Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Ob Osce.04 CTG Reading
Enviado por
Dasha VeeDescrição original:
Título original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Ob Osce.04 CTG Reading
Enviado por
Dasha VeeDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
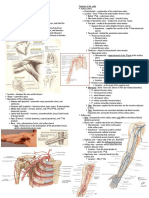
OBSTETRICS 2
CTG Reading
Dr. Candelario | OB clinics
I. FETAL CARDIOTOCOGRAPHY
A technical means of recording (GRAPHY)
Fetal Heart Rate (CARDIO) Fetal Heart Rate
Uterine Contractions (TOCO)
A test of fetal well-being (HEALTH)
Done by use of ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITOR (EFM)
Detect antepartum or intrapartum (LABOR) fetal hypoxia/asphyxia
Uterine contractions
II. WHAT REGULATES FETAL HEART RATE?
PRIMARY FACTORS SECONDARY FACTORS
- Autonomic NS (Sympathetic & Central Nervous system: IV. WHAT IS WRITTEN IN THE EFM/PAPER?
Parasympathetic) - Cerebral cortex Date; Time; Name; Age; OB score; Risk Factor; Diagnosis
- Baroreceptors - Hypothalamus Internal Exam: Cervix; BOW; Amniotic Fluid
- Chemoreceptors - Medulla Oblongata Vital signs
Adrenals Drugs
III. PARTS OF AN ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITOR V. POSITIONING OF ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITOR
History taking (Risk assessment)
Take vital signs every 5 minutes
Auscultate FHR
Apply transducers (Doppler/tocodynamometer)
o Apply gel on the Doppler tranducer (where FHR is best auscultated)
o DO NOT apply gel on the tocodynamometer (fundus)
Position: Semi-fowler (avoid supine)
o Upright
o Half sitting
o Lateral recumbent
VI. TYPES OF FETAL CTG
EXTERNAL MONITORING INTERNAL MONITORING
Transducers (externally) Spiral electrode and internal pressure
Antepartum/intrapartum catheter (internal)
Requirement: Cervix dilated and
ruptured BOW
Intrapartum ONLY
1. Doppler or ultrasound transducer
Will detect FHR
Placed on area where FHR is best auscultated
2. Tocodynamometer (Pressure sensing device)
Placed at the uterine fundus to detect uterine contractions
3. Event marker
pushed by the mother when she feels fetal movement
4. CTG Paper
Paper speed: 1 cm/min or 3 cm/min
Transcribers: OB NOTES TEAM Page 1 of 6
OBSTETRICS 2
VII. INDICATIONS OF FETAL CTG 2. FHR VARIABILITY
Predominant indication of antenatal testing is a pregnancy at increased risk for fetal Normal 6-25 beats (FIGO 5-25)
hypoxia/asphyxia/death.
Reduced 3-5 beats
MATERNAL CONDITIONS FETAL CONDITIONS:
- Hypertension - IUGR Poor 0-2 beats
- Diabetes - Decreased fetal movement
Saltatory >25 beats
- Isoimmunization - Postdate pregnancy
- Chronic renal disease - Multiple pregnancy a. INCREASED VARIABILITY (SALTATORY)
- SLE - Prior history of unexplained Causes:
- Cardiac disease fetal death o Excessive fetal movement
- Hemoglobinopathies o Transient hypoxia – cord compression during 2nd stage of labor
- hyperthyroidism
PLACENTA AMNIOTIC FLUID
- Placenta previa - Meconium staining
- Abruption placenta - oligohydramnios
VIII. BASIC COMPONENTS OF FETAL HEART PATTERN
1. Baseline FHR
2. FHR variability
3. Periodic changes: accelerations and decelerations
4. Change in trends over time
1. BASELINE FHR b. DECREASED/REDUCED VARIABILITY
It is the estimated in the time period of 10 minutes and expressed in beats per minute (bpm) Causes:
