Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Uses and Applications of Centrifugation, Radiation and Sedimentation
Enviado por
Vanjared OcampoDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Uses and Applications of Centrifugation, Radiation and Sedimentation
Enviado por
Vanjared OcampoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
MARTIJA, NELYKAH RIANNE P. Engr. Efren B.
Chavez
CH42FB2 May 6, 2019
CENTRIFUGATION, SEDIMENTATION AND RADIATION
USES AND APPLICATIONS
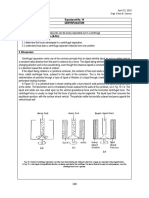
CENTRIFUGATION
Centrifugation is a process which involves the At the same time, objects that are less dense are
application of the centripetal force for the sedimentation of displaced and move to the center. In a laboratory
heterogeneous mixtures with a centrifuge, and is used in centrifuge that uses sample tubes, the radial acceleration
industrial and laboratory settings. The medical uses include causes denser particles to settle to the bottom of the tube,
the separation of blood cells from blood (plasma), and the while low- density substances rise to the top.
removal of fibrinogen (serum). They were also used to
Applications of Centrifugation
determine the hematocrit and to separate urinary
components. The following are an example of materials or
components that can be separated using centrifugation:
To separate two miscible substances
To analyze the hydrodynamic properties of
macromolecules
Purification of mammalian cells
Fractionation of sub-cellular organelles (including
A centrifuge uses small samples of liquid in the membranes / membrane fractions) Fractionation
form of tube samples to process. The particles are of membrane vesicles
separated from a solution according to their size, shape, Separating chalk powder from water
density, viscosity of the medium and rotor speed. It is
capable of separating blood samples into upper plasma Removing fat from milk to produce skimmed milk
layer, a thin interface layer consisting of white blood cells
Separating particles from an air-flow using
and platelets as well as a lower layer consisting of red blood
cyclonic separation
cells.
The clarification and stabilization of wine
It is the process where a mixture is separated
through spinning. Although centrifugation is primarily used Separation of urine components and blood
to separate mixtures, it is also used to test the effects of components in forensic and research laboratories
gravity on people and objects. Centrifugation uses a
centrifuge, or a device that can rapidly spin, to speed up Aids in separation of proteins using purification
this process. techniques such as salting out, e.g. ammonium
sulfate precipitation
The greater the difference in density, the faster
they move. If there is no difference in density (isopycnic Some of the application of centrifugation in the field of
conditions), the particles stay steady. To take advantage of medicine are blood sample separation and DNA or RNA
even tiny differences in density to separate various particles separation. This is a two-step process which involves
in a solution, gravity can be replaced with the much more spinning the sample at top speed for a short while and later
powerful “centrifugal force” provided by a centrifuge. The carrying out the second step in the laboratory using
centrifuge works using the sedimentation principle, where chemicals.
the centripetal acceleration causes denser substances and
particles to move outward in the radial direction.
PROJECT IN UNIT OPERATIONS LABORATORY 1 PRELIM – SUMMER 2019
MARTIJA, NELYKAH RIANNE P. Engr. Efren B. Chavez
CH42FB2 May 6, 2019
SEDIMENTATION Different factors control the sedimentation rate in
each.
Sedimentation is the process of allowing particles
in suspension in water to settle out of the suspension under
the effect of gravity. The particles that settle out from the
suspension become sediment, and in water treatment is
known as sludge. When a thick layer of sediment continues
to settle, this is known as consolidation. When
One of the applications is Potable water
consolidation of sediment, or sludge, is assisted by
treatment. Sedimentation in potable water treatment
mechanical means then this is known as thickening.
generally follows a step of chemical coagulation and
flocculation, which allows grouping particles together into
In water treatment, sedimentation might be used flocs of a bigger size. This increases the settling speed of
to reduce the concentration of particles in suspension suspended solids and allows settling colloids.
before the application of coagulation, to reduce the
amount of coagulating chemicals needed, or after
RADIATION
coagulation and, possibly, flocculation. When
sedimentation is applied after coagulation, its purpose is
Many uses of radiation help to ensure the high
usually to reduce the concentration of solids in suspension
quality and safety of our daily lives. Smoke detectors to
so that the subsequent filtration can function most
warn us of fire, x-ray machines to detect weapons or other
effectively.
