Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Milling Operation PDF
Enviado por
Raheem0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
261 visualizações16 páginasThere are two main types of milling machines - vertical and horizontal. A vertical mill has a spindle oriented vertically while a horizontal mill has a horizontal spindle. Both types of machines move the worktable to position the workpiece under the rotating cutter. Milling cutters come in various sizes and tooth configurations and are used to remove material by rotating and moving into the workpiece. The direction of cutter rotation and worktable feed determines whether it is an up-cut or down-cut milling operation.
Descrição original:
Título original
Milling operation.pdf
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThere are two main types of milling machines - vertical and horizontal. A vertical mill has a spindle oriented vertically while a horizontal mill has a horizontal spindle. Both types of machines move the worktable to position the workpiece under the rotating cutter. Milling cutters come in various sizes and tooth configurations and are used to remove material by rotating and moving into the workpiece. The direction of cutter rotation and worktable feed determines whether it is an up-cut or down-cut milling operation.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
261 visualizações16 páginasMilling Operation PDF
Enviado por
RaheemThere are two main types of milling machines - vertical and horizontal. A vertical mill has a spindle oriented vertically while a horizontal mill has a horizontal spindle. Both types of machines move the worktable to position the workpiece under the rotating cutter. Milling cutters come in various sizes and tooth configurations and are used to remove material by rotating and moving into the workpiece. The direction of cutter rotation and worktable feed determines whether it is an up-cut or down-cut milling operation.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 16
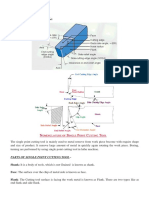
Milling Operation
A milling machine is a machine tool that removes
material from a work piece by rotating a cutter and
moving it into the material.
A milling machine produces:
Plane surfaces that may be parallel or perpendicular or at angle to
the work table.
Unlike the lathe or the shaping machine, the milling machine uses
a muti-tooth cutter
Types of milling machines
Types of Milling Machines
There are two major types of milling machines,
the vertical milling machine and
the horizontal milling machine.
A vertical milling machine has
its spindle axis vertical,
its machine table moves perpendicular to the spindle axis of
rotation and whilst
A horizontal milling machine
spindle axis is horizontal, here
the work table that moves parallel to the spindle axis of rotation
Basic movements
Of a vertical milling machine:
The movements and alignment are such that the axis of rotation
of the cutter by a spindle is perpendicular to the work table, or a
desired and controlled angle to the work table.
The work table provides datum surface from which the wor is set
as well as supporting the workpiece.
The working surface of the work table, therefore, must lie
horizontally beneath the cutter and perpendicular to the cutter
axis.
The work table must move in a direction at right angles to the
longitudinal traverse.
It is necessary to raise or lower the work table in order to feed
the work into the cutter and to compensate for different
thicknesses of work.
Table movements are controlled by lead screws fitted with
Basic movements
Of a vertical milling machine:
Table movements are controlled by lead screws fitted with
micrometer dials for accurate positioning of the table and
workpiece under the cutter.
Basic movements
Of a horizontal milling machine:
The movements and alignment required are the location and
movement of workpiece by the worktable in a plane beneath the
cutter, parallel to the spindle axis.
The spindle must have a horizontal axis.
The work table must move in a direction at right angles to the
longitudinal traverse.
The work table should be able to able to be raised or lowered in
order to feed the work into the cutter and to compensate for
different thicknesses of work.
Table movements are controlled by lead screws fitted with
micrometer dials for accurate positioning of the table and
workpiece under the cutter.
Milling cutters
A milling cutter is a cutting tool that is used on a milling
machine.
Milling cutters are available in many standard and special
types, forms, diameters, and widths.
The teeth maybe straight (parallel to the axis of rotation)
or at a helix angle.
The helix angle helps a
slow engagement of the
tool distributing the forces .
Milling cutters
The cutter may be right-hand (to turn clockwise) or left-
hand (to turn counterclockwise).The figure shows a
typical end milling cutter.
Milling cutters
Milling cutters have a secondary clearance angle to
prevent the heel of the tooth interfering with the
machined surface of the workpiece.
The tooth can be made up of a series of straight lines, or
it can be a curved profile.
Milling cutters
Cutting Action
Up-cut milling
Traditional method – great
advantage of not tending to drag the
work into the cutter – can be used
on worn and cheap machines.
