Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
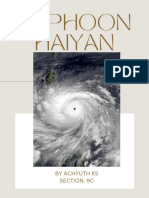
Analysis About Typhoon Haiyan
Enviado por
Mary Rose Silva GargarTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Analysis About Typhoon Haiyan
Enviado por
Mary Rose Silva GargarDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Analysis about Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda)
A Typhoon is an intense area of low atmospheric pressure. Like all low pressure weather
systems observed North of the Equator, the air rotates around the center of an area of low
pressure in an anti-clockwise direction (clockwise if South of the Equator). The more intense
the area of low pressure the higher the wind speeds near the center. A Typhoon is a low
pressure weather system with sustained wind speeds near its center of at least 56 knots
(about 105 kph). Typhoons are made over the ocean; typhoons are not made over land.
In 2013, Typhoon Yolanda (also known as Typhoon Haiyan) struck the Philippines and was
the deadliest typhoon in the country’s history. Over six thousand people lost their lives and
over 1 million people’s homes were damaged, displacing over 600,000 people. A monster
typhoon, with winds reaching 147mph, killed, tossed houses into the sea and sent millions
fleeing for shelter in the Philippines. On November 7th, 2013 Typhoon Yolanda hit the
Philippines. While the Philippines is no stranger to the power of tropical storms, it was not
prepared for the devastating effects of Typhoon Yolanda, which was one of the strongest
storms ever recorded. The fact that the Philippines is comprised of over 7,000 islands leaves
the country particularly vulnerable to strong winds and storm surges. In the Philippines, a
vast number of inhabitants live in areas with poor infrastructure and housing, which made
Typhoon Yolanda especially dangerous. In the wake of Yolanda’s destruction, thousands lost
their lives, 4.1 million people were left displaced from their homes, and 6 million workers
were left without means to support their livelihood. Typhoon Yolanda caused severe
damage to some of the Philippines biggest sources of income, destroying coconut farms all
over the islands, leaving over a million coconut farmers without a means to support
themselves as they’ve had to wait years for their farms to recover. The typhoon also greatly
affected local fisheries, which is one of the Philippines most important sectors, employing
1.6 million people. Many families lost everything during Typhoon Yolanda and were left
struggling once the storm was over. The lack of options for transitional and permanent
housing prolonged the displacement for many families, many of which are still trying to
recover.
The destruction typhoon Haiyan caused was immense. A category 5 super typhoon,
developed in the west-northern part of the North Pacific Ocean by thunderstorms
converting moisture into heat, causing more air to flow to the centre of the storm causing
evaporation, all the heat and air flow towards the eye thus creating a typhoon. The
diameter of the storm was about 300 miles. The wind speed was estimated to have reached
an average of 310 km/h (195mp/h).
Typhoons can be predicted. Though the predictions are not exact, scientists can make a
fairly accurate prediction of when typhoons will come. Meteorologists can use tools from
satellite images to Doppler radar to predict a typhoon up to a week in advance. Though the
tools have been improving through the past years, these tools aren’t exactly accurate, so
meteorologists are basically estimating when a typhoon will happen. But in the little time
you have left, you can prepare for it.
Você também pode gostar
- Landslide Hazard Map of Leyte On Project NOAH WebsiteDocumento8 páginasLandslide Hazard Map of Leyte On Project NOAH WebsiteStargazer 713Ainda não há avaliações
- Where Do Hurricanes, Typhoons & Cyclones Come From? | 2nd Grade Science Edition Vol 3No EverandWhere Do Hurricanes, Typhoons & Cyclones Come From? | 2nd Grade Science Edition Vol 3Ainda não há avaliações
- Case Study About Typhoon YolandaDocumento1 páginaCase Study About Typhoon YolandaLyka Jane Genobatin BinayAinda não há avaliações
- Hurricanes vs. Tornadoes vs Typhoons: Wind Systems of the World: Natural Disaster Books for KidsNo EverandHurricanes vs. Tornadoes vs Typhoons: Wind Systems of the World: Natural Disaster Books for KidsAinda não há avaliações
- History of Disaster in The PhilippinesDocumento3 páginasHistory of Disaster in The PhilippinesQueeni Marie SyAinda não há avaliações