devices in luggage and cargo, and certain types of imaging
to look for diseases are all application of radiation for the
Sedimentation is one of several methods for benefit of society.
application prior to filtration: other options include
dissolved air flotation and some methods of filtration. Naturally occurring radiation can be found all
Generically, such solids-liquid separation processes are around us. Radiation can be found in soils, in our air and
sometimes referred to as clarification processes. water, and in us. Because it occurs in our natural
environment, we encounter it every day through the food
There is a variety of methods for applying we eat, the water we drink, and the air we breathe. It is also
sedimentation and include: horizontal flow, radial flow, in building materials and items we commonly use.
inclined plate, ballasted floc and floc blanket
sedimentation. There are three groupings of naturally occurring
radiation, mostly based on where the radiation comes
from. First there is the radiation in the soils and rocks, called
Settling basins and clarifiers are designed to retain
primordial or terrestrial. Then there is radiation that comes
water so that suspended solids can settle. By sedimentation
from space, called cosmic or cosmogenic. The third is
principles, the suitable treatment technologies should be
human-made, something created by humans that wouldn’t
chosen depending on the specific gravity, size and shear
exist otherwise or something that contains more radiation
resistance of particles. Depending on the size and density
in it than normal (enhanced) because humans have done
of particles, and physical properties of the solids, there are
something to it.
four types of sedimentation processes:
The following are the application of radiation on
Type 1 – Dilutes, non-flocculent, free-settling
various fields:
(every particle settles independently.)
Type 2 – Dilute, flocculent (particles can flocculate
Medical Uses
as they settle).
Security Devices
Type 3 – Concentrated suspensions, zone settling,
hindered settling (sludge thickening). Household Products
Type 4 – Concentrated suspensions, compression Food Irradiation
Industrial Uses
(sludge thickening).
PROJECT IN UNIT OPERATIONS LABORATORY 1 PRELIM – SUMMER 2019
MARTIJA, NELYKAH RIANNE P. Engr. Efren B. Chavez
CH42FB2 May 6, 2019
There are many uses of radiation in medicine. The
most well-known is using x rays to see whether bones are
broken. The broad area of x-ray use is called radiology.
Within radiology, we find more specialized areas like
mammography, computerized tomography (CT), and
nuclear medicine (the specialty where radioactive material
is usually injected into the patient). Another area of x-ray
use is called cardiology—where special x-ray pictures are
taken of the heart.
Some products you own and use regularly might
contain radioactivity or emit radiation. They are an example
of the many ways radiation use benefits our modern
society. When they are used according to their instructions
for use, you are not exposed to radiation.
Products in your home that contain radioactivity,
but are not hazardous to anyone’s health, include smoke
detectors, some foods, and fertilizers.
Smoke detectors sometimes contain a small
amount of a radioactive source (americium-241) within a
metal chamber. In a smoke detector, the radioactivity in the
source emits a constant stream of alpha particles that are
sensed by a small radiation detector, causing a small
current. If smoke comes between the source and the
detector, the current is decreased, leaving nothing for the
detector to sense, and the alarm goes off.
Some foods become radioactive by absorbing
naturally occurring radionuclides from surrounding soils as
they grow or some of the ingredients used to make them
may be naturally radioactive. Fertilizers that you use for
your gardens, lawns, etc., might contain radioactive
potassium or uranium in small amounts.
It is important not to assume that all types of a
certain item contain radioactivity or emit radiation; for
example, some smoke detectors and old watches contain
radioactivity, but not all do. And these radioactivity-
containing items don’t pose a radiation hazard to you
unless you were to eat them—and eat a lot of them.
