Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Recs MCQs 2018
Enviado por
danielle0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
3 visualizações3 páginasRefs
Direitos autorais
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoRefs
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
0 notas0% acharam este documento útil (0 voto)
3 visualizações3 páginasRecs MCQs 2018
Enviado por
danielleRefs
Direitos autorais:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponíveis
Baixe no formato DOCX, PDF, TXT ou leia online no Scribd
Você está na página 1de 3
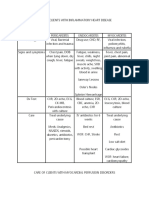
Recommendations about MCQs in Primary Care / Family Medicine
N Topic Recommendations - pay attention to the following issues:
1. Chest pain Symptoms and signs of angina pectoris, pulmonary embolism, Dressler’s
syndrome, aortic stenosis;
ECG patterns of pulmonary embolism;
Role of chest x-ray in assessment of chest pain;
2. Coronary Artery Risk factors of abdominal aneurysm, MI;
Disease Symptoms of angina pectoris (classic, atypical angina, anginal
equivalent);
Target level of LDL in patients with established CHD;
Interpretation of cardiac troponins elevation;
Development of tolerance when using nitrates;
Endpoint for the use of β-blockers (heart rate);
3. Heart Failure Role of β-Type natriuretic peptide in assessment of CHF;
Role of Echocardiogram in assessment of CHF;
New York Heart Association classification of heart failure;
Drug treatment of CHF with systolic disfunction;
Role of ACEI and ARB in treatment of CHF;
Role of Beta Blocker in treatment of CHF;
Use of digoxin in CHF;
4. Hypertension (use Routine tests for the assessment of hypertension;
JNC7 Role of lifestyle modifications in systolic blood pressure reduction
recommendations, as (which interventions are most effective);
it is in the textbook) Selection of initial drug for hypertension when there are no compelling
indications;
Treatment of hypertension when the patient has compelling indications
(e.g. diabetes, CHF, CHD, kidney disease etc.)
Side effects of ACEIs, Clonidine;
Indications for using two-drug combination of medications for effective
management of high blood pressure;
Selecting drugs for treating hypertension in African-American patients;
Symptoms and signs of a coarctation of the aorta;
Useful tests for assessment of the patient with renovascular
hypertension;
5. Diabetes Pathophysiology of Type I diabetes mellitus;
Factors associated with diabetic ketoacidosis;
Diagnostic criteria for the diabetes mellitus;
Diabetic foot ulcers – infection management;
Recommendations about insulin injections;
Role of GFR in assessment of kidney damage;
6. Thyroid problems Symptoms of Hypothyroidism, Hyperthyroidism and thyroid nodules;
Role of TSH and FT4 in assessment of Hyper- and Hypothyroidism;
Laboratory criteria for subclinical hypothyroidism;
Laboratory monitoring for Thyroid replacement therapy;
7. Obesity BMI for assessment of obesity;
8. Abdominal pain Symptoms of pancreatitis;
Symptoms of appendicitis;
Symptoms of Cholecystitis;
Symptoms and signs of Gallstones.
9. Dyspepsia and GERD Barrett’s esophagus;
Symptoms of peptic ulcer;
Assessment of dyspepsia, considering risk factors;
Indications for endoscopy in dyspepsia;
10. Dysuria and UTI Antibiotic for UTI in young women;
Indications for hospitalization during UTI;
Reasons for non-gonococcal urethritis;
Symptoms of Acute bacterial cystitis;
Indications for urine culture;
Antibiotic prevention of UTI in women;
Indications for cystoscopy;
Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria;
11. Low back pain Management of non-specific back pain;
Symptoms and management of lumbar disc disease;
Symptoms of Spinal stenosis;
Symptoms and lab findings of Multiple myeloma;
Back pain due to Inflammatory arthropathy;
Lab diagnosis of Ankylosing spondylitis;
Short- and long-term treatment of non-specific back pain;
Use of tricyclic antidepressant in the management of back pain;
12. Headache Symptoms of migraine headaches;
Use of Beta-blockers in prevention of migraine headache;
Use of Verapamil in prevention of migraine headache;
Use of Tricyclic antidepressants for the treatment of migraine
headache;
Use of triptans in migrane;
Considering age in assessment of headache;
13. Asthma Prevention of exercise-induced asthma attacks;