Disadvantages:
1. Tends to rub before biting into the
metal, resulting in cutter wear and
poor finish
2. Cutting forces at maximum as the
chip leaves the workpiece –
resulting in transmission bounce
(ramble).
Cutting Action
Up-cut milling
3. Cutting forces tend to lift the
component off the work table.
4. The feed mechanism drives the
workpiece against the full thrust of
the cutter.
Cutting Action
Down-cut milling
This process has a number of
advantages:
1. The cutter bites into the workpiece
immediately and the load is eased off the
tooth gradually – thus smoother
operating conditions; longer cutter and
machine life, and good surface finish.
2. Cutting forces press the workpiece down
on to the table – maximum rigidity
3. Feed mechanism controls the feed rate
only, as the cutter tends to draw the
work through.
Cutting Action
Down-cut milling
The major disadvantage is, it can only be
used on modern machine in good
condition and fitted with a backlash
eliminator.
Standard milling vs. climb milling
Plain milling and End milling
Você também pode gostar
- Milling Machine (Group 7)Documento52 páginasMilling Machine (Group 7)Faisal Maqsood100% (1)
- Millingmachinehusain 151003135158 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocumento49 páginasMillingmachinehusain 151003135158 Lva1 App6891 PDFpatlninadAinda não há avaliações
- Metrology Angular MeasurementDocumento25 páginasMetrology Angular Measurementegowdhaman100% (4)
- Kerney & Trecker AC, CH, &, CHL OperatorsManualDocumento27 páginasKerney & Trecker AC, CH, &, CHL OperatorsManualDavid100% (1)
- Drill DataDocumento5 páginasDrill DataDOBJANAinda não há avaliações
- Circular Motion - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento9 páginasCircular Motion - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAkshat TyagiAinda não há avaliações
- Broaching MachineDocumento26 páginasBroaching Machinesanaashraf100% (1)
- Milling MachineDocumento32 páginasMilling MachineIrfan Shaikh100% (2)
- Setup Guide GTR2 2Documento3 páginasSetup Guide GTR2 2cjohananAinda não há avaliações
- MTR 14Documento140 páginasMTR 14lehaphuong03Ainda não há avaliações
- Machine ToolDocumento23 páginasMachine ToolMohammad Anaitullah HassanAinda não há avaliações
- Milling Machine Definition Parts Types Operations WithDocumento19 páginasMilling Machine Definition Parts Types Operations WithMunem ShahriarAinda não há avaliações
- Chips Single PT Cutting ToolDocumento4 páginasChips Single PT Cutting Toolbalamurugan_meAinda não há avaliações
- CNC Wood Turning Lathe Cutters Bits Knife ToolsDocumento5 páginasCNC Wood Turning Lathe Cutters Bits Knife ToolsSalce SmithAinda não há avaliações
- Parts of Single Point Cutting ToolDocumento8 páginasParts of Single Point Cutting ToolMukesh sutharAinda não há avaliações
- Review On Single Point Cutting ToolDocumento5 páginasReview On Single Point Cutting ToolHarsh100% (1)
- Resolver Versus EncoderDocumento2 páginasResolver Versus EncodercoronaqcAinda não há avaliações
- Metal CuttingDocumento39 páginasMetal Cuttingavinashn12Ainda não há avaliações
- Turning and Lathe - Guia de Estudo - 2016Documento10 páginasTurning and Lathe - Guia de Estudo - 2016Anderson R. RojasAinda não há avaliações
- Surface GrindingDocumento3 páginasSurface GrindingNithish Kuttan100% (1)
- Theory of Metal CuttingTool GeometryDocumento25 páginasTheory of Metal CuttingTool GeometryNisha SharmaAinda não há avaliações
- Armory Function & DutiesDocumento4 páginasArmory Function & DutiesCj Nightsirk100% (1)
- Types of Chips Waqas MTMDocumento2 páginasTypes of Chips Waqas MTMirfan aminAinda não há avaliações
- ShaperDocumento20 páginasShaperMilan SainiAinda não há avaliações
- F - BoringDocumento44 páginasF - BoringedsaregAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages of High Speed MachiningDocumento6 páginasAdvantages of High Speed MachiningMahendra VadavaleAinda não há avaliações
