Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
HLTWHS002 PDF
Enviado por
Jase Harrison25%(4)25% acharam este documento útil (4 votos)
1K visualizações4 páginasThis document contains questions and answers about health and safety practices for direct client care. It discusses key topics like the Work Health and Safety Act 2011, WHS regulations, codes of practice, industry standards, employer and worker responsibilities, duty of care, manual handling tasks, infection control processes, hazards, safety signs, personal protective equipment, and risk minimization strategies. Specific examples are provided to illustrate concepts like additional infection controls, transmission of diseases, and common workplace hazards. Maintaining a safe work environment through identifying and reporting risks of infection is emphasized.
Descrição original:
Título original
HLTWHS002.pdf
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document contains questions and answers about health and safety practices for direct client care. It discusses key topics like the Work Health and Safety Act 2011, WHS regulations, codes of practice, industry standards, employer and worker responsibilities, duty of care, manual handling tasks, infection control processes, hazards, safety signs, personal protective equipment, and risk minimization strategies. Specific examples are provided to illustrate concepts like additional infection controls, transmission of diseases, and common workplace hazards. Maintaining a safe work environment through identifying and reporting risks of infection is emphasized.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
25%(4)25% acharam este documento útil (4 votos)
1K visualizações4 páginasHLTWHS002 PDF
Enviado por
Jase HarrisonThis document contains questions and answers about health and safety practices for direct client care. It discusses key topics like the Work Health and Safety Act 2011, WHS regulations, codes of practice, industry standards, employer and worker responsibilities, duty of care, manual handling tasks, infection control processes, hazards, safety signs, personal protective equipment, and risk minimization strategies. Specific examples are provided to illustrate concepts like additional infection controls, transmission of diseases, and common workplace hazards. Maintaining a safe work environment through identifying and reporting risks of infection is emphasized.
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 4
HLTWHS002 – Follow safe work practices
for direct client care
Final Assessment Tasks
Part A – Questions
Question 1 – Briefly explain why the Work Health and Safety Act 2011 (Cth) is important. Does this legislation apply to
all states/territories? Explain why or why not.
The Work Health and Safety Act 2011 came in to protect workers’ health safety and their welfare of all
individuals at their workplace, it also protects all other people who may be affected by the work. It is important
since it protects workers where there are issues, injuries at work, there are procedures to follow to ensure that
that person is looked after. Each state or territory has their own laws. In 2011, Worksafe Australia implemented
them.
Question 2 – Briefly explain what WHS regulations are why they are important.
Work health and safety is a safeguard that employees have to enforce onto employees and the workplace to
work for employees. Work health and safety monitors workers and conditions at the workplace and is also
there to prevent illness or injury. They protect our wellbeing.
Question 3 – Briefly explain what WHS codes of practice are and why they are important.
A code of practice s an easy to understand but practical guide developed by safe work Australia, informed by
the public and approved by workplace minister. There are 24 codes and they are there to protect everyone in
the workplace especially the clients. Codes of practice are important safeguard that protects workers and
participants. If some or one standard isn’t properly enforced and someone gets hurt that means that code
wasn’t fully implemented, so someone gets hurt, and Worksafe steps in or supports you.
Question 4 – Explain what industry standards are and why they are important.
Industry standards are Australian Standards which are particular standards that explain safety requirements for
people that work in certain areas, which require different equipment. So, these standards are added to
legislation for them to be legally binding. Standards are important because they provide people and businesses
with a mutual understanding. These tools help with communication and manufacturing standards.
Question 5 – What are the rights and responsibilities of employers and workers in a community services environment
as a result of Australian health and safety legislation?
It’s an employer’s job to make sure their workplace is free from hazards. Also to maintain the health and safety
of themselves, their employees and all the other people involved in that workplace. Employers who do not
follow the proper safety procedures under that particular act may face certain penalties and fines.
Question 6 – In Australian safety legislation, what is meant by a duty of care? How is this relevant to those who work in
the community services sector?
Duty of care – that employees must anticipate risks for the clients and take care to prevent them coming to
harm. WHS tries to make sure that employers uphold their duty of care to their employees so in turn
employees make safe choices in the workplace. So the duty of care are embedded in many laws and
regulations which aim to protect and maintain the health, wellbeing and safety of others.