PROJECT IN UNIT OPERATIONS LABORATORY 1 PRELIM – SUMMER 2019
Você também pode gostar
- Presented By: Seemab Javed Zunaira IrfanDocumento31 páginasPresented By: Seemab Javed Zunaira IrfanZaid YahyaAinda não há avaliações
- Bio Analytical TechniquesDocumento26 páginasBio Analytical TechniquesanimalfacilityAinda não há avaliações
- Oup 7 - EditedDocumento33 páginasOup 7 - EditedSophie TranAinda não há avaliações
- Biochemistry Notes DAB 3-TERM 3, 2021 (MARCH) Lesson Three Basic Biochemical Techniques Separation Technqiues (A) Cell FractionationDocumento6 páginasBiochemistry Notes DAB 3-TERM 3, 2021 (MARCH) Lesson Three Basic Biochemical Techniques Separation Technqiues (A) Cell Fractionationjohn mwangiAinda não há avaliações
- Separation Technique - Pharm Eng IDocumento43 páginasSeparation Technique - Pharm Eng Ihakita86Ainda não há avaliações
- Applications: Filtration Is Commonly The Mechanical or Physical Operation Which Is Used For The Separation ofDocumento9 páginasApplications: Filtration Is Commonly The Mechanical or Physical Operation Which Is Used For The Separation ofBrandon KingAinda não há avaliações
- GROUP 3 - Physical and Chemical Water Treatments, Disinfection PDFDocumento22 páginasGROUP 3 - Physical and Chemical Water Treatments, Disinfection PDFDonna Claire AngusAinda não há avaliações
- Ultracentrifugation: June 2010Documento8 páginasUltracentrifugation: June 2010Nayak Alok RanjanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3: Cell Fractionation - Introduction: HomogenizationDocumento6 páginasChapter 3: Cell Fractionation - Introduction: HomogenizationSarwan HamidAinda não há avaliações
- Pengantar Metode PemisahanDocumento43 páginasPengantar Metode PemisahanMili APRILIAAinda não há avaliações
- Types of CentrifugationDocumento2 páginasTypes of Centrifugationvijay kumar honnaliAinda não há avaliações
- 2018 BET CHEM 01water Analysis ExperimentsDocumento45 páginas2018 BET CHEM 01water Analysis ExperimentsDanish AliAinda não há avaliações
- CentrifugationDocumento8 páginasCentrifugation1ds20ch022Ainda não há avaliações
- Using Centrifugation To Isolate Organelles: Key TechniqueDocumento2 páginasUsing Centrifugation To Isolate Organelles: Key TechniqueLenard MerlinAinda não há avaliações
- Mass AssignmentDocumento7 páginasMass AssignmentHasieb Alam KhanAinda não há avaliações
- " Seperation Process": Seminar OnDocumento28 páginas" Seperation Process": Seminar OnKabilanAinda não há avaliações
- CentrifugationDocumento43 páginasCentrifugationSudeeksha RavikotiAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugation 4Documento44 páginasCentrifugation 4zafiharoAinda não há avaliações
- Diffun Campus: Laboratory HighschoolDocumento6 páginasDiffun Campus: Laboratory HighschoolhaydeeAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugation TechniquesDocumento4 páginasCentrifugation Techniquesajisebutumariam25Ainda não há avaliações
- Assignment Title: Considering An Industrial Process, Explain The Physio-Chemical Properties Exploited in Unit OperationsDocumento1 páginaAssignment Title: Considering An Industrial Process, Explain The Physio-Chemical Properties Exploited in Unit OperationsManasa UpadhyayaAinda não há avaliações
- Differential CentrifugationDocumento3 páginasDifferential CentrifugationMansi SingalAinda não há avaliações
- Unit - Ii CentrifugationDocumento6 páginasUnit - Ii CentrifugationUdayaraj NagarajanAinda não há avaliações
- Particle Concentration and Mixing in Microdrops Driven by Focused Surface Acoustic WavesDocumento10 páginasParticle Concentration and Mixing in Microdrops Driven by Focused Surface Acoustic Waveshani safariAinda não há avaliações
- Nanoparticles: 3.1 Nanoparticle SynthesisDocumento4 páginasNanoparticles: 3.1 Nanoparticle SynthesisRakib ChowdhuryAinda não há avaliações
- Group 2 - Experiment No. 2 - SedimentationDocumento17 páginasGroup 2 - Experiment No. 2 - SedimentationRobelyn CastilloAinda não há avaliações
