Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Teacher Rubrics
Enviado por
bruno1eroDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Teacher Rubrics
Enviado por
bruno1eroDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
KEEP Teacher Evaluation Rubrics
Construct 1: Learner and Learning
To ensure that each student learns new knowledge and skills, teachers must understand that learning and developmental patterns vary
individually, that students bring unique individual differences to the learning process, and that students need supportive and safe learning
environments to thrive. Demonstration of the teacher’s proficiency in Learner and Learning is evidenced by:
1.1 Learner Development
The teacher planned instruction based on the learning and developmental levels of all students.
Key indicators: planning instruction, aligning instruction with student learning needs, using a variety of approaches and resources, providing
adaptation of instruction.
1.2 Learner Differences
The teacher recognized and fostered individual differences to establish a positive classroom culture.
Key indicators: getting to know all students, using that knowledge of students to create a culture of respect, meeting needs of all students.
1.3 Learning Environment
The teacher established a classroom environment conducive to learning.
Key indicators: collaborating with students, establishing a safe, respectful and academically challenging environment.
1|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
1.1 Learner Development: The teacher planned instruction based on the learning and developmental levels of all students.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher planned instruction that teacher planned instruction that teacher consistently and effectively
planned instruction that aligns with partially aligns with students’ aligns with students’ developmental planned instruction that closely aligns
students’ developmental levels and developmental levels and learning levels and learning needs. with students’ learning needs and
learning needs. needs. developmental levels.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher relied on a single teaching teacher incorporated some teaching teacher regularly used a variety of teacher consistently and effectively
approach and resource. approaches and resources. teaching approaches and resources. used a variety of appropriate
teaching approaches and resources.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher provided some adaptation of teacher adapted plans and teacher consistently and effectively
provided adaptation of plans and plans and instruction that met some instruction, when appropriate, to adapted plans and instruction, when
instruction, and the adaptation that of the student’s learning needs. meet all students’ learning needs. appropriate, to meet all students’
was provided was often not learning needs.
appropriate to the students’ learning
needs.
Sources of Evidence for Planning Instruction Based on the Learning and Developmental Levels of All Students
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Planning and alignment of instruction Teacher lesson plans Lesson and unit plans reflected consistent
alignment with the students’ learning needs
and illustrate how the teacher takes into
consideration the developmental levels of all
students.
Using a variety of teaching approaches and Teacher lesson and/or unit plans Lesson plans and student work consistently
resources Student work samples reflected a variety of approaches to help
Learning style inventories students learn. Observations or artifacts of
Observations (by peers or evaluators) classroom activities over a period of time
provide evidence of the variety.
Adapting instruction to meet student needs Teacher reflection The teacher consistently reflected on
Samples of student work instruction both during and after and provided
Conference notes with colleagues both written and oral evidence of this.
2|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
1.2 Learner Differences: The teacher recognized and fostered individual differences to establish a positive classroom culture.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently took teacher took partial steps to learn teacher regularly took steps to learn teacher consistently and effectively
steps to learn about students as about students as individuals and as about students as individuals and as took steps to learn about students as
individuals and as learners. learners. learners. individuals and as learners.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to use knowledge of teacher regularly incorporated teacher consistently and effectively
incorporated knowledge of individual individual students to create a knowledge of student diversity to incorporated knowledge of student
students to create a classroom positive culture that meets the needs create a positive culture of respect diversity to create a positive culture
culture of respect and rapport that of all students. and rapport that meets the needs of of respect and rapport that meets
meets the needs of all students. most students the needs of all students.
Sources of Evidence for Recognizing and Fostering Individual Differences to Establish a Positive Classroom Culture
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Knowledge of all students Student surveys The teacher consistently interacted with
Student writing students in a respectful manner, encouraging
Parent surveys and respecting them as they share their
Student attendance data thoughts and experiences.
Using knowledge of students to create a culture Student reflections/contributions of personal Student writing and discussion provided
of respect among all students experience consistent evidence of contributions of
Classroom rules personal experiences to the topics being
Behavior and/or office referrals studied during class.
3|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
1.3 Learning Environment: The teacher established a classroom environment conducive to learning.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to collaborate with teacher regularly collaborated with teacher consistently and effectively
collaborated with students to students to promote student students to promote student collaborated with students to
promote student ownership of the ownership of the learning. ownership of the learning. promote student ownership of the
learning. learning.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to establish a safe, teacher regularly established a safe, teacher consistently and effectively
established a safe, respectful, and respectful, and academically respectful, and academically established a safe, respectful, and
academically engaging environment engaging environment for students. engaging environment for students. academically challenging
for students. environment for all students.
