Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
A Letterhead is the Heading at the Top of a Sheet of Letter Paper (Stationery). That Heading Usually Consists of a Name and an Address, And a Logo or Corporate Design, And Sometimes a Background Pattern (2)
Enviado por
ximenaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
A Letterhead is the Heading at the Top of a Sheet of Letter Paper (Stationery). That Heading Usually Consists of a Name and an Address, And a Logo or Corporate Design, And Sometimes a Background Pattern (2)
Enviado por
ximenaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Leonardo Leon Lopez
Email: Eliecerl.leonl@utadeo.edu.co
A REVIEW OF METHODS
A SUPPORTING SUPPLIER
SELECTION
Luitzen de Boer, Eva Labro, Pierangela Morlacchi
University of Twente, Faculty of Technology & Management, AE Enschede, Netherlands
"London School of Economics, Department of Accounting and Finance
University of Bath, Centre for Research in Strategic Purchasing and Supply,
Received 3 February 2000; received in revised form 8 September 2000; accepted 18 November 2000
KEY WORDS
Supplier, Logistics, Models, Costs, Envelopment, Selection.
MAIN IDEA
The main idea of the article is the way in which providers should be selected according to
a series of approaches to make the best decision.
SECOND IDEA
The article gives an idea of how suppliers have been selected in companies for a long
time, and from there, gives a set of parameters based on research and innovation to
reduce costs, time and labor when evaluating suppliers.
SUMMARY
Criteria for Evaluating Current Supplier Selection
* Cost
* Time
*Availability
*Logistics
Jorge Tadeo Lozano University
English B1
SUMMARY
Criteria for evaluating the selection of suppliers according to the parameters of
the article
Categorical methods
Categorical methods are qualitative models. On the basis of data and the buyer's
experience, current suppliers or family members will be able to evaluate
according to a set of criteria. Evaluations actually consist of categorizing the
supplier's performance on a criterion as either 'positive', and 'neutral' or 'negative'.
After a supplier has been rated on all criteria, the buyer gives an overall rating,
again by checking one of the three options. In this way, suppliers are classified into
three categories.
Data envelopment analysis
It is based on the "efficiency" concept of A Decision Alternative. The alternatives are
evaluated on "benefit" (output) and cost criteria (entry). The efficiency of an alternative
(for example, a vendor) is defined as the ratio of the weighted sum of its products (i.e. the
yield of the supplier) to the weighted sum of its inputs (i.e. the costs of use of the supplier).
Cluster Analysis (CA)
It is a basic method of statistics that uses a classification algorithm to group a series of
elements that are described by a set of numerical attribute scores into a series of groups
such that differences between elements within a group are minimal and differences
between elements in different groups are maximum.
Case Based Reasoning Systems (CBR)
CBR systems fall into the category of the so-called artificial intelligence (AI) approach.
Basically, a CBR system is a software-driven database that provides decision-makers with
useful information and experiences from similar previous decision situations.
Decision models for the final phase of the election
Linear weighting models
In linear weighting models, weightings are assigned to the criteria, the greater the weight,
the greater the importance.
SUMMARY
Total cost of ownership (TCO) models
TCO-based models attempt to include all quantifiable costs in supplier choice
incurred throughout the life cycle of the purchased item.
Mathematical programming models
Given an adequate decision fit, PM allows the decision-maker to formulate the
decision problem in terms of a mathematical objective function that must
subsequently be maximized or minimized by varying the values of the variables in
the objective function.
PERSONAL VIEW
The methodology for the selection of suppliers proposed in the article is excellent,
because it offers a much more objective selection, taking into account several criteria that
are relevant, but are usually discarded, the implementation of the method and tools work
transversally to any selection process by the organization, has multiple procedures and
various ways of selecting the best provider, based on needs.