- 7.06 Classifying Separation TechniquesDocumento12 páginas7.06 Classifying Separation TechniquesTewodirosAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment 1A The CellDocumento3 páginasExperiment 1A The CellLeah SunioAinda não há avaliações
- Durgapur Institute of Advanced Technology and ManagementDocumento7 páginasDurgapur Institute of Advanced Technology and ManagementChemical Engg Evensem2021Ainda não há avaliações
- Centrifugation TechniquesDocumento4 páginasCentrifugation TechniquesselviAinda não há avaliações
- Diafiltration A Fast Efficient Method For Desalting or Buffer Exchange of Biological Samples PDFDocumento6 páginasDiafiltration A Fast Efficient Method For Desalting or Buffer Exchange of Biological Samples PDFDario Jose Rincon GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- LECTURE NOTES Centrifugation 20-21 PDFDocumento10 páginasLECTURE NOTES Centrifugation 20-21 PDFtchy xclAinda não há avaliações
- 160 16SCCBT8 2020052605345882Documento25 páginas160 16SCCBT8 2020052605345882jeevalakshmanan29Ainda não há avaliações
- Primary SeparationDocumento34 páginasPrimary SeparationPia CabatinganAinda não há avaliações
- Cell PhysiologyDocumento12 páginasCell PhysiologyJaseme OtoyoAinda não há avaliações
- Fractionation of Cells Via Differential CentrifugationDocumento5 páginasFractionation of Cells Via Differential CentrifugationEthanAinda não há avaliações
- FiltrationDocumento75 páginasFiltrationSunjida Ali RiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Application CentrifugeDocumento18 páginasApplication CentrifugealyssaAinda não há avaliações
- MINI PROJECT ON Sutapa Mam UrgentDocumento18 páginasMINI PROJECT ON Sutapa Mam UrgentKunal DasAinda não há avaliações
- Presented To: Dr. Islam Ullah Khan Presented By: Khadeeja Ikram Roll No: 0164-BH-CHEM-11Documento45 páginasPresented To: Dr. Islam Ullah Khan Presented By: Khadeeja Ikram Roll No: 0164-BH-CHEM-11Abiyot NeguAinda não há avaliações
- BCH 415-Lecture Note 2023Documento23 páginasBCH 415-Lecture Note 2023Saheed DanielAinda não há avaliações
- CentrifugationDocumento37 páginasCentrifugationanurag srivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- A. Outline The Principles of The Following: ClassificationDocumento6 páginasA. Outline The Principles of The Following: Classificationliny GAinda não há avaliações
- Centrifugation 151029170742 Lva1 App6892Documento45 páginasCentrifugation 151029170742 Lva1 App6892arlene100% (1)
- Filter Applications For Organic RemovalDocumento10 páginasFilter Applications For Organic RemovalMWJornitzAinda não há avaliações
- ENVIRONMENTAL ENGG - Midterm ReviewerDocumento5 páginasENVIRONMENTAL ENGG - Midterm ReviewerAvestruz ReginoAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report 8Documento6 páginasLab Report 8Maureen DireroAinda não há avaliações
- Filtration: Sarvajanik College of Engineering & Technology SuratDocumento20 páginasFiltration: Sarvajanik College of Engineering & Technology SuratNautam ParasanaAinda não há avaliações
- Ultracentrifugation UltracentrifugationDocumento31 páginasUltracentrifugation Ultracentrifugation123Ainda não há avaliações
- The Basics of Centrifuge Operation and MaintenanceDocumento3 páginasThe Basics of Centrifuge Operation and MaintenanceMohamed AlhamdaniAinda não há avaliações
- Separation ProcessDocumento7 páginasSeparation ProcessLina alikhAinda não há avaliações
- Ws-Commercial-Watersense-At-Work Section 7.2 Water PurificationDocumento6 páginasWs-Commercial-Watersense-At-Work Section 7.2 Water PurificationPartha SheeAinda não há avaliações
- Ultracentrifugation AssignmentDocumento3 páginasUltracentrifugation AssignmentStuti SrivastavAinda não há avaliações
- Durgapur Institute of Advanced Technology and ManagementDocumento8 páginasDurgapur Institute of Advanced Technology and ManagementChemical Engg Evensem2021Ainda não há avaliações
- Dialysis QFRDocumento2 páginasDialysis QFRsyareeisyeeAinda não há avaliações