Normal: 110-160 o Fetus is sleeping o Drugs – opiates, benzodiazepines,
o Fetal acidosis methyldopa, magnesium sulfate
o Fetal tachycardia o Prematurity
o Congenital heart abnormalities
Bradycardia (<110 bpm) Tachycardia (>160 bpm)
- Hypoxia - Maternal fever
- Cord prolapse - Hyperthyroidism c. SINUSOIDAL VARIABILITY
- Prolonged cord compression - Prematurity seen in anemia, RH isoimmunization, and hypoxia
- Anxiety
Severe: <100 bpm Severe: >180 bpm
Transcribers: OB NOTES TEAM Page 2 of 6
OBSTETRICS 2
3. DECELERATIONS
a. EARLY DECELERATION
head compression
c. VARIABLE DECELERATION
cord compression
b. LATE DECELERATION
uteroplacental insufficiency
MEMORY TIP: VEAL CHOP
V – variable C – cord compression
E – early H – head compression
A – acceleration O – okay
L – late P – placental insufficiency
Transcribers: OB NOTES TEAM Page 3 of 6
OBSTETRICS 2
IX. UTERINE ACTIVITY - Absence: may suggest fetal distress
Interval - Physiology: Intact cortical function where fetal movement is elicited will result to FHR acceleration
Intensity - Loss of fetal reactivity may mean hypoxia and neurologic depression and acidosis
Duration - Done at 32 weeks
Resting tone
STEPS IN NON-STRESS TEST
A. Tachysystole 1. History/PE (auscultate FH tone)
- 5 uterine contractions in 10 minutes 2. Doppler Transducer (are FH tone)
- Risk for fetal hypoxia 3. Tocodynamometer (fundus of uterus)
- Interval (1-2 mins) 4. Position (semirecumbent position)
- Intensity: severe (80 mmHg/contraction) 5. Mother: push event marker (fetal movement)
- Duration (50-60 seconds) 6. Run paper (20 minutes)
- Resting tone (20 mmHg)
DEFINITION OF ACCELERATION
≥32 weeks (baseline rate 15 beats and duration of 15 seconds or more
>32 weeks (10 bpm/10 seconds)
INTERPRETATION
Reactive 2 or more accelerations
Non reactive 1 or no acceleration
Interpretation Reactive NST (Good fetal health)
Reactive NST
B. MONTEVIDEO UNITS
Non-reactive NST
X. CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
Nonstress Test (Antepartum)
Contraction Stress test
Intrapartum CTG
A. NONSTRESS TEST (ANTEPARTUM CTG)
- fetal heart rate accelerates with fetal movement
- Indicator: Good Fetal Health
Transcribers: OB NOTES TEAM Page 4 of 6
OBSTETRICS 2
B. INTRAPARTUM CTG XI. CASES
- Admission test (Labor) A 28 y/o woman G2P0 (0010) 34 weeks AOG, Preterm rupture of membranes for 24 hours
- Intrapartum monitoring
CATEGORY I - Normal rate
Reassuring pattern - Normal variability NST REPORT:
- No decelerations BFHR: 140 bpm
- (+/-) accelerations BFHR Variability: Normal
CATEGORY II - Tachycardia Acceleration: Present (7)
Suspicious pattern - Reduced variability Deceleration: Absent
- Moderate variable Interpretation: Reactive NST
decelerations
CATEGORY III - Abnormal FHR
Nonreassuring pattern - Late decelerations
- Severe variable decelerations
- Sinusoidal pattern
- Poor variability
An 18 y/o woman G1P0, 34 week with Preeclampsia, BP: 160/100mmHG. Ultrasound revealed small
baby and oligohydramnios.
I II III BFHR: 150 bpm
BFHR Variability: Poor or absent
Acceleration: Absent
Deceleration: Absent
Interpretation: Non-reactive NST
For more details: please read our transes from the lecture on Fetal Assessment last
semester: M.03 and M.04.
