Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Summary of Principles in Language Teaching
Enviado por
ImanissBliss0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
13 visualizações3 páginasThe document summarizes different approaches to language teaching:
1. Grammar-Translation focuses on reading literature and learning grammar/vocabulary, with the teacher as the authority. Evaluation is through written translations.
2. Audio-Lingual Method emphasizes communication through dialogues and drills, with the teacher directing imitation. Learning is viewed as habit formation.
3. Total Physical Response uses physical movement to teach basic speaking skills enjoyably, with the teacher also directing imitation and role reversal. Spoken language is emphasized over written.
4. Communicative Language Teaching promotes functional competence through communication activities negotiated between students. The teacher facilitates and manages learning. Evaluation considers fluency and accuracy in communication.
Descrição original:
Teaching principles
Título original
التوجيهات التربوّية
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document summarizes different approaches to language teaching:
1. Grammar-Translation focuses on reading literature and learning grammar/vocabulary, with the teacher as the authority. Evaluation is through written translations.
2. Audio-Lingual Method emphasizes communication through dialogues and drills, with the teacher directing imitation. Learning is viewed as habit formation.
3. Total Physical Response uses physical movement to teach basic speaking skills enjoyably, with the teacher also directing imitation and role reversal. Spoken language is emphasized over written.
4. Communicative Language Teaching promotes functional competence through communication activities negotiated between students. The teacher facilitates and manages learning. Evaluation considers fluency and accuracy in communication.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
13 visualizações3 páginasSummary of Principles in Language Teaching
Enviado por
ImanissBlissThe document summarizes different approaches to language teaching:
1. Grammar-Translation focuses on reading literature and learning grammar/vocabulary, with the teacher as the authority. Evaluation is through written translations.
2. Audio-Lingual Method emphasizes communication through dialogues and drills, with the teacher directing imitation. Learning is viewed as habit formation.
3. Total Physical Response uses physical movement to teach basic speaking skills enjoyably, with the teacher also directing imitation and role reversal. Spoken language is emphasized over written.
4. Communicative Language Teaching promotes functional competence through communication activities negotiated between students. The teacher facilitates and manages learning. Evaluation considers fluency and accuracy in communication.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
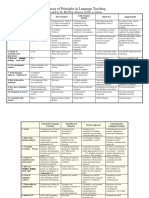
Summary of Principles in Language Teaching
Grammar- Audio-Lingual Total Physical Total Physical
Translation Method Response Response
1. Goals Read literature in Communication. Communication. Communication.
L2. Develop Automaticity by Learning L1= Learning L1=
mind. Learn learning new learning L2. learning L2.
grammar, habits. -teach basic -teach basic
vocabulary, and speaking skills speaking skills
culture. -provide an -provide an
enjoyable enjoyable
learning learning
experience experience
2. Role of the Traditional. T is T-centered. T Director. T Director. T
teacher/stude the authority. Ss provides model provides model provides model
nt learn from the T. of L2 for of L2 for of L2 for
imitation imitation. Later imitation. Later
Sts: imitate and role reversal. role reversal.
produce the
correct output
3. Teaching/ Translation. New grammar Comprehension Comprehension
Learning Deductive study and vocabulary before before
Process? of grammar. through production. production.
Memorize dialogues. Modelling by T Modelling by T
vocabulary. Drills. followed by followed by
Inductive performance. performance.
grammar.
Learning is
habit formation.
4. Nature of T to S. T-directed. T speaks, Ss T speaks, Ss
student/teache S/S in drills. respond respond
r interaction nonverbally. nonverbally.
Later, Ss Later, Ss
verbalize. verbalize.
5. How are N.A. N.A. Ss have fun in a Ss have fun in a
students’ nonstressful nonstressful
feelings dealt situation. situation.
with?
6. View of Literary language Language as Spoken over Spoken over
language/ over spoken system of written written
culture? language. patterns/units. culture is the culture is the
Simple to lifestyle of lifestyle of
complex. speakers. speakers.
