Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
The Articles and Direct Indirect Objects
Enviado por
maulidah0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
11 visualizações7 páginasTítulo original
B. inggris.docx
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
11 visualizações7 páginasThe Articles and Direct Indirect Objects
Enviado por
maulidahDireitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 7
THE ARTICLES AND DIRECT INDIRECT OBJECTS
Makalah diajukan sebagai salah satu tugas mata kuliah
Bhs. Inggris
Dosen Pengampu : Kurnia Akbar, SS. MPd.
Pemakalah :
Azka Uswatun Tsaqofah ()
Nur Maulidah Fitriyani ()
PROGRAM STUDI PENDIDIKAN AGAMA ISLAM (PAI)
FAKULTAS TARBIYAH
NSTITUT ILMU AL-QUR’AN JAKARTA
TAHUN AJARAN 2018/2019
DIRECT-INDIRECT SPEECH
A. Direct Speech / Quoted Speech / Kalimat Langsung
Adalah kalimat yang diucapkan secara langsung oleh pembicara.
Ciri-ciri :
1. Terdapat tanda kutip
American “ ---“
British ‘---‘
2. Tidak terdapat Conjunction (kata penghubung)
B. Indirect Speech / Reported Speech / Kalimat Tidak Langsung
Adalah kalimat yang diucapkan tidak langsung oleh pembicara tanpa diberi
koma.
Ciri-ciri :
1. Tidak terdapat tanda kutip
2. Terdapat conjunction
Contoh :
Direct Speech : Venna bilang,”aku punya banyak air”.
Venna said,”I have much water”.
Indirect speech : Venna bilang bahwa dia mempunyai banyak air.
: Venna said that she had much water.
Venna said adalah Main Clause (kalimat utama) dan I have much water
adalah Sub Clause.
Tell, ask, say,…..disebut sebagai introductory verb (kata kerja pengantar)
yang menghubungkan Main Clause (MC) dan Sub Clause(SC).
C. Kinds of Direct-Indirect Speech
1. Statement (pernyataan)
Untuk mengubah kalimat dari Direct menjadi Inderect pada kalimat
pernyataan digunakan kata penghubung “that” sebelum kalimat yang
dikutip.
Aturan perubahan :
a) Perubahan tenses
b) Perubahan pronoun (kata ganti)
c) Perubahan adverb (kata keterangan)
a) Perubahan tenses
Perubahan hanya pada Sub Clause
Main Clause bertenses simple past
Tenses mundur 1 kali lampau
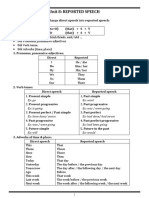
Direct Speech Indirect Speech
Simple present tense Simple past tense
(V1 (s/es)) (V2)
Present continuous tense Past continuous tense
(I/am/are + V.ing) (was/were + V.ing)
Present perfect tense Past perfect tense
(have/has + V3) (had + V3)
Present perfect continuous tense Past perfect continuous tense
(have/has + been + V.ing) (had + been + V.ing)
Simple past tense Past perfect tense
(V2) (had + V3)
Simple future tense Past future tense
(will/shall + V1) (Would/should + V1)
Future continuous tense Past future continuous tense
(will/shall + be + V.ing) (would/should + be + V.ing)
Contoh :
1. Direct : Usman said,”khodijah is sick”.
Indirect : Usman said that khodijah was sick.
2. Direct : Ulya said,”siti has eaten”.
Indirect : Ulya said that siti had eaten.
3. Direct : Kelly told her friend,”I will go to market” .
Indirect : Kelly told her friend that she would go to market.
Note :
Tenses dalam SC tidak berubah, apabila :
1. IV menggunakan tenses selain Simple past.
Contoh : DS = Dian has said,”vitri is happy”.
IS = Dian has said that vitri is happy.
2. SC menunjukkan kebenaran umum.
Contoh : DS = Irfan said,”the fire is hot”.