- Off To The Cellar We Go! A Guide to Extreme Weather - Nature Books for Beginners | Children's Nature BooksNo EverandOff To The Cellar We Go! A Guide to Extreme Weather - Nature Books for Beginners | Children's Nature BooksAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon Haiyan, Known in The Philippines As Super Typhoon YolandaDocumento19 páginasTyphoon Haiyan, Known in The Philippines As Super Typhoon YolandaJhon Syrhel Dela CruzAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon Haiyan Case Study FinishedDocumento1 páginaTyphoon Haiyan Case Study FinishedBea MorrisonAinda não há avaliações
- (The Devastating and Deadliest Typhoon History) : #Yolanda PHDocumento7 páginas(The Devastating and Deadliest Typhoon History) : #Yolanda PHLester ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Tropical Storms: Safety Measures Before, During, and After A TyphoonDocumento24 páginasTropical Storms: Safety Measures Before, During, and After A TyphoonRyou KinoshitaAinda não há avaliações
- Project in CwtsDocumento23 páginasProject in CwtsReinette LastrillaAinda não há avaliações
- On 8 November 2013Documento2 páginasOn 8 November 2013Jovi AbramAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon BophaDocumento2 páginasTyphoon BophaDeni ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- CHAPTER 1 YeahDocumento31 páginasCHAPTER 1 YeahEhem EhemAinda não há avaliações
- Thyphon HagibisDocumento22 páginasThyphon HagibisGunasundaryChandramohanAinda não há avaliações
- Summary of The Reaction Paper Without Any QuestionsDocumento2 páginasSummary of The Reaction Paper Without Any QuestionsRalph Gerard Saldajeno ValdespinaAinda não há avaliações
- Research in DRRRMDocumento19 páginasResearch in DRRRMEstelle BalbinAinda não há avaliações
- Tropical Storms: Safety Measures Before, During, and After A TyphoonDocumento14 páginasTropical Storms: Safety Measures Before, During, and After A TyphoonRyou KinoshitaAinda não há avaliações
- Science PresentationDocumento9 páginasScience PresentationzuludavidoffAinda não há avaliações
- The Relatives of Typhoon VictimDocumento3 páginasThe Relatives of Typhoon VictimFebz Canutab0% (1)
- Why Philippines Is Prone To TyphoonsDocumento2 páginasWhy Philippines Is Prone To TyphoonsJezz Betiz VergaraAinda não há avaliações
- LOOK BACK: The 1991 Flash Flood That Devastated Ormoc City: Super Typhoon YolandaDocumento19 páginasLOOK BACK: The 1991 Flash Flood That Devastated Ormoc City: Super Typhoon YolandaallanrnmanalotoAinda não há avaliações
- Delos Reyes, Rachel L - Flood Events PresentationDocumento22 páginasDelos Reyes, Rachel L - Flood Events PresentationRachel Delosreyes100% (1)
- Cyclones PDFDocumento13 páginasCyclones PDFNitsam7Ainda não há avaliações
- Typhoon in PhilippinesDocumento11 páginasTyphoon in Philippinescharlyneabay8Ainda não há avaliações
- 262 631 1 SMDocumento33 páginas262 631 1 SMJunnoKaiserAinda não há avaliações
- Performance Task in Science 8 - Pix OnlyDocumento12 páginasPerformance Task in Science 8 - Pix OnlyCrisanto Tesado Garzon100% (1)
- Hydrometeorological Hazards Group 3Documento60 páginasHydrometeorological Hazards Group 3Tammy Ogoy100% (1)
- DURING READING Reading Text Cyclone.. Download and Print. Long Back To BackDocumento1 páginaDURING READING Reading Text Cyclone.. Download and Print. Long Back To BackMarjulyn RafalloAinda não há avaliações
- White Grey Vintage Paper BorderDocumento2 páginasWhite Grey Vintage Paper BorderLeoni FrancAinda não há avaliações
- Jimenez, Sam Baiuxiene - NSTPDocumento2 páginasJimenez, Sam Baiuxiene - NSTPSam Baiuxiene JimenezAinda não há avaliações
- DRR Final Na GyudDocumento28 páginasDRR Final Na GyudAizack Gavrielle AbenganaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity # 1 (DRRR)Documento2 páginasActivity # 1 (DRRR)Juliana Xyrelle FutalanAinda não há avaliações
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: Topic: Typhoon Prone Philippines Tropical CycloneDocumento5 páginasDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: Topic: Typhoon Prone Philippines Tropical CycloneAlaiza LucasAinda não há avaliações
- Weather DisturbancesDocumento45 páginasWeather DisturbancesJulie BalogoAinda não há avaliações
- Disaster Around Me: Typhoon: YolandaDocumento2 páginasDisaster Around Me: Typhoon: YolandaCateleen BacaniAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon Haiyan Case Study FinishedDocumento1 páginaTyphoon Haiyan Case Study FinishedMarlop CasicasAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon HaiyanDocumento7 páginasTyphoon Haiyanachyuthks78Ainda não há avaliações
- Typhoon Bopha A Report and AnalysisDocumento9 páginasTyphoon Bopha A Report and Analysisapi-140165554Ainda não há avaliações
- 119Documento2 páginas119Nirmani RupasingheAinda não há avaliações