7. What Vocabulary/ Structure Grammar and Grammar and
language grammar. important. vocabulary vocabulary
skills are Reading/writing. Listen-speak- (initially via (initially via
emphasized? read- imperatives). imperatives).
write. Comprehension Comprehension
precedes precedes
production. production.
8. Role of the L1 in classroom. L1 habits -L1 is used for -L1 is used for
native Two-way interfere beginners but beginners but
language? translation. with L2. Avoid rarely used later rarely used later
L1. on. on.
9. How does Written Discrete point By observation. By observation.
evaluation translations. testing for
occur? Apply grammar accuracy.
rules.
10. Treatment T supplies Avoid errors by Unobtrusive Unobtrusive
of errors? correct answer. overlearning. correction. correction.
11. Associated Moses Charles Fries James Asher James Asher
with whom?
Communicative
Language
Teaching
1. Goals Communication in
social context.
Appropriacy.
Functional
competence.
2. Role of the Facilitator.
teacher/student? Manager of
learning activities.
Promotes
communication
among Ss.
3. Teaching/ Ss learn to
Learning communicate by
Process negotiating
meaning in real
context. Activities
include information
gap, choice,
feedback.
4. Nature of T arranges tasks for
student/teacher communication. S/S
interaction? interaction.
5. How are Ss are motivated to
students’ learn thru
feelings dealt usefulness of
with? language functions.
6. View of Language in social
language/ context, for
culture? communication.
7. What skills Function over form.
are Discourse and
emphasized? sociolinguistic
competence + all 4
skills.
8. Role of L1? Generally not used.
9. How does Communicative
evaluation tests. Fluency and
occur? accuracy.
10. Treatment No error correction
of errors? unless errors
interfere with
communication.
11. Associated Various.
with whom?
Você também pode gostar
- Summary of Principles in Language TeachingDocumento3 páginasSummary of Principles in Language TeachingAmal Altamimi100% (9)
- PDF Summary of Principles in Language Teaching Provided by DR Bill Flick Dir DDDocumento4 páginasPDF Summary of Principles in Language Teaching Provided by DR Bill Flick Dir DDTuyếtAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Principles in Language TeachingDocumento2 páginasSummary of Principles in Language TeachingCarol TanaAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Principles in Language Teaching: Provided by Dr. Bill Flick, Director of ESL at AuburnDocumento2 páginasSummary of Principles in Language Teaching: Provided by Dr. Bill Flick, Director of ESL at AuburnAfroz Shirin100% (1)
- Summary of Principles in Language TeachingDocumento3 páginasSummary of Principles in Language Teachingmyhoopoe100% (1)
- Summary of Principles in Language TeachingDocumento3 páginasSummary of Principles in Language TeachingCarolina BarbaAinda não há avaliações
- Principles in Language Teaching - A SummaryDocumento4 páginasPrinciples in Language Teaching - A SummaryAlejandra ParedesAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Language Teaching ApproachesDocumento1 páginaSummary of Language Teaching Approachesdiya100% (1)
- Young Learners' Educational ModeDocumento20 páginasYoung Learners' Educational ModeOkan EmanetAinda não há avaliações
- Communicative approaches and language teaching methodsDocumento1 páginaCommunicative approaches and language teaching methodsMaría B.Ainda não há avaliações
- Phnology 5658 Final Lesson PlanDocumento5 páginasPhnology 5658 Final Lesson PlanIshrat nazAinda não há avaliações
