Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
CE365 Functional Design of Buildings
Enviado por
Anagha Menon0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
580 visualizações3 páginasce FDB syllabus
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoce FDB syllabus
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
580 visualizações3 páginasCE365 Functional Design of Buildings
Enviado por
Anagha Menonce FDB syllabus
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
Course L-T-P- Year of
Course Name
Code Credits Introduction
CE365 FUNCTIONAL DESIGN OF BUILDINGS 3-0-0-3 2016
Prerequisite : CE204 Construction Technology
Course objectives:
To understand the acoustical design concepts and noise control techniques
To impart the fundamental concepts of natural and artificial lighting designs
To provide principles of climatic conscious design of buildings with special emphasis on
tropical climates.
To understand the apparent position of sun with respect to earth during different periods of
the year and apply it in computation of solar radiation and design of shading devices.
Syllabus:
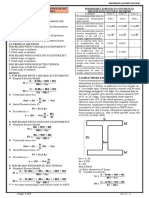
Acoustics : Physics of sound- Behavior of sound- Sound insulation and reverberation control
Lighting: Principles- Day lighting and artificial lighting – design methods
Thermal design of buildings: Climatic elements – classification- thermal comfort and indices-solar
radiation calculations and design of shading devices.
Thermo physical properties of building materials and thermal control- passive and active building
design- Steady and periodic heat flow through building envelope. Concept of green building.
Expected Outcomes:
On completion of the course, the students will be able to:
i. Analyze and make effective decisions in use of principles of functional planning of the
buildings with respect to Acoustics and Lighting and Thermal design of buildings in
various climatic zones that the student may encounter in his/her professional career.
ii. Select different building materials and explain the manner in which they can be used in
different types of buildings with respect to various functional requirements like
acoustics, lighting and thermal comfort.
iii. Apply the techniques learned to the estimate solar radiation falling on different
surfaces of the buildings, design shading devices to protect from direct sunlight,
design of energy efficient, functionally comfortable buildings, low energy buildings
and green buildings.
References :
1. Ajitha Simha.D, Building Environment, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co., New Delhi, 1985
2. Bureau of Indian standards, Handbook on Functional Requirement of Buildings – SP:41(S and T) –
1987
3. Givoni. B Man,. Climate and Architecture, Applied Science Publication, 1976
4. Knudsen V.O. and Harris C.M., Acoustical Design in Architecture, John Wiley, 1980
5. Koenigseberger, Manual of tropical Housing and Building Part I – Climatic design, Orient Longman,
2011
6. Krishnan, Climate responsive architecture, Tata McGraw Hill, 1999
7. M David Egan , Architectural Acoustics, J.Ross Publishing, 2007
8. Olgay Victor, Design with climate-A bioclimatic approach to architectural regionalism- Princeton
University press-1963
For more study materials>www.ktustudents.in
COURSE PLAN
Sem.
Exam
Module Contents Hours
Marks
%
Acoustics, fundamentals: Physics of sound-Frequency, period
amplitude. Intensity of sound- Watts/m2- Bel- Decibel scales- dBA-
Phon. Addition of sound levels. Human Audibility range. Behavior
I 7 15
of sound in free and reverberant fields. Noise- allowable limits-
effect of noise on human-Air and structure born noises-equivalent
noise levels-day and night equivalent.
Acoustics, applications: Measures of noise control- Source-path
and receiving end. TL value and computation of TL value,
Flanking paths. Sound absorption-materials and fixings.
II Reverberation-Sabines formula-Eyrings modification. Acoustical 7 15
defects- acoustical design of auditoriums and small lecture halls.
Acoustical considerations of offices, hospitals and Industrial
buildings.