Você também pode gostar
- 6 0LDies PDFDocumento101 páginas6 0LDies PDFscodavnx100% (1)
- WPS For Different Materail by BhelDocumento176 páginasWPS For Different Materail by Bhelsaisssms911691% (46)
- FG Wilson AtsDocumento5 páginasFG Wilson AtsErwan Shidiq FathoniAinda não há avaliações
- Michael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageNo EverandMichael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (1)
- Maths - 2B Imp QuestionsDocumento93 páginasMaths - 2B Imp QuestionsBandaru Chiranjeevi100% (1)
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection: Laura AITER Cengiz ÇOKAY Güven GÜLDocumento38 páginasSupplier Evaluation and Selection: Laura AITER Cengiz ÇOKAY Güven GÜLsrkadaliAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Evaluation The First Step in Effective SoDocumento4 páginasSupplier Evaluation The First Step in Effective SoShatender kumar Kumar100% (1)
- Supplier Selection Through Analytical Hierarchy Process: A Case Study in Small Scale Manufacturing OrganizationDocumento6 páginasSupplier Selection Through Analytical Hierarchy Process: A Case Study in Small Scale Manufacturing OrganizationseventhsensegroupAinda não há avaliações
- Speed Control of A Switched Reluctance Motor PDFDocumento67 páginasSpeed Control of A Switched Reluctance Motor PDFrijilpoothadi50% (2)
- Vendor Rating 1Documento9 páginasVendor Rating 1wilsongouveiaAinda não há avaliações
- 28 GenoveseA Suppliers Election Method Analysis REV FINDocumento15 páginas28 GenoveseA Suppliers Election Method Analysis REV FINSima Khademi DeljouAinda não há avaliações
- Factors Affecting The Selection of Optimal Suppliers in Procurement ManagementDocumento5 páginasFactors Affecting The Selection of Optimal Suppliers in Procurement ManagementMarcus Hah Kooi YewAinda não há avaliações
- Training Manual A 319/320/321: ATA 30 Ice and Rain ProtectionDocumento46 páginasTraining Manual A 319/320/321: ATA 30 Ice and Rain ProtectionHansraj Kayda100% (1)
- Comparison and Evaluation of Multi-Criteria Supplier Selection Approaches: A Case StudyDocumento19 páginasComparison and Evaluation of Multi-Criteria Supplier Selection Approaches: A Case StudyRamkumarArumugapandiAinda não há avaliações
- User Interface Inspection Methods: A User-Centered Design MethodNo EverandUser Interface Inspection Methods: A User-Centered Design MethodNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- GP Concept Note-Harshita KaarthikayaDocumento13 páginasGP Concept Note-Harshita KaarthikayakaarthikayaAinda não há avaliações
- Multi-criteria Decision Analysis for Supporting the Selection of Engineering Materials in Product DesignNo EverandMulti-criteria Decision Analysis for Supporting the Selection of Engineering Materials in Product DesignAinda não há avaliações
- Appication of Ahp and Topsis Method For Supplier Selection ProblemDocumento8 páginasAppication of Ahp and Topsis Method For Supplier Selection ProblemIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalAinda não há avaliações
- A Fuzzy Ahp Approach For Supplier Selection Problem A Case StudyDocumento13 páginasA Fuzzy Ahp Approach For Supplier Selection Problem A Case StudyWilliam ScottAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Selection Process Using ELECTRE Method: December 2010Documento7 páginasSupplier Selection Process Using ELECTRE Method: December 2010Diya UnarkerAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Selection by Technique of Order Pre-Ference by Similarity To Ideal Solution (Top-Sis) Method For Automotive IndustryDocumento4 páginasSupplier Selection by Technique of Order Pre-Ference by Similarity To Ideal Solution (Top-Sis) Method For Automotive IndustryJoseph WilliamsAinda não há avaliações