Sources of Evidence for Establishing a Classroom Environment Conducive to Learning
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Collaboration with students Classroom rules developed collaboratively The teacher was seen consistently involving
Student surveys students in various classroom activities, giving
Student developed rubrics the student opportunities to give direction to
their own learning.
Establishing a safe, respectful, and academically Lesson plans Student work provided consistent evidence
challenging environment Classroom expectations that students are being academically
Observations (by peers or evaluators) challenged at their appropriate level.
Student work samples
Feedback to students
4|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
Construct 2: Content Knowledge
Teachers must have a deep and flexible understanding of their content area(s) and be able to draw upon it as they work with students to access
information, apply knowledge in real world settings and work with meaningful issues. Demonstration of the teacher’s proficiency in Content
Knowledge is evidenced by:
2.1 Content Knowledge
The teacher demonstrated a thorough knowledge of content.
Key indicators: encouraging use of multiple representations, explanations and a wide variety of experiences building student understanding.
2.2 Innovative Applications of Content Knowledge
The teacher provided a variety of innovative applications of knowledge.
Key indicators: using problem solving, critical thinking skills and technology, exploring and delivering content through real world application of
knowledge, collaborating with colleagues to provide cross-curricular opportunities.
5|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
2.1 Content Knowledge: The teacher demonstrated a thorough knowledge of content.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher displayed limited knowledge teacher displayed knowledge of the teacher displayed extensive
displayed knowledge of the of the important content in the important content in the discipline, knowledge of the important concepts
important content in the discipline discipline and identification of used multiple representation and in the discipline by consistently and
and identification of possible student possible student misconceptions. explanations, understood how these effectively using multiple
misconceptions. relate to each other, and identified representations, explanations, and a
student misconceptions. wide variety of experiences and
opportunities.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently used teacher began to use strategies to teacher regularly used strategies to teacher consistently and effectively
strategies to build understanding of build understanding of content for all build a deep understanding of used strategies to build a deep
content for all students. students. content for all students. understanding of content for all
students.
Sources of Evidence for Showing Knowledge of Content
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Knowledge of content by encouraging use of Lesson plans aligned to content standards Evidence observed shows the teacher
multiple representations, explanations, and a Curriculum committee work documentation consistently provided a variety of instructional
wide variety of experiences Observations of strategies used to deliver strategies that provide students a range of
content (by peers or evaluators) experiences to learn content.
Built student understanding Student work samples Student work, judged according to a rubric,
Student feedback and reflection pieces consistently showed understanding of key
Teacher developed assessments and rubrics content area topics.
Student involvement in content contests
6|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
2.2 Innovative Applications of Content Knowledge: The teacher provided a variety of innovative applications of knowledge.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently used teacher used limited problem solving, teacher regularly used problem teacher consistently and effectively
problem solving, critical thinking critical thinking skills, and technology solving, critical thinking skills, and used problem solving, critical thinking
skills, and technology to explore and to explore and deliver content. technology to explore and deliver skills, and technology to explore and
deliver content. content. deliver content.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher provided limited teacher regularly provided teacher consistently and effectively
provided opportunities to students opportunities to students for real opportunities to students for real provided opportunities to students
for real world application of content. world application of content. world application of content. for real world application of content.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to collaborate with teacher regularly collaborated with teacher consistently and effectively
collaborated with colleagues to colleagues to provide purposeful colleagues to provide purposeful collaborated with colleagues to
provide purposeful cross-curricular cross-curricular learning cross-curricular learning provide purposeful cross-curricular
learning opportunities. opportunities. opportunities. learning opportunities.
Sources of Evidence for Providing a Variety of Innovative Applications of Knowledge
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Use of problem solving, critical thinking skills, and Problem-solving based assignments with Evidence consistently showed effective use of
technology student responses critical thinking skills in developing content-
Student created videos based assignments; questions promote
evaluation and synthesis rather than recall.
Explored and delivered content through real Portfolio of materials associated with real A collection of student work over a period of
world application of knowledge world application of topics of study time consistently showed practical application
Feedback from community member regarding of content
a project tied to a real-world activity
Collaborated to provide cross curricular learning Co-Curricular performances tied to the subject Evidence from lesson plans showed students
opportunities area making use of a variety of content areas within
Unit plans from collaborative planning one activity.