REPORT YOUR FINDINGS USING THE DR C BraVADO FORMAT
DR DEFINE RISK Low or high
C CONTRACTIONS Comment on frequency, etc. (intensity, duration)
Bra BASELINE RATE Bradycardia, normal, tachycardia
V VARIABILITY At least 10-15 bpm (persistent reduced variability is a
particularly ominous sign)
Increased (salutatory), reduced/poor, absent, sinusoidal or
normal
A ACCELERATIONS Present or absent
D DECELERATIONS Early, variable, or late
O OVERALL Assessment (category I/II/III) and plan of management
Transcribers: OB NOTES TEAM Page 5 of 6
OBSTETRICS 2
Transcribers: OB NOTES TEAM Page 6 of 6
Você também pode gostar
- Classification and Diagnosis of Endometrial HyperplasiaDocumento7 páginasClassification and Diagnosis of Endometrial HyperplasiaaksinuAinda não há avaliações
- DRUGS DURING PREGNANCY (Feso4, Folic Acid)Documento2 páginasDRUGS DURING PREGNANCY (Feso4, Folic Acid)Angelyn Bucaso50% (2)
- Ob CPCDocumento80 páginasOb CPCDonna Meryll Eduave-EsguerraAinda não há avaliações
- History Examination of Gynecology and Obstetrics PatientsDocumento3 páginasHistory Examination of Gynecology and Obstetrics PatientsAgus WijayaAinda não há avaliações
- The Medical Management of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding in Reproductive-Aged WomenDocumento14 páginasThe Medical Management of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding in Reproductive-Aged Womendiegoesteban1234Ainda não há avaliações
- Derma Case Write UpDocumento9 páginasDerma Case Write UpAmbhi GanaAinda não há avaliações
- Cervical Cancer in PregnancyDocumento21 páginasCervical Cancer in Pregnancymineresearch100% (1)
- Gynecology: Recurrent Pregnancy LossDocumento6 páginasGynecology: Recurrent Pregnancy LossDawn Marco100% (1)
- O and G Notes Notebank NumberedDocumento173 páginasO and G Notes Notebank NumberedPerscitus Ali القحطانيAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study CA Lower RectumDocumento47 páginasCase Study CA Lower RectumArtyom Granovskiy100% (1)
- Expectatant Management of Cesarean Scar Ectopic PregnancyDocumento5 páginasExpectatant Management of Cesarean Scar Ectopic PregnancyEricAinda não há avaliações
- Instrumental DeliveryDocumento25 páginasInstrumental DeliveryAhmed ElmohandesAinda não há avaliações
- CardiotocographyDocumento27 páginasCardiotocographyJesica CahyadyAinda não há avaliações
- Impey Obs and Gynae Revision Notes PDFDocumento9 páginasImpey Obs and Gynae Revision Notes PDFRoiseAinda não há avaliações
- 3 16Documento27 páginas3 16Iful SaifullahAinda não há avaliações
- OSCE Reviewer 2013Documento4 páginasOSCE Reviewer 2013rere choiAinda não há avaliações
- AUB StartedDocumento13 páginasAUB StartedIbrahim AbdullahAinda não há avaliações
- Obstetrics Case PresentationDocumento27 páginasObstetrics Case PresentationMahaprasad sahoo 77Ainda não há avaliações
- Basic Investigation of An Infertile CoupleDocumento53 páginasBasic Investigation of An Infertile CoupleRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorAinda não há avaliações
- Group II Makati Medical Center m8 1Documento107 páginasGroup II Makati Medical Center m8 1CASSANDRAJUL VARINAinda não há avaliações
- Tourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesDocumento4 páginasTourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesjoymaeannAinda não há avaliações
- Ob Gyn Sample HisotryDocumento4 páginasOb Gyn Sample HisotrySophia RubiaAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostic Work Up of Ovarian CystsDocumento12 páginasDiagnostic Work Up of Ovarian CystsAnshul KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocumento8 páginasPostpartum HemorrhageMazlina MaidinAinda não há avaliações
- Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Pregnancy - Prevention - UpToDateDocumento11 páginasDeep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Pregnancy - Prevention - UpToDateGabyta007Ainda não há avaliações
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome in PregnancyDocumento7 páginasAntiphospholipid Syndrome in PregnancyDara Dasawulansari SyamsuriAinda não há avaliações
- Gyne Case COCDocumento37 páginasGyne Case COCLian BaylosisAinda não há avaliações
- 11abnormal Uterine BleedingDocumento32 páginas11abnormal Uterine BleedingAkinbani MoyosoreAinda não há avaliações