- A Hybrid Multicriteria Decisionmaking Approach Based On Anpentropy Topsis For Building Materials Supplier SelectionentropyDocumento26 páginasA Hybrid Multicriteria Decisionmaking Approach Based On Anpentropy Topsis For Building Materials Supplier SelectionentropySmith Dávila ReymundoAinda não há avaliações
- A Review of Supplier Selection Methods in Manufact PDFDocumento9 páginasA Review of Supplier Selection Methods in Manufact PDFyskdonAinda não há avaliações
- Supply Base RationalisationDocumento9 páginasSupply Base RationalisationKim RavanzoAinda não há avaliações
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Dusanapudi Sivanagaraju Pitchaiah, Manzoor Hussaian, D. GovardhanDocumento5 páginasMaterials Today: Proceedings: Dusanapudi Sivanagaraju Pitchaiah, Manzoor Hussaian, D. GovardhanDanny WongAinda não há avaliações
- Selection of Suppliers Through Different Multi-Criteria Decision Making TechniquesDocumento13 páginasSelection of Suppliers Through Different Multi-Criteria Decision Making Techniquesidris_ali_7Ainda não há avaliações
- Supplier Selection Project Using An Integrated Delphi, AHP and Taguchi Loss FunctionDocumento17 páginasSupplier Selection Project Using An Integrated Delphi, AHP and Taguchi Loss FunctionAldy AnwarAinda não há avaliações
- 2015 - Abdollahi, Arvan, Razmi - An Integrated Approach For Supplier Portfolio Selection Lean or AgileDocumento41 páginas2015 - Abdollahi, Arvan, Razmi - An Integrated Approach For Supplier Portfolio Selection Lean or AgileJuliano S.M. BatistelaAinda não há avaliações
- 28 Icams2011 A10023Documento6 páginas28 Icams2011 A10023Ashwin DevAinda não há avaliações
- Ijrtem B021009014 PDFDocumento6 páginasIjrtem B021009014 PDFjournalAinda não há avaliações
- A Fuzzy AHP Approach For Supplier SelectionDocumento9 páginasA Fuzzy AHP Approach For Supplier SelectionEng.shadid1 Sh123456Ainda não há avaliações
- Chen, Huang - 2007 - International Journal - Bi-Negotiation Integrated AHP in Suppliers SelectionDocumento19 páginasChen, Huang - 2007 - International Journal - Bi-Negotiation Integrated AHP in Suppliers SelectionKlaus ElbernAinda não há avaliações
- Advances in Engineering Software: R. Mohammad Ebrahim, J. Razmi, H. HalehDocumento11 páginasAdvances in Engineering Software: R. Mohammad Ebrahim, J. Razmi, H. HalehzawadzahinAinda não há avaliações
- 1 s2.0 S0377221709003403 Main PDFDocumento9 páginas1 s2.0 S0377221709003403 Main PDFdev2945Ainda não há avaliações
- A Fuzzy AHP Approach For Supplier Selection Problem A Case Study in A Gear (Ayhan)Documento14 páginasA Fuzzy AHP Approach For Supplier Selection Problem A Case Study in A Gear (Ayhan)Luki HidayatiAinda não há avaliações
- NyDick 1992Documento6 páginasNyDick 1992rio ristyawanAinda não há avaliações
- Selecting The Best Supplier Using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) MethodDocumento9 páginasSelecting The Best Supplier Using Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) MethodEng.shadid1 Sh123456Ainda não há avaliações
- AHP MethodDocumento6 páginasAHP MethodKajal JoshiAinda não há avaliações
- The Voting Analytic Hierarchy Process Method For Selecting SupplierDocumento10 páginasThe Voting Analytic Hierarchy Process Method For Selecting SupplierEng.shadid1 Sh123456Ainda não há avaliações
- Application of Topsis Method For Supplier Selection in Manufacturing IndustryDocumento12 páginasApplication of Topsis Method For Supplier Selection in Manufacturing IndustryArshdeep SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Bài Báo QLTMDocumento20 páginasBài Báo QLTMduong.nguyenthuy2406Ainda não há avaliações
