Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Adverbs of Manner Exercises (Revised Winter 2016) (Opens PDF, 36kb)
Enviado por
santi_tena_10 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
41 visualizações2 páginasThis document summarizes the use of modal verbs - can, could, and be able to - to express ability in English. It explains:
1) Can is used to express ability in the present tense, could is used for ability in the past tense, and be able to expresses ability in all tenses.
2) The structures for each modal verb - can/can't, could/couldn't, and be able to - along with example questions.
3) Example sentences demonstrating how each modal verb is used to show ability in the present, past, and across all tenses.
Descrição original:
Exercises Adverbs of Manner
Título original
Adverbs of Manner Exercises (Revised Winter 2016)(Opens PDF, 36kb)
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document summarizes the use of modal verbs - can, could, and be able to - to express ability in English. It explains:
1) Can is used to express ability in the present tense, could is used for ability in the past tense, and be able to expresses ability in all tenses.
2) The structures for each modal verb - can/can't, could/couldn't, and be able to - along with example questions.
3) Example sentences demonstrating how each modal verb is used to show ability in the present, past, and across all tenses.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
41 visualizações2 páginasAdverbs of Manner Exercises (Revised Winter 2016) (Opens PDF, 36kb)
Enviado por
santi_tena_1This document summarizes the use of modal verbs - can, could, and be able to - to express ability in English. It explains:
1) Can is used to express ability in the present tense, could is used for ability in the past tense, and be able to expresses ability in all tenses.
2) The structures for each modal verb - can/can't, could/couldn't, and be able to - along with example questions.
3) Example sentences demonstrating how each modal verb is used to show ability in the present, past, and across all tenses.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 2
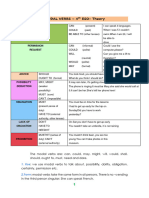
MODAL VERBS ABILITY
CAN COULD BE ABLE TO
STRUCTURE STRUCTURE STRUCTURE
+/- Subj. + can / can’t + base form. +/- Subj. + could / couldn’t + +/- Subj. + + be (in the correct
? QW + Can + subj. + base form? base form. tense) + able to + base form.
? QW + Could + subj. + base form? ? QW + be (in the correct tense)
+ subj. + able to + base form?
USE USE USE
We use can for ABILITY in the We use could for ABILITY in the PAST. We use be able to for ABILITY in ALL
PRESENT. TENSES.
I could swim when I was 5
I was able to drive...
She can drive a car. years old. I will be able to drive...
John can speak Spanish. My grandmother could speak I have been able to drive...
I cannot hear you. (I can't hear seven languages.
I have been able to swim since
you.) When we arrived home,
I was five. (present perfect)
Can you hear me? we could not open the door.
(...couldn't open the door.) You will be able to speak
perfect English very soon.
Could you understand what he
(future simple)
was saying?
I would like to be able to fly an
airplane. (infinitive)
* BE ABLE TO FOR ABILITY *
We use be able to to express ability. "Able" is an adjective meaning: having the power, skill or means to do
something. If we say "I am able to swim", it is like saying "I can swim". We sometimes use be able to instead of
"can" or "could" for ability. Be able to is possible in all tenses - but "CAN" is possible only in the present and
"COULD" is possible only in the past for ability. In addition, we use WAS/WERE ABLE TO when we talk about one
special / specific occasion in the past. Look at these examples:
The pilot was able to land the plane safely. (on that occasion).
I could design a web page when I was still a kid. (general ability at any time in that period).