- I. Intrapartum Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Ob Rotation OsceDocumento24 páginasI. Intrapartum Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Ob Rotation OsceAngelie Therese ChuaAinda não há avaliações
- #LungDocumento1 página#LungameerabestAinda não há avaliações
- CASE STUDY Lung Ca With Pleural EffDocumento8 páginasCASE STUDY Lung Ca With Pleural EffL4 CLERK - UY, Rhea Andrea F.Ainda não há avaliações
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocumento5 páginasHyperemesis GravidarumsalamredAinda não há avaliações
- Antenatal Fetal MonitoringDocumento28 páginasAntenatal Fetal MonitoringchestersudhakarAinda não há avaliações
- Collin Grimes Patient Write Up June 14Documento4 páginasCollin Grimes Patient Write Up June 14CollinAinda não há avaliações
- Gynecology - Comprehensive Examination of The Female CheckedDocumento3 páginasGynecology - Comprehensive Examination of The Female CheckedMuhammad AdnanAinda não há avaliações
- Neonatal Case Presentation 2Documento6 páginasNeonatal Case Presentation 2Rabi SyedAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Cwu OngDocumento18 páginas1st Cwu Ongdila_ayubAinda não há avaliações
- 107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineDocumento6 páginas107 Rle Virtual Duty - Opd: Internal MedicineGiel Margareth LindoAinda não há avaliações
- Gynecology 2.01.2 Benign Neoplasms of The Ovary and Oviducts - Dr. Co-HidalgoDocumento7 páginasGynecology 2.01.2 Benign Neoplasms of The Ovary and Oviducts - Dr. Co-HidalgoMarc Francis AlayAinda não há avaliações
- Myoma UteriDocumento8 páginasMyoma UteriFaraida Arvilla100% (1)
- Cme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Documento36 páginasCme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Hakimah K. SuhaimiAinda não há avaliações
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocumento7 páginasAbnormal Uterine BleedingBrian Fry100% (1)
- Case History Ob & Gyne 4Documento6 páginasCase History Ob & Gyne 4maksventileAinda não há avaliações
- Uterine Leiomyoma - Endometriosis.Documento48 páginasUterine Leiomyoma - Endometriosis.Inna CazacliuAinda não há avaliações
- Angelic - Doc - Neonatal JaundiceDocumento16 páginasAngelic - Doc - Neonatal JaundiceAngy100% (5)
- Changing Trends in Cesarean DeliveryDocumento7 páginasChanging Trends in Cesarean DeliveryEditor_IAIMAinda não há avaliações
- Correlative AnatomyDocumento19 páginasCorrelative AnatomyLicensed to HealAinda não há avaliações
- Ovarian Cysts and Cancer in PregnancyDocumento15 páginasOvarian Cysts and Cancer in Pregnancykarina100% (1)
- Postpartum CollapseDocumento54 páginasPostpartum Collapsemedical chroniclesAinda não há avaliações
- Mucinous Cystadenoma 0708Documento12 páginasMucinous Cystadenoma 0708eosfieldAinda não há avaliações
- Mass in Epigastrium-2Documento37 páginasMass in Epigastrium-2brown_chocolate87643100% (1)
- OSCE Revision OBG DocumentDocumento60 páginasOSCE Revision OBG DocumentshreyaAinda não há avaliações
- Sheehan Syndrom L. HaddockDocumento9 páginasSheehan Syndrom L. Haddockfreddyop72Ainda não há avaliações
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocumento5 páginasAbnormal Uterine Bleedingwuryan dewiAinda não há avaliações
- Case Protocol Kawasaki DiseaseDocumento5 páginasCase Protocol Kawasaki DiseaseFranz SalazarAinda não há avaliações
- OBGYN TransDocumento6 páginasOBGYN TransanonymousAinda não há avaliações
- Shivaani (Internal Medicine CWU)Documento12 páginasShivaani (Internal Medicine CWU)S.M. Manogaran Shivaani AP S.M. ManogaranAinda não há avaliações
- 1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyDocumento6 páginas1 GYNE 3 - History, PE, Prevention Interaction of Disease and PhysiologyIrene FranzAinda não há avaliações
- OB OSCE ReviewerDocumento5 páginasOB OSCE ReviewerPao Ali100% (1)
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyNo EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisAinda não há avaliações