- Factors Considered During Supplier Evaluation in Procurement ProcessDocumento15 páginasFactors Considered During Supplier Evaluation in Procurement Processwaghmodeakshay9337464Ainda não há avaliações
- 21 05 27 Purchasing ManagementDocumento26 páginas21 05 27 Purchasing ManagementBAYANI JR SAPARRIAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Selection Problem: A Literature Review of Multi-Criteria Approaches Based On DEADocumento13 páginasSupplier Selection Problem: A Literature Review of Multi-Criteria Approaches Based On DEAblack272727Ainda não há avaliações
- Best Criteria of Supplier Selection Model For Procurement Using Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ahp) and Expert Choice (Ec)Documento36 páginasBest Criteria of Supplier Selection Model For Procurement Using Analytical Hierarchy Process (Ahp) and Expert Choice (Ec)SasitaranAinda não há avaliações
- Ahp LPDocumento14 páginasAhp LPMohammad Husnain AbbasAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Selection: A Fuzzy-ANP ApproachDocumento10 páginasSupplier Selection: A Fuzzy-ANP ApproachAli UlusoyAinda não há avaliações
- Expert Systems With Applications: Saman Hassanzadeh Amin, Jafar RazmiDocumento10 páginasExpert Systems With Applications: Saman Hassanzadeh Amin, Jafar RazmiRenzo ErikssonAinda não há avaliações
- Review and Critique of Supplier Selection Process and Practices Review and Critique of Supplier Selection Process and PracticesDocumento36 páginasReview and Critique of Supplier Selection Process and Practices Review and Critique of Supplier Selection Process and PracticesYihenew MengistAinda não há avaliações
- SustainabilityDocumento17 páginasSustainabilitymallappaAinda não há avaliações
- 2020-2-May-Scopus-Supplier Selection in A Manufacturing-DOI 10.5373JARDCSV12SP520201784Documento9 páginas2020-2-May-Scopus-Supplier Selection in A Manufacturing-DOI 10.5373JARDCSV12SP520201784Sakthirama VadiveluAinda não há avaliações
- An AHP/DEA Methodology For 3PL Vendor Selection in 4PLDocumento10 páginasAn AHP/DEA Methodology For 3PL Vendor Selection in 4PLMoslem PersiaAinda não há avaliações
- An Integrated Approach Using AHP-ER To Supplier Selection in Railway ProjectsDocumento8 páginasAn Integrated Approach Using AHP-ER To Supplier Selection in Railway ProjectsNabila AinAinda não há avaliações
- Factor Analysis and Methods of Supplier Selection: Tak K. Mak, Fassil NebebeDocumento9 páginasFactor Analysis and Methods of Supplier Selection: Tak K. Mak, Fassil NebebeHarshit MishraAinda não há avaliações
- Ba 208Documento8 páginasBa 208rahmat wibowoAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Selection Based On Ahp QFD Methodology: SciencedirectDocumento10 páginasSupplier Selection Based On Ahp QFD Methodology: SciencedirectWahyunisAinda não há avaliações
- EN The Application of A Decision Making AppDocumento20 páginasEN The Application of A Decision Making AppSetianto PujiAinda não há avaliações
- 83-Article Text-587-1-10-20210320Documento17 páginas83-Article Text-587-1-10-20210320DiptoAinda não há avaliações
- Supplier Selection of Recycled Plastic Materials UDocumento8 páginasSupplier Selection of Recycled Plastic Materials UKarla Zorka Herrera UrlichAinda não há avaliações
- Work Injury Benefits ActsDocumento49 páginasWork Injury Benefits ActsjohnAinda não há avaliações
- 19-Article Text-104-2-10-20190413Documento19 páginas19-Article Text-104-2-10-20190413DiptoAinda não há avaliações
- Smes in Supply Chain: A Supplier Evaluation Model and Some Empirical ResultsDocumento18 páginasSmes in Supply Chain: A Supplier Evaluation Model and Some Empirical ResultsscriabelAinda não há avaliações