- SEO-Optimized Introduction Lesson Plan TitleDocumento7 páginasSEO-Optimized Introduction Lesson Plan TitleSiti FatimahAinda não há avaliações
- 10 Rules for Developing Listening and Speaking SkillsDocumento2 páginas10 Rules for Developing Listening and Speaking SkillsAngela MaldonadoAinda não há avaliações
- Comparative ChartDocumento2 páginasComparative ChartVaal de TamrielAinda não há avaliações
- English Didactic II: - The CoordinationDocumento3 páginasEnglish Didactic II: - The CoordinationJoseph VargasAinda não há avaliações
- English Language Teaching ApproachesDocumento8 páginasEnglish Language Teaching ApproachesBarış EriçokAinda não há avaliações
- Answers (Exam 1)Documento3 páginasAnswers (Exam 1)hhbflatAinda não há avaliações
- LISTENINGDocumento2 páginasLISTENINGileana6784Ainda não há avaliações
- Mod 2.1 Speaking ALLDocumento81 páginasMod 2.1 Speaking ALLivan.el.rey1340Ainda não há avaliações
- Thornbury S How To Teach SpeakingDocumento163 páginasThornbury S How To Teach SpeakingVítor Moura0% (1)
- Questions The Silent Way Suggestopedia Community Lang Learning Total Physical ResponseDocumento3 páginasQuestions The Silent Way Suggestopedia Community Lang Learning Total Physical ResponseNakı Dilber BüyükdağAinda não há avaliações
- Language Teaching Methods/ ApproachesDocumento2 páginasLanguage Teaching Methods/ ApproachesJuli ArjonaAinda não há avaliações
- Theories of L2 LearningDocumento37 páginasTheories of L2 LearningoctAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of Principles in Language TeachingDocumento2 páginasSummary of Principles in Language TeachingPatricia MedeirosAinda não há avaliações
- Week 4Documento5 páginasWeek 4Evan Maagad LutchaAinda não há avaliações
- Language Skills EnglishDocumento37 páginasLanguage Skills EnglishteresachidalaAinda não há avaliações
- Essential Teaching Methods and Learning ProcessesDocumento36 páginasEssential Teaching Methods and Learning ProcessesQuyền Huỳnh TuấnAinda não há avaliações
- Can Tho University English Language Teaching OverviewDocumento94 páginasCan Tho University English Language Teaching OverviewThien MaiAinda não há avaliações
- ALBARACIN - Teaching Reading and WritingDocumento57 páginasALBARACIN - Teaching Reading and WritingJessaMae AlbaracinAinda não há avaliações
- Audio Lingual MethodsDocumento8 páginasAudio Lingual MethodsJose ValladaresAinda não há avaliações
- Overview of Learning Process: Restricted ExposureDocumento23 páginasOverview of Learning Process: Restricted ExposureBeo YoonaddictAinda não há avaliações
- Template - Summary Table of Teaching MethodsDocumento4 páginasTemplate - Summary Table of Teaching MethodsTấn Tài VõAinda não há avaliações
- Methodology Task II 2023 TaskDocumento14 páginasMethodology Task II 2023 TaskSantos CarrascoAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 7 I. ObjectivesDocumento14 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan in English 7 I. ObjectivesVince BulayogAinda não há avaliações
- методыхроноDocumento2 páginasметодыхроноalyoka1503Ainda não há avaliações
- Core Sub EC-6 SampleDocumento38 páginasCore Sub EC-6 SampleAntolio DominguezAinda não há avaliações
- Approaches To Teach Reading: 1. Azrina 2. Naziha 3. KhavitraaDocumento38 páginasApproaches To Teach Reading: 1. Azrina 2. Naziha 3. KhavitraaSHUMETAinda não há avaliações
- Teaching Grammar in ESL ClassroomsDocumento57 páginasTeaching Grammar in ESL ClassroomsHeaven's Angel LaparaAinda não há avaliações
