Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Yield Point Stress Elastic Limit Elastic Limit
Enviado por
Carlito Jr JavilloDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Yield Point Stress Elastic Limit Elastic Limit
Enviado por
Carlito Jr JavilloDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
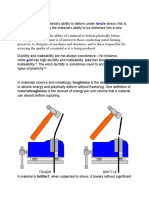
A yield strength or yield point is the material property defined as the stress at which a
material begins to deform plastically. Prior to the yield point the material will deform
elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed.
Elastic limit, maximum stress or force per unit area within a solid material that can arise before
the onset of permanent deformation. When stresses up to the elastic limit are removed,
the material resumes its original size and shape.
Elasticity (physics) In physics, elasticity (from Greek ἐλαστός "ductible") is the ability of a body
to resist a distorting influence or deforming force and to return to its original size and
shape when that influence or force is removed. Solid objects will deform when adequate
forces are applied on them.
Hardness is a measure of how resistant solid matter is to various kinds of permanent shape change
when a compressive force is applied. Some materials (e.g. metals) are harder than others
(e.g. plastics). Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular
bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, there are
different measurements of hardness: scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound
hardness.
Hardness is a measure of how resistant solid matter is to various kinds of permanent shape change
when a compressive force is applied. Some materials (e.g. metals) are harder than others (e.g.
plastics). Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the
behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, there are different measurements of
hardness: scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness.
Hardness is dependent
on ductility, elastic stiffness, plasticity, strain, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity.
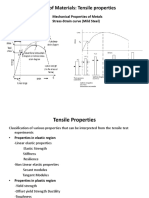
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS) or ultimate
strength, is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to
elongate, as opposed to compressive strength, which withstands loads tending to
reduce size.
In materials science and metallurgy, toughness is the ability of a material to absorb energy and
plastically deform without fracturing. One definition of material toughnessis the amount
of energy per unit volume that a material can absorb before rupturing.
Você também pode gostar
- DuctilityDocumento3 páginasDuctilityCarlo CastorAinda não há avaliações
- Construction Materials and TestingDocumento16 páginasConstruction Materials and TestingAvis pittAinda não há avaliações
- Chem 131......... 2Documento13 páginasChem 131......... 2Nicholas Bonn SingAinda não há avaliações
- Final PresentationDocumento24 páginasFinal PresentationJoy DumlaoAinda não há avaliações
- 02 Strength of Materials IntroDocumento19 páginas02 Strength of Materials IntroEricka HuseñaAinda não há avaliações
- Lab Report:1: STRUC-305Documento3 páginasLab Report:1: STRUC-305Gohar AliAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento7 páginasStrength of Materials: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAerocfdfreakAinda não há avaliações
- Cepc103 - Assignment No.2 - Elizamy Baya - Dcet-2Documento19 páginasCepc103 - Assignment No.2 - Elizamy Baya - Dcet-2Elizamy BayaAinda não há avaliações
- CHEM 1E - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocumento24 páginasCHEM 1E - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsYani BongatAinda não há avaliações
- Elasticity, Sterss and StrainDocumento19 páginasElasticity, Sterss and StrainKhairunnisa PutryAinda não há avaliações
- What Is ElasticityDocumento2 páginasWhat Is Elasticityzhungjian586Ainda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocumento3 páginasMechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsEngr.Hamid Ismail Cheema100% (1)
- Module 2 Biomechanics SolutionDocumento12 páginasModule 2 Biomechanics SolutionSnehasis RoutrayAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical PropDocumento23 páginasMechanical PropfareehaAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Dental Materials (Part 8)Documento27 páginasProperties of Dental Materials (Part 8)Moona WahabAinda não há avaliações
- HardnessDocumento22 páginasHardnessmina_karaliAinda não há avaliações
- Week 5 General Properties of MaterialsDocumento3 páginasWeek 5 General Properties of MaterialsSamantha NamzugAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Properties of RocksDocumento13 páginasMechanical Properties of RocksRizette Palogan100% (1)