7|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
Construct 3: Instructional Practice
Effective instructional practice requires that teachers understand and integrate planning, instructional strategies and assessment in coordinated
and engaging ways. Demonstration of the teacher’s proficiency in Instructional Practice is evidenced by:
3.1 Planning for Instruction
The teacher used methods and techniques that are effective in meeting student needs.
Key indicators: planning rigorous activities, using objectives that align with standards, meeting needs of students.
3.2 Assessment
The teacher used varied assessments to measure learner progress.
Key indicators: providing opportunities for students to demonstrate learning, using assessment data to inform instruction, providing feedback
that encourages students to take responsibility for the learning.
3.3 Instructional Strategies
The teacher delivered comprehensive instruction for students.
Key indicators: Using a variety of strategies to engage and challenge students, incorporating strategies to differentiate and scaffold instruction,
engaging student in higher order thinking skills.
8|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
3.1 Planning for Instruction: The teacher used methods and techniques that are effective in meeting student needs.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher planned activities that teacher regularly planned rigorous teacher consistently and effectively
planned activities that connect with partially connect with district, state and challenging activities using planned rigorous and challenging
district, state, and/or national and/or national standards to meet objectives that align with district, activities using objectives that align
standards to meet the needs of the needs of students. state and/or national standards to with district, state and/or national
students. meet the needs of all students. standards to meet the needs of all
students.
Sources of Evidence for Using Methods and Techniques that are Effective in Meeting Student Needs
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Planned rigorous activities Formative and summative assessments Evidence from student work consistently
Observations (by peers and evaluators) showed that lessons are planned using
Student work samples showing the rigor of the challenging and appropriate activities.
assignments
Teacher and student reflections
Used objectives that align with standards Lesson plans noting relevant standards Assessment data consistently showed
Assessment data students meeting district, state, and national
standards.
Met needs of all students Student need inventory Evidence from portfolios collected over a
Individual assessment data including portfolios period of time reflected student
understanding of content appropriate for their
individual needs.
9|Page KEEP Teacher Rubrics
3.2 Assessment: The teacher used varied assessments to measure learner progress.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher provided limited teacher regularly provided multiple teacher consistently and effectively
provided basic opportunities for opportunities for students to opportunities for students to provided multiple opportunities for
students to demonstrate learning by demonstrate learning by using demonstrate learning by using students to demonstrate learning by
using formative, summative, informal formative, summative, informal formative, summative, informal, using formative, summative,
and/or formal assessments. and/or formal assessments. and/or formal assessments. informal, and/or formal assessments.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently used teacher began to use student data to teacher regularly used student data teacher consistently and effectively
student data to inform future inform future instruction. to inform future instruction. used student data to inform future
instruction. instruction.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher provided some feedback to teacher regularly provided timely teacher consistently and effectively
provided feedback to students. encourage students. feedback to encourage students to provided timely feedback to
take responsibility for their own encourage students to take
learning. responsibility for their own learning.
Sources of Evidence for using varied assessments to measure learner progress
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Provided opportunities for students to Scored rubrics from performance assessments Evidence consistently showed that students
demonstrate learning Assessment samples (formative and have a variety of ways to demonstrate their
summative) learning: oral presentations, portfolios.
Portfolios
Student presentations
Used assessment data to inform instruction Teacher reflection Teacher consistently provided rationales for
Lesson plans linking activities to assessment chosen activities based on student assessment
results results.
Provided feedback to promote student Written feedback on student work Written evidence from teacher/student
responsibility Observations (by peers or evaluators) conference consistently showed student
Teacher/student conferences identification of next steps in the learning.
10 | P a g e KEEP Teacher Rubrics
3.3 Instructional Strategies: The teacher delivered comprehensive instruction for students.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently used teacher used some strategies and teacher regularly used a variety of teacher consistently and effectively
strategies and available technologies available technology to engage and strategies including available used a variety of strategies including
to engage students in the learning challenge students. technology to engage and challenge available technology to engage and
process. students in a variety of learning challenge students in a variety of
situations. learning situations.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently used teacher incorporated limited teacher regularly used strategies to teacher consistently and effectively
strategies for differentiating strategies to differentiate instruction. differentiate and scaffold information incorporated strategies to
instruction. so it is accessible to all students. differentiate and scaffold information
so it is accessible to all students.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to engage students in teacher regularly engaged students in teacher consistently and effectively
engaged students in the learning higher order thinking skills. higher order thinking skills. engaged students in higher order
process. thinking skills.