FIRST INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Lighting, Natural: Visual tasks – Natural lighting- illumination
requirements for various buildings –principles of day lighting – day
III 6 15
light factor and its components- Design of side-lit windows-BIS and
CBRI methods-skylights
Lighting, Artificial: Artificial lighting- illumination requirements-
lux meter – lamps and luminaries – polar distribution curves– 6
IV Colour temperature and colour rendering index- glare -Design of 15
artificial lighting – lumen method – point by point method. Basic
idea of street lighting and outside lighting
SECOND INTERNAL EXAMINATION
Thermal comfort: Factors affecting thermal comfort
Effective temperature –Thermal comfort indices-ET-CET Charts-
Bioclimatic chart- Psychrometry and Psycrometric chart.
Earth-Sun relationship: Sun’s apparent movement with respect to 8 20
V
the earth. Solar angles-Computation of solar radiation on different
surfaces-solar path diagram-shadow-throw concept and design of
shading devices
Heat flow through building envelope: Thermo physical properties
of building materials: Thermal quantities – heat flow – thermal
conductivity – resistance and transmittance and surface coefficient -
Sol- air temperature concept- solar gain factor. Thermal
transmittance of structural elements – thermal gradients – heat
gain/loss calculation. Periodic heat flow – time lag and decrement
VI 8 20
factor.
Design approaches: Climate conscious designs- Climatic zones in
India- orientation and shape of buildings in different climatic zones-
Passive solar-Active solar and Active approaches. Requirements of
buildings in tropical areas-Thermal insulation-Introduction to the
concept of green-building
END SEMESTER EXAMINATION
For more study materials>www.ktustudents.in
QUESTION PAPER PATTERN (End semester examination)
Maximum Marks :100 Exam Duration: 3 Hrs
Part A -Module I & II : 2 questions out of 3 questions carrying 15 marks each
Part B - Module III & IV: 2 questions out of 3 questions carrying 15 marks each
Part C - Module V & VI : 2 questions out of 3 questions carrying 20 marks each
Note : 1.Each part should have at least one question from each module
2 Each question can have a maximum of 4 subdivisions (a,b,c,d)
For more study materials>www.ktustudents.in
Você também pode gostar
- Model Illustrating Sustainable Architectural Design.No EverandModel Illustrating Sustainable Architectural Design.Ainda não há avaliações
- Rate Analysis of AanatoliDocumento59 páginasRate Analysis of Aanatoliujjwal sapkotaAinda não há avaliações
- Example1 1-StraightsupportedDocumento7 páginasExample1 1-StraightsupportedOmar BayouAinda não há avaliações
- Drain SpaceDocumento10 páginasDrain Spaceikhsan07Ainda não há avaliações
- Irc 22 2015Documento93 páginasIrc 22 2015rajpootsaurabhAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 3 - Influence LinesDocumento87 páginasLecture 3 - Influence LinesMary Dominique OnateAinda não há avaliações
- Fa D F B: Example 1Documento19 páginasFa D F B: Example 1Sevet Gnow DrachirAinda não há avaliações
- Prestressed Elastic StressesDocumento2 páginasPrestressed Elastic StressesMary Joy BaggayAinda não há avaliações
- Bridge Engineering RangwalaDocumento4 páginasBridge Engineering RangwalaKRISHNA BHUMBEAinda não há avaliações
- Co4 Shear WallDocumento3 páginasCo4 Shear WallCHARIAinda não há avaliações
- Slab Design Sandhi KholaDocumento15 páginasSlab Design Sandhi Kholasakar shresthaAinda não há avaliações
