Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
1333340893
Enviado por
Debdeep BhuniaDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
1333340893
Enviado por
Debdeep BhuniaDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
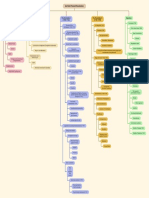
MIND
The French Revolution (1789-1799)
Path towards a Republican France
French Society Before French Revolution
Led to emergence of political club like the A new assembly called the
Louis XVI entered into secret negotiations
Jacobins whose members belonged to convention was elected with the
with king of Prussia to get power
lower middle class declaration of France a republic
Monarchy (Louis XVI at the Time of Revolution) Three Estates (In Republic government people
In counter, National Assembly declared Jacobins planned insurrection of elect the government including
war against Prussia and Austria in 1792 Parisians in 1792 who were angered by the head of the government)
high prices of food
First Estate-Clergy (vast and wealthy Second Estate-Nobility (enjoyed feudal Third Estate-Businessmen, Merchants,
class with exemption from paying taxes) priviliges and exempted from paying taxes) Lawyers, Peasants, Artisans, Servants etc. Large section of population participated as they King Louis XVI and Queen Marie
(paid tax (tithes) to the church and direct saw it a war against kings and aristocracies The Palace of the Tuileries was stormed Antoinette were sentenced to death
tax, taille, and indirect tax to the state) and the royal family was imprisoned
The Reign of Terror in France (1793-1794)
Causes of French Revolution
Rule of Jacobians
Maximilian Robespierre, the Jacobian leader, Robespierre was convicted, arrested and guillotined
Political Social Economic Ideas of followed policy of severe control and punishment in 1794 and the Jacobian government fell fell
Philosophers
Over exploitation of New constitution established denying concentration
Nobles and members against him were arrested and guillotined
Absolute Inefficient middle class due to Debt due to wars Unfair Taxes of power in a one-man executive
Monarchy Government feudal system
Inequality in taxes as the The government issued laws placing a maximum ceiling on wages and prices Led to the clash of the Directors with the Legislative Councils
burden was on the third estate
Louis XVI had Ministers were
unlimited power and corrupted and were France engaged in Participation in
lead a luxurious life selected on basis of long years of wars American war of Over exploitation by the policies led to the revolt of people Political instability paved the way for the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte
birth and favouritism. which drained the Independence Ideas given by philosophers like John
financial resources added more debt Locke, Jean Jacques Rousseau
influenced common people Women in France Slavery in France
Events of the French Revolution Women were denied education and job Slavery began in 17th century in the colonies of the Caribbean
training except noble class women for the supply of tobacco, indigo, sugar and coffee
Immediate Cause Louis XVI proposed to Assembly led by Mirabeau and Abbe Sieyes Feudal system and taxes including The condition of working women was Europeans denied to work at such distant places thus resulted in shortage of
increase taxes due to huge Royal Debt got busy in drafting the Constitution. tithes got abolished miserable due to low wages
Led to the emergence of a Triangular slave trade between Europe,
Led to the emergence of women’s political Africa and the Americas
He called Assembly of Estate Generals in On the other hand, economic condition Separation of power between clubs and newspapers to demand equal rights
1789 to pass the proposal. worsened due to bad harvest which legislature, executive and
forced people to revolt. judiciary established
Resulted in exploitation of slave to meet the growing demand in European markets
Dispute in assembly over voting procedure. Demands included right to vote
(1st and 2nd estate demanded 1 vote/estate and and to hold political office
Agitated crowd stormed and Constitution began with a Forced the National Assembly to pass the law to abolish slavery in 1794
3rd estate wanted 1 vote for each delegate)
destroyed the Bastille. declaration of the rights of
man and citizen Revolutionary government introduced laws
Louis XVI rejected the proposal and 3rd estate (Right to life, freedom of Slavery reemerged after 10 years during the reign of Napoleon Bonaparte
Louis XVI finally recognised National speech, freedom of opinion
withdrew from the assembly in protest.
Assembly and established constitutional and equality before law) Access to No forced Marriage as Divorce
monarchy. Revolt by the slaves for the rights paved the way for abolition of slavery in 1848
education marriage a contract made legal
They assembled in a tennis court is Versailles
and established National Assembly.