- Maag Gear Shaper CutterDocumento9 páginasMaag Gear Shaper CutterBence Levente Szabó100% (1)
- Tail Stock of LatheDocumento7 páginasTail Stock of LatheKIÊN HOÀNG TRUNG100% (1)
- Surface Grinding MachineDocumento26 páginasSurface Grinding MachinejohnAinda não há avaliações
- Manufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentDocumento5 páginasManufacturing of Spur Gear: Aim of The ExperimentParameshwara MeenaAinda não há avaliações
- Machining Processes Used To Produce Various Shapes: MillingDocumento28 páginasMachining Processes Used To Produce Various Shapes: MillingSuleiman SaidAinda não há avaliações
- Metal Cutting (F) SDocumento62 páginasMetal Cutting (F) SBrijesh VermaAinda não há avaliações
- Tool AnglesDocumento13 páginasTool AnglesAkshay KakaniAinda não há avaliações
- LatheDocumento14 páginasLatheHimanshu ModiAinda não há avaliações
- Name of The Experiment:: Study and Operation Bench Drilling MachineDocumento5 páginasName of The Experiment:: Study and Operation Bench Drilling MachinemadAinda não há avaliações
- Operation Manual: Vertical Machining CenterDocumento27 páginasOperation Manual: Vertical Machining CenterAmauriGarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Machine Tools and Machining1Documento62 páginasMachine Tools and Machining1Faisal MaqsoodAinda não há avaliações
- MST II NotesDocumento309 páginasMST II NotesAman Jain100% (2)
- Chapter 6 High Speed MachiningDocumento31 páginasChapter 6 High Speed Machiningmuhamadsaidi100% (5)
- 26 Broaching - Principles, Systems and ApplicationsDocumento16 páginas26 Broaching - Principles, Systems and ApplicationsPRASAD326100% (2)
- LatheDocumento63 páginasLatheRandom100% (1)
- Design and Fabrication of Self Centering Vice Ppt-1Documento36 páginasDesign and Fabrication of Self Centering Vice Ppt-1KarthickAinda não há avaliações
- BroachingDocumento35 páginasBroachingAbdulaziz FarhanAinda não há avaliações
- Presentation of Drilling Machine by Anil Dahiya SirDocumento72 páginasPresentation of Drilling Machine by Anil Dahiya SirRAMAKANT RANA100% (1)
- CH 5 DrillingDocumento39 páginasCH 5 DrillingMANJEET KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Shaping MachineDocumento25 páginasShaping Machinekatakamharish100% (1)
- Theory of Metal Cutting 2Documento39 páginasTheory of Metal Cutting 2Anonymous p0mg44x100% (1)
- Drilling Speeds and FeedsDocumento1 páginaDrilling Speeds and FeedsLe Hoang HiepAinda não há avaliações
- Spline BroachingDocumento28 páginasSpline BroachingFaraz IshaniAinda não há avaliações
- Study of Grinding MachinesDocumento10 páginasStudy of Grinding Machinesdeepa82ece100% (1)
- Lathe AccessoriesDocumento4 páginasLathe AccessoriesBOT-X GAMING100% (1)
- Generalized Kinematics of Five-Axis Serial Machines WithDocumento47 páginasGeneralized Kinematics of Five-Axis Serial Machines WithJoss Joss100% (1)
- Milling OperationDocumento16 páginasMilling OperationDerrick Maatla MoadiAinda não há avaliações
- BME Milling and GrindingDocumento16 páginasBME Milling and GrindingalysonmicheaalaAinda não há avaliações
- JJ 104 Workshop Technology 1 MillingDocumento44 páginasJJ 104 Workshop Technology 1 MillingHusaini Zamzury0% (1)
- MILLINGDocumento5 páginasMILLINGArun Prasad100% (1)
- Machine Shop: DefinitionDocumento10 páginasMachine Shop: DefinitionAliAinda não há avaliações
- Milling NotesDocumento20 páginasMilling NotesleoandresmessiAinda não há avaliações
- Shaping Machine Manual FinalDocumento4 páginasShaping Machine Manual FinalBarun DeAinda não há avaliações
- Milling Machine ManualDocumento5 páginasMilling Machine ManualBarun DeAinda não há avaliações
- Portland PortDocumento18 páginasPortland PortAnonymous Lx3jPjHAVLAinda não há avaliações