Você também pode gostar
- Can, Could, Be Able ToDocumento3 páginasCan, Could, Be Able ToMaria Ines RoqueAinda não há avaliações
- Can Could Be Able To Okokoko PDFDocumento7 páginasCan Could Be Able To Okokoko PDFAndy Aguirre CamposAinda não há avaliações
- INGLES - Can, Could, Be Able ToDocumento2 páginasINGLES - Can, Could, Be Able ToDanilo Zarta FAinda não há avaliações
- 7speaking Lms Can - Could - Be Able ToDocumento2 páginas7speaking Lms Can - Could - Be Able ToMarisol Lasso EcheverríaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 - Full Bai Giang-SvDocumento68 páginasUnit 1 - Full Bai Giang-SvThư Nguyễn Ngọc MinhAinda não há avaliações
- Capacidad - Can, Could, Be Able ToDocumento2 páginasCapacidad - Can, Could, Be Able ToBrayanAinda não há avaliações
- Expressing AbilityDocumento7 páginasExpressing AbilityNurhana Tri RizqiAinda não há avaliações
- Modals ÖzetDocumento21 páginasModals ÖzetmehmetAinda não há avaliações
- Ressum of The All LessonsDocumento44 páginasRessum of The All LessonsFray Juan María OPAinda não há avaliações
- Can and Could Are Modal Auxiliary Verbs. Be Able To Is NOT An Auxiliary Verb (ItDocumento9 páginasCan and Could Are Modal Auxiliary Verbs. Be Able To Is NOT An Auxiliary Verb (ItAKbarAinda não há avaliações
- Ability - Session 1 English 4Documento7 páginasAbility - Session 1 English 4Hartiana DewiAinda não há avaliações
- Could I Use Your Computer To Email My Boss? Request: ConditionalDocumento4 páginasCould I Use Your Computer To Email My Boss? Request: ConditionalRené RamosAinda não há avaliações
- Can / Be Able To: Am (Not) Is (Not) Are (Not) Was (Not) Was (Not) Were (Not)Documento2 páginasCan / Be Able To: Am (Not) Is (Not) Are (Not) Was (Not) Was (Not) Were (Not)Sarah BarnardAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs ExerciseDocumento4 páginasModal Verbs ExerciseVân ChiAinda não há avaliações
- Can and CouldDocumento7 páginasCan and Couldarmy19 bangtanAinda não há avaliações
- Can, Could and Be Able To1Documento10 páginasCan, Could and Be Able To1aryam aliAinda não há avaliações
- CAN, COULD, BE ABLE TO - EnglishClub 3Documento6 páginasCAN, COULD, BE ABLE TO - EnglishClub 3aAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs2Documento10 páginasModal Verbs2Anastasia KuzmnkAinda não há avaliações
- Modals ChartDocumento9 páginasModals ChartMarc GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Be Able ToDocumento2 páginasBe Able ToMoises ToledoAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs To Express AbilityDocumento1 páginaModal Verbs To Express AbilityStoica MirelaAinda não há avaliações
- Конспект открытого урока в 5-м классе по теме: "Can you play the guitar?"Documento4 páginasКонспект открытого урока в 5-м классе по теме: "Can you play the guitar?"A'Di Let AdayAinda não há avaliações
- Can Is An Auxiliary Verb, A Modal Auxiliary Verb. We Use Can ToDocumento5 páginasCan Is An Auxiliary Verb, A Modal Auxiliary Verb. We Use Can Tocharfi abdelhamidAinda não há avaliações
- Workbook ENGLISH CLASSDocumento71 páginasWorkbook ENGLISH CLASSNilbia GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- A1. Modal Verbs - Can CouldDocumento9 páginasA1. Modal Verbs - Can CouldAngie DanielaAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar 2.5Documento7 páginasGrammar 2.5Juan Diego Lozano RojasAinda não há avaliações
- English Modal VerbsDocumento37 páginasEnglish Modal VerbsDeniz FerahAinda não há avaliações
- Modal VerbsDocumento3 páginasModal Verbsabimtzbj255Ainda não há avaliações
- Possessive Pronouns: Now! (See You Understood.)Documento10 páginasPossessive Pronouns: Now! (See You Understood.)dianAinda não há avaliações
- English - Modal Auxiliaries or ModalsDocumento23 páginasEnglish - Modal Auxiliaries or ModalsHéctor Reynaldo Acosta EspinalAinda não há avaliações
- English - Modal Auxiliaries or ModalsDocumento23 páginasEnglish - Modal Auxiliaries or ModalsHéctor Reynaldo Acosta EspinalAinda não há avaliações
- ПланDocumento7 páginasПланA'Di Let AdayAinda não há avaliações
- Verbe Modale 2Documento7 páginasVerbe Modale 2Andra SrbAinda não há avaliações
- Básico 3Documento33 páginasBásico 3Francklin Alejandro Cruz PadillaAinda não há avaliações
- Class Unit IDocumento10 páginasClass Unit IHamilton VilemaAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs Can Could May MightDocumento3 páginasModal Verbs Can Could May Mightadriandobre2014Ainda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs: Here's A List of The Modal Verbs in EnglishDocumento12 páginasModal Verbs: Here's A List of The Modal Verbs in Englishshahzeb khanAinda não há avaliações
