/OFF Control conditions
When any of the following conditions is met:
- When ignition is switched ON (for approx. 1 sec)
ON - During engine cranking
- While engine is running
- When engine is stopped by i-stop control
When engine is stopped (excludes engine stop by i-stop
OFF
control)
Fuel pump control module
The PCM determines the fuel pump discharge amount according to the engine
operation conditions, and controls the output duty ratio to the fuel pump control
module according to the discharge amount.
Duty cycle Fuel pump speed Operational condition
When any of the following conditions is met:
- At engine start
95% MAX
- Fuel pump control module malfunction (if
request voltage is unobtainable)
- Feedback value from fuel pressure sensor is
the specified value or more (Determined that
Depending on the
10% – 90% high pressure fuel pump compression is high.)
duty cycle
- Except for control conditions with output duty
ratio of 5% or 95%
When engine is stopped (excludes engine
5% 0 stop by i-stop control for SKYACTIV-G with
i-stop)
Fuel injection control
The PCM determines the engine operation conditions based on the signals from each
input device and drives the fuel injectors at the optimal fuel injection time (fuel
injection amount) and the fuel injection timing to inject fuel.
By controlling the combustion conditions between uniform combustion and stratified
combustion based on the fuel injection amount, fuel injection timing, and fuel injection
times, emission performance while the engine is cold and higher engine output have
been realized.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 37
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Reference
Uniform combustion: Fuel injected during intake stroke is well mixed with intake
air, avoiding uneven air-fuel mixture. In general, homogenous combustion
contributes to generating more power, but less contribution to improving fuel
economy. It is also known as Homogeneous combustion.
Stratified combustion: The spark plug ignites richer air-fuel mixture, producing a
frame which is strong enough to grow the frame with leaner air-fuel mixture.
Generally, stratified combustion is used for lean combustion.
Uniform combustion Stratified combustion
Rich
air-fuel
Uniformed mixture
air-fuel
mixture Lean
air-fuel
mixture
Fuel can be injected at any moment for direct injection. But, it is hard to form ideal
stratification of the air-fuel mixture. In SKYACTIV-G, it is solved by adopting cavity
piston, improved port design, etc.
Fuel system related Fail-safe
P0089:00 Spill valve control • Limits the intake air amount.
solenoid valve control • Stops the high pressure fuel pump control.
circuit range/performance • The upper limit of the engine speed is
problem 2,500 rpm.
P0091:00 Fuel pressure regulator • Limits the intake air amount.
control circuit low input • Stops the high pressure fuel pump control.
P0092:00 Fuel pressure regulator • Limits the intake air amount.
control circuit high input • Stops the high pressure fuel pump control.
P025B:00 Fuel pump control • Stops the fuel pump control (when
module circuit overheating is detected).
range/performance
problem
P0629:00 Fuel pump control • Stops the fuel pump control.
module circuit high input
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 38
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Exhaust system
Exhaust manifold
WU-TWC
WU-TWC Pre-silencer
TWC
Main silencer
Exhaust manifold (4-2-1 exhaust system)
4-2-1 exhaust system
When the No.1 cylinder is at the intake stroke, the No.3 cylinder is at the exhaust
stroke. By inducing the high temperature gas exhausted from the No.3 cylinder into
the No.1 cylinder, the high temperature gas in the No.1 cylinder remains. If the
amount of residual gas is high, the temperature in the combustion chamber rises and
knocking can easily occur.
With the 4-2-1 exhaust system, the transmission of exhaust pressure waves between
each cylinder is delayed by the long exhaust pipes. The major issue with the 4-2-1
exhaust system is that the long distance cools the exhaust gas before it reaches the
catalyst, delaying the catalyst’s activation. So the exhaust gas temperature is
increased by retarding the ignition timing without sacrificing stable combustion. (Too
much retarded ignition timing causes unstable combustion)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 39
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Emission system
Purge solenoid valve
Charcoal canister
Catch tank
Ventilation hose Check valve
Rollover
valve Fuel-filler
cap
Check valve
Rollover
PCV valve valve Fuel-filler
cap
To the PCM
WU-TWC TWC
A single-nano catalyst has been adopted for the under-floor three-way catalyst. With a
conventional three-way catalyst, the precious metals move and agglutinate to each
other by the heat of the exhaust gas because they are structured such that they
adhere on catalyst material.
Therefore, it was necessary to use a large amount of precious metal because it is
estimated that the purification performance lowers due to the decrease in the surface
area of the precious metals.
The single-nano catalyst is structured such that it embeds small precious metal
particles into the catalyst material.
Because the precious metal particles do not agglutinate on the surface of the
three-way catalyst, it can maintain superior purification performance using less
precious metal than the conventional system.
Item Specification
Three-way catalytic converter (Monolith catalyst), immediate
Catalyst type
after the exhaust manifold
Emission system Canister
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 40
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Catch tank
Quick release connector
Ventilation hose
PCV valve
Purge solenoid valve
Fuel filler cap
Rollover valve
Plug
Check valve
Charcoal canister
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 41
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Ignition system
New features
An ignition coil built-into the ion sensor has been adopted.
An iridium spark plug has been adopted to prevent pre-ignition from occurring.
Ignition coil connector
Ignition coil & spark plug
Iridium alloy
Platinum tip
Item Specification
Type Direct ignition
Ignition
Spark advance Electronically-controlled
system
Firing order 1-3-4-2 (Sequential ignition)
PE01 18 110 (DILKAR7F8)
Type
PE02 18 110 (FC20HPR8)
Spark plug
NGK PE01 18 110 (DILKAR7F8)
Supplier
DENSO PE02 18 110 (FC20HPR8)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 42
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Pre-ignition and Knocking
Pre-ignition: Air-fuel mixture is ignited due to excessive heat before the ignition by
sparks.
Knocking: It is a collision between the intended combustion propagations and
unintended combustion propagation such as self-ignition due to high compressed end
gas.
How to prevent pre-ignition/knocking from occurring?
1. Avoid rise in gas temperature inside the cylinder: cool down the air-fuel mixture
Abnormal combustions tend to occur when gas temperature is high
2. Complete combustion rapidly
Abnormal combustions tend to occur when there is unevenness in combustion
propagation
Pre-ignition Knocking
Ion sensor
Ions are generated based on: fuel combustion = chemical reaction / disassociation.
The generated negative ions move to the center electrode of the spark plug to which
bias voltage is applied, positive ions move to the grounded engine wall surface.
Spark plug Spark plug
Bias capacitor
Cylinder Negative
head ions
Positive
ions
Piston
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 43
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Detecting the amount of ion
The ionic electrical current (2) is detected by applying the voltage, which is
accumulated in the capacitor (1) due to the secondary ignition current.
Electric current (4), which is amplified by the ion detection circuit (3) is pulled in to the
ignition coil from the PCM.
The PCM detects the amount of ion produced in the combustion chamber by
measuring and converting the current (4) into voltage.
Spark plug
Battery
Main relay Ignition coil
PCM
Ignition
control
circuit
CPU
Current/
voltage
converter
circuit Ion detection circuit
The input signals from ion sensors are used for Fuel injection control and Electric
variable valve timing control, not for Electric spark advance control.
Ion sensor related DTCs
P2302:00 Ion sensor No. 1 circuit problem (Detection condition)
P2305:00 Ion sensor No. 2 circuit problem After the engine is started, when the
engine speed is 2,000 rpm or less,
P2308:00 Ion sensor No. 3 circuit problem the signal input to the PCM from the
P2311:00 Ion sensor No. 4 circuit problem ion sensor is in error.
Ignition system related fail-safe
P0300:00 Random misfire detected Limits the intake air amount
P0301:00 Cylinder No.1 misfire detected - Stops the fuel injection to the
misfiring cylinder.
P0302:00 Cylinder No.2 misfire detected
- Limits the intake air amount.
P0303:00 Cylinder No.3 misfire detected
P0304:00 Cylinder No.4 misfire detected
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 44
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Control system
ew features
Location in this
New parts, devices, control items
textbook
New parts/devices Fuel pump control module Fuel system
Ion sensor Ignition system
Electric variable valve timing driver Mechanical
Electric variable valve timing motor &
Mechanical
actuator
Intake camshaft position sensor Mechanical
Exhaust camshaft position sensor Mechanical
Engine oil solenoid valve Lubrication system
New control items Variable valve timing control Mechanical
Fuel pump control Fuel system
Engine oil control Lubrication system
Control item Location in this textbook
Main relay control -
Drive-by-wire control -
Hydraulic variable valve timing control -
Electric variable valve timing control 01 Engine - Mechanical
Fuel injection control 01 Engine - Fuel system
Fuel pump control 01 Engine - Fuel system
High pressure fuel pump control 01 Engine - Fuel system
Electric spark advance control -
Purge control -
HO2S/A/F sensor heater control -
A/C cut-off control -
Engine cooling fan control -
Starter cut-off control -
Generator power control 01 Engine - Charging system
i-stop control 11 i-stop
DC-DC converter control 01 Engine - Charging system
Engine oil control 01 Engine - Lubrication system
CAN (10 Multiplex Communication System)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 45
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Output devices (1)
1 Fuel injector 6 Spill valve control solenoid valve
2 Electric variable valve timing 7 Relay and fuse block
motor/driver 8 Generator
3 OCV 9 Starter motor
4 Ignition coil 10 Throttle valve actuator
5 Purge valve 11 DC-DC converter
Relay and fuse block
Fuel pump relay, Starter relay, Electric variable valve timing relay, Fuel injector relay,
main relay, A/C relay, Cooling fan relay No.1, Cooling fan relay No.2, Cooling fan
relay No.3
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 46
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Output devices (2)
1 Fuel pump control module 3 A/F sensor heater
2 HO2S heater 4 Engine oil solenoid valve
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 47
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Input devices (1)
1 Electric variable valve timing 11 Fuel pressure sensor
motor/driver
2 Refrigerant pressure sensor 12 Generator
3 Ion sensor 13 KS
4 Power brake unit vacuum sensor 14 Ambient temperature sensor
5 Intake CMP sensor 15 MAP sensor/IAT No.2 sensor
6 ECT sensor 16 TP sensor
7 Exhaust CMP sensor 17 Neutral switch No. 1 (MTX)
8 PCM (BARO sensor) 18 MAF sensor/IAT No.2 sensor
9 Current sensor 19 Neutral switch No. 2 (MTX)
10 Power brake unit vacuum sensor 20 DC-DC converter
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 48
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Input devices (2)
1 Starter interlock switch (MTX) 6 i-stop OFF switch
2 Clutch stroke sensor 7 A/F sensor
3 CPP switch (MTX) 8 CKP sensor
4 Brake switch 9 HO2S
5 APP sensor 10 Transaxle range sensor (ATX)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 49
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Output devices
1 Throttle valve actuator 6 OCV
2 Purge solenoid valve 7 Fuel pump control module
3 Electric variable valve timing 8 Fuel injector No. 1 – No. 4
motor/driver 9 Engine oil solenoid valve
4 Ignition coil No. 1 – No. 4 10 A/F sensor heater
5 Spill valve control solenoid valve 11 HO2S heater
Generator field coil, DC-DC converter*, Cooling fan relay No. 1, No. 2, No. 3, Fuel
pump relay, Starter, Starter relay, Electric variable valve timing relay, Fuel injector
relay, Main relay, A/C relay, CAN
*: Vehicles with i-stop system
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 50
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Input devices
1 MAF sensor/IAT sensor No. 1 8 ECT sensor
2 TP sensor No. 1, No. 2 9 Fuel pressure sensor
3 MAP sensor/IAT sensor No. 2 10 KS
4 Electric variable valve timing 11 CKP sensor
motor/driver 12 Oil pressure switch
5 Intake CMP sensor 13 A/F sensor
6 Ion sensor No. 1 – No. 4 14 HO2S
7 Exhaust CMP sensor 15 BARO sensor
APP sensor No. 1, No. 2, IG1 relay, Generator (Stator coil), Brake switch (No. 1
signal, No. 2 signal), Battery, Refrigerant pressure sensor, Ambient temperature
sensor, Transaxle range sensor, Starter interlock switch (MTX), Neutral switch No.
1(MTX), Neutral switch no. 2 (MTX)*, CPP switch (MTX), Clutch stroke sensor
(MTX)*, CAN
*: Vehicles with i-stop system
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 51
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Output devices associated with the control items
Hydraulic variable valve timing control
Electric variable valve timing control
HO2S/A/F sensor heater control
High pressure fuel pump control
Electric spark advance control
Engine cooling fan control
DC-DC converter control
Generator power control
Starter cut-off control
Drive-by-wire control
Fuel injection control
Fuel pump control
A/C cut-off control
Main relay control
Engine oil control
Purge control
i-stop control
Main relay X
Throttle valve actuator X X
Electric variable valve timing motor/driver X X
Electric variable valve timing relay X X
OCV X
Fuel injector No.1 - No.4 X X
Fuel injector relay X X
Fuel pump control module X
Fuel pump relay (Circuit opening relay) X
Spill valve control solenoid valve X
Ignition coil No.1 - No.4 X X
Purge solenoid valve X
A/F sensor heater X
HO2S heater X
A/C relay X
Cooling fan relay no. 1, no. 2, No. 3 X
Starter relay X X
Generator (field coil) X X
DC-DC converter X X
Engine oil solenoid valve X
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 52
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Input devices associated with the control items
Hydraulic variable valve timing control
Electric variable valve timing control
HO2S/A/F sensor heater control
High pressure fuel pump control
Electric spark advance control
Engine cooling fan control
DC-DC converter control
Generator power control
Starter cut-off control
Drive-by-wire control
Fuel injection control
Fuel pump control
A/C cut-off control
Main relay control
Engine oil control
Purge control
i-stop control
APP sensor No.1, No.2 X X X X X X X X
TP sensor X X X X
MAF sensor X X X X X X X X X X X
IAT sensor No.1 X X X X X X X X
IAT sensor No.2 X X X X X
MAP sensor X X X X X X X
CKP sensor X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
Intake CMP sensor X X X X X
Exhaust CMP sensor X X X X X X
ECT sensor X X X X X X X X X X X X X X
Fuel pressure sensor X X X X X
BARO sensor X X X X X X X
Power brake unit vacuum sensor X
Ion sensor No.1 - No.4 X X
KS X
A/F sensor X X
HO2S X
Refrigerant pressure sensor X X
*2 *2, *3
Engine switch (IG1) , (STA) IG1 relay X X X X X X X X X X
Oil pressure switch
Brake switch (No.1 signal) X X
Brake switch (No.2 signal) X
Transaxle range sensor (ATX) X X X X
CPP switch (MTX) X X X X X
Starter interlock switch (MTX) X
Clutch stroke sensor (MTX) X
Neutral switch No. 1 (MTX) X X X X X
Neutral switch No. 2 (MTX) X
Fuel pump control module
Electric variable valve timing motor/driver X X
Battery X X X X X X X
Generator stator coil X
*1
CAN related components X X X X X X X X
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 53
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Control System Wiring Diagram (1/3)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 54
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Control System Wiring Diagram (2/3)
With i-stop system
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 55
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Control System Wiring Diagram (3/3)
With i-stop system
With i-stop system
As indicated in the diagram, the lines between injectors and the PCM are twisted pair
cables which reduce noise. They are not CAN lines.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 56
Mazda CX-5
01G – Engine – SKYACTIV-G 2.0
TN-CX5-1203
Technical tip PCM replacement
There are two types of PCM settings. If the incorrect PCM is installed, it could cause
interference with engine control. When replacing the PCM, verify the first four digits
of the part number indicated on the PCM label before replacement, and replace the
PCM with one having the same part number.