- DocumentDocumento17 páginasDocumentRizwan ArshadAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Azealdeen Salih Al-Jawadi: Importance of Rock Mechanics and Its HistoryDocumento5 páginasDr. Azealdeen Salih Al-Jawadi: Importance of Rock Mechanics and Its HistoryAzealdeen AlJawadiAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of MaterialsDocumento7 páginasStrength of Materialsletter_ashish4444100% (1)
- Stress Vs Strain: Stress Is The Force Applied To A Material, Divided by The Material's Cross-Sectional AreaDocumento9 páginasStress Vs Strain: Stress Is The Force Applied To A Material, Divided by The Material's Cross-Sectional AreaAranas TrishaAinda não há avaliações
- ErsdgDocumento8 páginasErsdgOlle rrAinda não há avaliações
- Definitions: (Note: They Still Don't Show Any Plastic Deformation Beyond Proportionality Limit)Documento2 páginasDefinitions: (Note: They Still Don't Show Any Plastic Deformation Beyond Proportionality Limit)WaqasKhanAinda não há avaliações
- Tensile Compressive Strength DeterminationDocumento7 páginasTensile Compressive Strength DeterminationSleepy SpettoAinda não há avaliações
- Rezistenta MetalelorDocumento7 páginasRezistenta Metalelorion_senAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials and CreepDocumento14 páginasStrength of Materials and Creepfabyan mayharAinda não há avaliações
- Ductility / Malleability: ToughnessDocumento3 páginasDuctility / Malleability: ToughnessEyob EyobAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocumento4 páginasMechanical Properties of MaterialsJomarie SojorAinda não há avaliações
- The Following General Properties Are Important in The Study of Dental MaterialsDocumento5 páginasThe Following General Properties Are Important in The Study of Dental MaterialsruchikaAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocumento61 páginasMechanical Properties of MaterialsSarumathiAinda não há avaliações
- "Mechanical Properties": September 2016Documento18 páginas"Mechanical Properties": September 2016Eric LamAinda não há avaliações
- EMATPPTWEEK7Documento25 páginasEMATPPTWEEK7Raniel GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNo EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingAinda não há avaliações
- 03 Properties of Composite MaterilasDocumento17 páginas03 Properties of Composite MaterilasMD Sunjin AhsunAinda não há avaliações
- Lecture 6Documento30 páginasLecture 6Mlkhr lgndbAinda não há avaliações
- Charpy Test: Cold WorkingDocumento5 páginasCharpy Test: Cold WorkingAJAinda não há avaliações
- CE 3133 Chapter 2 Mechanical Behavior and Testing ProceduresDocumento5 páginasCE 3133 Chapter 2 Mechanical Behavior and Testing ProceduresCharles DemaalaAinda não há avaliações
- AST 212 M2 2021 Strength of MaterialsDocumento15 páginasAST 212 M2 2021 Strength of MaterialsJessa BadilloAinda não há avaliações
- Ultimate Tensile Strength: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento2 páginasUltimate Tensile Strength: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaalokaAinda não há avaliações
- TA10 Destructive TestingDocumento12 páginasTA10 Destructive TestingElthon James AganAinda não há avaliações
- Propiedades de Los MetalesDocumento2 páginasPropiedades de Los MetalesÁngel Gabriel Hernández EstradaAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson 1-6 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocumento4 páginasLesson 1-6 Mechanical Properties of MaterialsVince Nixau PadelAinda não há avaliações
- Testing of Materials: Tensile Properties: Mechanical Properties of Metals Stress-Strain Curve (Mild Steel)Documento17 páginasTesting of Materials: Tensile Properties: Mechanical Properties of Metals Stress-Strain Curve (Mild Steel)Srushti MAinda não há avaliações
- Assignment 1Documento5 páginasAssignment 1Young BrotherAinda não há avaliações
- A.Mechanical Properties of Engineering Materials: F/A F/ADocumento11 páginasA.Mechanical Properties of Engineering Materials: F/A F/AsrknotesAinda não há avaliações
- April 7 2009Documento67 páginasApril 7 2009Williams AkandiAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Properties of Materials: Presentation ONDocumento23 páginasMechanical Properties of Materials: Presentation ONAbhishek SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Tata SteelDocumento3 páginasTata Steelmounika spoorthyAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsDocumento3 páginasStrength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsZoe FallurinAinda não há avaliações
- Steel StrengthDocumento8 páginasSteel StrengthVishalAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Strain Curve and Materials ClassificationDocumento16 páginasStress Strain Curve and Materials Classificationc9syfxzjftAinda não há avaliações
- Construction Complete TopicDocumento245 páginasConstruction Complete TopicGlen MacAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Concepts of Material MechanicsDocumento2 páginasBasic Concepts of Material MechanicsGuitar & moreAinda não há avaliações