Sources of Evidence for Delivering Comprehensive Instruction for Students
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Used a variety of strategies to engage and Professional growth log Evidence from lesson plans consistently
challenge students in a variety of learning Lesson plans showed use of strategies to engage students in
situations Observations worthwhile content learning activities.
Incorporated strategies for differentiation and Teacher reflection Teacher consistently developed assignments
scaffolding for all students Lesson plans showing how strategies were that provide students with a variety of options
used for scaffolding/differentiation and submission schedules.
Engaged students in higher order thinking Student work samples that reflect use of Teacher consistently provided students with
higher level thinking skills problem solving activities related to the
classroom content.
11 | P a g e KEEP Teacher Rubrics
Construct 4: Professional Responsibility
Creating and supporting learning environments that result in students achieving at the highest levels is a teacher’s primary responsibility. To do
this well, teachers must engage in professional self-renewal, which means they regularly examine their own and each other’s practice through
self-reflection and collaboration, providing collegial support and feedback that assures a continuous cycle of self-improvement. Demonstration
of the teacher’s proficiency in Professional Responsibility is evidenced by:
4.1 Reflection and Continuous Growth
The teacher engaged in reflection and continuous growth.
Key indicators: engaging in ongoing, purposeful professional development, reflecting on practice and seeking professional development,
analyzing and reflecting on student data to guide instruction.
4.2 Collaboration and Leadership
The teacher participated in collaboration and leadership opportunities. Key indicators: collaborating with multiple stakeholders, communicating
in a variety of ways, demonstrating leadership skills.
12 | P a g e KEEP Teacher Rubrics
4.1 Reflection and Continuous Growth: The teacher engaged in reflection and continuous growth.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to participate in teacher engaged in ongoing, teacher consistently and effectively
participated in professional ongoing professional development purposeful professional development engaged in ongoing, purposeful
development. relevant to student learning. relevant to student learning. professional development relevant to
student learning.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates teacher The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to reflect on practices regularly reflected on his/her practice teacher consistently and effectively
reflected on his/her practices and is aware of opportunities for and seeks opportunities for reflected on his/her practice and
improvement. improvement. actively seeks opportunities for
improvement.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to analyze and reflect teacher regularly analyzed and teacher consistently and effectively
analyzed and reflected on student on student data to guide planning reflects on student data to guide analyzed and reflected on student
data to guide planning. and instruction. planning, instruction, and student data to guide planning, instruction,
growth. and student growth.
Sources of Evidence for Engaging in Reflection and Continuous Growth
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Engaged in ongoing, purposeful professional Professional development log noting Teacher consistently sought professional
learning connected to student learning connections to classroom application of learning experiences (workshops, courses, and
learning self-study) and applied the learning to
Written evaluation of a professional learning classroom activities.
experience
Professional portfolio
Reflecting on practice and actively seeks Lesson plans with reflections on effectiveness Teacher consistently welcomed feedback from
opportunities for improvement of lesson and ideas for future improvements peers in the development of lesson plans and
Video recording of a lesson with feedback the implementation of instruction and
from a peer or evaluator activities.
Analyzing and reflecting on student data to Formative and summative assessments Teacher consistently collected data from a
impact student growth Data collection device for use over an variety of sources and determined what
extended period of time to see student growth students have and have not learned in order
to address student learning needs.
13 | P a g e KEEP Teacher Rubrics
4.2 Collaboration and Leadership: The teacher participated in collaboration and leadership opportunities.
Ineffective Developing Effective Highly Effective
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to meet with and teacher regularly collaborated with teacher consistently and effectively
communicated with colleagues about discusses school issues with colleagues and stakeholders in collaborated with multiple
school issues. colleagues and other stakeholders. leadership, school, and professional stakeholders in school and
activities using multiple professional activities using a variety
communications. of methods of communication.
The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the The evidence indicates that the
teacher did not or infrequently teacher began to demonstrate some teacher regularly demonstrated teacher consistently and effectively
demonstrated leadership skills by leadership skills by initiating, leadership skills by initiating, demonstrated leadership skills by
initiating, advocating, and/or leading advocating, or leading activities. advocating, and/or leading activities initiating, advocating, and/or leading
activities. to improve and support student activities to improve and support
learning. student learning.
Sources of Evidence for Participation in Collaboration and Leadership Opportunities
What You Want to Demonstrate Possible Evidence Performance Considerations
Collaborated with multiple stakeholders in school Minutes of meetings: IEP, PLC, Student Evidence shows the teacher’s consistent
and professional activities Improvement Team meetings communication with a mentor to discuss a
Notes from meetings with mentor variety of learning strategies.