Question 7 – how does Australian safety regulation impact on the way hazardous manual tasks are carried out?
Australian safety regulation dictates that hazardous manual tasks (when an employee is required to push, pull,
lift carry or otherwise move a heavy or bulky item) must be done in a way that does not hurt the employee or
cause strains on them. This could include safe manual handling like lifting with your knees instead of your back.
Question 8 – How does Australian safety regulation impact on the way that infection control professes are carried out?
By having standard precautions are the work practices required to achieve a basic level of infection prevention.
Workplace legislations places a duty to ensure health and safety. Its WSH job to implement infection control.
WHS are like a watchdog that makes sure all policies and procedures are followed properly. All the correct
professes concerning infection control are followed.
Leanne Scaffidi – Aged Care/HACC – 9/04/2019
Question 9 – What is a hazard? Give an example of a hazard you may find in a workplace.
Anything that can cause spills like buckets full of water, cords running across the floor, working on a ladder. A
hazard is a danger of risk, flammable liquid (not stored properly) carpet or rug with a corner bent up or tripping
hazard.
Question 10 – Where is the most suitable place to install a smoke alarm in (a) a home and (b) a workplace?
(a) It is always important to have an electrician install a smoke alarm. You should check smoke alarms are in
every bedroom, hallway where all bedroom s are connected and on each level of residence including the
basement.
(b) Smoke alarms should be in every room in a workplace, especially where food is prepared or electrical
equipment is used.
Question 11 – What are the recommended maintenance requirements for a smoke alarm?
It is required that every smoke alarm’s batteries are changed every year by a professional electrician with
proper accreditation. Replace the entire smoke alarm every ten years. Also smoke alarms are to be installed
properly in corridors and sleeping quarters, kitchens and a certain amount per level.
Question 12 – What is the purpose of safety signs and symbols in the community services environment?
The purpose of having signage in the workplace is to identify and warn workers who may be exposed to
hazards in the workplace. Safety signs can assist in the communication of important instructions, reinforce
safety messages, and provide instruction for emergency situations.
Question 13 – Describe the appearance and use of poison safety signs and symbols in the community services
environment.
Safety signs and symbols have a dangerous looking sign like the human skull and two bones crossed together is
a warning that it is poisonous and poisonous substances are present.
Question 14 – Describe the appearance and use of emergency equipment safety signs and symbols in the community
services environment.
The look of emergency equipment is a white background with blue writing or symbols stating what is in a bucket
or container. It could even be a sign telling the worker to warn them of a hazard or danger. When dealing with
equipment that has signs that show danger we must use PPE to handle, like googles to protect the eyes and
face masks.
Question 15 – Describe the appearance and use of personal protective equipment safety signs and symbols in the
community services environment.
The appearance of these signs will be white background on a blue circular background and will include the
following protective wear, use of goggles, protective eyewear, and use of facemasks or shield, use of gloves.
Question 16 – Describe the appearance and use of specific safety signs and symbols for specific hazards (such as
sharps and radiation) in the community services environment.
It is to prevent injury, a hazard sign should be black on yellow. Sharps container is a yellow container labelled
‘Danger, contaminated sharps’ and marked black biohazard symbol also with the word ‘poison’.
Question 17 – Give an example of a control measure for minimising manual handling risk.
These hazards can be identified in different ways. Walk through a workplace and look for potential hazards –
talk over risk factors with workers, check through injury records to help pinpoint recurring problems, regularly
monitor and update risk identification.
Question 18 – Give an example of a situation where additional infection controls are required.
Additional infection controls wold be necessary if there was an outbreak of gastroenteritis. Staff would need
gowns, gloves and masks to protect themselves from spreading the infection. Ward would go into lockdown as
a precaution.
Question 19 – Imagine you are a worker providing care to a person with pulmonary tuberculosis. In this situation
standard precautions alone may not be sufficient to prevent transmission of infections. Give two examples of
additional precautions that you could apply to minimise risk of transmission.