Role of spirometry;
14. COPD Infections in COPD
Role of spirometry;
15. Common cold Symptoms of Pertussis;
16. Sore throat Symptoms of strep throat;
Role of rapid streptococcal screening tests (enzyme immunoassays);
Assessment of streptococcal pharyngitis;
Diagnosis of peritonsillar abscess;
Treatment of mild to moderate croup;
17. Acute Rhinosinusitis, Role of Intranasal steroids in the management of chronic allergic
Rhinitis rhinitis;
Damage of specific sinuses in young children;
18. Acute Bronchitis Common causes of chronic cough;
19. Influenza Symptoms of Influenza;
Role of antivirals in treatment of Influenza;
Contraindications to influenza vaccination;
20. Community-acquired Most common causes of a community-acquired pneumonia;
Pneumonia Pneumococcal vaccination;
Você também pode gostar
- CRS Topics From SydneyDocumento8 páginasCRS Topics From SydneySubashan VadibelerAinda não há avaliações
- Able of Ontents: EdiatricsDocumento4 páginasAble of Ontents: EdiatricsDrx ahmed MaherAinda não há avaliações
- Internal Medicine VivasDocumento9 páginasInternal Medicine Vivasponcus payAinda não há avaliações
- Pharmacotherapeutics-Iii Fourth Pharm DDocumento15 páginasPharmacotherapeutics-Iii Fourth Pharm Dshasvina05Ainda não há avaliações
- Important MD QuestionsDocumento42 páginasImportant MD QuestionsSomnath Das GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Medical Israeli Syllabus For Internal Medicine For Exam LicenseDocumento4 páginasMedical Israeli Syllabus For Internal Medicine For Exam Licensemohammadeid0% (2)
- GLUMERULONEPHRITISDocumento3 páginasGLUMERULONEPHRITISLordgelyn Diane ViernesAinda não há avaliações
- MBBS Pediatrics Question BankDocumento17 páginasMBBS Pediatrics Question BankpolluAinda não há avaliações
- Leptospirosis - Policy Guide by PhilhealthDocumento6 páginasLeptospirosis - Policy Guide by PhilhealthKathrina AbastarAinda não há avaliações
- Glomerulopatías PrimariasDocumento8 páginasGlomerulopatías PrimariasGSEAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study On AGNDocumento28 páginasCase Study On AGNArchana SahuAinda não há avaliações
- Fourth Pharm D-Pharmacotherapeutics-IiiDocumento15 páginasFourth Pharm D-Pharmacotherapeutics-IiiAnoop TandurAinda não há avaliações
- Pembahasan To Online 3Documento201 páginasPembahasan To Online 3Fate DreamworkAinda não há avaliações
- CH 072 Immune Thrombocytopenic PurpuraDocumento8 páginasCH 072 Immune Thrombocytopenic PurpuratrilokAinda não há avaliações
- Must Know TopicDocumento3 páginasMust Know TopicyapAinda não há avaliações
- 8 Cirrhosis NewDocumento10 páginas8 Cirrhosis Newb_rahman2k39603Ainda não há avaliações
- Synopsis Internal DiseasesDocumento3 páginasSynopsis Internal DiseasesPepa KaradzhovaAinda não há avaliações
- The Heart in Rheumatic, Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Pathophysiology, Clinical Aspects and Therapeutic ApproachesNo EverandThe Heart in Rheumatic, Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Pathophysiology, Clinical Aspects and Therapeutic ApproachesUdi NussinovitchAinda não há avaliações
- ED Internal Medicine Oral Exam TopicsDocumento10 páginasED Internal Medicine Oral Exam TopicsalirbidiAinda não há avaliações
- 2021 V PR GEP NENs June Carcinoid Heart Disease FSDocumento24 páginas2021 V PR GEP NENs June Carcinoid Heart Disease FSΒΑΣΙΛΗΣ ΚΟΛΙΝΤΖΙΚΗΣAinda não há avaliações
- Case Presentation: Cagayan Valley Medical CenterDocumento57 páginasCase Presentation: Cagayan Valley Medical CenterGian PagadduAinda não há avaliações
- FERRET - Evaluating and Stabilizing The Critical FerretDocumento7 páginasFERRET - Evaluating and Stabilizing The Critical Ferrettaner_soysurenAinda não há avaliações
- SpecialityDocumento243 páginasSpecialitySkshah1974Ainda não há avaliações
- 2019 Chinese Guideline For The Management of Hypertension in The ElderlyDocumento33 páginas2019 Chinese Guideline For The Management of Hypertension in The ElderlyGerry MokoagowAinda não há avaliações
- Gen Medicine - Finalized Scheme of ExaminationDocumento30 páginasGen Medicine - Finalized Scheme of Examinationsp_rao2000Ainda não há avaliações
- Buerger's Disease, Thromboangitis Obliterans, TAODocumento5 páginasBuerger's Disease, Thromboangitis Obliterans, TAOshowmerAinda não há avaliações
- BMJ CCFDocumento94 páginasBMJ CCFaliakbar178Ainda não há avaliações