IS = Irfan said that the fire is hot.
b) Perubahan Pronoun
Aturan :
1. Jika terdapat pronoun I, my, me, mine……, maka kembali ke subject
MC.
Contoh : DS = Ulya said,”My honey likes my bike”.
IS = Ulya said that her honey liked her bike.
2. Jika terdapat pronoun you, your, yours……, maka kembali ke object
MC (jika MC tidak mempunyai object,maka object nya adalah me).
Contoh : DS = Harianto said to Bibah,”I love You”.
IS = Harianto said to Bibah that He loved Her.
DS = Irfan has told,”Nisa will kill you”.
IS = Irfan has told that Nisa would kill me.
3. Jika terdapat pronoun we,us,our,ours….., maka :
Tetap “we” jika speaker termasuk dalam “we”.
Menjadi “they” jika speaker tidak termasuk dalam “we” .
Contoh : DS = Desi and Oesman said,”we will marry”.
IS = Desi and Oesman said that they would marry.
DS = Hasbi and I said,”we study English”.
IS = Hasbi and I said that we studied English.
c) Perubahan Adverb
Syarat = sama dengan perubahan tenses.
Adverb (DS) Adverb (IS)
Now Then
Yesterday The day before / the previous day
Tomorrow The day after / the following day
Next week The week after
Last week The week before
2 days ago 2 days before
2 days latter 2 days after
Today That day
Contoh :
DS : Dani said to Desi,”I am waiting for you now”.
IS : Dani said to Desi that he were waiting for her then.
DS : Khodijah asked,” I met jay in the jungle last week”.
IS : Khodijah asked that she had met jay in the jungle.
2. Imperative (perindan dan larangan)
Untuk merubah kalimat direct ke indirect pada kalimat perintah / larangan
harus di tambahkan kata “to” sebelum kalimat yang dilaporkan.
Kinds :
Positive (+) Pola V1 + !
Negative (-) Pola Don’t + V1 + !
Aturan perubahan
Tenses = menggunakan kata kerja bentuk pertama (verb dasar / V1)
Pronoun dan Adverb sama dengan statement
Bentuk : DS = Imperative (!)
IS = Statement (.)
IV : DS = Say
IS = Dirubah dengan verb yang bermakna perintah
Ask = Meminta
Beg = Memohon
Advice = Meminta
Order = Meminta
Command = Menyuruh
Request = Meminta
Implore = Memohon
Forbide = Melarang
Tell = Meminta
Pola :
a. Positive
DS : S + V +,”V1 + !”
IS : S + V + to + V1 + .
Contoh :
DS : Jay said to Bibah,”open it”.
IS : Jay asked Bibah to open it.
b. Negative
DS : S + V +,”Don’t + V1 + !”
IS : S + V + Not + to + V1 + .
S + Forbide + to + V1 + .
Contoh :
DS : Nisa said to jay,”don’t love me !”
IS : Nisa asked jay not to love her.
Nisa forbide jay to love her.
3. Question (pertanyaan)
Untuk mengubah kalimat dari direct ke indirect pada kata Tanya, question
words seperti what, who, when, why, and soon dijadikan kata penghubung
antara main clause and sub clause.
Conjunction :
1. Yes / No Question
If ………….= Apakah
Whether……or not = Apakah….atau tidak.
2. Information Question
QW (8W + 1H)
Aturan perubahan :
Tenses,pronoun,adverb = statement
Bentuk : DS = Question (?)
IS = Statement (.)
IV : DS = Asked
IS = Asked
Contoh :
1. DS = Usman asked Desi, “where do you live?”
IS = Usman asked Desi where she lived.