In this situation no immune-compromised person would be allowed to enter the room. The patient must be
quarantined to a solitary room, equipment used on the patient must only be used on this patient, and the
Leanne Scaffidi – Aged Care/HACC – 9/04/2019
patient must not leave his/her room. They should also use their own toilet and gown and gloves must be
provided when dealing directly with this patient.
Question 20 – Outline why workers must identify risks of infection and report them according to workplace procedures.
Also provide two examples of common sources of infection and two examples of common causes of disease
transmission.
Successful infection control is critical to maintaining a safe work environment. Identifying hazards and reporting
them help to control and or prevent risks of infection outbreak so it is imperative to be extremely attentive
when signs start or before exposure and the likelihood of transmission.
Two examples of common sources of infection include strep throat, urinary tract infections and the common
cold.
Two examples of common causes of disease transmission include direct contact, droplets, or a mosquito can
carry the infection and then bite us, or carried on food, or airborne.
Part B – Case study questions
CS Question 1 – What common workplace hazards should Abdul be aware of when completing his safety inspection?
Different types of hazards, smoke detectors, make sufficient gloves, proper PPE, fire extinguishers, machinery.
CS Question 2 – What are some common infectious disease hazards risks that Tahlia and Abdul should be aware of?
Gastro, flue, staph, shingles, MRSA, HIV, Hepatitis C.
CS Question 3 – What types of common personal safety hazards might Abdul screen for during his inspection?
Are staff properly trained? Are you provided with distress alarms? Walking to your car. Do you feel safe in your
workplace? Adequate lighting, tolerance to bullying.
CS Question 4 – What are some hazard identification methods that may be recommended in Abdul’s hazard
identification procedure?
Policies and procedures, safety signs and fire/evacuation plan, repair and replace equipment.
CS Question 5 – What are some common strategies for minimising workplace risk that might be in use in Abdul’s
workplace?
Routine inspection
Maintenance check reducing risk of hazards, management of risks.
CS Question 6 – Outline how Nerelee and the client’s rights and responsibilities are upheld with regard to ensuring
safety in a home-based environment?
- Caseworker does hazard report (duty of care)
- Individualised plan, keep in contact with supervisor updated regularly to maintain client’s risks and
needs safely.
CS Question 7 – What important information on basic fire safety should Nerelee consider before providing services in a
home-based environment?
Smoke detectors exist to make sure, evacuation plan, risky behaviour, overloaded power points, and draperies
close to heaters.
CS Question 8 – Give two examples of client groups that may be at higher risk of behaviours or actions that can result
in danger from fire.
Smokers, alcohol drinkers, people with mental health issues, people with dementia, people with disabilities,
people that fall asleep with cigarette in hand.
CS Question 9 – Give two examples of client behaviours that contribute to fire injury and fatalities, and outline who you
should report to.
A person that is on medication that sedates overtaking car control. Someone drunk and falling asleep in bed,
forget to turn gas off and leaves food unattended. Write everything down and report it to supervisor.
CS Question 10 – What important information regarding behaviours of concern should Nerelee be aware of in order to
minimise risk to her personal safety?
Know her client
Assess situation before you even get in the house
Know their triggers
Leanne Scaffidi – Aged Care/HACC – 9/04/2019
Know when you are in risk of danger.
CS Question 11 – What are two common sources of infection in the home-based environment that Nerelee needs to be
aware of in order to minimise infection control risk?
Dirty dishes, toilet seat
Bins, carry.
Fridge, sinks, dirty clothes
Pets carry contaminants.
CS Question 12 – What is the musculoskeletal system and which tasks place Nerelee at risk of harm to her
musculoskeletal system?
Skeleton, muscles tendons.
Don’t lift things the wrong way
Don’t lift heavy things
CS Question 13 – Give two examples of safe work practices that Nerelee could use to minimise the risk of
musculoskeletal injury to herself and the clients.
Have a specific risk management strategy for home based community service.
Never attempt to lift or carry loads if you think they are too heavy. If you have to bend to pick up something you
need to use your legs to lift, use mechanical aids to help you carry a heavy load wherever possible.
CS Question 14 – What important manual handling information should Phillip find in his workplace WHS policies and
procedures?
Handling equipment, prepare a manual handling plan for assisting each person, make sure you are trained to
use all equipment and know how to safely assist when transferring people or objects. Plan ahead and fin the
best route for transferring that person.