Aftermath of French Revolution
Various Changes
Freedom of speech and expression Introduced laws including protection of private property
Changes in lives of women, men
declared as the natural right and uniform system of weights and measures
and children due to certain laws
Led to the emergence of Napoleon Later became dictator of France which led to his
Abolition of censorship paved fall and he was defeated in waterloo in 1815
Bonaparte as the French ruler
way for freedom of press
Você também pode gostar
- CompressedDocumento33 páginasCompressedanastasia nandaAinda não há avaliações
- 2nd Unit II French RevolutionDocumento1 página2nd Unit II French Revolutiondanile62Ainda não há avaliações
- History - Year 3 IP Mid-Year Examination 2011 Revision NotesDocumento4 páginasHistory - Year 3 IP Mid-Year Examination 2011 Revision NotesLee Kay HoweAinda não há avaliações
- The Age of The Liberal Revolutions (1789 - 1871) Unit 2 - 2Documento49 páginasThe Age of The Liberal Revolutions (1789 - 1871) Unit 2 - 2naiuwu69Ainda não há avaliações
- French Revolution Explained In 10 Words: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo EverandFrench Revolution Explained In 10 Words: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 5.2 FRENCH REVOLUTIONDocumento38 páginasUnit 5.2 FRENCH REVOLUTIONVega Suffo JiménezAinda não há avaliações
- Napoleon BonaparteDocumento8 páginasNapoleon BonaparteLouelle Bernadette DadanAinda não há avaliações
- Bill of RightDocumento26 páginasBill of RightsenoritaAinda não há avaliações
- History CH 1Documento6 páginasHistory CH 1Ravinder KumarAinda não há avaliações
- The French Revolution HistoryDocumento14 páginasThe French Revolution HistoryMaría Campal GarcíaAinda não há avaliações
- French Revolution Fact File English The French Revolution Fact File - Ver - 7Documento3 páginasFrench Revolution Fact File English The French Revolution Fact File - Ver - 7tamilore.ishola.101Ainda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionDocumento20 páginasFrench Revolutionapi-27015740Ainda não há avaliações
- French Revolution - World History EncyclopediaDocumento9 páginasFrench Revolution - World History Encyclopedia•Suki• •Chan•Ainda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionDocumento16 páginasFrench RevolutionRohit SaxenaAinda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionDocumento25 páginasFrench RevolutionUdit JainAinda não há avaliações
- Ix History The French RevolutionDocumento7 páginasIx History The French RevolutionRonak SoniAinda não há avaliações
- Chap-1 Historyxam IdeaDocumento1 páginaChap-1 Historyxam IdeaAditi AgrawalAinda não há avaliações
- French Revolution, 9, Ch-1Documento2 páginasFrench Revolution, 9, Ch-1Khan ArshiAinda não há avaliações
- French Revolution IntroductionDocumento25 páginasFrench Revolution Introductiontsanghoyi980317Ainda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionIASbabaDocumento20 páginasFrench RevolutionIASbabaDhawan GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Class 9 Cbse RevolutionDocumento27 páginasClass 9 Cbse RevolutionKaleelur RahmanAinda não há avaliações
- The French Revolution: Presented By: 1789 - 1815Documento41 páginasThe French Revolution: Presented By: 1789 - 1815tanyagargAinda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionDocumento27 páginasFrench Revolutionapi-237266847Ainda não há avaliações
- The French RevolutionDocumento9 páginasThe French RevolutionAtiq AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- 1st Estate 2nd Estate 3rd Estate: - Clergy - Churchman - Noble - Royal Family - Poor Peasants - Common ManDocumento6 páginas1st Estate 2nd Estate 3rd Estate: - Clergy - Churchman - Noble - Royal Family - Poor Peasants - Common Manamarsinha1987Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 Liberalism and Nationalism (1789-1871)Documento24 páginasUnit 2 Liberalism and Nationalism (1789-1871)Andrés Tallón CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter-1 French RevolutionDocumento36 páginasChapter-1 French Revolutionsid011Ainda não há avaliações