- Addison's Disease:: Clinical IntelligenceDocumento3 páginasAddison's Disease:: Clinical Intelligencemira tianiAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter Wise Questions PDFDocumento53 páginasChapter Wise Questions PDFBhageerath AttheAinda não há avaliações
- Practical guidelines for management of sickle cell diseaseDocumento2 páginasPractical guidelines for management of sickle cell diseaseAhmed BadrAinda não há avaliações
- Intro PDFDocumento2 páginasIntro PDFPharmacotherapyAinda não há avaliações
- Glomerular DiseasesDocumento5 páginasGlomerular DiseasesAdrian ZapataAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Presentation & Management of Glomerular Diseases: Hematuria, Nephritic & Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento4 páginasClinical Presentation & Management of Glomerular Diseases: Hematuria, Nephritic & Nephrotic SyndromeMutiara FauzaAinda não há avaliações
- 5 6289632017583702313Documento4 páginas5 6289632017583702313Dita Ambarsari SyafruddinAinda não há avaliações
- Tti Articulo 2Documento5 páginasTti Articulo 2Luu ZandovalAinda não há avaliações
- Toacs 2Documento104 páginasToacs 2aliakbar178Ainda não há avaliações
- Medurg MidtermDocumento4 páginasMedurg Midtermmark OrpillaAinda não há avaliações
- Medication AdultDocumento40 páginasMedication AdultFarah HusseinAinda não há avaliações
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDocumento29 páginasAcute Rheumatic FeverFelix Wafula MusibiAinda não há avaliações
- Kidney Problems Research GuideDocumento4 páginasKidney Problems Research GuideKim GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- Speciality: General Medicine Case: Nephrotic Syndrome HistoryDocumento49 páginasSpeciality: General Medicine Case: Nephrotic Syndrome Historydrtpk100% (2)
- Glomerulonefritis Primaria Medicine 2015Documento6 páginasGlomerulonefritis Primaria Medicine 2015Francisco Rebollar GarduñoAinda não há avaliações
- Problem 1 PDFDocumento4 páginasProblem 1 PDFSameer MohammedAinda não há avaliações
- Capstone Final ExamDocumento19 páginasCapstone Final ExamEileen Arboleda100% (3)
- Diagnostic Approach To Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento3 páginasDiagnostic Approach To Chronic Kidney DiseaseBlomblom Pow00Ainda não há avaliações
- Medicine & PaediatricsDocumento4 páginasMedicine & Paediatricspritoms108Ainda não há avaliações
- Kingston Hospital Blue Book 2019Documento207 páginasKingston Hospital Blue Book 2019Chris Jardine LiAinda não há avaliações
- 3-Inflammatory-and-Immunologic-responseDocumento15 páginas3-Inflammatory-and-Immunologic-responseJanely EstreraAinda não há avaliações
- Plan CursuriDocumento7 páginasPlan CursuriYener SulimanAinda não há avaliações
- Review of nephrotic syndrome managementDocumento7 páginasReview of nephrotic syndrome managementGarit Hapsari KiranaAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence-Based Gastroenterology and HepatologyNo EverandEvidence-Based Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn W. D. McDonaldAinda não há avaliações
- Hospital and Clinical PharmacyDocumento47 páginasHospital and Clinical Pharmacysachinpatidar986Ainda não há avaliações
- Shelf Questions From The CLIPP CasesDocumento54 páginasShelf Questions From The CLIPP CasesJoe Cone100% (1)
- Hypertension in Children and Adolescents: Recommendations of the ESHDocumento21 páginasHypertension in Children and Adolescents: Recommendations of the ESHdragonletalAinda não há avaliações
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel BakyDocumento8 páginasSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Lecture Salah Abdel Bakyahmed gabrAinda não há avaliações
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Department of Pediatrics The First Affiliated Hospital Sun Yat-Sen UniversityDocumento67 páginasNephrotic Syndrome: Department of Pediatrics The First Affiliated Hospital Sun Yat-Sen UniversityBuwaneka VidanageAinda não há avaliações
- Finals QuestionsDocumento10 páginasFinals QuestionsBobet ReñaAinda não há avaliações
- Fever of Unknown OriginDocumento19 páginasFever of Unknown OriginSUNIL KUMARAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Care Plans e Book Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention 9th Edition Ebook PDFDocumento62 páginasNursing Care Plans e Book Nursing Diagnosis and Intervention 9th Edition Ebook PDFmichael.lynch155100% (46)