Você também pode gostar
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento3 páginasDirect and Indirect SpeechRais RifatAinda não há avaliações
- Toefl Preparation Paper Assignments "Direct-Indirect Speech"Documento6 páginasToefl Preparation Paper Assignments "Direct-Indirect Speech"Siti Ramlah SiregarAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Indirect Speech (KK)Documento5 páginasDirect and Indirect Speech (KK)muhammadrazikhanAinda não há avaliações
- Rules For Reported SpeechDocumento7 páginasRules For Reported SpeechPannaAinda não há avaliações
- Rules For Reported Speech 1Documento10 páginasRules For Reported Speech 1Panna100% (1)
- Direct VS Indirect SpeechDocumento4 páginasDirect VS Indirect SpeechKetua EE 2021 AndrianoAinda não há avaliações
- Direct & Indirect (Reported) SpeechDocumento15 páginasDirect & Indirect (Reported) SpeechdikiAinda não há avaliações
- Indirect SpeechDocumento29 páginasIndirect SpeechGabriel Antonio Macavilca AlmanzaAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech in English GrammarDocumento11 páginasDirect Speech Into Indirect Speech in English GrammarGunnie Pandher100% (1)
- Assignment Group 7Documento15 páginasAssignment Group 7Yuli LarosaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 10 Reported SpeechDocumento8 páginasLesson 10 Reported SpeechKurumi TokisakiAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Indirect Speech: Naufal Arvien Nieza Zahra Nisrina SriwahyuniDocumento17 páginasDirect and Indirect Speech: Naufal Arvien Nieza Zahra Nisrina SriwahyuniCherilyn MabananAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Speech RulesDocumento5 páginasDirect Speech Rulesusman ghaniAinda não há avaliações
- Câu gián tiếp (ôn tập) + BT Trắc nghiệmDocumento11 páginasCâu gián tiếp (ôn tập) + BT Trắc nghiệmCẩm Chi LêAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Reported Speech: Understanding the DifferenceDocumento23 páginasDirect and Reported Speech: Understanding the DifferenceTeacher Dee TV100% (1)
- Reported SpeechDocumento9 páginasReported Speech꧁༒•Ѵιཌཇའ•MAx•༒꧂Ainda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech ReviewDocumento2 páginasReported Speech ReviewMinh AnhAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech GrammarDocumento5 páginasReported Speech GrammarJara Funez FernándezAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Dan Indirect SpeechDocumento5 páginasDirect Dan Indirect SpeechFerdianugrahaAinda não há avaliações
- S2 Grammar 10 - Direct Speech and Indirect Speech PDFDocumento26 páginasS2 Grammar 10 - Direct Speech and Indirect Speech PDFguanqi tanAinda não há avaliações
- RandomDocumento8 páginasRandomEsha GrouptraderAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Indirect Speech in EnglishDocumento6 páginasDirect and Indirect Speech in EnglishjhieeztAinda não há avaliações
- Direct Speech and Reported SpeechDocumento22 páginasDirect Speech and Reported SpeechGee RomanoAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento34 páginasDirect and Indirect SpeechJimin MochiAinda não há avaliações
- Ly Thuyet Anh k12-17.4Documento4 páginasLy Thuyet Anh k12-17.4baongantran2122002Ainda não há avaliações
- Rule For Changing Direct Speech Into Indirect SpeechDocumento6 páginasRule For Changing Direct Speech Into Indirect SpeechVanita AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- Indirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceDocumento22 páginasIndirect Speech, Relative Clause, Passive VoiceFebby DwiAinda não há avaliações
- Past Perfect and Past Perfect Progressive TenseDocumento9 páginasPast Perfect and Past Perfect Progressive TenseSailurrahmahAinda não há avaliações
- G5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 2Documento6 páginasG5+8 - Ms. Amara - Reported Speech 2Hadjab LyesAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech ExplainedDocumento6 páginasReported Speech ExplainedHyakuya YuuichiroAinda não há avaliações