CS Question 15 – What are some common manual handling procedures and work instructions that Phillip may be
required to follow in order to minimise manual handling risk?
Wear appropriate footwear and uniform. Get equipment in good condition. Follow instructions in care plan.
When assisting a person get them to participate as much as they can. Use clear communication and explain
your role and movement cues. Make sure all equipment works and is safely restrained and secured.
CS Question 16 – What are some ways that Zoe may identify hazardous manual tasks in the workplace?
Walk around and do a visual, incident forms, identify a hazard – maintenance reports, routine inspections, and
audit.
CS Question 17 – Why is it important that the workplace emergency procedures in Janice’s workplace are current?
It is important workplace procedures are current because someone like Janice must ensure an emergency plan
is prepared for the workplace. Effective communication between the people authorised to coordinate the
emergency response and all people at the workplace testing of the emergency procedures including the
frequency of testing.
CS Question 18 – Janie reviews the workplace system documents relating to current housekeeping practices. Briefly
explain how Janice could ensure current housekeeping practices are kept up-to-date.
Refer to Worksafe Australia 2011. Update policies and procedures, tell everyone of the change. Make sure
everything is current and all up to standard.
CS Question 19 – Janice reviews the documents relating to personal protective equipment. Briefly explain how Janice
could ensure current practices relating to personal protective equipment are kept up to date.
Making staff aware of any changes.
Keep stocktake order and keep a record. Keep a record of what policies and procedures are in line what
legislation.
CS Question 20 – How could Janice determine if the organization’s routine work practices are up to date with current
best practice standards?
Aged care standards, check work health and safety department safety. Ring up company to find out work
practices are up to date with current best practice and standards.
Leanne Scaffidi – Aged Care/HACC – 9/04/2019
Você também pode gostar
- STUDENT ASSESSMENT FOR SAFE PRACTICESDocumento55 páginasSTUDENT ASSESSMENT FOR SAFE PRACTICESSebin George0% (7)
- Student assessment for safe work practicesDocumento15 páginasStudent assessment for safe work practicesradhika100% (1)
- Assessment Guide: CHCDIS007 Facilitate The Empowerment of People With A DisabilityDocumento23 páginasAssessment Guide: CHCDIS007 Facilitate The Empowerment of People With A DisabilitySamir Bhandari100% (1)
- Topic 1: Before You Begin Determine Personal Support RequirementsDocumento20 páginasTopic 1: Before You Begin Determine Personal Support Requirementsdefa reyAinda não há avaliações
- Classroom Activity CHCDIS003Documento4 páginasClassroom Activity CHCDIS003Sonam GurungAinda não há avaliações
- Student Assessment Booklet: CHC33015 C III I SDocumento26 páginasStudent Assessment Booklet: CHC33015 C III I SSibani Kar0% (2)
- ART Empowering People With A Disability (ID 97385)Documento16 páginasART Empowering People With A Disability (ID 97385)amir abbasiAinda não há avaliações
- Ariane HLTWHS002 Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client Care CASE STUDY 2Documento1 páginaAriane HLTWHS002 Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client Care CASE STUDY 2Sandip Paudel0% (1)
- HLTWHS002 Safe Work Practices 5 PDFDocumento1 páginaHLTWHS002 Safe Work Practices 5 PDFSandip PaudelAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Click or Tap Here To Enter Text. Click or Tap Here To Enter TextDocumento15 páginasAssessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Click or Tap Here To Enter Text. Click or Tap Here To Enter TextGurpreet Singh WirringAinda não há avaliações