- Inset Strategiesinpromotingnumeracyandliteracy 210329092926Documento23 páginasInset Strategiesinpromotingnumeracyandliteracy 210329092926Alvin ButilAinda não há avaliações
- Unit7 8tkt 201106021005Documento31 páginasUnit7 8tkt 201106021005Leyla JumaevaAinda não há avaliações
- It's Not What You Say, But How You Say It!: Chin Ese, Vietnam Ese, Japan Ese) - Ask Learners Which PartDocumento6 páginasIt's Not What You Say, But How You Say It!: Chin Ese, Vietnam Ese, Japan Ese) - Ask Learners Which PartGabriela AlboresAinda não há avaliações
- School Grade Level Teacher Subject Week Week 3 Quarter: Palengke (Market Day)Documento4 páginasSchool Grade Level Teacher Subject Week Week 3 Quarter: Palengke (Market Day)Evan Maagad LutchaAinda não há avaliações
- Esl ReviewerDocumento14 páginasEsl ReviewerZyra Jamer Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- School Grade Level ONE Teacher Subject ENGLISH Week Week 3 Quarter Fourth QuarterDocumento4 páginasSchool Grade Level ONE Teacher Subject ENGLISH Week Week 3 Quarter Fourth QuarterEvan Maagad LutchaAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 14 (Second Language Acquisition:Learning)Documento3 páginasUnit 14 (Second Language Acquisition:Learning)Guadalupe Escobar GómezAinda não há avaliações
- Met1 Methods InfoDocumento3 páginasMet1 Methods InfobetoAinda não há avaliações
- FOREIGN LANGUAGE DIDACTICS 1Documento41 páginasFOREIGN LANGUAGE DIDACTICS 1Santiago BarajasAinda não há avaliações
- e doc plan for portfolio e doc planDocumento4 páginase doc plan for portfolio e doc planapi-503751269Ainda não há avaliações
- DLL - English 5 - Q3 - W6Documento5 páginasDLL - English 5 - Q3 - W6LUCELE CORDEROAinda não há avaliações
- Scheme of Work English Stage 2Documento49 páginasScheme of Work English Stage 2Carolyne Achieng100% (1)
- Primary English Work Plan Stage 2 - 2017Documento49 páginasPrimary English Work Plan Stage 2 - 2017Emad Ahmed100% (1)
- Oral Com Q1 W4Documento3 páginasOral Com Q1 W4Jade SolerAinda não há avaliações
- Content - Based Instruction - Exe 23bDocumento2 páginasContent - Based Instruction - Exe 23bMonse AlbeAinda não há avaliações
- Brown and Lee - Teaching by Principles (4th Edition) - OcredDocumento1 páginaBrown and Lee - Teaching by Principles (4th Edition) - OcredMargie100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in English 9Documento3 páginasLesson Plan in English 9edjean franciscoAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 2: Foundations of Language EducationDocumento49 páginasLecture 2: Foundations of Language EducationAlexanderOcbaAgoyloAinda não há avaliações
- Approach ChartDocumento5 páginasApproach ChartChagualo Alpargate LuisAinda não há avaliações
- Teach Reading with Orton-Gillingham: Early Reading Skills: A Companion Guide with Dictation Activities, Decodable Passages, and Other Supplemental Materials for Struggling Readers and Students with DyslexiaNo EverandTeach Reading with Orton-Gillingham: Early Reading Skills: A Companion Guide with Dictation Activities, Decodable Passages, and Other Supplemental Materials for Struggling Readers and Students with DyslexiaAinda não há avaliações
- Action Plan For Teaching EngDocumento44 páginasAction Plan For Teaching EngMatt Drew100% (39)
- Sex, Crime, Drugs, and Just Plain Stupid Behaviors: Christopher SalvatoreDocumento105 páginasSex, Crime, Drugs, and Just Plain Stupid Behaviors: Christopher SalvatoreImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- ArshedandDanson2015 PDFDocumento9 páginasArshedandDanson2015 PDFImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar summary: Present and past tensesDocumento8 páginasGrammar summary: Present and past tensesEduardo JavierAinda não há avaliações