- Direct SpeechDocumento9 páginasDirect SpeechCami Inthesky WithDiamondsAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Grammar TopicsDocumento8 páginasEssential Grammar TopicsDepiiAinda não há avaliações
- Nesti Puji Astuti - 5117011 - Perbaikan NilaiDocumento24 páginasNesti Puji Astuti - 5117011 - Perbaikan NilaiNesti PujiaAinda não há avaliações
- Reported SpeechDocumento2 páginasReported SpeechNurwahidah HasanuddinAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento12 páginasDirect and Indirect Speechkanbouch100% (1)
- Meeting 8 1ma14 (3-4) (FS)Documento29 páginasMeeting 8 1ma14 (3-4) (FS)Aufar yodha kazhimiAinda não há avaliações
- Reported SpeechDocumento14 páginasReported Speechnotmiri01Ainda não há avaliações
- Câu CH Đ NG) : Teachero English Center 0936.821.022 Unit 3: Teen Stress and Pressure Practice Exercise 1 & 2Documento6 páginasCâu CH Đ NG) : Teachero English Center 0936.821.022 Unit 3: Teen Stress and Pressure Practice Exercise 1 & 2Harley NguyenAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech/Direct and Indirect Speech in Present: By: USDocumento20 páginasReported Speech/Direct and Indirect Speech in Present: By: USAzka KamilahAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech - Statement, Command, RequestDocumento8 páginasReported Speech - Statement, Command, Requestmujmmilp904100% (1)
- Unit 8: Reported SpeechDocumento8 páginasUnit 8: Reported Speechlylyngoc90Ainda não há avaliações
- Simple Past Tense & ContinuousDocumento17 páginasSimple Past Tense & ContinuousshellagherinaAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech / Indirect Speech / El Estilo Indirecto: Tell & SayDocumento6 páginasReported Speech / Indirect Speech / El Estilo Indirecto: Tell & SayradgullAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech - TeorieDocumento4 páginasReported Speech - TeorieMargineanu SimonaAinda não há avaliações
- Professionla CommunicationDocumento28 páginasProfessionla CommunicationaishwaryasamantaAinda não há avaliações
- Tugas Mandiri Bhs - InggrisDocumento31 páginasTugas Mandiri Bhs - InggrisMaria DeboraAinda não há avaliações
- Các Loại Câu Thường Gặp Trong Lớp 8Documento15 páginasCác Loại Câu Thường Gặp Trong Lớp 8Cao Thị Phương ThủyAinda não há avaliações
- Reported SpeechDocumento13 páginasReported SpeechNam Du NguyễnAinda não há avaliações
- Report direct and indirect speech rulesDocumento31 páginasReport direct and indirect speech rulesDiana GonzalesAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento22 páginasDirect and Indirect SpeechObaid KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Bhs InggrisDocumento16 páginasBhs InggrisMuhammad WardiAinda não há avaliações
- The Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasThe Passive VoicesaaAinda não há avaliações
- Usage of English Tenses Grammar GuideDocumento8 páginasUsage of English Tenses Grammar Guidecmpatel.chemAinda não há avaliações
- Reported Speech 2º BachilleratoDocumento4 páginasReported Speech 2º BachilleratoBlancaAinda não há avaliações
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocumento5 páginasDirect and Indirect Speechalangudi100% (1)
- Direct and Reported Speech-1Documento13 páginasDirect and Reported Speech-1itumelengskosana01Ainda não há avaliações
- How to Use the Word “Have” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Have”No EverandHow to Use the Word “Have” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Have”Ainda não há avaliações
- How to Use the Word “Go” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Go”No EverandHow to Use the Word “Go” In English: A Comprehensive Guide to the Word “Go”Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Coach ListDocumento295 páginasCoach ListMustafa Şahin AYDINAinda não há avaliações