- H&H accredited training australasia incDocumento139 páginasH&H accredited training australasia incBùi Thắng50% (2)
- Afshan-Work Legally and Ethically - Written TaskDocumento12 páginasAfshan-Work Legally and Ethically - Written TaskAsh Amin50% (2)
- CHCHCS001 Home & Community SupportDocumento23 páginasCHCHCS001 Home & Community SupportSibani KarAinda não há avaliações
- HLTWHS002 - HO - HLTWHS002-Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client CareDocumento34 páginasHLTWHS002 - HO - HLTWHS002-Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client CareTalhaFarrukh67% (6)
- CHCAGE002Documento16 páginasCHCAGE002Niraj NepalAinda não há avaliações
- CHCCCS011 AssignmentDocumento24 páginasCHCCCS011 AssignmentUgyen Lhamo100% (2)
- CHCAGE001 AssignmentDocumento6 páginasCHCAGE001 AssignmentyESHEy TAinda não há avaliações
- CHCLEG001 Student Assessment. V3. 300616Documento33 páginasCHCLEG001 Student Assessment. V3. 300616PUNEET KOUR0% (4)
- Information Book CHC33015 Cert III Individual Support Ageing HACC 2019 v1Documento15 páginasInformation Book CHC33015 Cert III Individual Support Ageing HACC 2019 v1Andrew100% (1)
- Supporting Relationships with Carers and FamiliesDocumento13 páginasSupporting Relationships with Carers and FamiliesshwetaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Student Assessment HLTWHS002 Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client CareDocumento24 páginasAssessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Student Assessment HLTWHS002 Follow Safe Work Practices For Direct Client CareGurpreet Singh WirringAinda não há avaliações
- LearnerGuide 3 - CHCCOM005 - CHCDIV001Documento69 páginasLearnerGuide 3 - CHCCOM005 - CHCDIV001Raju Subedi50% (2)
- Community Sector Legal EthicsDocumento5 páginasCommunity Sector Legal EthicsIndy Efu100% (1)
- Home and Community Support CHCHCS001 Provide Home and Community Support ServicesDocumento31 páginasHome and Community Support CHCHCS001 Provide Home and Community Support Serviceskul1990100% (1)
- Task 2 Meet Personal NeedsDocumento3 páginasTask 2 Meet Personal Needsdev kumarAinda não há avaliações
- Classroom Activity CHCDIS007Documento3 páginasClassroom Activity CHCDIS007Sonam Gurung100% (1)
- Task 1 Meet Personal NeedsDocumento6 páginasTask 1 Meet Personal Needsdev kumar67% (3)
- (Type Text) : Student Assessment Booklet Chchcs001 Provide Home and Community Support ServicesDocumento32 páginas(Type Text) : Student Assessment Booklet Chchcs001 Provide Home and Community Support ServicesPriyanka Singla100% (2)
- CHCCOM005 Communication and Work in Health and Community Services 4Documento13 páginasCHCCOM005 Communication and Work in Health and Community Services 4yESHEy TAinda não há avaliações
- Assess Case Studies on Ethical DilemmasDocumento2 páginasAssess Case Studies on Ethical Dilemmaskul199067% (6)
- CHCLEG001 Assessment - Tahlia O'Keefe-QuinnDocumento3 páginasCHCLEG001 Assessment - Tahlia O'Keefe-QuinnSamantha Abel100% (4)
- Individual Support Work Skills Workshop Student Assessments BookletDocumento68 páginasIndividual Support Work Skills Workshop Student Assessments BookletPranav Prajapati0% (2)
- HLTINF006 Assessment Task 1 With AnswerDocumento8 páginasHLTINF006 Assessment Task 1 With AnswerRebeca Raducu100% (1)
- Guidelines For Infection Prevention and Control - IrlandaDocumento120 páginasGuidelines For Infection Prevention and Control - IrlandaRaquel LopesAinda não há avaliações
- CHCAGE002 Implement Falls Prevention SAB v3.1 THEORYDocumento20 páginasCHCAGE002 Implement Falls Prevention SAB v3.1 THEORYAbhishek Dhungel33% (3)
- Assessment Summary / Cover SheetDocumento14 páginasAssessment Summary / Cover Sheetradhika33% (3)
- CHCCCS015 Provide Individualised Support SAB v3.2 THEORYDocumento27 páginasCHCCCS015 Provide Individualised Support SAB v3.2 THEORYShufali Sherchan100% (1)
- 32476C/P3 Work Placement Portfolio: 1. Background/overviewDocumento31 páginas32476C/P3 Work Placement Portfolio: 1. Background/overviewtetyanaAinda não há avaliações