- Fractionation of Granulocytes From Whole Human Blood by Centrifugation. Practical HintsDocumento6 páginasFractionation of Granulocytes From Whole Human Blood by Centrifugation. Practical HintsVikash JaiswalAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Sirshendu de Professor, Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur E-MailDocumento6 páginasDr. Sirshendu de Professor, Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur E-MailPyari MohanAinda não há avaliações
- Membranes: The Key Properties Determining Membrane Performance AreDocumento14 páginasMembranes: The Key Properties Determining Membrane Performance ArePRAJWAL RASTOGIAinda não há avaliações
- Reverse Osmosis Treatment of Drinking WaterNo EverandReverse Osmosis Treatment of Drinking WaterNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (4)
- Marine Impacts of Seawater Desalination: Science, Management, and PolicyNo EverandMarine Impacts of Seawater Desalination: Science, Management, and PolicyAinda não há avaliações
- Experiment No. 10 Centrifugation 1. Objective: 2. Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilos)Documento3 páginasExperiment No. 10 Centrifugation 1. Objective: 2. Intended Learning Outcomes (Ilos)Vanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- CHE408-Lecture 1 PDFDocumento24 páginasCHE408-Lecture 1 PDFVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Product Description (KNO3)Documento2 páginasProduct Description (KNO3)Vanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Congratulations!: Che DSC A.Y. 2017 - 2018Documento10 páginasCongratulations!: Che DSC A.Y. 2017 - 2018Vanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- CHE408-Lecture 1 PDFDocumento24 páginasCHE408-Lecture 1 PDFVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Partech Midterms PDFDocumento1 páginaPartech Midterms PDFVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocumento1 páginaTechnological Institute of The Philippines Chemical Engineering DepartmentVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Seminar 3 Speaker Certificate TugadeDocumento1 páginaSeminar 3 Speaker Certificate TugadeVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Where E Is Enzyme, S Is Substrate, and P Is ProductDocumento1 páginaWhere E Is Enzyme, S Is Substrate, and P Is ProductVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Sensitivity Analysis: Production of Ammonium Nitrate From Ammonia and Nitric AcidDocumento27 páginasSensitivity Analysis: Production of Ammonium Nitrate From Ammonia and Nitric AcidVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Future": Kristian Carlo B. Victorio, REE, RMEDocumento1 páginaFuture": Kristian Carlo B. Victorio, REE, RMEVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Width MM F'C Mpa Height MM Fy Mpa Cover MM e MM No. of Bars Pcs. Pu Actual KN Bar Dia. MM Mu Actual KN-MDocumento1 páginaWidth MM F'C Mpa Height MM Fy Mpa Cover MM e MM No. of Bars Pcs. Pu Actual KN Bar Dia. MM Mu Actual KN-MVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment No. 1Documento2 páginasAssignment No. 1Vanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3-4Documento129 páginasChapter 3-4Vanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Mr. Yong Bong Kim: Plant Manager, Kepco-Kps Calaca, BatangasDocumento2 páginasMr. Yong Bong Kim: Plant Manager, Kepco-Kps Calaca, BatangasVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 3Documento84 páginasChapter 3Vanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Beam Group 13 - EusebioDocumento9 páginasBeam Group 13 - EusebioVanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Storage of Hot Ammonium Nitrate Solutions (BPE)Documento48 páginasStorage of Hot Ammonium Nitrate Solutions (BPE)Vanjared OcampoAinda não há avaliações
- Allergic Rhinitis & Vasomotor Rhinitis: Dr. Ritesh Mahajan ENT Consultant GMC, KathuaDocumento70 páginasAllergic Rhinitis & Vasomotor Rhinitis: Dr. Ritesh Mahajan ENT Consultant GMC, Kathuamanoj kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Home PDFDocumento38 páginasHome PDFJeimy MaciasAinda não há avaliações