- Qutbuddin Bakhtiar Kaki - SufiWikiDocumento18 páginasQutbuddin Bakhtiar Kaki - SufiWikimaher0zainAinda não há avaliações
- Ellet Joseph WaggonerDocumento134 páginasEllet Joseph WaggonersifundochibiAinda não há avaliações
- Forecast ReadingDocumento6 páginasForecast ReadingQuang Minh TrầnAinda não há avaliações
- Desirable African American History For Website 7-31-2012Documento27 páginasDesirable African American History For Website 7-31-2012api-163940557Ainda não há avaliações
- Francesca Nestande Resume 2013Documento1 páginaFrancesca Nestande Resume 2013Francesca NestandeAinda não há avaliações
- Control Activities 5Documento4 páginasControl Activities 5Trisha Mae BahandeAinda não há avaliações
- How To Do Business: Investors' Guide PolandDocumento150 páginasHow To Do Business: Investors' Guide PolandFrankAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Language Practice KEY Final TestDocumento3 páginasAdvanced Language Practice KEY Final TestPetro Nela50% (2)
- Municipal Burial Assistance Program UpheldDocumento10 páginasMunicipal Burial Assistance Program UpheldMichael DizonAinda não há avaliações
- As 1770-2003 Steel - Hardenability Test by End Quench (Jominy Test)Documento8 páginasAs 1770-2003 Steel - Hardenability Test by End Quench (Jominy Test)SAI Global - APACAinda não há avaliações
- Arguments over caring and authenticity erupt at gatheringDocumento4 páginasArguments over caring and authenticity erupt at gatheringAngieAinda não há avaliações
- Delhi Kashmere Gate ISBT FactfileDocumento5 páginasDelhi Kashmere Gate ISBT Factfilesuryakeshwar singhAinda não há avaliações
- Peugeot Landtrek Pen Malaysia Price List 200323Documento2 páginasPeugeot Landtrek Pen Malaysia Price List 200323Azly M SabinAinda não há avaliações
- Panos London 01 Who Rules The InternetDocumento6 páginasPanos London 01 Who Rules The InternetMurali ShanmugavelanAinda não há avaliações
- Operator's Manual M224 D00011Documento206 páginasOperator's Manual M224 D00011czud50% (2)
- LaporanDocumento55 páginasLaporanArisHadiansyahAinda não há avaliações
- Their Education and OursDocumento20 páginasTheir Education and OursDeborah HermannsAinda não há avaliações
- 2020-07-01consumer Reports - July 2020 (USA)Documento81 páginas2020-07-01consumer Reports - July 2020 (USA)enock-readersAinda não há avaliações
- Testamentary Petition For Succession Certificate ProjectDocumento30 páginasTestamentary Petition For Succession Certificate ProjectVikramaditya MuralidharanAinda não há avaliações
- Academic Writing 1 A2-1 Academic Writing 1 A2-1: An Informal EmailDocumento29 páginasAcademic Writing 1 A2-1 Academic Writing 1 A2-1: An Informal EmailTamar OkroshidzeAinda não há avaliações
- English Cala 1 Home WorkDocumento5 páginasEnglish Cala 1 Home Workkuzivakwashe sakupwanyaAinda não há avaliações
- Cis - ORITECH TECHNOLOGY JOINT STOCK COMPANY PDFDocumento4 páginasCis - ORITECH TECHNOLOGY JOINT STOCK COMPANY PDFRian Hidayat0% (1)
- Hangcha Forklift ServiceDocumento1 páginaHangcha Forklift Servicesilenkodmitrij33Ainda não há avaliações
- List of Countries and Dependencies by AreaDocumento16 páginasList of Countries and Dependencies by Arearpraj3135Ainda não há avaliações
- TitleDocumento79 páginasTitleDedi MeidiantoAinda não há avaliações
- ORF SpecialReport 150 NER-BIMSTECDocumento22 páginasORF SpecialReport 150 NER-BIMSTECTanmay PremanAinda não há avaliações
- Architect Consultant AgreementDocumento7 páginasArchitect Consultant AgreementCzabrina Chanel AlmarezAinda não há avaliações
- ILO JudgementsDocumento28 páginasILO JudgementsArshima RAinda não há avaliações
- Virtues of a Long Life, Reaching Times of Goodness and Righteous DeedsDocumento2 páginasVirtues of a Long Life, Reaching Times of Goodness and Righteous DeedsDede RahmatAinda não há avaliações