- Outsourcing Paper CostingDocumento19 páginasOutsourcing Paper CostingkhairitkrAinda não há avaliações
- Definition of Supplier SelectionDocumento4 páginasDefinition of Supplier SelectionKashif Niaz Meo100% (1)
- Ijcrt 188727Documento5 páginasIjcrt 188727Roopesh BabuAinda não há avaliações
- Process Monitoring and Improvement HandbookNo EverandProcess Monitoring and Improvement HandbookAinda não há avaliações
- Serto Up To Date 33Documento7 páginasSerto Up To Date 33Teesing BVAinda não há avaliações
- Huawei KPIs 10thsep2011Documento15 páginasHuawei KPIs 10thsep2011Amr Mohamed Abd El-baryAinda não há avaliações
- LAMIGAS - BSN2H-Laboratory No. 2Documento3 páginasLAMIGAS - BSN2H-Laboratory No. 2Juliemae LamigasAinda não há avaliações
- UNIT 5 Matrices and System of EquationsDocumento8 páginasUNIT 5 Matrices and System of EquationsrishiAinda não há avaliações
- ISCSI OptimizationDocumento28 páginasISCSI OptimizationrahulhclAinda não há avaliações
- Act MCQDocumento10 páginasAct MCQKARTHICKAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1-Part 1: Half-Wave RectifiersDocumento50 páginasChapter 1-Part 1: Half-Wave RectifiersWeehao SiowAinda não há avaliações
- Generalized Digital Butterworth Filter Design: IEEE Transactions On Signal Processing May 1998Documento31 páginasGeneralized Digital Butterworth Filter Design: IEEE Transactions On Signal Processing May 1998domnuljanAinda não há avaliações
- Physics Practice Worksheet 0625Documento6 páginasPhysics Practice Worksheet 0625emmanuelAinda não há avaliações
- First Quarter Summative Test in Math 7Documento2 páginasFirst Quarter Summative Test in Math 7Lemanuel097 FloresAinda não há avaliações
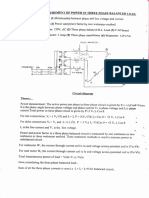
- Experiment: Measurement of Power in Three Phase Balanced LoadDocumento2 páginasExperiment: Measurement of Power in Three Phase Balanced LoadTripti GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- GOC & EAS CPP-II - PMDDocumento14 páginasGOC & EAS CPP-II - PMDVansh sareenAinda não há avaliações
- Module One 4 BAKERY INGREDIENTSDocumento46 páginasModule One 4 BAKERY INGREDIENTSIhsan BadshaAinda não há avaliações
- Liquid Solutions: Physical Chemistry by Prince SirDocumento14 páginasLiquid Solutions: Physical Chemistry by Prince SirSunnyAinda não há avaliações
- Preliminary Wing Design Parameter Selection Rev 3 PDFDocumento8 páginasPreliminary Wing Design Parameter Selection Rev 3 PDFvirgilioAinda não há avaliações
- KEIYU NDT Ultrasonic TransducerDocumento6 páginasKEIYU NDT Ultrasonic TransducersrgokuAinda não há avaliações
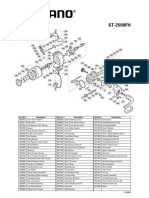
- ST-2500FH: Part No. Description Part No. Description Part No. DescriptionDocumento1 páginaST-2500FH: Part No. Description Part No. Description Part No. DescriptionGergely IvánovicsAinda não há avaliações
- MODULE 0 CPE105 Review On StatisticsDocumento12 páginasMODULE 0 CPE105 Review On StatisticsKishiane Ysabelle L. CabaticAinda não há avaliações
- Price DeterminationDocumento2 páginasPrice DeterminationSikander BehalAinda não há avaliações
- HW 5, 448Documento16 páginasHW 5, 448pdrogos02100% (1)
- MID TEST Integer, Fraction 20092010Documento5 páginasMID TEST Integer, Fraction 20092010mathholic111Ainda não há avaliações
- Audi A6 2.7t Component LocationDocumento3 páginasAudi A6 2.7t Component LocationLucian MicurescuAinda não há avaliações
- Tutorial 4 JawapanDocumento6 páginasTutorial 4 JawapanlimAinda não há avaliações
- Application Note: Vishay General SemiconductorDocumento4 páginasApplication Note: Vishay General SemiconductorMamoon AlrimawiAinda não há avaliações