Contact logs
Used a variety of methods of communication Copies of communication: emails, letters, The teacher consistently used a reflective
newsletters journal and shared ideas from that with
Log of phone calls colleagues in a team meeting.
Demonstrated leadership skills used to support Agendas generated by the teacher in a team Teacher consistently initiated meetings with a
and improve student learning leadership role variety of groups such as care givers, peers
Portfolio of leadership activities and teachers of the same content to improve
student learning.
14 | P a g e KEEP Teacher Rubrics
Você também pode gostar
- Unit 6 - External Influences On Business Activity IGCSE O'Level Business StudiesDocumento1 páginaUnit 6 - External Influences On Business Activity IGCSE O'Level Business StudiesQliqbaitAinda não há avaliações
- An Inspector Calls by PriestleyDocumento16 páginasAn Inspector Calls by PriestleyTimoAinda não há avaliações
- Magazine 1Documento13 páginasMagazine 1api-571063103Ainda não há avaliações
- Unit 1 - Understanding Business Activity IGCSE O'Level Business StudiesDocumento1 páginaUnit 1 - Understanding Business Activity IGCSE O'Level Business StudiesQliqbaitAinda não há avaliações
- Igcse Migration and Gcse MigrationDocumento11 páginasIgcse Migration and Gcse Migrationapi-261914272100% (2)
- Communication and GlobalizationDocumento32 páginasCommunication and GlobalizationYrrehc CawisAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 2 - People in Business IGCSE O'Level Business StudiesDocumento1 páginaUnit 2 - People in Business IGCSE O'Level Business StudiesQliqbaitAinda não há avaliações
- Florence Gough, Amanda Brent, Susan Robinson One in Eleven Teaching Adolescents With A Language Learning Disability 2002Documento156 páginasFlorence Gough, Amanda Brent, Susan Robinson One in Eleven Teaching Adolescents With A Language Learning Disability 2002Marijo100% (1)
- Harry Potter Chapter QuizDocumento96 páginasHarry Potter Chapter QuizМария МакароваAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus General and DailyDocumento6 páginasSyllabus General and DailyJan RiemanAinda não há avaliações
- Training Program For Kindergarten TeachersDocumento2 páginasTraining Program For Kindergarten TeachersJanice Gentile Alison100% (1)
- Math Micro TeachingDocumento13 páginasMath Micro Teachingapi-347068176Ainda não há avaliações
- General Paper 8001 SyllabusDocumento17 páginasGeneral Paper 8001 SyllabusNileshAinda não há avaliações
- CLIL and ICTDocumento28 páginasCLIL and ICTcl_lanuzaAinda não há avaliações
- 105595564.a Operations TeacherDocumento61 páginas105595564.a Operations TeacherSnehal IyerAinda não há avaliações
- ScienceDocumento84 páginasScienceParas PatharAinda não há avaliações
- 3rd Grade Geometry Unit PlanDocumento7 páginas3rd Grade Geometry Unit PlanalyssamanningAinda não há avaliações
- Topic 3 Summarising PDFDocumento10 páginasTopic 3 Summarising PDFTan Lee FenAinda não há avaliações
- Year 2 Maths Money Intro LessonDocumento2 páginasYear 2 Maths Money Intro Lessonapi-296657831Ainda não há avaliações
- How to Complete a Job ApplicationDocumento5 páginasHow to Complete a Job ApplicationnaninhaorAinda não há avaliações
- KB2 Home BookletDocumento32 páginasKB2 Home BookletKris Eduardo100% (1)
- Literature ComponentDocumento75 páginasLiterature ComponentFasihah FasAinda não há avaliações
- IB Poster ProjectDocumento2 páginasIB Poster ProjectMeredith SummerAinda não há avaliações
- Rubrics For Story WritingDocumento1 páginaRubrics For Story WritingNorma HipperdingerAinda não há avaliações
- ESOL Level DescriptorsDocumento2 páginasESOL Level DescriptorsnjennsAinda não há avaliações
- CbiDocumento21 páginasCbiJennifer Sayong100% (1)
- Wong Unit C NotesDocumento4 páginasWong Unit C Notesapi-455384768Ainda não há avaliações
- ATL Rubric: Teacher/Student ATL ChecklistDocumento3 páginasATL Rubric: Teacher/Student ATL ChecklistAhmed HushamAinda não há avaliações