- Assessing Risk and Implementing Interventions for SeniorsDocumento17 páginasAssessing Risk and Implementing Interventions for SeniorsAkis Drallos0% (3)
- LEGAL AND ETHICAL ASSESSMENTDocumento33 páginasLEGAL AND ETHICAL ASSESSMENTGurpreet Singh Wirring50% (2)
- CHCDIS003 AssessmentDocumento28 páginasCHCDIS003 AssessmentVipin Kc100% (1)
- SAB CHCAGE005 Provide Support To People Living With DementiaDocumento114 páginasSAB CHCAGE005 Provide Support To People Living With DementiaAnonymous wWCGc6fzUX100% (3)
- IS01Documento8 páginasIS01Anonymous lSPAn1V100% (1)
- HLTWHS002 Follow Safe Practices For Direct Client Care SAB v3.0 - THEORYDocumento22 páginasHLTWHS002 Follow Safe Practices For Direct Client Care SAB v3.0 - THEORYSujan Adhikari100% (2)
- Coordinating Client SupportDocumento15 páginasCoordinating Client Supportwaniya shaikhAinda não há avaliações
- CHCCOM005 Marking GuideDocumento26 páginasCHCCOM005 Marking GuideDHRUV KHULLAR40% (5)
- LearnerGuide 2 - CHCLEG001 - HLTWHS002Documento81 páginasLearnerGuide 2 - CHCLEG001 - HLTWHS002Raju Subedi75% (4)
- CHCCCS015 Assessment Tool V1.4 Nov 2018Documento12 páginasCHCCCS015 Assessment Tool V1.4 Nov 2018yESHEy T100% (1)
- Chcdis003 Case StudyDocumento15 páginasChcdis003 Case StudyRajina MaharjanAinda não há avaliações
- Learner Guide CHCCCS023 Support Independence and Well Being: International CollegeDocumento172 páginasLearner Guide CHCCCS023 Support Independence and Well Being: International CollegeElsie GibbsAinda não há avaliações
- Person-centered aged care optionsDocumento9 páginasPerson-centered aged care optionsSoniya Ghising100% (2)
- Work Placement Log Book - CHC33015 Certificate III in Individual SupportDocumento16 páginasWork Placement Log Book - CHC33015 Certificate III in Individual SupportSalina Bohara40% (5)
- HLTHPS007 Student Work Book V2 15.02.19Documento92 páginasHLTHPS007 Student Work Book V2 15.02.19Bùi Thắng0% (1)
- CHCCCS011 Meet Personal Support Needs Resource InterCare1Documento146 páginasCHCCCS011 Meet Personal Support Needs Resource InterCare1komalbajaj100% (1)
- Assessment WorkbookDocumento87 páginasAssessment WorkbookMaimuna100% (1)
- Assessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Click Here To Enter Text. Click Here To Enter Text. Click Here To Enter TextDocumento18 páginasAssessment Summary / Cover Sheet: Click Here To Enter Text. Click Here To Enter Text. Click Here To Enter Textradhika100% (1)
- CHCPAL001 Deliver Care Services Using A Palliative ApproachDocumento11 páginasCHCPAL001 Deliver Care Services Using A Palliative ApproachAfifa M Afzal100% (1)
- E1144 Module2 Assessment3 SAQrubric 32469 03 v2 3 THyde 1 01 04 2020 2159Documento25 páginasE1144 Module2 Assessment3 SAQrubric 32469 03 v2 3 THyde 1 01 04 2020 2159tetyana0% (1)
- Shyna Assessment 2Documento17 páginasShyna Assessment 2dev kumar100% (1)
- Safety Basics Utility IndustryDocumento9 páginasSafety Basics Utility IndustryCesar García MataAinda não há avaliações
- Bersma hl60Documento1 páginaBersma hl60Jase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- 2005indonSL InddDocumento17 páginas2005indonSL InddJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Akmajian Demers Farmer Harnish Linguistics An Introduction To Language and CommunicationDocumento309 páginasAkmajian Demers Farmer Harnish Linguistics An Introduction To Language and CommunicationJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Indonesian Second Language: Written ExaminationDocumento18 páginasIndonesian Second Language: Written ExaminationJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- VSL Indonesian Unit 2 Workbook 2Documento144 páginasVSL Indonesian Unit 2 Workbook 2Jase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- PDFDocumento285 páginasPDFJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Senior Booklist Instructions 2019 PDFDocumento5 páginasSenior Booklist Instructions 2019 PDFJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- vocAB TEST YEAR 8 PDFDocumento2 páginasvocAB TEST YEAR 8 PDFJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Nutcracker Suite Tchaikovski2Documento54 páginasNutcracker Suite Tchaikovski2Jase Harrison100% (1)