- Basic ConceptsDocumento2 páginasBasic ConceptsGuitar & moreAinda não há avaliações
- Stainless SteelDocumento162 páginasStainless SteelNavya AnilAinda não há avaliações
- Plasticity and Elasticity TheoryDocumento1 páginaPlasticity and Elasticity TheoryJef Michael L. DahuylaAinda não há avaliações
- Useful Solutions For Standard ProblemsDocumento2 páginasUseful Solutions For Standard ProblemsAmjad Khan BanuzaiAinda não há avaliações
- Deformation (Engineering) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento2 páginasDeformation (Engineering) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadidodido_67Ainda não há avaliações
- Code - Aster: Integration of The Relations of Behavior Elastoplastic of Von MisesDocumento27 páginasCode - Aster: Integration of The Relations of Behavior Elastoplastic of Von MisesVinícius GonçalvesAinda não há avaliações
- Mec411 NL Chapter1 1Documento91 páginasMec411 NL Chapter1 1Naavalan Krishnaga Art'wAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Steel Frames With Buckling Restrained Braces: M. Bosco, E.M. Marino & P.P. RossiDocumento10 páginasDesign of Steel Frames With Buckling Restrained Braces: M. Bosco, E.M. Marino & P.P. RossiPremalatha JeyaramAinda não há avaliações
- Normality CriterionDocumento10 páginasNormality Criteriong401992Ainda não há avaliações
- Chip FormationDocumento27 páginasChip FormationJasvinder SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Green Book SolutionDocumento44 páginasGreen Book SolutionCaleb RaphaelAinda não há avaliações
- MDP Module 2Documento84 páginasMDP Module 2ADITYA RAJ CHOUDHARYAinda não há avaliações
- Tensile Properties and Morphology PP/EPDM/Glass Bead Ternary CompositesDocumento10 páginasTensile Properties and Morphology PP/EPDM/Glass Bead Ternary CompositesmahinevareAinda não há avaliações
- A Critical Review of Friction Measurement of Textile MaterialsDocumento10 páginasA Critical Review of Friction Measurement of Textile MaterialsNilavan MuthuAinda não há avaliações
- Laterally LoadedDocumento13 páginasLaterally LoadedbiniAinda não há avaliações
- Design Fundamentals-FullDocumento64 páginasDesign Fundamentals-FullNishant DeyAinda não há avaliações
- Recent Advances in Active Metal Brazing of Ceramics and Process-S12540-019-00536-4Documento12 páginasRecent Advances in Active Metal Brazing of Ceramics and Process-S12540-019-00536-4sebjangAinda não há avaliações
- Properties of Construction Materials and Their Stress/strain BehaviourDocumento15 páginasProperties of Construction Materials and Their Stress/strain BehaviourOmokhiboria JoshuaAinda não há avaliações
- Ch. 7 Dislocation and StrengtheningDocumento6 páginasCh. 7 Dislocation and Strengtheningravi hargassnerAinda não há avaliações
- Using The Failure Assessment Diagram Method With Fatigue Crack Growth To Determine Leak-before-RuptureDocumento15 páginasUsing The Failure Assessment Diagram Method With Fatigue Crack Growth To Determine Leak-before-RuptureMohammed EljammalAinda não há avaliações
- Hapter: MetalsDocumento55 páginasHapter: Metalsbedo39Ainda não há avaliações
- Automotive Stabilizer BarDocumento9 páginasAutomotive Stabilizer BarEidolon CosplayAinda não há avaliações
- Advanced Drilling Practices - Casing Design PDFDocumento92 páginasAdvanced Drilling Practices - Casing Design PDFAnonymous H9n5g3aaCEAinda não há avaliações
- LS-DYNA Wood Material Model 143 PDFDocumento166 páginasLS-DYNA Wood Material Model 143 PDFAnonymous Vi1lrHAinda não há avaliações
- Set 01Documento161 páginasSet 01ashishjakateAinda não há avaliações
- Elementary Design of StructuresDocumento75 páginasElementary Design of StructuresNADS UG100% (1)
- Alistair Doig - Some Metallurgical Aspects of Shaped Charge LinersDocumento3 páginasAlistair Doig - Some Metallurgical Aspects of Shaped Charge LinersGhoree23456Ainda não há avaliações
- 2016 Turning of The AISI 1045Documento8 páginas2016 Turning of The AISI 1045HERNANDO CORREAAinda não há avaliações
- AbcDocumento14 páginasAbcEjaz Ahmed RanaAinda não há avaliações
- Forming Notes PDFDocumento4 páginasForming Notes PDFMuthuKumarAinda não há avaliações
- Ship Structures II Lecture NotesDocumento174 páginasShip Structures II Lecture NotesDina ANDRIAMAHEFAHERYAinda não há avaliações
- Foundation of The New Botlek Lifting Bridge in The NetherlandsDocumento12 páginasFoundation of The New Botlek Lifting Bridge in The NetherlandsmabuhamdAinda não há avaliações
- D) Dcam Part 66 - Module 6Documento358 páginasD) Dcam Part 66 - Module 6Tharrmaselan VmanimaranAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapters 1-4Documento219 páginasMechanical Behaviour of Materials Chapters 1-4brettbook67% (3)
- MaterialsDocumento285 páginasMaterialsMurdock Howling MadAinda não há avaliações