Technical tip PCM connector
Do not touch the PCM connector terminal. The terminal is extremely thin and can be
damaged by touching it. If the PCM connector is inserted at an angle and the lever is
moved, the connector could be damaged. Verify that the PCM connector is inserted
straight.
Because the PCM uses a waterproof connector, the inspection for the voltage/wave
pattern cannot be performed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. TN-CX5-1203 57
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
Front suspension
Item Specification
Type Strut type
Spring type Coil spring
Low-pressure gas charged,
Shock absorber type
cylindrical, double-acting
Type Torsion bar
Stabilizer
Diameter (mm {in}) 21.0 {0.827}
Tire (mm {in})
2 {0.08}
Total toe-in [Tolerance ±4 {0.2}]
[Tolerance Rim inner (mm {in})
1.0 {0.04}
±4 {0.2}] [Tolerance ±3 {0.1}]
(Degree) 0°10′±0°20′
Wheel
alignment Maximum steering Inner 37°48′
(Unloaded) angle [Tolerance ±3°] Outer 30°54′
SKYACTIV-G 2.0: 6°29′
Caster angle [Tolerance ±1°]
SKYACTIV-D 2.2: 6°25′
Camber angle [Tolerance ±1°] -0°22′ (Reference)
Steering axis inclination 12°00’ (Reference)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
Rear suspension
2WD
4WD
Item Specification
Type Multi-link
Spring type Coil spring
Low-pressure gas charged,
Shock absorber type
cylindrical, double-acting
Type Torsion bar
Stabilizer 2WD: 18.0 {0.709}
Diameter (mm {in})
4WD: 19.0 {0.748}
Tire (mm {in})
1.0 {0.04}
Total toe-in [Tolerance ±4 {0.2}]
Wheel [Tolerance Rim inner (mm {in}) With 17 inch wheel: 1.4 {0.04}
alignment ±4 {0.2}] [Tolerance ±3 {0.1}] With 19 inch wheel: 1.4 {0.04}
(Unloaded) (Degree) 0°10′±0°20′
Camber angle [Tolerance ±1°] -1°01′ (Reference)
Thrust angle [Tolerance ±0°48’] 0°00’
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
Tire & Wheel
Item Specification
Tire size 225/65R17 102V 225/55R19 99V
Supplier Yokohama Toyo
Front 230 250
Tire air pressure (kPa)
Rear 230 250
Wheel size 17×7J 19×7J
Steel
Material Aluminum alloy
Aluminum alloy
Inset (mm {in}) 50 {in}
Pitch Circle Diameter (mm {in}) 114.3 {4.50}
Hub diameter (mm {in}) 67 {in}
Temporary spare tire & wheel (Except Mexico specs)
Item Specification
Tire size T145/90D16 106M T155/90D18 103M
Wheel size 16 x 4T 18 x 4T
Inset (mm {in}) 40 {1.6}
Pitch Circle Diameter (mm {in}) 114.3 {4.50}
Material Steel
Temporary spare tire & wheel (Mexico specs)
Item Specification
Tire size 185/80R17 95M
Wheel size 17 x 5 1/2J
Inset (mm {in}) 45 {1.8}
Pitch Circle Diameter (mm {in}) 114.3 {4.50}
Material Steel
CX- 5 air pressure
(kPa {bar <psi>}) 225/65R17 102V 225/55R19 99V
Front Up to 3 persons 230 {2.3, <33>}*3 250 {2.5, <36>}
250 {2.5, <36>}*3
Full load 260 {2.6, <38>}*3 260 {2.6, <38>}
270 {2.7, <39>}*3
Rear Up to 3 persons 230 {2.3, <33>}*3 250 {2.5, <36>}
250 {2.5, <36>}*3
Full load 280 {2.8, <41>}*3 290.9, <42>}
290 {2.9, <42>}*3
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
TPMS (Tire Pressure monitoring System)
This TPMS is a supplementary system, which indirectly detects tire air pressure drop
and warns the driver that a tire pressure has lowered.
Tire air pressure is estimated by sensing the difference in rotational speed of wheels
and peak of frequency in the torsional vibration that varies depending on tire air
pressure.
TPMS monitors the gap between the previously determined value by an initialization
with TPMS set switch and the monitored value.
TPMS warning light
Rear ABS
wheel speed
2WD
sensor
4WD
Instrument cluster
TPMS set switch
Rear ABS
wheel speed
sensor
DSC
HU/C
Ambient
temperature BARO
sensor sensor
(PCM*) Front ABS wheel speed sensor
* PCM: The PCM location indicated in the image above is for SKYACTIV-g 2.0.
TPMS warning light
Illuminates or flashes based on the DSC HU/CM command.
Illuminates if a tire pressure decreases below the specified value based on the
initialization.
flashes for 1 min if a malfunction in the tire pressure monitoring system is detected,
and then it illuminates.
The initialization is to be performed if TPMS warning light has illuminated by
pressing TPMS set switch. If it is not performed, the TPMS light will illuminate
again when the ignition is switched from OFF to ON.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
Operation chart
Warning light comes on
Tire air pressure adjusted
TPMS initialization (set switch)
Warning light goes off
Tire air pressure
Gap detected by
the system
Initialization learning
(It takes for about 20 min to complete.)
Time
ON
TPMS set switch OFF OFF
ON Blink
TPMS warning light OFF OFF
Misuse prevention
If TPMS is initialized without adjusting the tire air pressures after the TPMS warning
light illuminated, but the difference between the predetermined value and the value
determined by the initialization is within the specification, the TPMS warning light
comes on for the driver to adjust the tire air pressure and perform initialization. This
misuse prevention logic operates two times.
Tire air pressure
Without tire pressure adjustment
Initialization Initialization Initialization Initialization
learning learning learning learning
ON ON ON ON Time
TPMS set switch
Blink ON Blink Blink Blink
TPMS warning light
1. TPMS warning light illuminates due to a decrease in tire air pressure
2. TPMS warning light illuminates due to misuse prevention (1st time)
3. TPMS warning light illuminates due to misuse prevention (2nd time)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
TPMS initialization
Learning value can be reset (TPMS initialization) by TPMS set switch located in the
cabin.
TPMS initialization must be performed when any of the following is met:
Tire air pressure is adjusted
Tire rotation is performed
Tire or wheel is replaced
DSC/ABS unit is replaced
The battery is replaced or completely dead
Wheel speed sensor is replaced
TPMS warning light comes on “Perform it after tire air adjustment”
Technical tip Check completion of TPMS initialization
TPMS initialization is to be completed after the vehicle is driven for a certain time.
But, on top of that, it actually takes several minutes or several tens of minutes after
the ignition switch has been made OFF in order to complete the initialization.
If the battery cable is disconnected soon after the ignition switch is made off, the
initialization will not be completed.
The status of initialization completion can be checked with M-MDS: DDS_MODE.
Before pressing After TPMS set Driving IG-OFF IG-ON
TPMS set switch switch pressed
Status of In progress In progress In progress Completed
initialization
DDS_MODE Learned/Learning Learning Learning - Learned
Note that DDS_MODE PID will indicate “Learned” even if the initialization has not
been completed due to disconnection of battery cable (DSC HU/CM lost power
before initialization completion.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
System wiring diagram
Components
Tire pressure monitoring system warning light
Output device
Tire pressure monitoring warning alarm
Module DSC HU/CM
ABS wheel-speed sensors
Ambient temperature sensor
Input device
BARO sensor
Tire pressure monitoring system set switch
Communication signal via CAN
Signal/Information Module
BARO sensor PCM
Tire pressure monitoring system set switch Instrument cluster
Tire pressure monitoring system warning light Instrument cluster
Tire pressure monitoring warning chime Instrument cluster
Other signals Other control modules
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
Inoperable conditions
TPMS will not work properly under the following conditions:
Size, manufacturer, or the type of tires is different from the specified ones
Size, manufacturer, or the type of a tire is different from the others, or the level of
tire wear is excessively different between them
A run-flat tire, studless tire, snow tire, or tire chains are used
An emergency tire is used (The tire pressure monitoring system warning light
may flash and then continue illuminating)
A tire is repaired using the emergency flat tire repair kit
Tire pressure is excessively higher than the specified pressure, or the tire
pressure is suddenly lowered for some reason such as a tire burst during driving
Vehicle speed is less than about 15 km/h (including when the vehicle is stopped),
or the drive period is shorter than 5 minutes
Vehicle is driven on an extremely rough road or a slippery, icy road
Hard steering and rapid acceleration/deceleration are repeated such as during
aggressive driving on a winding road.
Reference
Unlike the previous TPMS system, this new TPMS estimates tire pressure based on
the rotational speed and the peak of frequency in torsional vibration of the tires,
which enables to calculate dynamically-loaded radius of tires.
Therefore, it is regarded as an indirect TPMS in order to differentiate it from the
previous systems. Some other auto-manufacturers introduced similar indirect
TPMS, which estimates tire pressure merely based on the tire rotational speed, not
referring to torsional vibrations.
Direct TPMS Indirect TPMS Indirect TPMS for CX-5
Pressure sensor with Wheel speed sensor, Wheel speed sensor,
transmitter sensing wheel speeds sensing wheel speeds and
torsional-vibration
Pressure sensor with transmitter is costly.
Simultaneous air pressure drop occurring in all tires cannot be detected by only tire
rotational speed. But, it is possible to detect such simultaneous air drop in all tires
by using the rotational speed and torsional vibration of tires in relation.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
Detection method
Torsional vibration is detected in frequency of around 30 - 50 Hz. The peak of this
frequency varies depending on the tire air pressure. Air drop at a tire can be
individually detected by monitoring the variation of this frequency.
Integrated value of the
variety of frequency
Variation in frequency
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 (Hz)
Input from wheel speed sensor
With low air pressure
With specified air pressure
Range of variation with
respect to the pressure
changes
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 (Hz)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
02 – Suspension
TN-CX5-1203
TPMS related DTC
C1031:35 Tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) set switch
Detection Continuous ON signal from the TPMS set switch for 60 s or more is
condition detected.
Fail-safe - TPMS warning light illuminates after flashes.
function - Inhibits the TPMS control.
Possible - The driver pressed and held the TPMS set switch for 60 s or more.
causes - TPMS set switch malfunction
C1031:41 Tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) system
Detection When the DSC HU/CM detects malfunction in the memory for storing
condition a calculated tire pressure value.
Fail-safe - TPMS warning light illuminates after flashes.
function - Inhibits the TPMS control.
Possible - DSC HU/CM internal error
causes - DSC HU/CM malfunction
C1031:54 Tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) system
- Detects that tire such as temporary spare tire with outer diameter of
Detection considerable difference is installed
condition - There is a large fluctuation in steering angle and
acceleration/deceleration speed repeatedly over short intervals.
Fail-safe - TPMS warning light illuminates after flashes.
function - Inhibits the TPMS control.
- Diameter of currently installed tires differs from Mazda
recommended tires
Possible
- There is a large fluctuation in steering angle and
causes
acceleration/deceleration speed repeatedly over short intervals.
- DSC HU/CM malfunction
C1031:68 Tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) system
Detection Error is detected in ambient temperature sensor from PCM via CAN
condition communication.
Fail-safe - TPMS warning light illuminates after flashes.
function - Inhibits the TPMS control.
Possible - Ambient temperature sensor malfunction
causes - PCM malfunction
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 10
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Specifications
Item SKYACTIV-G 2.0 SKYACTIV-D 2.2
Front axle type Wheel bearing type Angular ball bearing
Rear axle type Wheel bearing type Angular ball bearing
Joint Wheel side Bell joint
type Differential side Tripod joint
Front drive LH: 26.0 {1.024} LH: 27.0 {1.063}
ATX
shaft Shaft diameter RH: 27.5 {1.08} RH: 29.0 {1.142}
(mm {inc.}) LH: 27.0 {1.063}
MTX
RH: 29.0 {1.142}
Joint Wheel side Bell joint
Rear drive
type Differential side Tripod joint
shaft (4WD)
Joint diameter (mm {inc.}) 22.0 {0.87}
Reduction gear type Hypoid gear
Differential gear type Straight bevel gear
Ring gear size (inc.) 7.4
Rear Final reduction ratio 2.928
differential No. of Drive pinion 14
teeth Ring gear 41
Genuine long-life hypoid
Differenti Type
API GL-5, SAE 80W-90
al oil
Qty. (L) 0.45 (Reference)
Genuine long-life hypoid
Transfer Type
Transfer API GL-5, SAE 80W-90
oil
Qty. (L) 0.45 Reference)
Item SKYACTIV-G 2.0 SKYACTIV-D 2.2
L1 741.5 {29.19}
Length (mm {inc.})
L2 1353.8 {53.299}
Propeller Outer diameter D1 75 {3.0}
Shaft (4WD) (mm {inc.}) D2 68 {2.7}
Joint type CV joint with hook joint
CV joint Double-offset joint
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Axle
An angular ball bearing, with a low rotational resistance, has been adopted,
improving drivability.
A unit bearing that does not require pre-load setting has been adopted, improving
serviceability.
Front axle Rear axle (2WD) Rear axle (4WD)
Technical tip
Knuckle and hub bolts are to be tightened in angle after tightened in torque.
20 – 24 N·m + 60.0° - 70.0°
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Drive shaft
Rear drive shaft (RH)
Front drive shaft (RH)
Integrated with joint shaft
Rear drive shaft (LH)
Front drive shaft (LH)
Technical tip Front drive shaft removal
Remove the front drive shaft (RH) from the transfer. Front drive shaft can be
separated from joint shaft.
Drive shaft (RH) Drive shaft (LH)
Joint shaft
Bearing
Transfer
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Transfer
A transfer with simple, one-axis construction has been adopted for size and
weight reduction.
A thinner transfer case has been adopted for weight reduction.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Rear differential
Rear differential and coupling component are integrated to reduce size and
weight.
Differential carrier made of aluminum alloy contributes to reducing weight.
Front view Rear view Side view
CX-7
Do not compare in size.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Bearing cap is eliminated. The side bearings are supported by the rear end cover to
downsize and reduce the size and weight.