- Unit 3 SAC 2 PDFDocumento2 páginasUnit 3 SAC 2 PDFJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Indonesian Flash CardsDocumento2 páginasIndonesian Flash CardsJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Indonesian Second Language: Written ExaminationDocumento18 páginasIndonesian Second Language: Written ExaminationJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Style and Submission TipsDocumento14 páginasStyle and Submission TipsJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Global Citizenship Program: Activities and Outcomes FormDocumento4 páginasGlobal Citizenship Program: Activities and Outcomes FormJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- How To Use A DictionaryDocumento3 páginasHow To Use A DictionaryJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- AIS302 Developed and Developing Worlds Assessment Tasks 11 JulyDocumento9 páginasAIS302 Developed and Developing Worlds Assessment Tasks 11 JulyJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Indonesian SL Study DesignDocumento61 páginasIndonesian SL Study DesignJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges of Chronic and Structural Poverty in South AfricaDocumento33 páginasChallenges of Chronic and Structural Poverty in South AfricaJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Eramet Sustainable Development PolicyDocumento7 páginasEramet Sustainable Development PolicyJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Weda Bay Public Report Oct2013Documento85 páginasWeda Bay Public Report Oct2013Jase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Working Paper Number 107 Does It Matter That We Don't Agree On The Definition of Poverty? A Comparison of Four ApproachesDocumento41 páginasWorking Paper Number 107 Does It Matter That We Don't Agree On The Definition of Poverty? A Comparison of Four ApproachesJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Weda Bay Public Report Oct2013Documento85 páginasWeda Bay Public Report Oct2013Jase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Ayurveda: A Multilectic InterpretationDocumento8 páginasAyurveda: A Multilectic InterpretationJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Deakin University: This Unit Guide Is Applicable For The Year and Teaching Period Specified Above OnlyDocumento11 páginasDeakin University: This Unit Guide Is Applicable For The Year and Teaching Period Specified Above OnlyJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Ex Exec SummaryDocumento1 páginaEx Exec SummaryMohd AfiqAinda não há avaliações
- Deakin University: This Unit Guide Is Applicable For The Year and Teaching Period Specified Above OnlyDocumento15 páginasDeakin University: This Unit Guide Is Applicable For The Year and Teaching Period Specified Above OnlyJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Ex Exec SummaryDocumento1 páginaEx Exec SummaryMohd AfiqAinda não há avaliações
- ACOSS Poverty Report 2012 - FinalDocumento40 páginasACOSS Poverty Report 2012 - FinalMark RowleyAinda não há avaliações
- The Quest For Evidence-Based Ayurveda: Lessons Learned: Bhushan PatwardhanDocumento13 páginasThe Quest For Evidence-Based Ayurveda: Lessons Learned: Bhushan PatwardhanJase HarrisonAinda não há avaliações
- Principles of Veterinary SuturingDocumento25 páginasPrinciples of Veterinary Suturingnandhus2227Ainda não há avaliações
- Reviewer (Gen. Biology 2)Documento5 páginasReviewer (Gen. Biology 2)ianah aloriaAinda não há avaliações
- Part 7 Pyeloroplasty: Quick and BloodlessDocumento31 páginasPart 7 Pyeloroplasty: Quick and BloodlessAnonymous MmiBnqnDyAinda não há avaliações