- Untitled Spreadsheet PDFDocumento1 páginaUntitled Spreadsheet PDFImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- Passive ExplanationDocumento4 páginasPassive Explanationapi-319884721Ainda não há avaliações
- MATE 39th Annual Conference: ELT Curriculum Towards Building CapacityDocumento1 páginaMATE 39th Annual Conference: ELT Curriculum Towards Building CapacityImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- Passive ExplanationDocumento5 páginasPassive ExplanationImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- Acquiring Vs LearningDocumento10 páginasAcquiring Vs LearningImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- ELT Methods OverviewDocumento301 páginasELT Methods OverviewImanissBliss100% (1)
- Education PsychologyDocumento164 páginasEducation PsychologySheikh Eras100% (6)
- TKT Glossary 2011Documento49 páginasTKT Glossary 2011Vladimir Osorio Cornejo100% (2)
- Woman and SexDocumento104 páginasWoman and SexRachiduBrahim0% (1)
- Languageassessment 131031091216 Phpapp02Documento172 páginasLanguageassessment 131031091216 Phpapp02rar93Ainda não há avaliações
- ELT Methods OverviewDocumento301 páginasELT Methods OverviewImanissBliss100% (1)
- الفشل الدراسي و أساليب الدعم التربويDocumento13 páginasالفشل الدراسي و أساليب الدعم التربويImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- ELT Methods OverviewDocumento301 páginasELT Methods OverviewImanissBliss100% (1)
- Guidelines SecondaryDocumento92 páginasGuidelines SecondaryMohammed BenayadAinda não há avaliações
- Sex, Crime, Drugs, and Just Plain Stupid Behaviors: Christopher SalvatoreDocumento105 páginasSex, Crime, Drugs, and Just Plain Stupid Behaviors: Christopher SalvatoreImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- The Childrens Bible PDFDocumento290 páginasThe Childrens Bible PDFDimitri1Ainda não há avaliações
- Abd Alilah Sati SIYASEYYA 49-50 FINAL - Indd-6Documento17 páginasAbd Alilah Sati SIYASEYYA 49-50 FINAL - Indd-6ImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- ECCE 2013 Sample Test BookletDocumento36 páginasECCE 2013 Sample Test BookletMarinaPenelope100% (2)
- Espresso English Table of ContentsDocumento209 páginasEspresso English Table of ContentsJose M. Lorente Aparicio100% (2)
- Unit 7 - Teaching New LanguageDocumento8 páginasUnit 7 - Teaching New LanguageImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Grammar PDFDocumento59 páginasAdvanced Grammar PDFImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- 6050 Notes On Learning TheoriesDocumento3 páginas6050 Notes On Learning TheorieskabadadAinda não há avaliações
- 7000 22599 1 SMDocumento12 páginas7000 22599 1 SMImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- Critical Thinking Lecture NotesDocumento10 páginasCritical Thinking Lecture NotesImanissBlissAinda não há avaliações
- An Outline of British HistoryDocumento28 páginasAn Outline of British HistoryThe CSS PointAinda não há avaliações
- UNMASKDocumento10 páginasUNMASKNoella E. ArriesgadoAinda não há avaliações
- Epgc&Printsec Frontcover&Dq Korean+Pop&Hl En&Ei P9Ujtreahmxymaxc6Bmla Q&Sa X&Oi Book - Result&Ct Result&Resnum 2&ved 0Cc0Q6Aewaq#V Onepage& Q&F FalseDocumento1 páginaEpgc&Printsec Frontcover&Dq Korean+Pop&Hl En&Ei P9Ujtreahmxymaxc6Bmla Q&Sa X&Oi Book - Result&Ct Result&Resnum 2&ved 0Cc0Q6Aewaq#V Onepage& Q&F FalseNJPMsmashAinda não há avaliações
- The Id, Ego, Superego GameDocumento4 páginasThe Id, Ego, Superego Gameshashi1986Ainda não há avaliações