- Chapter 1 The French RevolutionDocumento16 páginasChapter 1 The French Revolutionsanjeevani GargAinda não há avaliações
- Anyab StuffDocumento7 páginasAnyab StuffDARREN B. ESPINARAinda não há avaliações
- French Revolution (Autosaved)Documento52 páginasFrench Revolution (Autosaved)DevanshAinda não há avaliações
- Share 9th History-French Revolution-Ppt (Teacher)Documento28 páginasShare 9th History-French Revolution-Ppt (Teacher)LakshAinda não há avaliações
- Summary 1° Part of The UnitDocumento4 páginasSummary 1° Part of The UnitSerginho Jiménez LópezAinda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionDocumento12 páginasFrench Revolutionshaileshawasthi100% (1)
- French RevolutionDocumento7 páginasFrench Revolutionraman baviskarAinda não há avaliações
- The French Revolution: Ancien Regime & The Reign of Terror: LibertéDocumento27 páginasThe French Revolution: Ancien Regime & The Reign of Terror: Liberté(1A) Arran KellyAinda não há avaliações
- The French Revolution: People Power in Action - History 5th Grade | Children's European HistoryNo EverandThe French Revolution: People Power in Action - History 5th Grade | Children's European HistoryAinda não há avaliações
- The French Revolution 1Documento8 páginasThe French Revolution 1Mehul ChaturvediAinda não há avaliações
- Edexcel Notes On French Revolution 1780-1799Documento50 páginasEdexcel Notes On French Revolution 1780-1799unknown shooter100% (2)
- The French RevolutionDocumento60 páginasThe French RevolutionArjie GabrielAinda não há avaliações
- Causes of The French RevolutionDocumento13 páginasCauses of The French Revolution91gonzascountAinda não há avaliações
- Class IX French Revolution PPT For RevisionDocumento31 páginasClass IX French Revolution PPT For Revisionnaman mahawer85% (20)
- Kerala STD X Social Science I UNIT 01 Revolutions That Influenced The World Study Notes (Eng Med) - Cropped-Pages-1,2-3Documento3 páginasKerala STD X Social Science I UNIT 01 Revolutions That Influenced The World Study Notes (Eng Med) - Cropped-Pages-1,2-3Saja ZameerAinda não há avaliações
- French ProjectDocumento5 páginasFrench ProjectLakshay KhannaAinda não há avaliações
- History Chapter 1 and 2 (SST Whole) Byrajnish SirDocumento68 páginasHistory Chapter 1 and 2 (SST Whole) Byrajnish Sirvivektripathi11619Ainda não há avaliações
- Untitled PresentationDocumento12 páginasUntitled Presentationapi-511395988Ainda não há avaliações
- The French RevolutionDocumento5 páginasThe French RevolutionAditya Ratn SinglaAinda não há avaliações
- The French RevolutionDocumento26 páginasThe French RevolutionApoorva JakharAinda não há avaliações
- The French Revolution: Facts That MatterDocumento21 páginasThe French Revolution: Facts That Mattersunilkhairnar38Ainda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionDocumento7 páginasFrench RevolutionRahimahameedAinda não há avaliações
- Background of The French Revolution (Final)Documento15 páginasBackground of The French Revolution (Final)humza hunainAinda não há avaliações
- History Chapter 1-The French Revolution NotesDocumento3 páginasHistory Chapter 1-The French Revolution NotesKhushi TanejaAinda não há avaliações
- French Revolution People: Napoleon BonaparteDocumento4 páginasFrench Revolution People: Napoleon BonapartepremiutopiaAinda não há avaliações
- First Draft MindmapDocumento1 páginaFirst Draft Mindmapapi-335646206Ainda não há avaliações
- French Revolution RM 23-24Documento8 páginasFrench Revolution RM 23-24Harit ManvarAinda não há avaliações
- Carlos III: Túpac Amaru RebellionDocumento2 páginasCarlos III: Túpac Amaru RebellionWilliam_KeethAinda não há avaliações
- French RevolutionDocumento8 páginasFrench RevolutionArooj ZamanAinda não há avaliações
- Tema 2 The Age of RevolutionsDocumento20 páginasTema 2 The Age of Revolutionssalma kasmiAinda não há avaliações
- India: Size and LocationDocumento1 páginaIndia: Size and LocationDebdeep BhuniaAinda não há avaliações
- The Story of Village Palampur: ProductionDocumento1 páginaThe Story of Village Palampur: ProductionDebdeep Bhunia100% (1)
- 10 Years Question Paper of CBSE Class 10 MATHS 2015Documento7 páginas10 Years Question Paper of CBSE Class 10 MATHS 2015Debdeep BhuniaAinda não há avaliações