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion NCPDocumento5 páginasIneffective Tissue Perfusion NCPJasmin Calata50% (2)
- Circular Covid-19 Measures: INCO International Fz. Co. ح م ش ﺔﯾﻟودﻟا وﻛﻧاDocumento2 páginasCircular Covid-19 Measures: INCO International Fz. Co. ح م ش ﺔﯾﻟودﻟا وﻛﻧاErin JohnsonAinda não há avaliações
- What Is Cancer? What Causes Cancer?: Discovered An Important Clue As To Why Cancer Cells SpreadDocumento8 páginasWhat Is Cancer? What Causes Cancer?: Discovered An Important Clue As To Why Cancer Cells SpreadAlfred Melvin SolivaAinda não há avaliações
- Peroneus Longus Tendon Rupture Case ReportDocumento14 páginasPeroneus Longus Tendon Rupture Case ReportAlgivar DaudAinda não há avaliações
- How Do We Take Care of Our Endocrine SystemDocumento7 páginasHow Do We Take Care of Our Endocrine SystemAndrei CunananAinda não há avaliações
- History of RotaryDocumento5 páginasHistory of Rotaryestela togononAinda não há avaliações
- What To Expect After VaccinationsDocumento2 páginasWhat To Expect After Vaccinationsmunshimbwe munshimbweAinda não há avaliações
- Breast FeedingDocumento76 páginasBreast FeedingDina GamalAinda não há avaliações
- Mh-Somatic Symptom Disorders - 2Documento9 páginasMh-Somatic Symptom Disorders - 2martinAinda não há avaliações
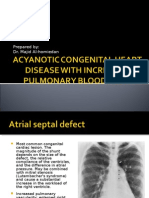
- Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease With Increased Pulmonary Blood FlowDocumento9 páginasAcyanotic Congenital Heart Disease With Increased Pulmonary Blood Flowdrhomiedan100% (1)
- Traditional Medicine: Heated Moxibustion and Bloodletting in Tibetan Medical Literature of Dunhuang HeritageDocumento3 páginasTraditional Medicine: Heated Moxibustion and Bloodletting in Tibetan Medical Literature of Dunhuang HeritageAigo Seiga CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Amphetamine Drug Fact Sheet: Uses, Effects, Legal StatusDocumento1 páginaAmphetamine Drug Fact Sheet: Uses, Effects, Legal StatusEvandro Ricardo GomesAinda não há avaliações
- Pre Medical Form PDFDocumento11 páginasPre Medical Form PDFNitin KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Employer's Work Accident ReportDocumento1 páginaEmployer's Work Accident ReportAlex Elle0% (1)
- List of 10 Abiotic Factors Causing Plant DiseaseDocumento3 páginasList of 10 Abiotic Factors Causing Plant DiseaseFrances Jay FerrerAinda não há avaliações
- AMI Case ReportDocumento19 páginasAMI Case ReportTimothy TanAinda não há avaliações
- Vancomycin - 3rd Generation GlycopeptideDocumento3 páginasVancomycin - 3rd Generation GlycopeptideJenny Agustin FabrosAinda não há avaliações
- PSCM Guidelines For Clinical Practice PhilippinesDocumento10 páginasPSCM Guidelines For Clinical Practice PhilippinesanthonyAinda não há avaliações
- Revascularization-Associated Intracanal Calcification: A Case Report With An 8-Year ReviewDocumento4 páginasRevascularization-Associated Intracanal Calcification: A Case Report With An 8-Year ReviewIvan PolancoAinda não há avaliações
- Cer 212 Urinary Incontinence Updated 1Documento643 páginasCer 212 Urinary Incontinence Updated 1rahmat_husein1Ainda não há avaliações
- Paediatric Protocols Kenya PDFDocumento35 páginasPaediatric Protocols Kenya PDFMusab Ahmed HirshiAinda não há avaliações
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDocumento8 páginasGuillain Barre SyndromeStephanie AureliaAinda não há avaliações
- Dr. Kuntal Das - ResumeDocumento5 páginasDr. Kuntal Das - ResumeKuntal DasAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmaceutics 13 01313Documento23 páginasPharmaceutics 13 01313maizhafiraAinda não há avaliações
- MCQ 2019 Part 1 UseDocumento94 páginasMCQ 2019 Part 1 UseMimmey YeniwAinda não há avaliações
- Chronic Kidney Disease Case StudyDocumento52 páginasChronic Kidney Disease Case StudyGi100% (1)
- The Rules of The Cancer Patient Diet and Dr. Hammer GNMDocumento71 páginasThe Rules of The Cancer Patient Diet and Dr. Hammer GNMshivapuja100% (1)