- Module # 21 - Auxiliary Verb "Can" HabilitiesDocumento5 páginasModule # 21 - Auxiliary Verb "Can" HabilitiesCELISA MORETO DIAZAinda não há avaliações
- Construcţii Cu Verbele Modale Modal Constructions: Modal Verb Substitute Form Meaning ExamplesDocumento7 páginasConstrucţii Cu Verbele Modale Modal Constructions: Modal Verb Substitute Form Meaning Exampleslorecosic6368Ainda não há avaliações
- Summary 7 Topic: (Be) Able To: General ConceptDocumento3 páginasSummary 7 Topic: (Be) Able To: General ConceptJaime G. MendozaAinda não há avaliações
- Ficha 3 - Und 03 - Semana3 - 3er Grado - My Past Abilities!Documento2 páginasFicha 3 - Und 03 - Semana3 - 3er Grado - My Past Abilities!Leonardo Ayrton Alvarez ShuanAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs 1 Ability American English StudentDocumento3 páginasModal Verbs 1 Ability American English Studentaeiteachers4Ainda não há avaliações
- Guide Lesson 06Documento4 páginasGuide Lesson 06Monica Rojas RhrmAinda não há avaliações
- MODAL VERBS Theory 4º ESODocumento3 páginasMODAL VERBS Theory 4º ESOyergaoliverAinda não há avaliações
- Sujeto + Said (That) .-Sujeto + Told + C. Indirecto + (That) .Documento2 páginasSujeto + Said (That) .-Sujeto + Told + C. Indirecto + (That) .bpxamzAinda não há avaliações
- We Use The Modal Verbs Can, Could and Be Able To + Verb Infinitive To Talk About Ability. Here's An Overview, With Examples: PastDocumento3 páginasWe Use The Modal Verbs Can, Could and Be Able To + Verb Infinitive To Talk About Ability. Here's An Overview, With Examples: PastLaura Campos AngelesAinda não há avaliações
- Gestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de AprendizajeDocumento8 páginasGestión de Formación Profesional Integral Procedimiento Desarrollo Curricular Guía de AprendizajeMARIA FERNANDA ORTIZ BELTRANAinda não há avaliações
- Prefixes and Suffixes WorksheetDocumento5 páginasPrefixes and Suffixes WorksheetJerome MetierreAinda não há avaliações
- French and Modal VerbsDocumento2 páginasFrench and Modal VerbsLuis A G. C.Ainda não há avaliações
- Ingles Expo CanDocumento16 páginasIngles Expo Can6B LUIS ALBERTO GARCIA MEJIAAinda não há avaliações
- Functions of Modal Verbs: I Know But If I've Got It, He Play It EitherDocumento9 páginasFunctions of Modal Verbs: I Know But If I've Got It, He Play It EitherАлекс Гриненко100% (1)
- Miraa Active and PassiveDocumento9 páginasMiraa Active and PassiveMira FebrianelAinda não há avaliações
- Prefixes and Suffixes WorksheetDocumento6 páginasPrefixes and Suffixes WorksheetJerome Metierre100% (1)
- Flir: : AbilityDocumento5 páginasFlir: : Abilityhubert djAinda não há avaliações
- Can, Could, Able ToDocumento8 páginasCan, Could, Able ToAna Karem Kashmir DelgadoAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs 1 Ability British English StudentDocumento3 páginasModal Verbs 1 Ability British English StudentІлля ГончаренкоAinda não há avaliações
- Be Able + Infinitive or CAN?: Can & Could: Ability PresentDocumento2 páginasBe Able + Infinitive or CAN?: Can & Could: Ability PresentKaren HagueAinda não há avaliações
- Modal Verbs 1 Ability American English Student Ver2Documento3 páginasModal Verbs 1 Ability American English Student Ver2thiagomaboniAinda não há avaliações
- Guía completa de modales en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #2No EverandGuía completa de modales en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #2Ainda não há avaliações
- Easy Italian: Lower Intermediate Level - Vol. 1No EverandEasy Italian: Lower Intermediate Level - Vol. 1Nota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Comparatives Superlatives ETB Beginner PDFDocumento25 páginasComparatives Superlatives ETB Beginner PDFsanti_tena_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Adverbs of Manner Exercises (Revised Winter 2016) (Opens PDF, 36kb)Documento3 páginasAdverbs of Manner Exercises (Revised Winter 2016) (Opens PDF, 36kb)NOXIOUS0% (1)
- Adverbs Adjectives Ending - LY 2º ESO 1617Documento2 páginasAdverbs Adjectives Ending - LY 2º ESO 1617santi_tena_1100% (1)
- Listening: Exam Practice 1Documento16 páginasListening: Exam Practice 1santi_tena_1Ainda não há avaliações
- EX Will Going To Grammarway 1Documento2 páginasEX Will Going To Grammarway 1santi_tena_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Emaco1e1 PDFDocumento1 páginaEmaco1e1 PDFsanti_tena_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Vocabulary and GrammarDocumento11 páginasVocabulary and Grammarsanti_tena_1Ainda não há avaliações