- The Characteristic Ultrasound Features of Specific Types of Ovarian Pathology (Review) PDFDocumento14 páginasThe Characteristic Ultrasound Features of Specific Types of Ovarian Pathology (Review) PDFDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- OB OSCE.06 OB GYNE ULTRASOUND (Dr. Ursua) PDFDocumento1 páginaOB OSCE.06 OB GYNE ULTRASOUND (Dr. Ursua) PDFDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Journal of Gynecologic Oncology Volume 9 Number 1 2012Documento48 páginasPhilippine Journal of Gynecologic Oncology Volume 9 Number 1 2012Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- F.07 STD AND INFECTIONS IN PREGNANCY (DR - Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 2)Documento3 páginasF.07 STD AND INFECTIONS IN PREGNANCY (DR - Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 2)Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- WJR 5 113Documento13 páginasWJR 5 113Valian IndrianyAinda não há avaliações
- F.08 PULMONARY DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr.-Badua) 5-7-2019Documento5 páginasF.08 PULMONARY DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr.-Badua) 5-7-2019Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- F.07 STD AND INFECTIONS IN PREGNANCY (DR - Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 2)Documento3 páginasF.07 STD AND INFECTIONS IN PREGNANCY (DR - Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 2)Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- F.03 HEMATOLOGIC DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (DR - Taguiling) 04-25-2019 (Part 1) PDFDocumento4 páginasF.03 HEMATOLOGIC DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (DR - Taguiling) 04-25-2019 (Part 1) PDFDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Diagnostico y Manejo de Masas AnexialesDocumento6 páginasDiagnostico y Manejo de Masas AnexialesChristopher Hernán Valenzuela ArancibiaAinda não há avaliações
- F.01 NEUROLOGIC AND PSYCHIATRIC DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr. Arcellan) 04-10-2019 PDFDocumento10 páginasF.01 NEUROLOGIC AND PSYCHIATRIC DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr. Arcellan) 04-10-2019 PDFDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- F.02 DERMATOLOGIC DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr. Taguiling) 04-12-2019 PDFDocumento5 páginasF.02 DERMATOLOGIC DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr. Taguiling) 04-12-2019 PDFDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- P.07 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Dr. Manalo 9-8-16Documento4 páginasP.07 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Dr. Manalo 9-8-16Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Practice Bulletin: Management of Adnexal MassesDocumento14 páginasPractice Bulletin: Management of Adnexal MassesDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- F.08 PULMONARY DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr.-Badua) 5-7-2019Documento5 páginasF.08 PULMONARY DISEASES IN PREGNANCY (Dr.-Badua) 5-7-2019Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Mental HealthDocumento4 páginasMental HealthDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- P.09 OBSTETRIC HEMORRHAGE (Dr. Ursua) 02-07-2019 (Part 1)Documento3 páginasP.09 OBSTETRIC HEMORRHAGE (Dr. Ursua) 02-07-2019 (Part 1)Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- F.06 STD and Infections in Pregnancy (Dr. Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 1)Documento5 páginasF.06 STD and Infections in Pregnancy (Dr. Jandoc) 05-03-2019 (Part 1)Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- 2011 Full Page Calendar - TomKat StudioDocumento12 páginas2011 Full Page Calendar - TomKat StudioThe TomKat StudioAinda não há avaliações
- DiagnosisDocumento8 páginasDiagnosisDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Embryogenesis & Fetal DevelopementDocumento38 páginasEmbryogenesis & Fetal DevelopementDasha Vee100% (1)
- F.09 BONE RADIOLOGY - Dr. GalangDocumento11 páginasF.09 BONE RADIOLOGY - Dr. GalangDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFDocumento140 páginasPhilippine CPG On The Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Adults-2015 Update - Part 2 PDFspringdingAinda não há avaliações