- LL Unit Planner Example 1Documento4 páginasLL Unit Planner Example 1nukifahrurAinda não há avaliações
- Common Errors GrammarDocumento4 páginasCommon Errors GrammarSarahGill0% (1)
- Supporting Teaching and Learning in Schools NVQ Level 3 Unit 35 Support Bilingual/multilingual PupilsDocumento5 páginasSupporting Teaching and Learning in Schools NVQ Level 3 Unit 35 Support Bilingual/multilingual PupilsDoodah2100% (1)
- 60 Años Formando Maestros y Maestras para La Infancia: Escuela Normal Superior Distrital Maria MontessoriDocumento10 páginas60 Años Formando Maestros y Maestras para La Infancia: Escuela Normal Superior Distrital Maria Montessoriyecenia fernandezAinda não há avaliações
- Speaking Assessment Criteria: CEFR B2Documento1 páginaSpeaking Assessment Criteria: CEFR B2GERESAinda não há avaliações
- Hong Kong Teacher Education Series - Rita Berry - Assessment For LearningDocumento221 páginasHong Kong Teacher Education Series - Rita Berry - Assessment For LearningSWidy WidiyaAinda não há avaliações
- MYP Unit Planner <40Documento8 páginasMYP Unit Planner <40Anan BarghouthyAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluating Vocabulary in CoursebooksDocumento5 páginasEvaluating Vocabulary in CoursebooksKatherine MondaAinda não há avaliações
- Private TutoringDocumento47 páginasPrivate TutoringHồ Hoàng Huy100% (2)
- The Blanket Exercise Dec 12th 3Documento9 páginasThe Blanket Exercise Dec 12th 3api-390378000Ainda não há avaliações
- Jeremiah in The Dark Woods Janet Allan AhlbergDocumento4 páginasJeremiah in The Dark Woods Janet Allan AhlbergS TANCREDAinda não há avaliações
- Multiplying and Dividing Polynomials - Learn How with ExamplesDocumento18 páginasMultiplying and Dividing Polynomials - Learn How with ExamplesTeacher AnnAinda não há avaliações
- First Quarter DLL June 26 29Documento3 páginasFirst Quarter DLL June 26 29BabyrrechBalilu100% (1)
- 4th Ela PlacematDocumento1 página4th Ela Placematapi-276971164Ainda não há avaliações
- Pyp Programme Brochure en PDFDocumento4 páginasPyp Programme Brochure en PDFSorin IordacheAinda não há avaliações
- TESOL LTCL Diploma - 2017 Validation Requirements, Syllabus and BibliographyDocumento112 páginasTESOL LTCL Diploma - 2017 Validation Requirements, Syllabus and BibliographyMigsAinda não há avaliações
- Seton Hill University Lesson Plan Template: Name Subject Grade Level Date/DurationDocumento5 páginasSeton Hill University Lesson Plan Template: Name Subject Grade Level Date/Durationapi-266496943Ainda não há avaliações
- Annual Planning 6th GradeDocumento3 páginasAnnual Planning 6th GradeAnthonyScottBarrenecheaRodríguezAinda não há avaliações
- Summary WritingDocumento12 páginasSummary Writingcikmurabbi100% (2)
- Scheme of Work – English Stage 1Documento52 páginasScheme of Work – English Stage 1Idam Supiana100% (1)
- Roles in Cooperative LearningDocumento8 páginasRoles in Cooperative Learningjoan_alberichAinda não há avaliações
- Interactive Learning ActivitiesDocumento3 páginasInteractive Learning Activitiesapi-480270859Ainda não há avaliações
- ES1 English Scope and Sequence ChecklistDocumento18 páginasES1 English Scope and Sequence ChecklistS TANCRED100% (1)
- Spanish Beginner Grammar PDFDocumento38 páginasSpanish Beginner Grammar PDFmiraji Alphonce KyaruziAinda não há avaliações
- Designing Scoring Rubrics For Your ClassroomDocumento9 páginasDesigning Scoring Rubrics For Your ClassroomRobinson AntonioAinda não há avaliações
- No.91 Elementary Geography LessonDocumento40 páginasNo.91 Elementary Geography LessonErenjaeger TitanAinda não há avaliações
- Inclusion Lesson PlanDocumento5 páginasInclusion Lesson Planapi-532813028Ainda não há avaliações
- Tellin G Time Unit: - A Free Mini-UnitDocumento21 páginasTellin G Time Unit: - A Free Mini-UnitidaAinda não há avaliações
- Bellaire PS Instructional ModelDocumento1 páginaBellaire PS Instructional ModelBen RaidmeAinda não há avaliações
- Keep Teacher Evaluation Rubrics 12-10-2013Documento14 páginasKeep Teacher Evaluation Rubrics 12-10-2013api-266095824Ainda não há avaliações