- PDF ESL Entrance TestDocumento8 páginasPDF ESL Entrance Testsanti_tena_1100% (1)
- Like Love Hate Ing Fun Activities Games - 42084Documento1 páginaLike Love Hate Ing Fun Activities Games - 42084santi_tena_1100% (1)
- Like Love Hate Ing Fun Activities Games 42084Documento1 páginaLike Love Hate Ing Fun Activities Games 42084santi_tena_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Machine Translation Post-Editing InterfacesDocumento40 páginasMachine Translation Post-Editing Interfacessanti_tena_1Ainda não há avaliações
- Winda - Uas B. InggrisDocumento5 páginasWinda - Uas B. InggrisWinda SyaqiifaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 5 Reading and WritingDocumento9 páginasLesson 5 Reading and WritingAkiruo NeroAinda não há avaliações
- The Database ApproachDocumento9 páginasThe Database ApproachRhoda Mae BucadAinda não há avaliações
- EDUC 105-AMBROCIO (Reflections)Documento5 páginasEDUC 105-AMBROCIO (Reflections)YeshËin LØuiseAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching Music in Elementary Grades: Preliminary Examination SY: 2021-2022 Test 1Documento3 páginasTeaching Music in Elementary Grades: Preliminary Examination SY: 2021-2022 Test 1Saturnino Jr Morales FerolinoAinda não há avaliações
- Function ModulesDocumento5 páginasFunction ModulesArun S PrabhuAinda não há avaliações
- InfoBasic Programming LanguageDocumento108 páginasInfoBasic Programming LanguageSajiloAinda não há avaliações
- Computer MCQ Part-02 EngDocumento72 páginasComputer MCQ Part-02 Engnirmalkumargaurav96305Ainda não há avaliações
- Min Oh 1995 PHD ThesisDocumento183 páginasMin Oh 1995 PHD ThesisPriya DasAinda não há avaliações
- 1.5 Use of The Oedometer Test To Derive Consolidation ParametersDocumento36 páginas1.5 Use of The Oedometer Test To Derive Consolidation ParametersrihongkeeAinda não há avaliações
- LECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsDocumento3 páginasLECTURE 1 - Definition and Classifications of Differential EquationsCamille SalmasanAinda não há avaliações
- Future Tense ReviewDocumento2 páginasFuture Tense Reviewlilianepc0% (1)
- (Music and Letters 1973-Oct Vol. 54 Iss. 4) Review by - C. P. - Music and Painting - A Study in Comparative Ideas From Turner To Schoenbergby Edward Lockspeiser (1973) (10.2307 - 734424) - Libgen - LiDocumento4 páginas(Music and Letters 1973-Oct Vol. 54 Iss. 4) Review by - C. P. - Music and Painting - A Study in Comparative Ideas From Turner To Schoenbergby Edward Lockspeiser (1973) (10.2307 - 734424) - Libgen - Libeatriz100% (1)
- Active To PassiveDocumento1 páginaActive To PassiveElena LeoAinda não há avaliações
- English For Academics and Professional Purposes - Weeks 1-2Documento8 páginasEnglish For Academics and Professional Purposes - Weeks 1-2Danilo Siquig Jr.Ainda não há avaliações
- 4 .Airport Air Traffic ControlDocumento43 páginas4 .Airport Air Traffic ControlEsrah HareemAinda não há avaliações
- Present-Continuous 5202Documento3 páginasPresent-Continuous 5202Raquel Hernandez100% (1)
- CSE Semester VIDocumento23 páginasCSE Semester VIKHEMRAJ PRAJAPATIAinda não há avaliações
- Review Questionnaire in DanceDocumento3 páginasReview Questionnaire in DanceJessa MitraAinda não há avaliações
- CNS - HT - 1Documento4 páginasCNS - HT - 1Ãbhilâśh Rêddÿ100% (1)
- AutoCAD 2016 English-Brazilian Portuguese Commands and Aliases ListDocumento20 páginasAutoCAD 2016 English-Brazilian Portuguese Commands and Aliases ListPaulo BisattoAinda não há avaliações
- Welcome To Spoken Telugu Learning CornerDocumento18 páginasWelcome To Spoken Telugu Learning CornerRama Krishna BAinda não há avaliações
- Bridging GapsDocumento18 páginasBridging Gapssci PantallanoAinda não há avaliações
- The Prayer of Ibn Mashīsh (As Salāt Al-Mashīshīyah) (Titus Burckhardt) PDFDocumento4 páginasThe Prayer of Ibn Mashīsh (As Salāt Al-Mashīshīyah) (Titus Burckhardt) PDFIsraelAinda não há avaliações
- Holy Quran para 24 PDFDocumento26 páginasHoly Quran para 24 PDFkhalid100% (1)
- GE 4 MMW Week 8 9 (Revised)Documento35 páginasGE 4 MMW Week 8 9 (Revised)jumbo fernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Writing Good SQLDocumento13 páginasWriting Good SQLKumara55Ainda não há avaliações
- Translation Services BrochureDocumento8 páginasTranslation Services Brochureapi-251019229Ainda não há avaliações
- GOM Shortcut KeysDocumento4 páginasGOM Shortcut KeysClarence Tuazon FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Zusak Markus The Book Thief Teacher's NotesDocumento18 páginasZusak Markus The Book Thief Teacher's NotesDandelion440% (1)