- Thyroid PDFDocumento9 páginasThyroid PDFDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Obstetrics 2: Obstetric Hemorrhage (Part 2)Documento4 páginasObstetrics 2: Obstetric Hemorrhage (Part 2)Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- m.13 Dietary Supplements & Herbal Medications (Dr. Buñag) 04-04-18Documento4 páginasm.13 Dietary Supplements & Herbal Medications (Dr. Buñag) 04-04-18Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- Antiviral Chemotherapy and Prophylaxis: Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and FamciclovirDocumento8 páginasAntiviral Chemotherapy and Prophylaxis: Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and FamciclovirDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- m.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Documento3 páginasm.10b Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases 03-26-18 (Table)Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- f.02 Intellectual Disabilities (Dr. Rebucal) 04-11-2019Documento4 páginasf.02 Intellectual Disabilities (Dr. Rebucal) 04-11-2019Dasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- F.08 Death CertificateDocumento7 páginasF.08 Death CertificateDasha VeeAinda não há avaliações
- HyperkalemiaDocumento9 páginasHyperkalemiaFabdul RaufAinda não há avaliações
- Gross HSB A - Axillary RegionDocumento3 páginasGross HSB A - Axillary RegionAngelo BautistaAinda não há avaliações
- Nicotine: How Does Nicotine Deliver Its Effect?Documento6 páginasNicotine: How Does Nicotine Deliver Its Effect?jmolaecheaAinda não há avaliações
- NCCT Phlebotomy ReviewDocumento138 páginasNCCT Phlebotomy ReviewArturo ColinAinda não há avaliações
- Approach To A Child With Coma by Dr. M. A. Rahim 2 Year PGT Paediatric MedicineDocumento64 páginasApproach To A Child With Coma by Dr. M. A. Rahim 2 Year PGT Paediatric MedicineRipan SahaAinda não há avaliações
- CVS Examination ProformaDocumento4 páginasCVS Examination ProformaAnantha KrishnanAinda não há avaliações
- EpicHospitalAhmedabad BrochureDocumento32 páginasEpicHospitalAhmedabad Brochurerakesh jayal100% (1)
- Compre PE and ROSDocumento7 páginasCompre PE and ROSBatch V Med 2 SY 21-22Ainda não há avaliações
- Presciption MBBS CVS 2003Documento17 páginasPresciption MBBS CVS 2003PDummyAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Failure in ChildrenDocumento27 páginasHeart Failure in ChildrendenakarinaAinda não há avaliações
- Hospital Acquired PneumoniaDocumento23 páginasHospital Acquired Pneumoniadarmarianto100% (1)
- AssessmentDocumento3 páginasAssessmentharlequingirl_116Ainda não há avaliações
- Notes On Cardiovascular SystemDocumento3 páginasNotes On Cardiovascular Systemmohamed waleedAinda não há avaliações
- Certificate of IsolationDocumento19 páginasCertificate of IsolationSweet SimyunnAinda não há avaliações
- Another Research Paper For FypDocumento13 páginasAnother Research Paper For FypSehar KhanAinda não há avaliações
- Sin Heart Smart ZoneDocumento20 páginasSin Heart Smart ZoneMatteo PanciroliAinda não há avaliações
- Rheumatic Fever Is AnDocumento7 páginasRheumatic Fever Is AnHamza SaeedAinda não há avaliações
- CHF FC III Ec Mitral StenosisDocumento36 páginasCHF FC III Ec Mitral Stenosisbroken18bear100% (1)
- Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion For Stroke Prevention in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation 2021Documento18 páginasLeft Atrial Appendage Occlusion For Stroke Prevention in Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation 2021吳醫師Ainda não há avaliações
- 3ef0b9f5 Cc1jurnalvco99Documento36 páginas3ef0b9f5 Cc1jurnalvco99Tasha FarahAinda não há avaliações
- Body Fluids Analysis LectureDocumento17 páginasBody Fluids Analysis LectureAsd Asd100% (1)
- Respiration PHYSIODocumento23 páginasRespiration PHYSIOTauseef AfridiAinda não há avaliações
- Arterial Thrombosis by AbrarDocumento20 páginasArterial Thrombosis by AbrarZain HadiAinda não há avaliações
- Class Presentation CVADocumento23 páginasClass Presentation CVAAmbika Ghosh SenAinda não há avaliações
- PHARMACOLOGY Semi FinalDocumento10 páginasPHARMACOLOGY Semi FinalCyberLifeAinda não há avaliações
- ACLS 2020 Update FOR CMEDocumento51 páginasACLS 2020 Update FOR CMEyrx8k8j9qyAinda não há avaliações
- 418RLE M2 SL1 Basic ECGDocumento8 páginas418RLE M2 SL1 Basic ECGCamille Neypes CarreraAinda não há avaliações
- نسخة Biomarkers of Myocardial Infarction 4Documento49 páginasنسخة Biomarkers of Myocardial Infarction 4نوف الحربي.Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiopulmonary McqsDocumento2 páginasCardiopulmonary McqsmohtishimAinda não há avaliações