- CSTP 4 - EvidenceDocumento2 páginasCSTP 4 - EvidenceNancy CampAinda não há avaliações
- Together We Teach - Transforming Education Through Co-Teaching: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsNo EverandTogether We Teach - Transforming Education Through Co-Teaching: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsAinda não há avaliações
- The Rise of Mexican DTOs - MilitarizatioDocumento49 páginasThe Rise of Mexican DTOs - Militarizatiobruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Mexican-American War Activities WorksheetsDocumento72 páginasMexican-American War Activities Worksheetsbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Rubric For Scoring Oral PresentationDocumento5 páginasRubric For Scoring Oral PresentationBosco BonillaAinda não há avaliações
- Bilingualism. 2. Ed PDFDocumento402 páginasBilingualism. 2. Ed PDFbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation Format MaricelaDocumento5 páginasEvaluation Format Maricelabruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Bilingual Education Cognitive BenefitsDocumento20 páginasBilingual Education Cognitive Benefitsbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Identifying The Concept of Bilingualism and BilingDocumento12 páginasIdentifying The Concept of Bilingualism and Bilingbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Make Games With PythonDocumento154 páginasMake Games With Pythonremco_de_wolf4664100% (9)
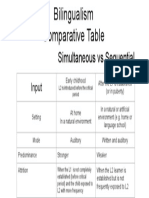
- Bilingualism Comparative Table Simultaneous Vs SequentialDocumento1 páginaBilingualism Comparative Table Simultaneous Vs Sequentialbruno1ero100% (1)
- English Idioms EjerciciosDocumento294 páginasEnglish Idioms Ejerciciosal_veddero100% (5)
- Victor Lopez - Latin RhythmsDocumento29 páginasVictor Lopez - Latin RhythmsXanthus Ching100% (4)
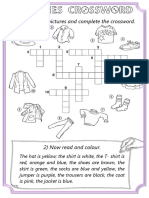
- Clothes Crossword 1 PDFDocumento2 páginasClothes Crossword 1 PDFbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Grammar 2Documento6 páginasGrammar 2Zigla MooreAinda não há avaliações
- English Language Exam - A2-B1Documento10 páginasEnglish Language Exam - A2-B1dule8350% (2)
- Placement Test OutcomesDocumento18 páginasPlacement Test OutcomesAlis MocanuAinda não há avaliações
- Markee1992 PDFDocumento17 páginasMarkee1992 PDFbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Sample Class FINAL PROJECTDocumento2 páginasLesson Plan Sample Class FINAL PROJECTbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Clothes Crossword 1 PDFDocumento2 páginasClothes Crossword 1 PDFbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Mandala Coloring Pages PDFDocumento34 páginasMandala Coloring Pages PDFbruno1ero100% (6)
- Enhancing Teaching and LearningDocumento19 páginasEnhancing Teaching and Learningbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Reflecting About My Teaching EssayDocumento5 páginasReflecting About My Teaching Essaybruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan Communicative AproachDocumento1 páginaLesson Plan Communicative Aproachbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- Applied Linguistics To Foreign Language Teaching and LearningDocumento61 páginasApplied Linguistics To Foreign Language Teaching and Learningbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- A Review of Research On Project Based Learning PDFDocumento46 páginasA Review of Research On Project Based Learning PDFsaraAinda não há avaliações
- Evaluation FormatDocumento5 páginasEvaluation Formatbruno1eroAinda não há avaliações
- A Review of Research On Project Based Learning PDFDocumento46 páginasA Review of Research On Project Based Learning PDFsaraAinda não há avaliações
- Imanami Interview Evaluation Form.Documento2 páginasImanami Interview Evaluation Form.EmRan WaHeedAinda não há avaliações
- BS601-Self-Development and Interpersonal Skills Syllabus PDFDocumento3 páginasBS601-Self-Development and Interpersonal Skills Syllabus PDFpaku deyAinda não há avaliações