Rear end cover
Side bearing
housing portion
Technical tip
When the rear end cover is removed, the outer shims will be inclined as a half of its
part will be free. Use a hydraulic press to clamp the differential components together
with the outer shims in order to install the rear end cover.
Hydraulic
press
SST: 49 B032 335A
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
4-Wheel Drive system
Differential oil temperature sensor
Rear differential
4WD warning light
Electronic control coupling
4WD control module (4WD solenoid)
Instrument cluster
DSC HU/CM
PCM
TCM
Components
Output device Electronic control coupling (4WD solenoid)
Module 4WD CM
Input device Differential oil temperature sensor
Communication signal via CAN
Signal/Information Module
Accelerator Pedal Position
PCM
Engine speed
Shift position TCM
Wheel speeds
DSC operating condition DSC HU/CM
Coupling torque request
Parking brake position Instrument cluster
Technical tip When replacing the 4WD CM
Always perform the configuration before removing the 4WD CM. Replacing the
4WD CM without performing the configuration procedure will result in a system
malfunction.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
System wiring diagram
Block diagram
DSC EPS Instrument
PCM TCM SSU
HU/CM CM cluster
4WD CM
4WD
Transfer solenoid
Transaxle Pilot clutch Ball main Main Rear
Pilot cam cam clutch differential
Rear
: Torque transmission drive
Front
drive : Electric signal shaft
shaft : Solenoid activation
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Normal Control
When starting off or accelerating during straight-ahead driving, torque transmitted
to the rear wheels is optimally controlled to ensure sufficient acceleration
performance. Due to this, standing-start and acceleration performance is
improved.
If a parking brake signal input to the 4WD CM indicates, the module controls the
torque transmitted to the rear wheels.
Tight Cornering Control
When the 4WD CM determines, based on the four-wheel speed signal, that the
vehicle is in tight cornering, it reduces the torque transmitted to the rear wheels to
avoid tight corner braking characteristics.
Integrated DSC Control
If a signal from the DSC HU/CM input to the 4WD CM indicates that ABS control
is activated, the module controls the torque transmitted to the rear wheels to
prevent undue influence on ABS control.
Also, when a coupling torque request signal is received from the DSC CM, the
module controls the torque transmitted to the rear wheels to match the amount of
requested torque.
Other Control
In case the rear differential oil temperature exceeds the specified amount, or
when there is an unusually large variation in the rotation speed of the front and
rear wheels (ex. when trying to get unstuck), control is temporarily suspended in
order to protect the 4WD system. When this occurs, the 4WD warning light
flashes to indicate the situation to the driver.
Reference
The scheme of toque distribution has changed from the throttle valve opening
angle, which was adopted for the previous models, to the required torque: when
required the required torque is distributed to the rear wheels according to the
degree of slippage.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
Electronic Control Coupling
The electronic control coupling basically consists of an electromagnetic clutch, a
cam mechanism and a torque transmission system.
The electromagnetic clutch consists of a 4WD solenoid (electromagnetic coil),
rear-housing that forms a magnetic path, pilot clutch, and armature. The cam
mechanism consists of a pilot cam, balls, and main cam.
The torque transmission system consists of a main clutch and hydraulic oil (ATF).
Electromagnetic clutch
Torque transmission system
Rear housing
4WD solenoid
Cam mechanism
Cam ball
Front Rear
Pilot cam
Pilot clutch
Main clutch
Main cam
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 10
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
To distribute torque to the rear wheels, the 4WD CM energizes the 4WD solenoid.
The pilot cam is locked by the pilot clutch when 4WD solenoid is energized. The
difference in speed between Pilot cam and Main cam produces a wedge effect
through the balls. This wedge effect generates clutch force of the main clutch.
Main clutch Pilot clutch 4WD solenoid
4WD CM
Pilot cam
Mail cam
Cam ball
Armature
Cam ball
Main cam Pilot cam
4WD solenoid OFF 4WD solenoid ON
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 11
Mazda CX-5
03 – Drivetrain/Axle
TN-CX5-1203
4WD control module configuration
Technical tip
Coupling component calibration
Configuration and/or calibration are required when replacing 4WD CM and/or
Coupling component. This is to correct the individual difference due to
manufacturing tolerance and variations.
See the table below to identify what is required:
Component to be replaced Required operation Remark
4WD CM Configuration Perform calibration if data
cannot be retrieved.
Coupling component Calibration -
4WD CM & Coupling Configuration & Either configuration or
component Calibration calibration can be performed
first.
DTC U2100:00 will be stored if configuration is not properly done.
DTC P164D:00 will be stored if calibration is not properly done.
Data for configuration
Read the special character string before removing the coupling component and
write it to the 4WD CM after replacement.
The special character string is indicated in the two locations shown in the figure.
Description label for special character string
Laser-mark special character string
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 12
Mazda CX-5
04 – Brakes
TN-CX5-1203
New Features
Conventional brake system
Brake pedal intrusion is minimized to improve driver safety.
Master cylinder with a small diameter and long stroke is employed to improve
operability and response.
A vacuum pump is employed to ensure braking force.
Master cylinder
Power brake unit
Brake pedal
Rear disc brake with
built-in parking
Vacuum pump
Front disc brake
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
04 – Brakes
TN-CX5-1203
Specifications
Item Specification
Type Suspended
Brake pedal Pedal lever ratio 2.79
Maximum stroke (mm {in}) 132.7 {5.224}
Master Type Tandem
cylinder Cylinder bore (mm {in}) 20.64 {0.8126}
Type Ventilated disc
Cylinder bore (mm {in}) 60.3 {2.37}
Front brake Pad dimensions (area x thickness)
6,000 × 10 {9.300 × 0.39}
(mm2 x mm {in2 x in})
Disc plate dimensions (mm {in}) 297 × 28 {11.7 × 1.1}
Type Solid disc
Cylinder bore (mm {in}) 38.1 {1.50}
Rear brake Pad dimensions (area x thickness)
2,800 × 8.5 {4.340 × 0.33}
(mm2 x mm {in2 x in})
Disc plate dimensions (mm {in}) 303 × 10 {11.9 × 0.39}
Vacuum multiplier, single
Power brake Type
diaphragm
unit
Outer diameter (mm {in}) 248.5 {9.783}
Brake force EBD (Electronic brake force
Type
control distribution)
Brake piping Piping X pattern
Mechanical design, rear
Type
two-wheel braking
Parking
Manually operated lever
brake Operating method
design
Adjusting mechanism Auto-adjusting
SAE J1703 or FMVSS116
Brake fluid Type
DOT-3
Vacuum pump maximum vacuum (reference value)
Condition Specification
While idling 93.3 kPa [700 mmHg, 27.6 inHg] or more
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
04 – Brakes
TN-CX5-1203
Vacuum pump
Retarded intake valve closing timing allows intake air being pushed back from the
cylinder to the intake manifold, causing unstable negative pressure inside the intake
manifold. Intake valves are kept open until around 90º crank angle (ABDC) after
bottom dead center during idling. In addition to the engine manifold vacuum, vacuum
created by the vacuum pump is utilized to ensure the brake performance.
Air inlet
Vacuum pump
Engine oil inlet
Vane
Engine oil and air outlet
Vehicle front
Because the vacuum pump is directly engaged with the exhaust camshaft, the vane in
the vacuum pump rotates together with the exhaust camshaft, and the vacuum
chamber is expanded and vacuum is generated.
Exhaust camshaft
Exhaust camshaft
Vacuum
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
04 – Brakes
TN-CX5-1203
Hill Launch Assist (HLA)
The hill launch assist (HLA) is a function provided by using the system and
components such as DSC HU/CM already equipped with the vehicle. Without using
any new and particular components, HLA functions to assist the driver to safely start
the vehicle on a slope of 7% or more. The major features are:
The traction control solenoid valve in the DSC HU/CM is activated to maintain or
reduce brake fluid pressure for a specified time.
The hill launch assist (HLA) operates constantly without affecting the TCS OFF
switch operation.
HLA does not operate when the parking brake is applied or when the DSC indicator
light illuminates.
G-sensor is initialized at the point of production. In addition, there is self-learning
function to correct changes due to aging.
R position Other than R position
Gradient of 7% or approx. 4 degree
R position: When the selector/shift lever position is in the position other than R
position, HLA operates on an upslope.
Other than R position: When the selector/shift lever position is in the R position, HLA
operates on a downslope.
Components
Output device Traction control solenoid valve (built in the DCS HU/CM)
Module DSC HU/CM
Brake fluid pressure sensor (built in the DCS HU/CM)
Input device
ABS wheel speed sensors
Communication
Signal/Information Module
Engine torque, Engine speed, Acceleration pedal position, PCM
Brake switch, Clutch pedal position (MTX), Shift lever
position (ATX), HLA request signal
Parking brake switch, Back-up light switch BCM
Selector lever position (ATX) TCM
Longitudinal-G signal SAS control module
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Outline
Primary gear
Secondary gear
Torque converter
Planetary gear units:
Oil pump Front, Rear, Reduction
Low clutch/ Differential
High clutch
Transaxle oil Control valve body
cap
Connector
SKYACTIV-Drive has a full-range lock-up mechanism and modulated control valve
body, drastically improving fundamental performance such as fuel economy, direct
feel, and shift feeling.
The full-range lock-up mechanism is realized by the torque converter clutch and
dampers inside the torque converter, which contribute to improving high transmission
efficiency and direct feel like manual transaxles even immediately after start-up of the
vehicle.
On the other hand, it effectively utilizes the advantages of torque converter to powerful
and smooth start-up, which consequently contributes to minimizing the torque
converter.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Specification
Item Specification
Transaxle type FW6A-EL/FW6AX-EL GW6A-EL/GW6AX-EL
SKYACTIV-G 2.0 SKYACTIV-D 2.2
1GR 3.552 3.487
2GR 2.022 1.992
3GR 1.452 1.449
Gear ratio 4GR 1.000 1.000
5GR 0.708 0.707
6GR 0.599 0.600
Reverse 3.893 3.990
Final gear ratio 4.624 4.090
Type Genuine ATF FZ
Capacity
7.8 {8.2, 6.9} 8.0 {8.5, 7.0}
ATF (Approx. quantity)
Added amount if ATF is 3.5—4.9 L 3.5—4.9 L
drained from drain plug {3.7—5.1 US qt, {3.7—5.1 US qt,
(approx. quantity) 3.1—4.3 lmp qt} 3.1—4.3 lmp qt}
Hydraulic Clutch 2
components Brake 3
Linear/Duty 5/0
Solenoid valve
ON-OFF 1
D, M (1GR) 330—470 {3.37—4.79, 47.9—68.1}
Idle
Line R 500—700 {5.10—7.13, 72.6—101.0}
pressure
(kPa) D, M (1GR) 970—1,170 {9.90—11.93, 141.0—169.6}
Stall
R 1,790—2,100 {18.26—21.41, 259.7—304.5}
D range
Stall speed 1,900—2,600 2,100—3,100
M range
(rpm)
R range 1,700—2,200 1,800—2,400
Stall torque ratio 1.82 1.88
Weight (kg) [reference] 86 -
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Planetary gear unit
Planetary gear unit Number of teeth
FW6A-EL/FW6AX-EL GW6A-EL/GW6AX-EL
Internal gear 97 97
Front planetary
Pinion gear 29 29
gear
Sun gear 38 39
Internal gear 95 95
Rear planetary
Pinion gear 27 27
gear
Sun gear 40 41
Internal gear 109 109
Reduction
Pinion gear 21 22
planetary gear
Sun gear 68 66
Control system wiring diagram
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
System diagram
Planetary Clutches Torque
gear Brakes converter
Tire Differential Tire
Control valve body
Pressure Shift Shift Shift Shift TCC
control ON/OFF
solenoid solenoid solenoid solenoid control
solenoid solenoid
No.1 No.2 No.3 No.4 solenoid
Oil Electric AT
pump oil pump
TCM
Input devices
: Power flow
Control
: Hydraulic pressure Modules
: Electronic signals
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Cross-section diagram
Front planetary
Rear planetary
planetary gear
Reduction
Torque converter
gear
gear
clutch
Oil pump
High clutch
R-3-5 brake Low clutch
2-6 brake Low & reverse
brake
Torque converter
One-way clutch clutch piston
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Planetary gear train and friction elements
R-3-5 brake Low & reverse brake Low clutch
2-6 brake
One-way clutch High clutch
Primary gear
Reduction planetary gear Front planetary gear
Rear planetary gear
Centrifugal clutch is used for Low clutch and High clutch. This prevents clutch drug
and ensure stable clutch piston thrust force in all ranges.
All friction elements are multi disc type; brake band is not used. This contributes to
improving controllability.
Planetary gear train is consists of three sets of simple Simpson type planetary gear.
Friction element
Low clutch
Multiple-disc clutch
High clutch
R-3-5 brake
Multiple-disc brake 2-6 brake
Low & reverse brake
One-way clutch
Front planetary gear
Simple Simpson planetary gear unit Rear planetary gear
Reduction planetary gear
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Reverse brake
One-way clutch
Low clutch
2-6 brake
R-3-5 brake
High clutch
Primary gear
Front planetary gear
Rear planetary gear
Reduction planetary gear
Components Description
It is activated when in 1GR, 2GR, 3GR, and 4GR,
Low clutch
transmitting power from the turbine shaft to the sun gear.
It is activated when in 4GR, 5GR, and 6GR, transmitting
High clutch
power from the turbine shaft to the rear planetary carrier.
It is activated when in 1GR and Reverse, holding the front
Low & reverse brake
internal gear and the rear planetary carrier.
It is activated when in 2GR and 5GR, holding the rear and
2-6 brake
the reduction planetary gear.
It is activated when in 5GR, holding the reduction internal
R-3-5 brake
gear.
It functions when in 1GR, holding the front internal gear. (It
One-way clutch
does not rotate counterclockwise.)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Automatic transaxle operation chart
Solenoids
Direct linear solenoid No. 1 Normally-closed type; when it is ON, it opens its
hydraulic passage to activate low clutch.
Direct linear solenoid No. 2 Normally-closed type; when it is ON, it opens its
hydraulic passage to activate 2-6 brake.
Direct linear solenoid No. 3 Normally-closed type; when it is OFF, it opens its
hydraulic passage to activate R3-5 brake.
Direct linear solenoid No. 4 Normally-open type: when it is OFF, it opens its
hydraulic passage to activate Low & reverse brake or
High clutch. Whether it is Low & reverse brake or High
clutch depends on the status of On/OFF solenoid.
ON/OFF solenoid Normally open type: when it is OFF, Low & reverse
brake is activated. When it is ON, High clutch is
activated.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Torque converter
SKYACTIV-Drive starts to mechanically couple the torque converter cover (Pump
impeller) and Turbine runner at extremely low vehicle speed (approximately 7 km/h).
To improve fuel economy and direct feel, it is indispensable to overcome the
disadvantages of fluid coupling. Widening the lock-up range where the pump impeller
and turbine runner is mechanically coupled would be the means of solving this
problem.