- Endoxan: List of ExcipientsDocumento4 páginasEndoxan: List of ExcipientsBashyam RamAinda não há avaliações
- Tetralogy of Fallot - General Principles of ManagementDocumento11 páginasTetralogy of Fallot - General Principles of ManagementFajar Yuniftiadi100% (1)
- Future Scope and Challenges For Congestive Heart Failure Moving Towards Development of PharmacotherapyDocumento47 páginasFuture Scope and Challenges For Congestive Heart Failure Moving Towards Development of PharmacotherapysunhaolanAinda não há avaliações
- Risk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocumento2 páginasRisk NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputMICHELLE FACTOAinda não há avaliações
- MyocarditisDocumento29 páginasMyocarditispanvilai0% (1)
- Day Case Surgery 1LDocumento21 páginasDay Case Surgery 1LdrhiwaomerAinda não há avaliações
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocumento6 páginasIschemic Heart DiseaseApril Joy Villacorta PonceAinda não há avaliações
- Clinical Trial Protocol Synopsis Protocol TitleDocumento5 páginasClinical Trial Protocol Synopsis Protocol TitleGoutham Bharadwaj MadhadiAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Failure Clinical Pathway TemplateDocumento3 páginasHeart Failure Clinical Pathway Templategusmarinda fauziahAinda não há avaliações
- Heart Failure - Cardiovascular Medicine - MKSAP 17Documento16 páginasHeart Failure - Cardiovascular Medicine - MKSAP 17alaaAinda não há avaliações
- Prevalence of Pulmonary Hypertension in COPD: Original Research ArticleDocumento5 páginasPrevalence of Pulmonary Hypertension in COPD: Original Research ArticleMuhamad AgungAinda não há avaliações
- Preparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimDocumento14 páginasPreparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimclarimerAinda não há avaliações
- Cardio Q&aDocumento147 páginasCardio Q&aHoney Lyn AlebioAinda não há avaliações
- Advances in Managing Acute Decompensated Heart FailureDocumento14 páginasAdvances in Managing Acute Decompensated Heart FailureAnonymous NeRC5JYiSAinda não há avaliações
- 6-Minute Walk Test PDFDocumento3 páginas6-Minute Walk Test PDFtheragoAinda não há avaliações
- CH17 Cardiac Surgery in The Adult 5th Edition 2018Documento26 páginasCH17 Cardiac Surgery in The Adult 5th Edition 2018ChengShiun ShiueAinda não há avaliações
- Role of The Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Heart Failure and Cardiovascular DiseaseDocumento12 páginasRole of The Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Heart Failure and Cardiovascular DiseaseW CnAinda não há avaliações
- Simman Latest File 2023Documento42 páginasSimman Latest File 2023risingphoenix121212Ainda não há avaliações
- Pilar College Cardiac Catheterization ProcedureDocumento7 páginasPilar College Cardiac Catheterization ProcedureCake ManAinda não há avaliações
- Vitamins, Supplements, Herbal Medicines, and ArrhythmiasDocumento12 páginasVitamins, Supplements, Herbal Medicines, and ArrhythmiashyntnenAinda não há avaliações
- Running Head: REFLECTION ARTIFACT 1Documento21 páginasRunning Head: REFLECTION ARTIFACT 1api-396212664Ainda não há avaliações
- Cardiology Dissertation TitlesDocumento7 páginasCardiology Dissertation TitlesCustomWritingPapersUK100% (1)
- Bisoprolol in Heart Failure PDFDocumento37 páginasBisoprolol in Heart Failure PDFMega AlmiraAinda não há avaliações
- The Quiescent Benefits and Drawbacks of Coffee IntakeDocumento6 páginasThe Quiescent Benefits and Drawbacks of Coffee IntakeVikram Singh ChauhanAinda não há avaliações
- Improving Adherence in Cardiovascular Care ToolkitDocumento152 páginasImproving Adherence in Cardiovascular Care ToolkitDenis MiokovićAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study: Medical Colleges of Northern PhilippinesDocumento16 páginasCase Study: Medical Colleges of Northern Philippinesmark OrpillaAinda não há avaliações
- NCM 118 - Course Time TableDocumento6 páginasNCM 118 - Course Time TableLaurence Zerna100% (1)
- Valvular Heart DiseaseDocumento73 páginasValvular Heart Diseaseindia2puppy100% (4)
- COVID-19 AstraZeneca Vaccine Analysis PrintDocumento65 páginasCOVID-19 AstraZeneca Vaccine Analysis PrintcorreaAinda não há avaliações
- Nursing Drug CardsDocumento32 páginasNursing Drug CardsJenna Rasmussen100% (3)