- Group ProposalDocumento13 páginasGroup Proposalapi-500041382Ainda não há avaliações
- PDQ TL Module1guide PDFDocumento52 páginasPDQ TL Module1guide PDFAbdulAinda não há avaliações
- How To Measure Resilience: 8 Scales For Youth & Adults at Work (+ PDFDocumento25 páginasHow To Measure Resilience: 8 Scales For Youth & Adults at Work (+ PDFRuth NinaAinda não há avaliações
- Approaches of CounsellingDocumento7 páginasApproaches of CounsellingSamjhana Neupane100% (2)
- Lesson Plan Multiplication: Essential QuestionsDocumento7 páginasLesson Plan Multiplication: Essential Questionsapi-368183330Ainda não há avaliações
- Grade 1-12 school uses future tense verbsDocumento3 páginasGrade 1-12 school uses future tense verbsLeand Anthony CatahumberAinda não há avaliações
- Lesson Plan 1Documento3 páginasLesson Plan 1api-406946907Ainda não há avaliações
- Learning Journals: What Is A Learning Journal?Documento4 páginasLearning Journals: What Is A Learning Journal?larrysaligaAinda não há avaliações
- Daily Lesson Plan in English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocumento3 páginasDaily Lesson Plan in English For Academic and Professional PurposesGarcia Myrrha Leigh SalviaAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Lesson Study: Presenter: Mr. Kifle Yilma Regional SMASEE TrainerDocumento27 páginasIntroduction To Lesson Study: Presenter: Mr. Kifle Yilma Regional SMASEE TrainerbezawitwubshetAinda não há avaliações
- Rubric For Assessing Oral ParticipationDocumento2 páginasRubric For Assessing Oral ParticipationChromagrafxAinda não há avaliações
- Create A Game Lesson PlanDocumento4 páginasCreate A Game Lesson Planapi-269567696Ainda não há avaliações
- Plan - To - Implement - ReflectionGuide Taking NotesDocumento3 páginasPlan - To - Implement - ReflectionGuide Taking NotesChristinaAinda não há avaliações
- Compare and Contrast LessonDocumento8 páginasCompare and Contrast Lessonapi-394692942Ainda não há avaliações
- WR Decodable Lesson Plan Week 25 (My Pug Has Fun)Documento2 páginasWR Decodable Lesson Plan Week 25 (My Pug Has Fun)AtishaAinda não há avaliações
- HR Management Course OverviewDocumento5 páginasHR Management Course OverviewWalid Mohamed AnwarAinda não há avaliações
- RTI/MTSS For Behavior: Resources: Jim Wright, Presenter 31 January 2019 North Babylon Schools North Babylon, NYDocumento42 páginasRTI/MTSS For Behavior: Resources: Jim Wright, Presenter 31 January 2019 North Babylon Schools North Babylon, NYmasterplan100% (1)
- Leadership Skills QuestionnaireDocumento3 páginasLeadership Skills QuestionnaireOdesa Aviles100% (1)
- Ap Psychology UnitsDocumento39 páginasAp Psychology Unitsapi-325580763Ainda não há avaliações
- Anomalisa Film Analysis of Fregoli SyndromeDocumento12 páginasAnomalisa Film Analysis of Fregoli SyndromeCG Patron BamboAinda não há avaliações
- A Review of Client Self-Criticism in Psychotherapy: Divya Kannan Heidi M. LevittDocumento13 páginasA Review of Client Self-Criticism in Psychotherapy: Divya Kannan Heidi M. LevittCatarina C.100% (1)
- H.O.P.E. lesson on preventing hypo-hyperthermiaDocumento2 páginasH.O.P.E. lesson on preventing hypo-hyperthermiaMyra Paddayuman50% (2)
- TKT Module 1 Motivation PDFDocumento6 páginasTKT Module 1 Motivation PDFRachel Maria Ribeiro100% (1)
- CatDocumento12 páginasCatnini345Ainda não há avaliações
- Analyzing Speaking Difficulties and Strategies for English StudentsDocumento6 páginasAnalyzing Speaking Difficulties and Strategies for English StudentsDini Dwi HastutikAinda não há avaliações
- Personality Development - Written Assignment: Part 1-Self Development Part 2 - Effective Communication Skills PassDocumento19 páginasPersonality Development - Written Assignment: Part 1-Self Development Part 2 - Effective Communication Skills PassShamshad aliAinda não há avaliações
- Riggio PPT Ch01Documento15 páginasRiggio PPT Ch01Rosy Guzman100% (1)
- Management Ch5 LeadingDocumento48 páginasManagement Ch5 LeadingAhmed Mohamed WalidAinda não há avaliações