- EC2-BE-dubble Reinforced Beams SLS-crackwidth Rev6Documento7 páginasEC2-BE-dubble Reinforced Beams SLS-crackwidth Rev6Dong LIAinda não há avaliações
- VivaDocumento76 páginasVivaRam NepaliAinda não há avaliações
- M.Tech Project Presentation (Stage I) : College of Engineering Pune (COEP)Documento31 páginasM.Tech Project Presentation (Stage I) : College of Engineering Pune (COEP)kajal jadhavAinda não há avaliações
- One Way SlabDocumento3 páginasOne Way SlabMuhammad Sulaiman100% (1)
- 6 Halaba Bridge PierDocumento79 páginas6 Halaba Bridge PierReader of Down HillAinda não há avaliações
- Example 1.5:: Stair Supported by Landing Spanning Perpendicular To Stair FlightDocumento8 páginasExample 1.5:: Stair Supported by Landing Spanning Perpendicular To Stair FlightKHAI HONG GANAinda não há avaliações
- Transpo Eng'g Slides 1 PDFDocumento79 páginasTranspo Eng'g Slides 1 PDFEloisa PonceAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Footings: Foundation SystemDocumento12 páginasDesign of Footings: Foundation SystemAbdirahman Ahmed IsseAinda não há avaliações
- Appendix GB - 16.6m C/C SPAN & 7.32m CLEAR BRIDGE WIDTH R.C.D.Girder Superstructure Design by LRFD MethodDocumento28 páginasAppendix GB - 16.6m C/C SPAN & 7.32m CLEAR BRIDGE WIDTH R.C.D.Girder Superstructure Design by LRFD MethodSudip ShresthaAinda não há avaliações
- A Comparative Design of Reinforced Concrete Solid Slab Bridge For Different SpansDocumento6 páginasA Comparative Design of Reinforced Concrete Solid Slab Bridge For Different SpansHabeeb ShaikAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Overhead RCC Rectangular WaterDocumento4 páginasDesign of Overhead RCC Rectangular WaterAhmed AwadAinda não há avaliações
- RC Practice Set 2 2016 SolutionsDocumento5 páginasRC Practice Set 2 2016 SolutionsSayed YusufAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 6.11.2 Design of Trapezoidal Combined FootingsDocumento10 páginasCHAPTER 6.11.2 Design of Trapezoidal Combined Footingsalufuq companyAinda não há avaliações
- Acoustic MaterialsDocumento16 páginasAcoustic MaterialsSansar PanchalAinda não há avaliações
- Analytical and Numerical Methods in Structural EngineeringDocumento4 páginasAnalytical and Numerical Methods in Structural EngineeringJasper AgbakwuruAinda não há avaliações
- CE 470-Lect-3 (Analysis of Biaxially Loaded Columns) (Read-Only)Documento22 páginasCE 470-Lect-3 (Analysis of Biaxially Loaded Columns) (Read-Only)Jamal RkhAinda não há avaliações
- Portal Frame Method: General AssumptionsDocumento4 páginasPortal Frame Method: General AssumptionsArslan QureshiAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Slabs For ResidentialDocumento12 páginasDesign of Slabs For ResidentialWilbert ReuyanAinda não há avaliações
- Temam Mohammed HS 2Documento16 páginasTemam Mohammed HS 2Temam MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Analysis of Roof LoadingDocumento6 páginasAnalysis of Roof LoadinghamieraAinda não há avaliações
- 7.continuous BeamsDocumento35 páginas7.continuous BeamsTareck BOU JAOUDEAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials Courseware by A.A JimohDocumento37 páginasStrength of Materials Courseware by A.A JimohSamuelShinaAyodele100% (2)
- Akashi Kaikyo Bridge 1Documento29 páginasAkashi Kaikyo Bridge 1Ssiddhartha VemuriAinda não há avaliações
- RCC Developers LTD.: Design of Retaining Walls @bridge Approach KM 368+385Documento13 páginasRCC Developers LTD.: Design of Retaining Walls @bridge Approach KM 368+385Shivendra KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Arch Dam and Buttress DamDocumento29 páginasArch Dam and Buttress DamsidAinda não há avaliações