- 25 Questions to Ace Your Next Job InterviewDocumento8 páginas25 Questions to Ace Your Next Job InterviewanukayssalAinda não há avaliações
- Political SocializationDocumento14 páginasPolitical SocializationTanzeel SheikhAinda não há avaliações
- Papillon69 - RenovndomeDocumento303 páginasPapillon69 - RenovndomePatriciaAinda não há avaliações
- The Turkish Embassy Letters 발제 최종Documento6 páginasThe Turkish Embassy Letters 발제 최종지민Ainda não há avaliações
- EurasianStudies 0210Documento150 páginasEurasianStudies 0210bdalcin5512Ainda não há avaliações
- Gaynesh Postcolonial StudiesDocumento18 páginasGaynesh Postcolonial StudiesAmanda WiseAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Course Reading - Doc 1Documento4 páginasPre Course Reading - Doc 1elmer2323Ainda não há avaliações
- Final Exam A1 Speaking Test Rating SheetDocumento2 páginasFinal Exam A1 Speaking Test Rating Sheetkathryn mcnultyAinda não há avaliações
- Arts and Crafts Traditions of Southeast AsiaDocumento28 páginasArts and Crafts Traditions of Southeast AsiaJohnrey TabuadaAinda não há avaliações
- ASEAN Corner Quiz 8Documento3 páginasASEAN Corner Quiz 8Chalinthorn ButdeewongAinda não há avaliações
- Tatauing The Post-Colonial Body - Albert WendtDocumento8 páginasTatauing The Post-Colonial Body - Albert WendtPaula Zorzi100% (1)
- 4-CGC 1D1 Unit 3 Changing Populations - INDIGENOUS PEOPLE - Brief LookDocumento46 páginas4-CGC 1D1 Unit 3 Changing Populations - INDIGENOUS PEOPLE - Brief LookMichael KeAinda não há avaliações
- Glocal Limits of Postfeminist Advertising: The Case of Orkid's #Likeagirl CampaignDocumento10 páginasGlocal Limits of Postfeminist Advertising: The Case of Orkid's #Likeagirl CampaignStella SAinda não há avaliações
- Reflecting on Transexperiences and Cultural PerspectivesDocumento1 páginaReflecting on Transexperiences and Cultural PerspectivesChristina XiongAinda não há avaliações
- UMBC Baltimore Intercultural Calendar 2019Documento40 páginasUMBC Baltimore Intercultural Calendar 2019UMBC SGAAinda não há avaliações
- CUPID and PSYCHE - Mythological AnalysisDocumento28 páginasCUPID and PSYCHE - Mythological Analysisrolz986100% (2)
- Dying For A DrinkDocumento9 páginasDying For A DrinkNorthSouthNZ100% (1)
- Soal Latihan Bahasa Inggris Folktale Kelas 6 SDDocumento9 páginasSoal Latihan Bahasa Inggris Folktale Kelas 6 SDDiniAinda não há avaliações
- Xiao'erjing: ٍْدرَع ْوَیِش/ٍْڭرَع ْوَیِثDocumento2 páginasXiao'erjing: ٍْدرَع ْوَیِش/ٍْڭرَع ْوَیِثMuhammadShakeelBhattiAinda não há avaliações
- List of Translators and Interpreters in IndonesiaDocumento22 páginasList of Translators and Interpreters in IndonesiaFikka AnastasiaAinda não há avaliações
- Diagrama Arg. 14X14 Desde El 09 Al 23 de Febrero de 2023Documento7 páginasDiagrama Arg. 14X14 Desde El 09 Al 23 de Febrero de 2023Alejandro TurpieAinda não há avaliações
- Etimologiuri Dziebani 2010 N7Documento98 páginasEtimologiuri Dziebani 2010 N7giorgi javakhadzeAinda não há avaliações
- Mysteries of Ancient AmericaDocumento59 páginasMysteries of Ancient AmericaJason Colavito91% (11)
- Natalia 19 (1989) CompleteDocumento93 páginasNatalia 19 (1989) CompletePeter CroeserAinda não há avaliações
- Answer Sheet Arts8 Q1Documento12 páginasAnswer Sheet Arts8 Q1Nancy GelizonAinda não há avaliações
- Ernesto Q. Celeste: Sigma Lenn M. RafananDocumento2 páginasErnesto Q. Celeste: Sigma Lenn M. RafananArnel VicenteAinda não há avaliações
- Form 5 Catch Us If You CanDocumento103 páginasForm 5 Catch Us If You CanSani UntongAinda não há avaliações