- "Titanic" Diary EntriesDocumento1 página"Titanic" Diary EntriesDebdeep BhuniaAinda não há avaliações
- New Doc 2018-12-29 21.27.10 - Page 1Documento1 páginaNew Doc 2018-12-29 21.27.10 - Page 1Debdeep BhuniaAinda não há avaliações
- Media ReportDocumento46 páginasMedia ReportAndrew AB BurgoonAinda não há avaliações
- Revised Estimate Draft 24-12-2021Documento100 páginasRevised Estimate Draft 24-12-2021Reenu CherianAinda não há avaliações
- Fouzia AnjumDocumento3 páginasFouzia AnjumAbdul SyedAinda não há avaliações
- The Truth About Customer ExperienceDocumento11 páginasThe Truth About Customer Experienceaksr27Ainda não há avaliações
- HRM Ass1Documento3 páginasHRM Ass1asdas asfasfasdAinda não há avaliações
- Zambia MTEF 2015 - 2017 (Green Paper)Documento27 páginasZambia MTEF 2015 - 2017 (Green Paper)Chola MukangaAinda não há avaliações
- Output Vat Zero-Rated Sales ch8Documento3 páginasOutput Vat Zero-Rated Sales ch8Marionne GAinda não há avaliações
- EPM Cloud Tax Reporting Overview - EMEA Training May 2020Documento25 páginasEPM Cloud Tax Reporting Overview - EMEA Training May 2020zaymounAinda não há avaliações
- Sampling PowerpointDocumento21 páginasSampling PowerpointMuhammad Furqan Aslam AwanAinda não há avaliações
- SecureCore Datasheet V2Documento2 páginasSecureCore Datasheet V2chepogaviriaf83Ainda não há avaliações
- 1 General: Fig. 1.1 Industrial RobotDocumento40 páginas1 General: Fig. 1.1 Industrial RobotArunAinda não há avaliações
- TFTV3225 Service Manual 102010 Coby 26-32Documento21 páginasTFTV3225 Service Manual 102010 Coby 26-32bigbrother4275% (4)
- RECRUITMENT AGENCIES IN U.A.E. (Here Is A List Containing 150+ Names)Documento22 páginasRECRUITMENT AGENCIES IN U.A.E. (Here Is A List Containing 150+ Names)raajc12380% (5)
- OPERATING MANUAL Micro Powder MillDocumento51 páginasOPERATING MANUAL Micro Powder MillSher AhmadAinda não há avaliações
- Financial Analysis of OGDCLDocumento16 páginasFinancial Analysis of OGDCLsehrish_sadaqat7873100% (1)
- MTBE - Module - 3Documento83 páginasMTBE - Module - 3ABHIJITH V SAinda não há avaliações
- Annex 1C - Ice Plant and Cold Storage Inspection ChecklistDocumento9 páginasAnnex 1C - Ice Plant and Cold Storage Inspection ChecklistMaxmore Karumamupiyo100% (2)
- Nfjpia Mockboard 2011 BLTDocumento12 páginasNfjpia Mockboard 2011 BLTVon Wilson AjocAinda não há avaliações
- LESSON - STEM-based Research ProblemsDocumento49 páginasLESSON - STEM-based Research ProblemsLee JenoAinda não há avaliações
- Consolidated Digests - Part 2Documento314 páginasConsolidated Digests - Part 2Neil Patrick Pepito ErmacAinda não há avaliações
- Branding HS TalksDocumento17 páginasBranding HS TalksumairAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Content AnalysisDocumento10 páginasIntroduction To Content AnalysisfelixAinda não há avaliações
- Technical Specification For Flue Gas Desulfurization of Thermal Power Plant Limestone / Lime - Gypsum MethodDocumento17 páginasTechnical Specification For Flue Gas Desulfurization of Thermal Power Plant Limestone / Lime - Gypsum Methodpramod_tryAinda não há avaliações
- Detroit ManualDocumento435 páginasDetroit Manualvictorhernandezrega50% (2)
- Past Simple and Continuous - When - While Worksheet - Live WorksheetsDocumento4 páginasPast Simple and Continuous - When - While Worksheet - Live WorksheetsSaraí CaracúnAinda não há avaliações
- PCIB Vs ESCOLIN (G.R. No. L-27860 & L-27896)Documento61 páginasPCIB Vs ESCOLIN (G.R. No. L-27860 & L-27896)strgrlAinda não há avaliações
- D.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Documento5 páginasD.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Pritam Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Demand Letter Template 39Documento3 páginasDemand Letter Template 39AIG1 LOGISTICAinda não há avaliações
- Part List SR-DVM70AG, SR-DVM70EUDocumento28 páginasPart List SR-DVM70AG, SR-DVM70EUAndrea BarbadoroAinda não há avaliações
- Successfully Allocating Risk and Negotiating A PPP ContractDocumento12 páginasSuccessfully Allocating Risk and Negotiating A PPP ContractWilliam Tong100% (1)