- MVSE-101: M.E./M.Tech. I Semester Advance Mathematics & Numerical AnalysisDocumento2 páginasMVSE-101: M.E./M.Tech. I Semester Advance Mathematics & Numerical AnalysisLikky LAinda não há avaliações
- Design of 0.60 M Vertical Drop at KM 0.675 of D-8R Major of Teegaleru CanalDocumento9 páginasDesign of 0.60 M Vertical Drop at KM 0.675 of D-8R Major of Teegaleru CanalVenkataLakshmiKorrapatiAinda não há avaliações
- Question Bank: Cem701 Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Ii Unit 1Documento7 páginasQuestion Bank: Cem701 Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Ii Unit 1RaAinda não há avaliações
- Twist&DrainDocumento2 páginasTwist&DrainPHONY BALONEYAinda não há avaliações
- Cable Stayed BridgeDocumento11 páginasCable Stayed BridgeXan SnaxAinda não há avaliações
- 15a - Tabla de Deflexion para Vigas PDFDocumento4 páginas15a - Tabla de Deflexion para Vigas PDFKarla BonillaAinda não há avaliações
- Sunita BhusalDocumento35 páginasSunita BhusalAbhay SuwalAinda não há avaliações
- Advantages and DisadvantagesDocumento14 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantagespaul machariaAinda não há avaliações
- Retaining Wal DESIGNDocumento7 páginasRetaining Wal DESIGNpankajppatilAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-4 - Analysis of Wind Load Lecture-OneDocumento121 páginasChapter-4 - Analysis of Wind Load Lecture-OneTadesse Megersa100% (1)
- Design of CW Channel For Section 'A-A'Documento30 páginasDesign of CW Channel For Section 'A-A'Hemant SonawadekarAinda não há avaliações
- This Study Resource Was: Transition CurvesDocumento7 páginasThis Study Resource Was: Transition CurvesJoe NjoreAinda não há avaliações
- Problem LossesDocumento5 páginasProblem LossesArvee GavinoAinda não há avaliações
- Isolated - Foundation Design ES en 2015Documento10 páginasIsolated - Foundation Design ES en 2015Dino AbdelaAinda não há avaliações
- CE 315 - HYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 1Documento14 páginasCE 315 - HYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 1Rey Angelo Carbilledo Jr.100% (1)
- (Lecture - 1) Dynamics of Structures Chapter 1Documento40 páginas(Lecture - 1) Dynamics of Structures Chapter 1Masood Ahmed50% (2)
- Two Way SlabDocumento19 páginasTwo Way SlabAllysa Joy MoralesAinda não há avaliações
- Seismicdesign 120341225048028 5Documento82 páginasSeismicdesign 120341225048028 5ssbboossAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Box Type Culvert: Thickness of Side Wall Is OKDocumento11 páginasDesign of Box Type Culvert: Thickness of Side Wall Is OKsanjay vermaAinda não há avaliações
- Types of Sliding DoorsDocumento4 páginasTypes of Sliding Doorsnaveenarora298040Ainda não há avaliações
- Elearning - Vtu.ac - in 17 E-Notes 10CV52 Unit6-MCNDocumento24 páginasElearning - Vtu.ac - in 17 E-Notes 10CV52 Unit6-MCNKunwarKhaliqeAhmad0% (1)
- Sway Concrete Column ExampleDocumento15 páginasSway Concrete Column ExampleIgor GjorgjievAinda não há avaliações
- Deepthi Peshkar II Year Arch. DeptDocumento6 páginasDeepthi Peshkar II Year Arch. DeptPriya DarshniAinda não há avaliações
- Vii Sem B.arch. (CBCS - 2018 Scheme) - Detailed Syllabus PDFDocumento16 páginasVii Sem B.arch. (CBCS - 2018 Scheme) - Detailed Syllabus PDFbhuneshwar paswanAinda não há avaliações
- SAP Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS)Documento13 páginasSAP Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS)SAFETY VOFPLAinda não há avaliações