Because of such a wide range of lock-up operation, the torque converter is required
responsive torque converter clutch without sacrificing clutch torque capacity.
Also it is required for the torque to be equipped with an enhanced damper mechanism
to prevent shift shock due to torque converter clutch engagement at low speed.
SKYACTIV-Drive made it possible to meet all the requirements above by using
multiple-disc torque converter clutch.
Contrary, the range which the torque converter hydraulically transmits the power from
the pump impeller to the turbine runner is reduced. It is mainly used for start-up.
As a result, torque converter is downsized for the space for new designed multi-disc
torque converter clutch and contributes to downsizing ATX itself and reducing weight.
Due to optimized blade design, the torque converter for SKYACTIV-Drive exerts high
performance in torque multiplication equivalent of that of FS5A-EL. This contributes to
ensuring ease to startup performance.
The damper spring is designed to suppress NVH effectively. Two springs are used in
combination (inner spring and outer spring). They are different in winding pitch and
diameter, wire diameter, and pitch.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Torque converter clutch
SKYACTIV-Drive is equipped with a multiple-disc clutch. This multiple-disc clutch
outperforms conventional torque converter clutch in controllability and durability,
which contribute to reduce noise and vibration and to enhance reliability for more
frequent use.
Reference
Clutch torque capacity is obtained by the formula below.
The size (diameter) of the multiple-disc clutch is smaller than that of conventional
one. But, the clutch torque capacity can be increased by increasing the number of
clutch discs.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 10
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
The structure of the torque converter clutch (TCC) is similar to that of those friction
elements used for the planetary gear units in the transaxle. Torque converter clutch
control solenoid regulates the pressure to the torque converter clutch piston.
TCC control solenoid is normally closed type linear solenoid. When it is OFF, no
pressure applies to the TCC piston. When it is ON, TCC converter clutch is activated.
Pressure applying to the piston is gradually applied by TCC control solenoid to reduce
shift shock.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 11
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
TCC engagement
A current signal is sent from the TCM to the TCC control solenoid during TCC
engagement. At the same time, the TCC piston engagement pressure is gradually
increased.
As a result, the TCC piston is pressure-bonded to the TCC clutch slowly to perform
smooth TCC engagement.
TCC release
A current signal is sent from the TCM to the TCC control solenoid during TCC release.
At the same time, the TCC piston engagement pressure is gradually drained.
As a result, the TCC piston releases the TCC clutch slowly to release the TCC
smoothly.
Inhibition of TCC control
If any one of the following conditions is met, the torque converter clutch control is
inhibited.
― TCC solenoid malfunction
― ATF temperature is specification or less
― Engine speed signal is specification or less
― Turbine shaft speed is specification or less
― Other than D/M position
One-way clutch
The one-way clutch consists of a mechanical diode-type one-way clutch, inner plate,
and outer plate. The inner plate for the one-way clutch is connected to the front
internal gear and the outer plate is connected to the transaxle.
1. Strut pressed against the inner plate side along the slop of the outer plate.
2. Strut engages notch of the outer plate, restricting the inner plates’ rotation.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 12
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Low clutch/High clutch
By activating Low clutch or High clutch, the power from the turbine shaft is transmitted
to either Rear sun gear or Rear planetary carrier. Both clutches are equipped with
centrifugal balance chambers, engaging or disengaging clutches smoothly.
Low clutch
Low clutch connects Turbine shaft with Rear sun gear and Front sun gear. It is
activated when in 1GR, 2GR, 3GR, and 4GR.
High clutch
High clutch connects Turbine shaft with Rear planetary carrier and Front internal gear.
It is activated when in 4GR, 5GR, and 6GR.
When in 4GR, both Low clutch and High clutch are activated. Them Front sun gear
and Front internal gear rotate at the same speed. Consequently, all components of
Front planetary gear unit rotate together.
Turbine shaft
One side of Turbine shaft end is meshed with Turbine runner, and the other side is
meshed with Reduction sun gear. Regardless of the status of Low clutch and High
clutch, Reduction sun gear is rotated by Turbine shaft.
Reduction sun gear is effective when in 3GR, 5GR, and R.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 13
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Control Valve Body Assembly
Control valve body assembly consists of TCM, Upper control valve body, Main control
valve body, and Solenoids control valve body. By integrating TCM into the hydraulic
control valve body, reliability and performance are improved. TCM can not be
replaced separately from the hydraulic control valve body.
Transaxle range switch
Turbine/input shaft speed sensor
Output shaft speed sensor
Control valve body
TCM
Solenoid valves
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 14
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
(Solenoid control valve body)
(Lower harness and TFT sensor)
TFT sensor
Direct linear solenoids are used as shift valves. Unlike conventional ATX, which the
friction elements (clutches and brakes) are activated by the shift solenoids and
hydraulic valves in combination, the friction elements for SKYACTIV-Drive are
activated by the direct linear solenoids directly. The TCM has the calibration data of
each direct linear solenoid.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 15
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
(TCM)
The input devices and output devices are connected by the lower harness located in
the ATX or integrated into TCM. These input and output devices and their connectors
are not accessible from outside the ATX. This design and arrangement contribute to
reducing the wires and enhance reliability.
The schematics below indicate what lines are connected to devices outside the ATX.
CAN lines are more used to communicate with other modules. For example, signals
from the shift switch are sent to the TCM via Instrument cluster.
(TR switch)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 16
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
TR switch is integrated into the TCM. It consists of a magnet and hole elements
embedded into the base plate. TR switch inspection is only possible by monitoring
PID. If TR switch has a malfunction, it is required to replace the control valve body
ass’y with new one.
Turbine Speed Shaft (TSS) Sensor and Output Shaft Speed (OSS) sensor are
integrated into the TCM.
TSS sensor detects the rotational speed of Low clutch drum, which is installed in
Turbine shaft.
OSS sensor detects the rotational speed of Primary gear.
Low clutch drum Primary gear (output)
TSS
(Turbine shaft OSS
speed sensor) (Output speed sensor)
TCM
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 17
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
(Oil pressure switch)
Oil pressure switch senses oil pressure which applies to the friction elements. TCM
judges whether or not pressure is applied to the friction elements according to the
driving condition as a result of the executed control.
Oil pressure switch and associated friction elements
Oil pressure switch Friction element 1GR 2GR 3GR 4GR 5GR 6GR
No.2 2-6brake ON ON
A
No.3 R-3-5brake ON ON
No.1 Low clutch ON ON ON ON
B
No.4 High clutch ON ON ON
Each oil pressure switch A or B has two switches.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 18
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
ATX Control
Control items
Control item Main control content
- Implements automatic shift control while in D position
Auto shift control - Performs automatic shift corresponding to vehicle speed
and accelerator pedal depression amount
Normal mode - Mode selection during normal driving
- Inhibits shift-up for specified time when accelerator pedal is
fully depressed and released
- Selects lower than normal gear when brake pedal is
Auto shift control
Driving mode
AAS strongly depressed
Shift point
(Active - Moves shift point to high vehicle speed side when cornering
Adaptive Shift - Selects gear appropriate to driving conditions during high
mode) degree of vehicle ascent/descent
- Determines vehicle on slope based on estimated slope
value calculated by TCM and selects gear appropriate to
driving conditions
High ATF
- Controls torque when ATF temperature is high control
temp. mode
- When M position is selected, performs manual shifting
Manual shift control according to vehicle speed and shift up/shift down
operations by driver
- Based on adoption of full range TCC control, active TCC
control directly after acceleration from stop
- By gradually engaging/disengaging TCC piston, shock
TCC control during operation is reduced
- Implements TCC control when accelerator pedal is fully
closed for improved fuel economy and emission
performance
- Controls line pressure with high accuracy and fine control
Line pressure control corresponding to engine load conditions and vehicle driving
conditions
Shift control
Clutch pressure direct - Performs direct, electronic control of clutch engagement
control (direct electric pressure appropriate to engine load conditions and vehicle
shift control) driving conditions
- Learns engine performance changes and transaxle
Learning control deterioration over time to optimally correct clutch
engagement pressure
- Optimally controls engine output torque when shifting
Engine transaxle total control - Calculates optimum clutch engagement pressure according
to engine output torque
- Main part of transaxle control includes self-diagnosis
function. In case of malfunction, automatic transmission
warning light illuminates to alert driver, and DTC is stored in
On-board diagnostic system TCM
- When transaxle malfunction is determined resulting from
onboard diagnostic test, system control is switched to
prevent any dangerous situation while driving
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 19
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Correlation between control and input/output parts
Shift point control Shift control
Automatic sift
control
Engine-Transaxle toral control
On-bord diagnostic system
Direct electric shift control
High ATF temp. mode
Line pressure control
Manual shift control
Learning control
Normal mode
TCC control
AAS mode
TR sensor X X X X X X X X X X
Turbine/Input shaft speed
X X X X X X X X
sensor
TCM Output shaft speed sensor X X X X X X X
TFT sensor X X X X X X
Oil pressure switch X X X X X X X X
Acceleration Pedal
X X X X X X X
depression condition
Brake pedal depression
X X X X
condition
INPUT
PCM Engine torque signal X X X X X X X X
Engine speed X X X X X X X
ECT X X
MAF X
M position switch X X
I/C* UP switch X X
Down switch X X
DSC Forward-G signal X
HU/C Lateral-G signal X
M ABS wheel-speed signal X X
BCM Steering angle signal X
ON/OFF solenoid X X X X X X
Shift solenoid No. 1 X X X X X X X
Shift solenoid No. 2 X X X X X X X
ATX Shift solenoid No. 3 X X X X X X X
Shift solenoid No. 4 X X X X X X X
Output
TCC control solenoid X X X X X X X X
Pressure control solenoid X X X X X X X X X
Shift position indicator light
X X X X
illumination operation
I/C
Gear position indicator
X
illumination flash request
AT warning light illumination
X X
request
Input/Output (CAN) X X X X X X X X X
* I/C: Instrument Cluster
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 20
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Block diagram
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 21
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Shift point control
Outline
The TCM implements auto shift control according to the vehicle speed and accelerator
pedal depression amount while in D position.
When the vehicle is stopped with the selector lever is in the D position and the brake
pedal depressed, the neutral idle control is performed which internally controls the
automatic transaxle to be in the neutral condition while the selector lever is in the D
position. When the brake pedal is being released, the clutch is engaged immediately
and the automatic transaxle returns to the normal D position condition.
When implementing the automatic shift control, the TCM determines the driving
conditions based on each input signal and selects the drive mode appropriate to the
driving conditions. In addition, information such as torque and gear changes is
exchanged via PCM and CAN communication and control is performed so as to
achieve optimum drive force according to the driving scenario.
Operation
Driving range determination
If a D position signal is input and an M position signal is not input, the TCM
implements auto shift control.
Driving mode determination
For the auto shift control, NORMAL mode is usually selected, however it automatically
switches to driving mode depending on the driving conditions.
AAS (Active Adaptive Shift) mode: Automatically controls the optimum shift point
according to the road conditions and the driver operation.
High ATF temperature mode: When the ATF temperature rises to a high temperature,
the engine torque is restricted so that the increase in ATF temperature is suppressed
to protect the transaxle.
AAS (Active Adaptive Shift) mode operation
Accelerator pedal fully closed suddenly and returned
When the accelerator pedal is fully closed and returned at a certain speed or more,
shift-up is inhibited for specified time to improve speed control and reacceleration
performance.
Brake is strongly depressed
When decelerating at a certain speed or more, a lower gear is selected so that
re-acceleration is performed smoothly.
During a shift change with the brake pedal depressed firmly, blipping control
(synchronization to engine speed) is performed to shorten the shifting time.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 22
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
When cornering
While cornering at a turn with a radius of less than a specified value, shift up is
suppressed to improve vehicle speed performance while cornering and reacceleration
performance after cornering.
During high degree of vehicle ascent/descent
During a certain level of vehicle ascent/descent, gears are selected appropriate to the
driving conditions for driving comfort.
During ascent
While ascending a slope of a certain grade or more, slope mode control prevents
unnecessary shift-up by maintaining the appropriate gear.
During descent
While descending a slope of a certain grade or more and depressing the brake pedal,
the gears are appropriately shifted down according to the estimated slope angle for
effective use of engine braking. As a result, frequent brake pedal operation is reduced.
AAS (active adaptive shift) operation scenario and effect
The AAS (active adaptive shift) is a mode which estimates the driving environment
and drive’s intentions according to the vehicle driving conditions and the drive’s
operations, and selects the optimum gear for driving.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 23
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Ex.1: Cornering
During cornering, shift up is suppressed to improve acceleration performance after
cornering.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 24
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Ex. 2: Merging onto high speed expressways
— In a scenario such as temporarily decelerating while merging onto a high speed
expressway, shift up is suppressed directly afterwards to improve re-acceleration
performance.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 25
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Power flow
1GR
Activated friction elements Associated solenoids
Low clutch Direct linear solenoid No. 1: ON
Direct linear solenoid No. 4: OFF
Low & reverse brake
ON/OFF solenoid: OFF
1. Front sun gear is rotated by Turbine shaft via Low clutch.
2. Front pinion gears are rotated by Front sun gear/
3. Since Front internal gear is held by Low & reverse brake, Front planetary pinions
are revolving around Front sun gear while they rotate on their own axis.
4. Primary gear is rotated is rotated by Front planetary pinions’ revolution via Front
planetary carrier.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 26
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
2GR
Activated friction elements Associated solenoids
Low clutch Direct linear solenoid No. 1: ON
2-6 brake Direct linear solenoid No. 2: ON
1. Front sun gear and Rear sun gear are rotated by Turbine shaft via Low clutch.
2. Rear sun gear rotates Rear planetary pinions.
3. Since Rear internal gear is held by 2-6 brake, Rear planetary pinions are revolving
around Rear sun gear while they are rotating on their own axis.
4. Together with Front internal gear, Front planetary carrier is rotated by Rear
planetary carrier, which is rotated by Rear planetary pinions’ revolution.
5. Due to Front internal gear’s rotation, Front planetary pinions are revolving around
the Front sun gear while they are rotating on their own axis.
6. Primary gear is rotated by Front planetary pinions’ revolution via Front planetary
carrier.
Due to the difference in rotational speed between Front sun gear and Front internal
gear, which is absorbed by Front planetary pinions’ rotation, Front planetary carrier is
rotated slower than Front sun gear.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 27
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
3GR
Activated friction elements Associated solenoids
Low clutch Direct linear solenoid No. 1: ON
R-3-5 brake Direct linear solenoid No. 3: OFF
1. Reduction sun gear is rotated by Turbine shaft. Also Front sun gear and Rear sun
gear are rotated via Low clutch.
2. Reduction planetary pinions are rotated by Reduction sun gear.
3. Since Reduction internal gear is held by R-3-5brake, Reduction planetary pinions
are revolving around Reduction sun gear while they are rotating on their own axis.