- Manuel D'utilisation Maison AnglaisDocumento17 páginasManuel D'utilisation Maison AnglaisVanesssAinda não há avaliações
- Antena Kathrein 742266 PDFDocumento2 páginasAntena Kathrein 742266 PDFcesarbayonaAinda não há avaliações
- Vet CareplanexampleDocumento6 páginasVet CareplanexampleAnonymous eJZ5HcAinda não há avaliações
- Labangon Elementary School Diagbostic Test in Epp/Tle 6 Directions: Multiple Choice. Choose The Correct The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocumento4 páginasLabangon Elementary School Diagbostic Test in Epp/Tle 6 Directions: Multiple Choice. Choose The Correct The Letter of The Correct AnswerJulianFlorenzFalconeAinda não há avaliações
- Paracetamol BPDocumento4 páginasParacetamol BPjaimurugeshAinda não há avaliações
- Civil 416Documento2 páginasCivil 416tskh11Ainda não há avaliações
- Maxon - Gas Electro-Mechanical ValvesDocumento4 páginasMaxon - Gas Electro-Mechanical ValvesThiagoAinda não há avaliações
- IBH Link UA Manual PDFDocumento302 páginasIBH Link UA Manual PDFjavixl1Ainda não há avaliações
- Da13 DDR N1 14000305 254 0Documento3 páginasDa13 DDR N1 14000305 254 0Hamed NazariAinda não há avaliações
- Markov Interest Rate Models - Hagan and WoodwardDocumento28 páginasMarkov Interest Rate Models - Hagan and WoodwardlucaliberaceAinda não há avaliações
- CF1900SS-DF Example Spec - Rev1Documento1 páginaCF1900SS-DF Example Spec - Rev1parsiti unnesAinda não há avaliações
- ISNGI 2017 ProgrammeDocumento6 páginasISNGI 2017 ProgrammeJoanna JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- B11R Jonckheere JHV2 SpecDocumento1 páginaB11R Jonckheere JHV2 SpecVishwanath SeetaramAinda não há avaliações
- Roles and Responsibilities of ASHADocumento3 páginasRoles and Responsibilities of ASHAmohanpskohli8310Ainda não há avaliações
- 120Documento349 páginas120xdyj2005Ainda não há avaliações
- Standard MissileDocumento2 páginasStandard Missilemadox_3m100% (1)
- Commissioning/Troubleshooting: Check List: C B A Yellow Grey Black TBPDocumento2 páginasCommissioning/Troubleshooting: Check List: C B A Yellow Grey Black TBPmohamedAinda não há avaliações
- Haruki Murakami - MirrorDocumento5 páginasHaruki Murakami - Mirrorhhellakoski25% (4)
- Valvula Reguladoras Pilotados DANFOSSDocumento2 páginasValvula Reguladoras Pilotados DANFOSSJurandir Laureano SILVA JUNIORAinda não há avaliações
- Beautiful Results: Simple Procedure 1. Etch 2. Bond 3. RestoreDocumento4 páginasBeautiful Results: Simple Procedure 1. Etch 2. Bond 3. RestoreEuclides Soza CalvoAinda não há avaliações
- Origami PapiroflexiaDocumento6 páginasOrigami PapiroflexiaBraulio RomeroAinda não há avaliações
- Revision For The First 1 English 8Documento6 páginasRevision For The First 1 English 8hiidaxneee urrrmAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 Nissan 370Z 3.7L Eng VIN A BaseDocumento69 páginas2015 Nissan 370Z 3.7L Eng VIN A BaseData TécnicaAinda não há avaliações
- Chola MS: Motor Policy Schedule Cum Certificate of InsuranceDocumento2 páginasChola MS: Motor Policy Schedule Cum Certificate of InsuranceSRI DURGA KEDARI0% (1)
- Disorders of The Endocrine System and Dental ManagementDocumento63 páginasDisorders of The Endocrine System and Dental ManagementSanni FatimaAinda não há avaliações
- 365-M - City Bus Route & Timings, Bangalore (BMTC) Map, First & Last BusDocumento10 páginas365-M - City Bus Route & Timings, Bangalore (BMTC) Map, First & Last BusER Aditya DasAinda não há avaliações
- Mucosal Adjuvants: Charles O. Elson Mark T. DertzbaughDocumento1 páginaMucosal Adjuvants: Charles O. Elson Mark T. DertzbaughPortobello CadısıAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumentation & Measurement SystemsDocumento7 páginasInstrumentation & Measurement SystemsAnkit KumarAinda não há avaliações
- AsasDocumento2 páginasAsasbuntu2003Ainda não há avaliações