- Trainer Manual Internal Quality AuditDocumento32 páginasTrainer Manual Internal Quality AuditMuhammad Erwin Yamashita100% (5)
- American J of Comm Psychol - 2023 - Palmer - Looted Artifacts and Museums Perpetuation of Imperialism and RacismDocumento9 páginasAmerican J of Comm Psychol - 2023 - Palmer - Looted Artifacts and Museums Perpetuation of Imperialism and RacismeyeohneeduhAinda não há avaliações
- Sunrise - 12 AB-unlockedDocumento81 páginasSunrise - 12 AB-unlockedMohamed Thanoon50% (2)
- Disbursement VoucherDocumento7 páginasDisbursement VoucherDan MarkAinda não há avaliações
- 3Documento76 páginas3Uday ShankarAinda não há avaliações
- Investigation of The Microstructures, Properties, and Toughening Mechanism of Polypropylene/calcium Carbonate Toughening Masterbatch CompositesDocumento16 páginasInvestigation of The Microstructures, Properties, and Toughening Mechanism of Polypropylene/calcium Carbonate Toughening Masterbatch CompositesHatchi KouAinda não há avaliações
- IJISRT23JUL645Documento11 páginasIJISRT23JUL645International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Asian Paints Final v1Documento20 páginasAsian Paints Final v1Mukul MundleAinda não há avaliações
- Detailed Lesson Plan (Lit)Documento19 páginasDetailed Lesson Plan (Lit)Shan QueentalAinda não há avaliações
- Mericon™ Quant GMO HandbookDocumento44 páginasMericon™ Quant GMO HandbookAnisoara HolbanAinda não há avaliações
- Successful School LeadershipDocumento132 páginasSuccessful School LeadershipDabney90100% (2)
- CBLM - Interpreting Technical DrawingDocumento18 páginasCBLM - Interpreting Technical DrawingGlenn F. Salandanan89% (45)
- Building g5Documento45 páginasBuilding g5ammarsteel68Ainda não há avaliações
- Diagrama Hilux 1KD-2KD PDFDocumento11 páginasDiagrama Hilux 1KD-2KD PDFJeni100% (1)
- LampiranDocumento26 páginasLampiranSekar BeningAinda não há avaliações
- L Rexx PDFDocumento9 páginasL Rexx PDFborisg3Ainda não há avaliações
- BypassGoldManual PDFDocumento6 páginasBypassGoldManual PDFBrad FrancAinda não há avaliações
- Editorial WritingDocumento38 páginasEditorial WritingMelanie Antonio - Paino100% (1)
- 1013CCJ - T3 2019 - Assessment 2 - CompleteDocumento5 páginas1013CCJ - T3 2019 - Assessment 2 - CompleteGeorgie FriedrichsAinda não há avaliações
- Exam TimetableDocumento16 páginasExam Timetablenyarko_eAinda não há avaliações
- Yaskawa V7 ManualsDocumento155 páginasYaskawa V7 ManualsAnonymous GbfoQcCAinda não há avaliações
- Role of Micro-Financing in Women Empowerment: An Empirical Study of Urban PunjabDocumento16 páginasRole of Micro-Financing in Women Empowerment: An Empirical Study of Urban PunjabAnum ZubairAinda não há avaliações
- Prof Ed 3 Module 1Documento9 páginasProf Ed 3 Module 1alexa dawatAinda não há avaliações
- Calculus of Finite Differences: Andreas KlappeneckerDocumento30 páginasCalculus of Finite Differences: Andreas KlappeneckerSouvik RoyAinda não há avaliações
- DR - Rajinikanth - Pharmaceutical ValidationDocumento54 páginasDR - Rajinikanth - Pharmaceutical Validationمحمد عطاAinda não há avaliações
- Integra Facade BrochureDocumento2 páginasIntegra Facade BrochureHarshit PatadiyaAinda não há avaliações
- Model Personal StatementDocumento2 páginasModel Personal StatementSwayam Tripathy100% (1)
- Nielsen Report - The New Trend Among Indonesia's NetizensDocumento20 páginasNielsen Report - The New Trend Among Indonesia's NetizensMarsha ImaniaraAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 2.2 Quantitative Analysis NewDocumento44 páginasChapter 2.2 Quantitative Analysis NewMinase TilayeAinda não há avaliações