4. Together with Reduction planetary carrier, Rear internal gear is rotated by
Reduction planetary pinions’ revolution.
5. Rear planetary pinions are revolving around Rear sun gear while they are rotating
on their own axis due to the difference in rotational speed between Rear sun gear and
Rear internal gear: Rear sun gear’s rotational speed is faster than that of Rear internal
gear.
6. Together with Rear planetary carrier, Front internal gear is rotated by Rear
planetary pinions’ revolution.
7. Front planetary pinions are revolving around Front sun gear while they are rotating
on their own axis due to the difference in rotational speed between Front sun gear and
Front internal gear: Front sun gear’s rotational speed is faster than that of Front
internal gear.
8. Primary gear is rotated by Front planetary pinions’ revolution via Front planetary
carrier.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 28
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
4GR
Activated friction elements Associated solenoids
Low clutch Direct linear solenoid No. 1: ON
Direct linear solenoid No. 4: OFF
High clutch
ON/OFF solenoid: ON
1. Front sun gear is rotated by Turbine shaft via Low clutch.
2. Front internal gear is rotated by Turbine shaft via high clutch.
3. Front planetary carrier is rotated by Front sun gear and Front internal gear.
4. Primary gear is rotated by Front planetary gear unit’s rotation.
Front planetary pinions are revolving around Front sun gear. But, they are not rotating
on their own axis.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 29
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
5GR
Activated friction elements Associated solenoids
R-3-5 brake Direct linear solenoid No. 3: OFF
Direct linear solenoid No. 4: OFF
High clutch
ON/OFF solenoid: ON
1. Rear planetary carrier and Reduction sun gear are rotated by Turbine shaft via High
clutch.
2. Since Reduction internal gear is held by R-3-5 brake, Reduction planetary pinions
are revolving around Reduction sun gear while they are rotating on their own axis.
3. Together with Reduction planetary carrier, Rear internal gear is rotated by
Reduction planetary pinions’ revolution.
4. Rear planetary pinions are revolved around Rear sun gear due to Rear planetary
carrier’s rotation while they are rotating on their own axis. Rear planetary pinions’
rotation occurs due to difference in rotational speed between Rear internal gear and
Rear planetary carrier.
5. Together with Rear sung gear, Front sun gear is rotated by planetary pinions’
revolution and rotation.
6. Front planetary pinions are revolving while they are rotating on their own axis. Front
pinions’ rotation occur due to difference in rotational speed between Front internal
gear and Front sun gear.
7. Primary gear is rotated by Front planetary pinions’ revolution via Front planetary
carrier.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 30
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
6GR
Activated friction elements Associated solenoids
2-6 brake Direct linear solenoid No. 2: OFF
Direct linear solenoid No. 4: OFF
High clutch
ON/OFF solenoid: ON
1. Together with Front internal gear, Rear planetary carrier is rotated by Turbine shaft
via High clutch.
2. Since Rear internal gear is held by 2-6 brake, Rear planetary pinions are revolving
along the inner side of Rear internal gear while they are rotating on their own axis.
3. Together with Rear sun gear, Front sun gear is rotated by Rear planetary pinions’
revolution and rotation.
4. Since Front sun gear and Front internal gear are rotated, Front planetary pinions
are revolving while they are rotating on their own axis due to difference in rotational
speed between Front sun gear and Front internal gear.
5. Primary gear is rotated by Front planetary pinions’ revolution via Front planetary
carrier.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 31
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
R
Activated friction elements Associated solenoids
R-3-5 brake Direct linear solenoid No. 3: OFF
Direct linear solenoid No. 4: OFF
Low & reverse brake
ON/OFF solenoid: OFF
1. Rear internal gear is rotated through Reduction planetary carrier, Reduction
planetary pinions, and Reduction sun gear.
2. Since Rear planetary carrier is held by Low & reverse brake via Front internal gear,
Rear planetary carrier is locked, not allowing Rear planetary pinions to revolve.
3. As Rear internal gear is rotated, Rear sun gear is rotated via Rear planetary pinions.
The direction in which Rear sun gear is rotated is opposite of that of Rear internal gear
due to Rear planetary pinions’ rotation.
4. Primary gear is rotated by Front planetary pinions’ revolution via Front planetary
carrier, Front planetary pinions, Front sun gear, and Rear sun gear.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 32
Mazda CX-5
05A – Transmission/Transaxle (ATX)
TN-CX5-1203
Technical tip TCM configuration
TCM configuration can be performed from Configuration/PMI menu
If communication is not established due to TCM malfunction or else, it is possible to
do it by entering As-built data after TCM replacement.
However, at this moment (July 13, 2011), TCM is not ready for As-built data entry.
This is because the TCM (as spare part) is without calibration data. In such a case,
please contact Diagnostic Service Planning Group of Mazda Motor Corporation.
Replaced component Configuration TCM initial learning
Control valve body assembly Necessary Necessary
ATX complete (new) No need No need
ATX complete (Rebuilt) TBD TBD
Oil pressure switch A/B No need Necessary
ON/OFF solenoid No need No need
Lower harness with TFT sensor No need No need
At this moment, direct linear solenoid valves are not replaceable individually.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 33
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Outline
(1) Short stroke and increased lever ratio
Shortened the shift stroke, increased lever ratio to reduce required effort, and
downsized synchromesh mechanisms with lowered stroke.
Reduced sliding friction between the shift lock ball and detent plate when
selecting (shift lever's lateral movement left-right)
When shifting up, required effort for moving the shift lever is reduced by utilizing
the weight of the shift change mechanism.
(2) Downsized by optimized gear composition
A single input gear is commonly used for 2nd gear and 3rd gear, contributing to
reducing the length of the secondary shaft by 20% as compared with the previous
types.
A single gear is commonly used as 1st gear and reverse idle gear
(3) Fuel economy improvement
The transmission weight is reduced by approximately 30% due mainly to the new
design transmission case.
Lubricated with less amount of gear oil, reducing losses caused by a stir of gear
oil
Adopted ball bearings to reduce the primary shaft rolling resistance
Specification
Item Specification
Transaxle type C66M-R (2WD), C66MX-R (4WD)
Engine type SKYACTIV-G 2.0
1GR 3.700
2GR 1.947
3GR 1.300
Gear ratio 4GR 1.029
5GR 0.837
6GR 0.680
R 3.724
Final gear ratio 4.388 (2WD), 4.705 (4WD)
Manual transaxle oil grade API service GL-4
Manual transaxle oil viscosity SAE 75W-80
Manual transaxle oil capacity
1.65 L {1.74 US qt, 1.45 lmp qt}
(approx. quantity)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Overview
Shift control module
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Power flow
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Shift control module
The moving parts of the shift control module are vertically positioned.
In this module, the control lever which moves the shift rod end is directly assembled to
the control rod. In addition, because the control rod moves up and down, the weight of
the control rod is utilized when the control rod moves down.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Slide ball bearing
A slide ball bearing has been adopted to the sliding area between the control rod
and the transaxle case, and between the control rod and the control case.
In this part, the bearing case moves in the drive and thrust directions.
Compared to the conventional bushing, sliding resistance between the control rod
and the transaxle case, and between the control rod and the control case has been
reduced.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
1GR
1. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted to the left to shift to 1GR, the select lever
moves in the direction of arrow 1 shown in the figure.
2. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 2 shown in the figure.
3. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 3 shown in the figure.
4. Following the movement of the select lever, the control lever and the guide pin
move in the direction of arrow 4 shown in the figure.
5. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted forward to shift to 1GR, the shift lever in the
engine compartment moves in the direction of arrow 5 shown in the figure.
6. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
rod moves in the direction of arrow 6 shown in the figure.
7. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
lever and the guide pin move in the direction of arrow 7 shown in the figure.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
8. Because the control rod turns with the control lever, the control lever pushes the
shift rod end and moves it in the direction of arrow 8 shown in the figure.
9. The shift rod end and the shift fork are integrated with the shift rod. Therefore, the
movement of the shift rod end is transmitted to the shift fork via the shift rod, and the
shift fork moves in the direction of arrow 9.
10. The shift fork moves the clutch hub sleeve in the direction of arrow 10 shown in
the figure.
11. The shift change to 1GR is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
2nd
1. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted to the left to shift to 2GR, the select lever
moves in the direction of arrow 1 shown in the figure.
2. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 2 shown in the figure.
3. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 3 shown in the figure.
4. Following the movement of the select lever, the control lever and the guide pin
move in the direction of arrow 4 shown in the figure.
5. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted rearward to shift to 2GR, the shift lever in
the engine compartment moves in the direction of arrow 5 shown in the figure.
6. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
rod moves in the direction of arrow 6 shown in the figure.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
8. Because the control rod turns with the control lever, the control lever pushes the
shift rod end and moves it in the direction of arrow 8 shown in the figure.
9. The shift rod end and the shift fork are integrated with the shift rod. Therefore, the
movement of the shift rod end is transmitted to the shift fork via the shift rod, and the
shift fork moves in the direction of arrow 9.
10. The shift fork moves the clutch hub sleeve in the direction of arrow 10 shown in
the figure. 11. The shift change to 2GR is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
3GR
1. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted forward to shift to 3GR, the shift lever in the
engine compartment moves in the direction of arrow 1 shown in the figure.
2. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
rod moves in the direction of arrow 2 shown in the figure.
3. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
lever and the guide pin move in the direction of arrow 3 shown in the figure.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 10
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
4. Because the control rod turns with the control lever, the control lever pushes the
shift rod end and moves it in the direction of arrow 4 shown in the figure.
5. The shift rod end and the shift fork are integrated with the shift rod. Therefore, the
movement of the shift rod end is transmitted to the shift fork via the shift rod, and the
shift fork moves in the direction of arrow 5.
6. The shift fork moves the clutch hub sleeve in the direction of arrow 6 shown in the
figure.
7. The shift change to 3GR is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 11
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
4GR
1. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted rearward to shift to 4GR, the shift lever in
the engine compartment moves in the direction of arrow 1 shown in the figure.
2. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
rod moves in the direction of arrow 2 shown in the figure.
3. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
lever and the guide pin move in the direction of arrow 3 shown in the figure.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 12
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
4. Because the control rod turns with the control lever, the control lever pushes the
shift rod end and moves it in the direction of arrow 4 shown in the figure.
5. The shift rod end and the shift fork are integrated with the shift rod. Therefore, the
movement of the shift rod end is transmitted to the shift fork via the shift rod, and the
shift fork moves in the direction of arrow 5.
6. The shift fork moves the clutch hub sleeve in the direction of arrow 6 shown in the
figure.
7. The shift change to 4GR is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 13
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
5GR
1. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted to the right to shift to 5GR, the select lever
moves in the direction of arrow 1 shown in the figure.
2. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 2 shown in the figure.
3. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 3 shown in the figure.
4. Following the movement of the select lever, the control lever and the guide pin
move in the direction of arrow 4 shown in the figure.
5. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted forward to shift to 5GR, the shift lever in the
engine compartment moves in the direction of arrow 5 shown in the figure.
6. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
rod moves in the direction of arrow 6 shown in the figure.
7. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
lever and the guide pin move in the direction of arrow 7 shown in the figure.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 14
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
8. Because the control rod turns with the control lever, the control lever pushes the
shift rod end and moves it in the direction of arrow 8 shown in the figure.
9. The shift rod end and the shift fork are integrated with the shift rod. Therefore, the
movement of the shift rod end is transmitted to the shift fork via the shift rod, and the
shift fork moves in the direction of arrow 9.
10. The shift fork moves the clutch hub sleeve in the direction of arrow 10 shown in
the figure.
11. The shift change to 5GR is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 15
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
6GR
1. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted to the right to shift to 6GR, the select lever
moves in the direction of arrow 1 shown in the figure.
2. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 2 shown in the figure.
3. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 3 shown in the figure.
4. Following the movement of the select lever, the control lever and the guide pin
move in the direction of arrow 4 shown in the figure.
5. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted rearward to shift to 6GR, the shift lever in
the engine compartment moves in the direction of arrow 5 shown in the figure.
6. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
rod moves in the direction of arrow 6 shown in the figure.
7. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
lever and the guide pin move in the direction of arrow 7 shown in the figure.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 16
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
8. Because the control rod turns with the control lever, the control lever pushes the
shift rod end and moves it in the direction of arrow 8 shown in the figure.
9. The shift rod end and the shift fork are integrated with the shift rod. Therefore, the
movement of the shift rod end is transmitted to the shift fork via the shift rod, and the
shift fork moves in the direction of arrow 9.
10. The shift fork moves the clutch hub sleeve in the direction of arrow 10 shown in
the figure.
11. The shift change to 6GR is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 17
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Reverse
1. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted to the left to shift to the reverse gear, the
select lever moves in the direction of arrow 1 shown in the figure.
2. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 2 shown in the figure.
3. Following the movement of the select lever, the shift lever moves in the direction of
arrow 3 shown in the figure.
4. Following the movement of the select lever, the control lever and the guide pin
move in the direction of arrow 4 shown in the figure.
5. When the shift lever in the cabin is tilted forward to shift to the reverse gear, the shift
lever in the engine compartment moves in the direction of arrow 5 shown in the figure.
6. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
rod moves in the direction of arrow 6 shown in the figure.
7. Following the movement of the shift lever in the engine compartment, the control
lever and the guide pin move in the direction of arrow 7 shown in the figure.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 18
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
8. Because the control rod turns with the control lever, the control lever pushes the
shift rod end and moves it in the direction of arrow 8 shown in the figure.
9. The shift rod end and the shift fork are integrated with the shift rod. Therefore, the
movement of the shift rod end is transmitted to the shift fork via the shift rod, and the
shift fork moves in the direction of arrow 9.
10. The shift fork moves the clutch hub sleeve in the direction of arrow 10 shown in
the figure.
11. The shift change to the reverse gear is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 19
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
SYNCHRONIZER MECHANISM
Triple cone synchronizer mechanism (1ST/2ND)
Synchronizer mechanism (3RD/4TH)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 20
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Synchronizer mechanism (5TH/6TH)
Synchronizer mechanism (Reverse)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 21
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
Detent ball-type synchronizer key
A detent ball-type synchronizer key has been adopted for the synchronizer
mechanism except for the reverse gear.
The detent ball of this part provides the driver a crisp feel which the driver can
realize completed gear changes.
Because this part is smaller compared to the conventional synchronizer key, it
has contributed to the size reduction of the synchronizer mechanism, and also to
the shortened length of the primary and secondary shafts.
Because the smaller synchronizer mechanism has reduced the stroke amount of
the clutch hub sleeve, the stroke of the shift lever in the cabin has been
shortened.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 22
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
1GR, 2GR operation
Note
For 1st and 2nd gears, a triple-cone synchronizer mechanism has been adopted
with which a stronger synchronizing force is provided to synchronize the rotation
of the clutch hub and the gear.