- Excercise 2 Activity 7 DoniDocumento6 páginasExcercise 2 Activity 7 DoniDoni SaragihAinda não há avaliações
- Sexual Vs Asexual Reproduction and Plant Reproduction: IGCSE Biology (O610) Workbook Chapter 16 - Part ADocumento8 páginasSexual Vs Asexual Reproduction and Plant Reproduction: IGCSE Biology (O610) Workbook Chapter 16 - Part Awafa elias100% (1)
- Freon ™ MO59 (R-417A) Refrigerant: Safety Data SheetDocumento16 páginasFreon ™ MO59 (R-417A) Refrigerant: Safety Data SheetaAinda não há avaliações
- NutriophysiologyDocumento26 páginasNutriophysiologyAmal ShajuAinda não há avaliações
- COMKAT Compartment Model Kinetic Analysis ToolDocumento10 páginasCOMKAT Compartment Model Kinetic Analysis ToolIvoPetrovAinda não há avaliações
- Cement - Superplasticizer CompatibilityDocumento8 páginasCement - Superplasticizer CompatibilitySumit SrivastavaAinda não há avaliações
- Wet Milling of Corn-A Review of Laboratory-Scale and Pilot Plant Scale StudiesDocumento9 páginasWet Milling of Corn-A Review of Laboratory-Scale and Pilot Plant Scale StudiesMurali Krishna IndanaAinda não há avaliações
- FPP 15 Kulkarni PDFDocumento6 páginasFPP 15 Kulkarni PDFVishnukumarKulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- Finalsnake in HomoeopathygrassDocumento158 páginasFinalsnake in Homoeopathygrassaruen79100% (1)
- InovaDocumento16 páginasInovaMohamed AliAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Complexes Within Sars-Cov-2 Proteome: E7Dc3B2F002E/Fx1.JpgDocumento3 páginasUnderstanding Complexes Within Sars-Cov-2 Proteome: E7Dc3B2F002E/Fx1.JpgSoumyaAinda não há avaliações
- Cultural History After FoucaultDocumento245 páginasCultural History After Foucaultmortrik100% (2)
- 48 - Lecture - Presentation - 0 2Documento56 páginas48 - Lecture - Presentation - 0 2shea studiesAinda não há avaliações
- CSC338 Study Guide 1Documento3 páginasCSC338 Study Guide 1BartAinda não há avaliações
- Online Toefl Test-1Documento25 páginasOnline Toefl Test-1Aditya DwiprasetyoAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Group 3 Chapter 1-5Documento37 páginas02 Group 3 Chapter 1-5maryann ruedaAinda não há avaliações
- Eco Kids Planet Magazine - Issue 111 - January 2024Documento38 páginasEco Kids Planet Magazine - Issue 111 - January 2024Kübra YağmurAinda não há avaliações
- Antibiotik Topikal: MACP 2113Documento44 páginasAntibiotik Topikal: MACP 2113Wesley AcrafAinda não há avaliações
- Radiation Safety Manual (Duke Univ Laboratory, 2001)Documento54 páginasRadiation Safety Manual (Duke Univ Laboratory, 2001)AndréRochaAinda não há avaliações
- WEEK 16 LABORATORY EXERCISE Special SensesDocumento7 páginasWEEK 16 LABORATORY EXERCISE Special SensesGelo AlonzoAinda não há avaliações
- Fumaria OfficinalisDocumento9 páginasFumaria OfficinalisPiks DhAinda não há avaliações
- Chromosomal AbberationsDocumento33 páginasChromosomal AbberationsMubeena MoossaAinda não há avaliações
- Primary Motor Cortex Changes After Amputation Correlate With Phantom Limb Pain and The Ability To Move The Phantom Limb 2016 NeuroImageDocumento11 páginasPrimary Motor Cortex Changes After Amputation Correlate With Phantom Limb Pain and The Ability To Move The Phantom Limb 2016 NeuroImageLuís EduardoAinda não há avaliações
- 21 - 6182 - e (C) - PF1 (M) - F (P) - PF1 (PP) - Pfa (PR)Documento3 páginas21 - 6182 - e (C) - PF1 (M) - F (P) - PF1 (PP) - Pfa (PR)Vinna KusumawatiAinda não há avaliações
- Conflict of Interest List CIRM Directors Quest Awards June 2017Documento2 páginasConflict of Interest List CIRM Directors Quest Awards June 2017California Stem Cell ReportAinda não há avaliações
- Beauty MythDocumento10 páginasBeauty Mythgeraldygay100% (1)
- Pengaturan Sistem RespirasiDocumento18 páginasPengaturan Sistem RespirasiMaulidya MagfirahAinda não há avaliações
- Stratus OCT™ Real Answers in Real Time.: Software Version 4.0Documento12 páginasStratus OCT™ Real Answers in Real Time.: Software Version 4.0Mirella Carazas MontoyaAinda não há avaliações