Here, operation during 2GR operation is described as an example.
1. When the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the 2nd gear side, the synchronizer key
follows, and the synchronizer key contacts the end surface of the synchronizer ring.
2. When the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the 2nd gear side, the synchronizer key
which follows applies load to the synchronizer ring, and the load is transmitted from
the synchronizer ring to the middle cone ring, inner cone ring, and the gear.
3. The friction force on the contacting surface of the parts is generated by applying
load to the parts between the synchronizer ring and the gear.
4. For the friction force for the parts, the synchronizer ring rotates only the round
groove gap of the clutch hub sleeve.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 23
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
5. Because the synchronizer ring rotates, the spline of the clutch hub sleeve which
moves toward the secondary 2nd gear side and the chamfer of the synchronizer ring
are opposed to each other.
6. When the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the secondary 2nd gear side, the
transmitted load to the gear from the clutch hub sleeve increases because the spline
of the clutch hub sleeve pushes the chamfer of the synchronizer ring. In addition, the
friction force on the contacting surface of the parts is increased by increasing the load
transmitted from the clutch hub sleeve to the gear. The increased friction force
decreases the difference in rotation speed between the synchronizer ring, middle
cone ring, inner cone ring, and the gear and the rotation speed for the parts is
synchronized.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 24
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
7. When synchronization in rotation speed of the gear and the clutch hub sleeve is
performed, the spline of the clutch hub sleeve passes through the synchronizer ring.
8. When the spline of the clutch hub sleeve passes through the synchronizer ring, the
synchronizer key presses down the detent ball and the detent ball is removed from the
positioning groove of the clutch hub sleeve because the clutch hub sleeve moves
toward the secondary 2nd gear side.
9. when the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the secondary 2nd gear side, the spline
of the clutch hub sleeve and the spline of the gear are engaged, and the shifting
operation is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 25
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
3GR, 4GR, 5GR, 6GR, reverse operation
Note
Here, operation during 4GR operation is described as an example.
1. When the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the 4th gear side, the synchronizer key
follows, and the synchronizer key contacts the end surface of the synchronizer ring.
2. When the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the 4th gear side, the following
synchronizer key applies load to the synchronizer ring, and the load is transmitted
from the synchronizer ring to the gear.
3. The friction force on the contacting surface of the synchronizer ring and the gear is
generated by applying load to the parts between the synchronizer ring and the gear.
For the friction force of the synchronizer ring and the gear, synchronizer ring rotates
only the key groove gap of the clutch hub sleeve.
4. Because the synchronizer ring rotates, the spline of the clutch hub sleeve which
moves toward the 4th gear side and the chamfer of the synchronizer ring are opposed
to each other.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 26
Mazda CX-5
05M - Transmission/Transaxle (MTX)
TN-CX5-1203
5. When the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the 4th gear, the load transmitted from
the clutch hub sleeve to the gear increases because the spline of the clutch hub
sleeve pushes the chamfer of the synchronizer ring. In addition, the friction force on
the contacting surface of the parts is increased by increasing the load transmitted from
the clutch hub sleeve to the gear. The increased friction force disappears the
difference in the rotation speed between the synchronizer ring and the gear, and the
rotation is synchronized.
6. When synchronization in rotation speed of the gear and the clutch hub sleeve is
performed, the spline of the clutch hub sleeve passes through the synchronizer ring.
7. When the spline of the clutch hub sleeve passes through the synchronizer ring, the
synchronizer key presses down the ball and the ball is removed from the positioning
groove of the clutch hub sleeve because the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the
secondary 4th gear side.
8. When the clutch hub sleeve moves toward the secondary 4th gear side, the spline
of the clutch hub sleeve and the spline of the gear are engaged, and the shifting
operation is completed.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 27
Mazda CX-5
06 – Steering
TN-CX5-1203
Overview
High geared steering gear
Quick response at low and mid speed ranges
EPS
Supplied by JTECT
Improved motor output
Improved rigidity of the intermediate shaft
Reduced inertia force by adopting brushless motor
Automatic configuration function
When the ignition is switched to ON or the engine is started after the EPS CM have
been replaced, the EPS CM reads data from the instrument cluster via CAN
communication to perform automatic configuration.
Steering wheel angle neutral position automatic learning function
When the ignition is switched from OFF to ON and the vehicle is driven normally, the
steering wheel angle neutral position is detected automatically based on the signal
from the torque sensor.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
06 – Steering
TN-CX5-1203
Overview
Instrument cluster
w/o TFT-LCD display w/ TFT-LCD display
Power steering malfunction
indicator light
EPS CM,
DSC HU/CM EPS motor
Torque sensor,
Reduction gear
PCM
Block diagram
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
06 – Steering
TN-CX5-1203
Operation
1. Steering force generated by the driver's steering wheel operation is detected by the
torque sensor which is built in the steering column and shaft, and is output to the EPS
CM as a steering torque signal.
2. The EPS CM calculates optimum assist force based on the steering torque signal
from the torque sensor and the vehicle speed and engine speed signals from the PCM,
and outputs electric current to drive the EPS motor.
3. The EPS motor is driven by the current from the EPS CM and the force is
transmitted to the intermediate shaft via the reduction gears, thus assisting steering
operation of the driver.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
06 – Steering
TN-CX5-1203
Control system wiring diagram
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
06 – Steering
TN-CX5-1203
Steering lock mechanism
Steering lock mechanism is integrated into SSU. Lock or unlock is controlled by the
SSU directly. As it is for Mazda3 with push button start system, a lock pin is engaged
or disengaged by an electric motor.
Steering lock pin
SSU
Reference
Unused Electronic Steering Lock Warning Light
The warning light, which flashes if the steering wheel is not unlocked after the push
button start, is not used.
Existent models (Mazda3, Mazda6): The electronic steering lock warning light
flashes with a beep sound for 10 sec.
New models (CX-5): The status indicator of the push button flashes in green with
beep sound.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
Air-conditioning system
Performance is improved as compared with existent models.
Cooling capacity is improved by 6%
Weight is reduced by 13%
Specification
Item Specification
Heating capacity (kW {kcal/h}) 5,530 {4,755}
Cooling capacity (kW {kcal/h}) 5,000 {4,299}
HFO-1234yf
Type
HFC-134a
HFC-134a:
Refrigerant 465-515 {16.5-18.1}
Regular amount
HFO-1234yf:
(approx. quantity) (g {oz})
475-525 {16.8-18.5} (SKYACTIV-G 2.0)
445-495 {15.7-17.4} (SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
Type Swash plate
Discharge capacity 135 {135, 4.56} (SKYACTIV-G 2.0)
(ml {cc, fl oz}) 160 {160, 5.41} (SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
Max. allowable speed 8,500 (SKYACTIV-G 2.0)
A/C (rpm) 8,000 (SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
compressor Type FD46XG
Sealed volume
Lube oil (approx.
100 {100, 3.38}
quantity)
(ml {cc, fl oz})
Type Multi-flow (sub-cooling type)
HFC-134a:
7.350 {6,320} (SKYACTIV-G 2.0)
Radiated heat (kW
HFO-1234yf:
{kcal/h})
Condenser 7.150 {6,148} (SKYACTIV-G 2.0)
6.700 {5,761} (SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
Receiver/drier capacity
170 {170, 5.75}
(ml {cc, fl oz})
Desiccant Synthetic zeolite
Expansion valve Type External equalizing type
Evaporator Type Multi-flow type
Temperature control Reheat full air mix type
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
Control System (Full-auto air conditioner)
Specification
Item
Full-auto Manual
Airflow volume Blower motor (m3/h)
310
(during heater operation)
Electricity consumption Blower motor (W)
150
(during heater operation)
Heating capacity PTC heater (kW
1.0 {860}
(SKYACTIV-D 2.2) {kcal/h})
Electricity consumption PTC heater (W)
(during heater operation) 1,000
(SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
Airflow volume (during air Blower motor (m3/h)
475
conditioner operation)
Electricity consumption Blower motor (W) 200
(during air conditioner Magnetic clutch (W)
40
operation)
Magnetic clutch clearance (mm {in}) 0.35—0.65 {0.014—0.025}
Fan type Blower motor Sirocco fan
Refrigerant pressure sensor Type Capacitance type
Sensor Solar radiation sensor Photodiode NA
Ambient temperature sensor Thermistor
Cabin temperature sensor Thermistor NA
Evaporator temperature sensor Thermistor
Heater core temperature sensor (With
Thermistor NA
i-stop)
Actuator Air intake actuator Mechanical lock type
Air mix actuator Potentiometer
NA
Airflow mode actuator type
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Cabin temperature sensor
Main fuse block
Heater core temperature sensor
07 – HVAC
(with heater core temperature sensor)
Mazda CX-5
Blower relay
Driver-side air mix actuator
A/C relay
Evaporator temperature sensor
Overview (Full-auto air conditioner)
Airflow mode actuator
Passenger-side air mix actuator
Climate control unit
Blower motor
Power MOS FET
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Solar radiation sensor
PTC heater
Ambient temperature sensor
(with PTC heater)
Air intake actuator
Refrigerant pressure sensor
Magnet clutch
Water pump
3
TN-CX5-1203
(with water pump)
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
System wiring diagram (Full-auto air conditioner)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
Block diagram (Full-auto air conditioner)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
Overview (Manual auto air conditioner)
Evaporator temperature sensor
Ambient temperature sensor
Refrigerant pressure sensor
Air intake actuator
Blower motor
Resister
Magnet clutch
Main fuse block
A/C relay
Climate control unit
PTC heater
Blower relay (with PTC heater)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
System wiring diagram (Manual air conditioner)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
Block diagram (Manual air conditioner)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
07 – HVAC
TN-CX5-1203
Refrigerant pressure sensor
A capacitance type A/C pressure sensor is employed. This converts refrigerant
pressure into a linear electric signal.
The pressure detecting part is a variable capacity condenser, which changes
capacitance according to the pressure. The signal processing part detects the
capacitance of pressure detecting part, converts it to voltage, then outputs it to the
climate control unit.
Connector
Signal
processor
Pressure
sensor
Pressure
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
08 - Restraints
TN-CX5-1203
Overview
The number of front crush sensor is increased: from 1 to 2
Twin-air bag is employed. The head will be held by hollow portion of the air bag. In
addition, low repulsive materials softly hold the face.
Hold the head
Single air bag
Twin air bag
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
08 - Restraints
TN-CX5-1203
System wiring diagram
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
08 - Restraints
TN-CX5-1203
Front air bag
High inner pressure twin air bag
1. Driver/Front passenger inflators and air bags
2. Crash sensors, and diagnostic module (SAS unit)
3. Front seat belt pre-tensioners
4. Front air bag sensors
5. Side crash sensors
6. Air bag/front seat belt pre-tensioner system warning light
7. Side and curtain inflators and air bags
8. Front passenger air bag deactivation indicator light
9. Front passenger air bag deactivation switch
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
08 - Restraints
TN-CX5-1203
Technical tip Driver-side air bag module removal/installation
Using TORX driver (T30 (6 mm)), press the hook to release it from hook through the
serviced hole.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Contents
BODY PANELS
DOORS AND LIFTGATE
GLASS/WINDOWS/MIRRORS
SEATS
SECURITY AND LOCKS
EXTERIOR TRIM
INTERIOR TRIM
LIGHTING SYSTEMS
Warning/Indicator system
WIPER/WASHER SYSTEM
ENTERTAINMENT
POWER SYSTEMS
INSTRUMENTATION/DRIVER INFO
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Body panel
Triple H-shaped structure
An H-shaped structure has been adopted in which reinforcements are equipped in the
floor, side frame, and roof, and each connection area is strengthened. The
combination of these three structural areas provides the strong triple H-shaped
structure. The triple H structure distributes the impulse force at the side collision to
reinforcement of the roof, cabin side frame, and floor. The triple H-shaped structure
controls the twisting of the cabin while driving.
Side collision
Crushable structure
Engine mounting brackets and front suspension crossmember are made to break
away during a collision.
Engine
mounting
bracket
Engine
mounting
bracket Front suspension
crossmember
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Ring structure
For the ring structure, the basic framework is thoroughly straightened, and the frames
are circularly linked.
Multi-load path
The multi-load path is stabilized during a collision, and has set the load distribution
load path which carries out energy absorption.
The front side frame, front B frame and rear side frame are made into straight forms.
The front side frame is supported by the side sill, front B frame and side member.
Front B frame
Front
side
frame
Side
member
Frontal
collision
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Bonnet
The bonnet is constructed with a large space between the front end of the bonnet and
the engine to absorb an impact.
Bonnet Bonnet Bonnet
stiffener Engine
Space
Bonnet
Space Engine stiffener
DOORS AND LIFTGATE
Door structure for side impact
Two impact bars in front door and one in rear door arranged in a way that those
impact beams directly connected to the hinges or body of the triple-H structure,
dispersing impact into the body to prevent impact from transmitting to the cabin
Door impact
Due to layout change, the impact bar is connected to the hinge to utilize tension force
in addition to bending force, which contributes to reducing weight and ensuring safety
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Inner press door
Styrofoam door module panels have been adopted for reducing vehicle weight and
improving absorbing power and vibrational absorption.
Styrofoam is applied to the door module panels (shaded areas) during manufacture.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
GLASS/WINDOWS/MIRRORS
Power outer mirror
The design of the retract switch for CX-5 is different from those of existent models.
The retract switch is integrated into the power outer mirror switch. The symbol of
retract switch is found on the outer dial of the power outer mirror switch.
The ignition must be switched to ACC or ON position. To fold the mirror, rotate the
switch. To return the mirror to the driving position, rotate the switch to the center
position.
Auto-dimming mirror
As far as function is concerned, the auto-dimming mirror for CX-5 is the same as
those of existent models.
Technical tip Location of the sensor
The location of the light sensor is different from that of the existent models.
(Existent models)
It is located next to the ON/OFF switch for the auto-dimming mirror.
(CX-5)
It is built in the mirror located in the center. (It is not recognizable by appearance.)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Seat
Next generation front seat structure
Power seat switch layout is redesigned
The world’s first three independent seats with a remote fold down handle
Remote fold down handle in the lift-gate compartment
Three independent rear seats
Front seat structure for next generation
Reduced weight and improved rigidity of the seats, and improved seating comfort.
(1) Seat back: Optimized cross-member shape
(2) Sea cushion: Added cross-member
(3) Lifter unit is provided for both sides
(4) Cushion frame structure: instead of Pan frame, S-shape spring structure is
adopted
(5) Owing to the improved structure as a whole, no active headless inner pipe is
adopted
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Power seat switch layout
(1) Switches are arranged in accessible positions. Handleability is improved by
sufficient clearance (work space) between switches and peripheral components.
(2) Slide switch , Height adjustment switch, Seat bottom front height adjustment,
Reclining switch, and lumber switch are gathered together, designed in the
likeness of the seat enabling intuitive operation
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Security and Lock
Keyless entry system
(1) Key cylinder is directly connected to the latch. SSU and Electric steering lock are
integrated.
(2) A commonly designed transmitter is adopted for Remote Keyless Entry and
Advanced Keyless Entry
(3) The means of key authentication
The new structure, which the key cylinder is directly connected, is adopted to the latch
for theft prevention
Comparison between Advanced Keyless Entry and Keyless Entry
There are different features depending on whether it is WITH or WITHOUT advanced
keyless entry.
Item WITH WITHOUT
Door unlock/lock by request switch Available None
Are departure auto-lock control
Available None
(Personalization function)
Transmitter left-in-car prevention Available None
Door lock beep answer back Available None
Theft deterrent alarm Available None
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Advanced keyless system
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 10
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Wiring diagram
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 11
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
(Continued)
Lock/unlock operation using remote transmitter
Note: The lock/unlock operation is performed when the lock button of the remote
transmitter is pressed with all the following conditions met.
Ignition is switched OFF (LOCK)
All doors and liftgate are closed
The remote transmitter is within the operable range
1. When the lock or unlock button of the remote transmitter is pressed, the remote
transmitter sends ID data.
2. When the keyless receiver receives ID data, it transmits the data to the SSU.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 12
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
3. The SSU verifies the ID data, and if the ID data match, it sends a lock/unlock signal
to the rear body control module (RBCM) and at the same time, it sends a beeper
sound request signal to the smart entry control module.
4. The rear body control module (RBCM) operates the front/rear door lock actuator
motor to lock/unlock the front/rear doors. In addition, at the same time as the door
lock/unlock operation, it sends a hazard light flash request signal to the instrument
cluster as a CAN signal.
5. The smart entry control module operates the keyless beeper for the following
number of times:
When locking: Keyless beeper sounds once
When unlocking: Keyless beeper sounds twice
6. The instrument cluster sends the hazard light flash request signal to the front body
control module (FBCM) as a CAN signal.
7. The front body control module (FBCM) controls the hazard light to flash for the
following number of times to signal that the lock/unlock operation is completed.
When locking: Hazard light flashes once
When unlocking: Hazard light flashes twice
NOTE: Refer to the Technical Guide for other operation.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 13
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Exterior trim
1 2 3 4 5
3
1: Front under cover No. 1 4: Center under cover
2: Front under cover No. 2 5: Floor under cover
3: Side step molding
Technical tip Under cover removal
There are claws on the rear side of the under cover for assembling purpose in the
plant. These claws are fitted to the front member.
Procedure
Remove the front under cover No.1 in the direction of the arrow in the order of (1),
(2) shown in the figure while detaching the guide D.
Guide D
(1)
(2)
Front under cover No. 1
Even if the claws are broken, it does not disrupt installation. Under cover
replacement is unnecessary
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 14
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Interior trim
Light weight by foamed door module
Adopting door modules with formed material resulting in reduced weight contributes to
improving fuel economy. The weight is reduced by 11 - 13% as compared with
materials and manufacturing process used for the existent models.
Technical tip Door trim removal
The structure of the door trim is completely different from that of existent models.
Therefore, technicians should pay attention when removing.
Procedure
(Existent models)
(1) Remove the clips while pulling the door trim.
(2) Lift the door trim and remove the inner weather strip.
(CX-5)
(1) Remove the clips while pulling the door trim: and then, remove the door trim from
the door panel. (The inner weather strip remains on the door panel.)
Mazda3 CX-5
(2)
(3)
(4)
(1)
(2)
(1)
If the door trim is lifted when removing the door panel, the clips and pins for
the door panel will be broken.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 15
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Be careful so as not to break the claws.
Claws are to be inserted
into the groove.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 16
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
WIPER/WASHER SYSTEM
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 17
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 18
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Technical tip Washer nozzle adjustment
A movable ball in the tip of washer nozzle enables to adjust the angle of water
injection.
Insert a tape-wrapped precision flathead screwdriver into the adjustment hole of the
windshield washer nozzle and adjust it to the area where washer fluid is sprayed as
shown in the figure.
(Front)
(Rear)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 19
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
ENTERTAINMENT
Entertainment system
AM/FM shark fin antenna is employed.
Two types of audio units are available as follows:
Without Color LCD With Color LCD
Product outline
WITHOUT COLOR LCD WITH COLOR LCD
Radio, CD, Line-in/USB port Radio, CD, Line-in/USB port, Navigation,
Phone (Bluetooth)
(1) Applicable to USB/iPod as standard (1) USB connection
(2) Music in AAC format is playable (2) iPod connection
(3) Displaying in Latin characters (3) Bluetooth connection
(4) Improving reception performance by (4) HD Radio
on-board radio tuner
(5) Vehicle customization
(6) Improved functions of car navigation
system
Commander (with commander switch)
It is equipped with “WITH COLOR LCD” audio system. Though the touch screen is
available, it is equipped to enable the customer bind operations.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 20
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Technical tip Audio harness
The audio wire harness is extended, enabling technicians to remove/install the
audio system with less difficulty comparing to the arrangement of the existent
models.
Aerial
Shark-fin shape aerial is adopted to improve aerodynamics. An amplifier and band
pulse filter are built in the shark-fin shape aerial, ensuring reception performance.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 21
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
INSTRUMENTATION/DRIVER INFO
Instrument cluster
There are two types of instrument cluster: with TFT LCD display and without TFT LCD
display.
There are differences in location of warning/indicator lights. For example, key indicator
light is not equipped with Type A instrument cluster. If there is malfunction, a message
will appear on the display.
With TFT LCD display Without TFT LCD display
1 2 1 2
4 5 3 4 5
3
Item w/ TFT LCD w/o TFT LCD
Speedometer 1 1
Odometer trip, meter and trip meter selector 2, 4 2, 4
Tachometer 3 3
Fuel gauge 5 5
Instrument panel illumination 2 2
Outside temperature display 4 5
Cruise control set vehicle speed display 5 -
Maintenance monitor 5 -
Trip computer and INFO switch 5 5
Display items w/ TFT LCD w/o TFT LCD
Cruise control setting: vehicle speed X -
Maintenance monitor settings: Scheduled
maintenance, Tire rotation, Tire air pressure X -
check, Oil replacement
DIS settings: distance the vehicle possibly drive
with remained fuel, average fuel mileage, instant X X
fuel mileage, average vehicle speed
Vehicle speed warning X X
Accumulative time of i-stop X -
LDWS warning X -
Settings for vehicle speed warning, SCBS, LDWS,
i-stop duration, LDWS indication ON/OFF, volume X -
setting, unit preferences, language preference
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 22
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Warning/Indicator lights
Symbol Function w/ TFT LCD w/o TFT LCD
TCS/DSC indicator light X X
High beam control (HBC) system
indicator light (green)/high beam control
X X
system (hbc) warning light (amber) With
High beam control (HBC) system
Engine oil pressure warning light NA X
Glow indicator light
X X
SKYACTIV-D 2.2
Diesel particulate filter indicator light
NA X
SKYACTIV-D 2.2
KEY warning light (red)/indicator light
NA X
(green)
Front fog light indicator light
X X
With front fog light
Wrench indicator light
NA X
With wrench indicator light
Check engine light X X
Turn signal/hazard warning indicator
X X
lights
Automatic transaxle warning light
NA X
ATX
Cruise main indicator light
(amber)/cruise set indicatorlight (green) X X
With cruise control system
Lights-on indicator light X X
i-stop warning light (amber)/indicator
light (green) X X
With i-stop system
Lane departure warning system (LDWS)
indicator light (green)/lane departure
warning system (LDWS) arning light X X
(amber)
With LDWS
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 23
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
(Continued)
Symbol Function w/ TFT LCD w/o TFT LCD
Door-ajar warning light NA X
High engine coolant temperature
warning light (red)/low engine coolant X X
temperature indicator light (blue)
Low fuel warning light X X
120 km/h warning light
NA X
With 120 km/h warning light
ABS warning light X X
Low Washer Fluid Level Warning Light NA X
AFS OFF indicator light
X X
With AFS
Charging system warning light NA X
Brake system warning light X X
Headlight high-beam indicator light X X
Seat belt warning light X X
Rear Vehicle Monitoring (RVM) System
Warning Light (Amber)/Indicator Light
(Green) X X
With Rear Vehicle Monitoring (RVM)
System
BSM OFF indicator light
NA X
With BSM
Security indicator light
X X
With immobilizer system
Tire pressure monitoring system
X X
warning light
4WD warning light
NA X
With 4WD
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 24
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
(Continued)
Symbol Function w/ TFT LCD w/o TFT LCD
Master warning light X X
Air bag/front seat belt pretensioner
X X
system warning light
Power steering malfunction indicator
NA X
light
Rear fog light indicator light
X X
With rear fog light
Shift position indicator/gear position
indicator (ATX) X X
GEAR SHIFT INDICATOR (MTX)
TCS OFF indicator light X X
Master warning
The light illuminates continuously if any one of the following occurs.
There is a malfunction in the deceleration regeneration system.
There is a malfunction in the battery management system.
There is a malfunction in the brake switch.
The customer will be notified that there is a malfunction by the master warning light.
Actions that the customer is required vary according to the specification of the
instrument cluster type.
With TFT LCD display
It is required to check the details with the display because of a hazardous condition or
a system malfunction. Following the instruction on the display or the instruction
manual, it is necessary to take proper actions.
Without TFT LCD display
It is required to have the vehicle inspected due to a system malfunction as follows:
Current sensor (CX-5 with i-stop)
Stop lamp
Engine oil control (SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
Engine timing chain (SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
Blow-by heater (SKYACTIV-D 2.2)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 25
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Technical tip Wrench indicator light
Only for CX-5 SKYACTIV-D 2.2 (Without TFT LCD display instrument cluster)
- Water level in the sediment exceeded the specific level
(Reference)
Mazda3 (BL)
- Current sensor (vehicle with i-stop)
- Stop lamp switch malfunction
- Canceling brake override system
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 26
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
POWER SYSTEMS
Push button start system
Push button start system is adopted for all market for all types by utilizing advantages
of common architecture of the electric platform.
(1) The system adopted Start Stop Unit (SSU) consisting of F-BCM and electric
steering lock, and optimized location of Long-frequency (LF) antenna forms an
area in the cabin where push button start is activated with a single via LF antenna.
(2) The components formation is optimized that can establish Advanced Keyless
Entry system by adding LF control unit (LFU), LF antenna, and other components
to the basic systems. (Basic systems: Remote keyless and push button start)
(3) No IG key cylinder was adopted. SSU with steering lock mechanism is installed in
the steering shaft.
Comparison between Advanced Keyless Entry and Keyless Entry
There are different features depending on whether it is WITH or WITHOUT advanced
keyless entry.
Item WITH WITHOUT
The number of aerial in the cabin 2 1
LFU control unit Equipped None
Coil antenna location Push button Push button
Coil transponder location Key Key
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 27
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Operational range
The engine may not start if the key is placed in the following areas:
Around the instrument panel
In the storage compartments such as the glove box
On the rear parcel shelf
In the luggage compartment
LFU(LF Control Unit)
It is equipped with the vehicles with advance keyless entry. It is used for transmitting a
request signal based on the request signals via keyless antenna, and for controlling
the keyless buzzer.
It also sends signals of door lock/unlock to the RBCM based on the location of the key
recognized outside the vehicle.
Instrument panel
Technical tip Instrument panel
When removing the instrument cluster, the technician should pay attention.
The procedure for the instrument panel removal is similar to that of Mazda3 (BL).
But, HVAC unit should be remained in the body, not necessary to remove it.
There are two mounting screw bolting from outside the cabin (below the window
shield wiper motor).
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 28
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
Emergency key
When the battery for advanced key is weak or dead, it is necessary to carry out the
procedure for key identification to start the engine. This procedure for CX-5 is different
from that of existent models. The customer may be confused when encountering such
case.
Procedure
Touch the push button with the back side of the advanced key, and press the push
button with the brake pedal depressed.
CX-5 Push start button Mazda3 Coil antenna
CX-5 Push start button
Coil antenna
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 29
Mazda CX-5
09 – Body & Accessories
TN-CX5-1203
A new indication method of push button start power indication and malfunction
indication were adopted for CX-5.
The methods to indicate power and malfunction for push button start were changed
as shown in the table below.
Item Existent models CX-5
ACC: illuminating ACC characters
Power indicator Illuminating status indicator
ON: illuminating ON characters
Malfunction Illuminating status indicator Flashing status indicator
Unused KEY Warning Light (Red)/KEY Indicator Light (Green)
Key warning light/Key indicator light is not used for the instrument cluster with the
information display.
Existent models (Mazda3) New models (CX-5)
Display Display
Ready for ON ON ON
- -
engine start Green Green Green
Flash Characters Characters
Dead battery -
Green Displayed
-
Displayed
No key is Flash Characters Characters
- -
detected Amber Displayed Displayed
Keyless ON Characters Characters
- -
malfunction Amber Displayed Displayed
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 30
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
Multiplex communication system
A controller area network (CAN) system has been adopted in which multiplex
communication is performed using a single communication path.
A high-speed controller area network (HS-CAN) has been adopted for the
communication between the following modules:
PCM
DSC HU/CM
TCM (ATX vehicles)
AFS control module (with AFS system)
Front body control module (FBCM)
4WD control module (4WD vehicles)
Laser sensor (with smart city brake support system)
Forward sensing camera (with hi-beam control (HBC) system)
SSU
EPS control module
SAS control module
Instrument cluster
A mid-speed controller area network (MS-CAN) has been adopted for the
communication between the following modules:
Rear body control module (RBCM)
Rear mount camera (with rear mount camera)
BSM control module (LH) (with BSM system)
Rear vehicle monitoring control module (RH) (with rear vehicle monitoring
system)
BSM control module (RH) (with BSM system)
Parking sensor control module (with parking sensor system)
Climate control unit (with full-auto air conditioner)
Clock (with manual air conditioner)
Audio unit (with audio unit (color LCD))
Instrument cluster
BCM
The functions of BCM, equipped with existent models, are divided into three BCM:
FBCM (Front BCM), RBCM (Rear BCM), and SSU (Start Stop Unit).
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 1
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
Control module location (LHD)
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 2
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
HS-CAN system wiring diagram (LHD)
Terminator resistors are built into the PCM and instrument cluster which form the
HS-CAN between the PCM and instrument cluster.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 3
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
MS-CAN system wiring diagram (LHD)
Terminator resistors are built into the rear body control module (RBCM) and
instrument cluster which form the MS-CAN between the rear body control module
(RBCM) and instrument cluster.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 4
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
The instrument cluster is connected to the HS-CAN and MS-CAN which communicate
with each other via the instrument cluster.
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 5
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
Advantage of employing the 3 BCMs
In view of reducing cost and improving performance, the new architecture was
developed with 3 modules.
Module is located in place close to the output and input devices
The BCM which is the core to execute control items is in place close to the load
Existent models CX-5
FBCM
Wire
Wire harness Twisted Instrument
harness pair cluster
BCM
SSU
Twisted
pair
Wire
harness
RBCM
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 6
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
Integrated HS-CAN and MS-CAN
Example 1) Rear wiper
Rear wiper and Rear wiper
washer switch motor
SSU RBCM
HS-CAN MS-CAN
HS-CAN
FBCM Instrument cluster
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 7
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
Example 2) Auto-light system
Micro- LIN
computer Head light
LO relay
Auto- light
Head light
sensor
LO bulb
HS-CAN TNS relay
Light
SSU FBCM
switch TNS
Parking
light
Example 3) Front windshield wiper/washer
HS-CAN Washer motor
Windshield wiper
and washer switch SSU FBCM
Windshield
wiper motor
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 8
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
Example 4) Turn signal/Hazard
Light switch
(Turn switch)
Instrument
SSU FBCM
cluster
Hazard warning
switch
Example 5) Light-on indicator light
Instrument
Light SSU FBCM cluster
switch
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 9
Mazda CX-5
10 – Multiplex communication system
TN-CX5-1203
Control item FBCM RBCM SSU
Defroster X
Blower motor X
Front combination light X
Front fog light X
Auto-light system X
Front wiper X
Horn X
Power door lock X
Room light control X
Rear wiper X
Advanced keyless entry X
Keyless entry X
Push button start X
Immobilizer X
Input of combination switches X
Input of steering switches X
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved. 10
Intentionally blank
© Copyright, 2012 Mazda Motor Corporation. All Rights Reserved
All materials (texts, images, graphics, and other materials) on the documents are subject to
the copyrights and other intellectual property rights of Mazda Motor Corporation, its affiliated
companies, and its licensors. These materials may not be copied, processed, sold,
inspected, published not only for commercial use but also for third party, and these materials
may not be modified or reproduced in any medium without the written authorization of
Mazda Motor Corporation.
Você também pode gostar
- VW Transporter T4 ( Diesel - 2000-2004) Workshop Manual: Owners Edition (Owners' Workshop Manuals)No EverandVW Transporter T4 ( Diesel - 2000-2004) Workshop Manual: Owners Edition (Owners' Workshop Manuals)Nota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (3)
- Royal Enfield Classic 500 - Service ManualDocumento229 páginasRoyal Enfield Classic 500 - Service ManualDaniel Keith Steyn78% (9)
- 323 BA 2-0 94-98 (ECU Pinout)Documento5 páginas323 BA 2-0 94-98 (ECU Pinout)TimSmith76% (17)
- F4M2011Documento5 páginasF4M2011Fayez AlnamarnehAinda não há avaliações
- Mercedes - Benz Vito & V-Class Petrol & Diesel Models: Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003No EverandMercedes - Benz Vito & V-Class Petrol & Diesel Models: Workshop Manual - 2000 - 2003Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Mercedes 722.6Documento2 páginasMercedes 722.6Kelvin Tan Boon Lork100% (5)
- Tranny 722 RepairDocumento159 páginasTranny 722 Repairpaschov100% (3)
- Common Rail System (CRS) Service Manual: Mazda Skyactiv-D Engine (Euro 6)Documento63 páginasCommon Rail System (CRS) Service Manual: Mazda Skyactiv-D Engine (Euro 6)Carl Anthony Chamberlain100% (10)
- 722.6 Solenoid Truth TableDocumento4 páginas722.6 Solenoid Truth TableJack Carl100% (1)
- At 02e DSG RepairDocumento170 páginasAt 02e DSG Repairniculescuc100% (4)
- R4a51 - V4a51 - R5a51 - V5a51 PDFDocumento4 páginasR4a51 - V4a51 - R5a51 - V5a51 PDFJuan IdrovoAinda não há avaliações
- F4A4x at ManualDocumento135 páginasF4A4x at Manualcavp271% (7)
- Technical Service Information Technical Service Information: CVT 7 - JF015E/RE0F11A/F1CJBDocumento2 páginasTechnical Service Information Technical Service Information: CVT 7 - JF015E/RE0F11A/F1CJBmohammad100% (2)
- PM 9G TRONIC enDocumento40 páginasPM 9G TRONIC enStefan IlicAinda não há avaliações
- C9 Engine BrochureDocumento6 páginasC9 Engine Brochurebaghermanesh135450% (2)
- 1.6 Turbo Gdi Hyundai Kim eDocumento24 páginas1.6 Turbo Gdi Hyundai Kim egiampaoloAinda não há avaliações
- Fuel Injection Pump - RemoveDocumento6 páginasFuel Injection Pump - RemoveedwinAinda não há avaliações
- Anchor HandlingDocumento167 páginasAnchor HandlingSergiy Khadzhyoglo100% (2)
- The Upshift Delay DilemmaDocumento5 páginasThe Upshift Delay DilemmaAlin Nita100% (1)
- Dsi m78 6speed Son YongDocumento104 páginasDsi m78 6speed Son YongGlen15100% (4)
- Mazda - SKYACTIV TechnologiesDocumento25 páginasMazda - SKYACTIV TechnologiesPongchanok Paisitpatanapong100% (1)
- Automatic Transaxle (F4A51)Documento194 páginasAutomatic Transaxle (F4A51)Dayro GeneyAinda não há avaliações
- Mitsubish Manuals TransmissionDocumento118 páginasMitsubish Manuals TransmissionJoseGabrielGomez100% (4)
- 722.6 Failure To UpshiftDocumento3 páginas722.6 Failure To UpshiftJack CarlAinda não há avaliações
- Dog ClutchDocumento7 páginasDog ClutchSajoud MohsinAinda não há avaliações
- BMW Automatic 4L30EDocumento2 páginasBMW Automatic 4L30EMichaela FleischhackerAinda não há avaliações
- 01m Transmission RemovalDocumento33 páginas01m Transmission Removalbandwagoneer50% (2)
- Aisin Automatic TransaxleDocumento234 páginasAisin Automatic Transaxlenavifreak0100% (1)
- Mercedes a-B-Class CVT Transmission-1Documento111 páginasMercedes a-B-Class CVT Transmission-1Bernard Tripp100% (2)
- January Februari Buyers Guide PDFDocumento124 páginasJanuary Februari Buyers Guide PDFcherokewag100% (1)
- Hondametc Civic 2004Documento88 páginasHondametc Civic 2004hari yadiAinda não há avaliações
- 722 6 VacTestDocumento4 páginas722 6 VacTestMauricio Exequiel ChavezAinda não há avaliações
- DSG 02e SSP - 308 PDFDocumento64 páginasDSG 02e SSP - 308 PDFcataroxi100% (1)
- 2015 12 Feb JPAT 4WD Single Parts Cat PDFDocumento66 páginas2015 12 Feb JPAT 4WD Single Parts Cat PDFLuis MigueloAinda não há avaliações
- Re4r03a Jr403eDocumento5 páginasRe4r03a Jr403eجوني رويزAinda não há avaliações
- Mazda6 - Ja5a-El - Jf506eDocumento155 páginasMazda6 - Ja5a-El - Jf506evarelaf100% (1)
- Honda Px4bDocumento101 páginasHonda Px4bRoberto Perez100% (1)
- Manual Engleza Opel Signum - Vectra CDocumento330 páginasManual Engleza Opel Signum - Vectra CEmanuel Mihai100% (1)
- Seat Alhambra 2.0 TDi 2005-2010Documento11 páginasSeat Alhambra 2.0 TDi 2005-2010marquin84Ainda não há avaliações
- CVTDocumento201 páginasCVTJimena Arc100% (1)
- Toyota Landcruiser: (Kinetic Dynamic Suspension System)Documento1 páginaToyota Landcruiser: (Kinetic Dynamic Suspension System)george_mudura1Ainda não há avaliações
- U140E U241E Vac LocationsDocumento5 páginasU140E U241E Vac LocationsPedroMecanicoAinda não há avaliações
- ZF 4 HP 20Documento4 páginasZF 4 HP 20Irina VeresininaAinda não há avaliações
- Car Modifications - Stage 1, 2 & 3 - TeambhpDocumento7 páginasCar Modifications - Stage 1, 2 & 3 - TeambhpMuralidhar0% (1)
- Toyota NRC Nov2012Documento39 páginasToyota NRC Nov2012Sashi VelnatiAinda não há avaliações
- 7G PlusDocumento6 páginas7G PlusBogathrozAinda não há avaliações
- VHe New Hyundai-Kia 1,0 L Three-Cylinder Gasoline EngineDocumento8 páginasVHe New Hyundai-Kia 1,0 L Three-Cylinder Gasoline EngineIndranil BhattacharyyaAinda não há avaliações
- Sky ActiveDocumento57 páginasSky Activeespejorge100% (1)
- Latest Automobile TechnologiesDocumento22 páginasLatest Automobile TechnologiesAakar Gangrade93% (15)
- 2013-11-Uj Negyhengeres Mercedes MotorDocumento8 páginas2013-11-Uj Negyhengeres Mercedes MotorBenedek ZoltánAinda não há avaliações
- DD13 BrochureDocumento10 páginasDD13 BrochureecasayangAinda não há avaliações
- C9 Brochure LEDT7015-01Documento6 páginasC9 Brochure LEDT7015-01DraganAinda não há avaliações
- Development of The Next-Generation Half-Toroidal CVT With Geared Neutral and Power-Split Systems For 450 N-M EnginesDocumento9 páginasDevelopment of The Next-Generation Half-Toroidal CVT With Geared Neutral and Power-Split Systems For 450 N-M EnginesAbhishekJadhav100% (1)
- 2013-12-Uzemanyag Fogyasztas Csokkentese A JovobenDocumento6 páginas2013-12-Uzemanyag Fogyasztas Csokkentese A JovobenBenedek ZoltánAinda não há avaliações
- Bearing CapacityDocumento36 páginasBearing CapacityAjay SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Mo 4 811Documento8 páginasMo 4 811eng_ebrahim_2000Ainda não há avaliações
- Gasoline Direct Injection EnginesDocumento25 páginasGasoline Direct Injection EnginesJayant Raj SauravAinda não há avaliações
- What Is DTS-iDocumento8 páginasWhat Is DTS-iGaurao WarungaseAinda não há avaliações
- Detroit DD15 Engine: Horsepower LB-FT Torque LitersDocumento10 páginasDetroit DD15 Engine: Horsepower LB-FT Torque Litersramsi17100% (1)
- 32 - 40 - Four Stroke - 34210101Documento7 páginas32 - 40 - Four Stroke - 34210101Mulyo SetiawanAinda não há avaliações
- Acert EnginesDocumento12 páginasAcert EnginesAnonymous alQXB11EgQ100% (1)
- CatalogoDocumento28 páginasCatalogopolicryAinda não há avaliações
- Eccentric SleeveDocumento20 páginasEccentric SleeveSenthil KumarAinda não há avaliações
- New Opportunities As CVT Fleet GrowsDocumento8 páginasNew Opportunities As CVT Fleet GrowssrcattozziAinda não há avaliações
- Mining Truck: Engine Weights - Approximate Operating SpecificationsDocumento28 páginasMining Truck: Engine Weights - Approximate Operating SpecificationsJavier Alfonso Baquero PuelloAinda não há avaliações
- Piston and Rings: SpecificationsDocumento3 páginasPiston and Rings: SpecificationsPaulo100% (2)
- Qip Ice 01 IntroductionDocumento40 páginasQip Ice 01 IntroductionTiffany Powell100% (1)
- Diesel Information: DT5230 (EN)Documento2 páginasDiesel Information: DT5230 (EN)AminadavAinda não há avaliações
- Cod Falhas Cummins PDFDocumento7 páginasCod Falhas Cummins PDFOseasJuniorAinda não há avaliações
- Pruebas y Adjustes - Troubleshooting 3512G PDFDocumento32 páginasPruebas y Adjustes - Troubleshooting 3512G PDFPLANTAS ELECTRICAS H&BAinda não há avaliações
- RotaxDocumento12 páginasRotaxleopro_f1Ainda não há avaliações
- DTC P0130 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1)Documento4 páginasDTC P0130 Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1 Sensor 1)salusfrankAinda não há avaliações
- 1gr-Fe Engine Control System4Documento7 páginas1gr-Fe Engine Control System4mike chenAinda não há avaliações
- Service Bulletin Index CF6: Middle River Aircraft SystemsDocumento1 páginaService Bulletin Index CF6: Middle River Aircraft SystemsNour ZAAinda não há avaliações
- Engine Oil Cooler - Install - Engine Oil Cooler With A High Mounted Filter Base (KENR6081-15)Documento4 páginasEngine Oil Cooler - Install - Engine Oil Cooler With A High Mounted Filter Base (KENR6081-15)Anderson Oliveira SilvaAinda não há avaliações
- Self-Diagnosis Data Self-Diagnosis ParametersDocumento2 páginasSelf-Diagnosis Data Self-Diagnosis Parametersneoporsche15Ainda não há avaliações
- Avp07aa AP240CU2-BT4.5-C99 3742266-XXXXXXX 070430 ENDocumento75 páginasAvp07aa AP240CU2-BT4.5-C99 3742266-XXXXXXX 070430 ENCarlos Alberto Ramirez ParraAinda não há avaliações
- s2125 Service ManualDocumento222 páginass2125 Service ManualJomesAinda não há avaliações
- C9 Valve SpecDocumento7 páginasC9 Valve SpecWa TokeAinda não há avaliações
- Rudolf Diesel UkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkDocumento7 páginasRudolf Diesel UkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkkUday KiranAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of Fuel System MaintenanceDocumento37 páginasOverview of Fuel System MaintenanceMarwan NasserAinda não há avaliações
- J-Serise Engine-USADocumento29 páginasJ-Serise Engine-USACristian m VizcainoAinda não há avaliações
- Service Manual: Common Rail System For ISUZU 4HK1 / 6HK1 Type EngineDocumento49 páginasService Manual: Common Rail System For ISUZU 4HK1 / 6HK1 Type EngineLeonardo Medina100% (1)
- V10 1100 CRMDocumento4 páginasV10 1100 CRMditer najarAinda não há avaliações
- Clark C70Documento155 páginasClark C70Cesar Godoi100% (1)
- Modular Engine 1 Revision 2Documento15 páginasModular Engine 1 Revision 2Jan GroenewaldAinda não há avaliações
- Synhronous Motor Question Top Most 130 PDFDocumento26 páginasSynhronous Motor Question Top Most 130 PDFJennkihgfadet PyuengrtruipAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation1 SeminarDocumento18 páginasPresentation1 SeminarSatyabrataPradhanAinda não há avaliações
- The CFM56Documento4 páginasThe CFM56Okky Pangestoe WibowoAinda não há avaliações
- What Is VIRTUAL TAPDocumento2 páginasWhat Is VIRTUAL TAPAnakin Skywalker100% (1)