- All About Typhoon (Basic Geography)Documento5 páginasAll About Typhoon (Basic Geography)Angie100% (1)
- Typhoon and Tsunami 2Documento7 páginasTyphoon and Tsunami 2unknownAinda não há avaliações
- Gahhahahaha Typhoon YummyDocumento17 páginasGahhahahaha Typhoon Yummyアブドゥルカリム エミールAinda não há avaliações
- BernadethDocumento3 páginasBernadethBernadeth PlanasAinda não há avaliações
- TyphoonDocumento8 páginasTyphoonRhom DumapiAinda não há avaliações
- Hydro Meteorological Hazards FinalllDocumento27 páginasHydro Meteorological Hazards Finallljerielseguido-1Ainda não há avaliações
- Typhoon Haiyan 2013Documento2 páginasTyphoon Haiyan 2013iGotheInfoAinda não há avaliações
- 2013 Typhoon YolandaDocumento7 páginas2013 Typhoon YolandaDieanne MaeAinda não há avaliações
- Floods and Cyclones 1Documento15 páginasFloods and Cyclones 1Shahzoab ShafiAinda não há avaliações
- Grade5 SCIENCE Q4 W3 New EditDocumento13 páginasGrade5 SCIENCE Q4 W3 New EditAbbie Soniega0% (1)
- Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocumento11 páginasDisaster Readiness and Risk ReductionAnime FreeAinda não há avaliações
- TyphoonsDocumento45 páginasTyphoonsChristian James EdadesAinda não há avaliações
- Storm Surge Script ?Documento4 páginasStorm Surge Script ?aira ninaAinda não há avaliações
- Hydrometeorological Hazards in The Philippines: GwennDocumento6 páginasHydrometeorological Hazards in The Philippines: GwennJeahun KimAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Mapping of Disasters in The PhilippinesDocumento2 páginasBasic Mapping of Disasters in The PhilippinesMikaela Mae MercadoAinda não há avaliações
- Understandingtyphoons 141127052908 Conversion Gate02Documento21 páginasUnderstandingtyphoons 141127052908 Conversion Gate02RosielAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon DadoDocumento6 páginasTyphoon DadoEdmar TabinasAinda não há avaliações
- Natural Hazards, Mitigation and Adaptation: Hydro Meteorological Phenomenon and HazardsDocumento32 páginasNatural Hazards, Mitigation and Adaptation: Hydro Meteorological Phenomenon and Hazardstriciavitto77Ainda não há avaliações
- Facts About TyphoonDocumento1 páginaFacts About TyphoonChristian Dave SemillaAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 2: Timeline of DumpawaDocumento1 páginaActivity 2: Timeline of DumpawaMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Early Detection and ScreeningDocumento3 páginasEarly Detection and ScreeningMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Health HX&SBARDocumento6 páginasHealth HX&SBARMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- 1.1related Learning Experience - NepDocumento6 páginas1.1related Learning Experience - NepMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Critical CarenursingDocumento3 páginasIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Critical CarenursingMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Common Oncology DrugsDocumento2 páginasCommon Oncology DrugsMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Ambo, Pilita Gargar, Mary Rose Quiñonez, Anna Marie Rodriguez, Jam MikaDocumento26 páginasAmbo, Pilita Gargar, Mary Rose Quiñonez, Anna Marie Rodriguez, Jam MikaMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- NCM 105Documento13 páginasNCM 105Mary Rose Silva Gargar100% (1)
- Mary Rose S. Gargar Bsn-Iv Cancer of The Female ReproductiveDocumento9 páginasMary Rose S. Gargar Bsn-Iv Cancer of The Female ReproductiveMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- FCASESTUDYRLEDocumento6 páginasFCASESTUDYRLEMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Bipolar Mood DisorderDocumento7 páginasBipolar Mood DisorderMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- St. Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing A.Y. 1st SEMESTER 2020-2021Documento17 páginasSt. Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing A.Y. 1st SEMESTER 2020-2021Mary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Activity 4Documento7 páginasActivity 4Mary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Premarital SexDocumento2 páginasPremarital SexMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing Nursing Care Plan FormDocumento10 páginasSaint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing Nursing Care Plan FormMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Ectopic Pregnancy Clinical PaperDocumento30 páginasEctopic Pregnancy Clinical PaperMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Case Study On Dengue FeverDocumento76 páginasCase Study On Dengue FeverMary Rose Silva Gargar0% (1)
- Acute Glumerolunephritis: Genetic Factors Streptococcal InfectionsDocumento1 páginaAcute Glumerolunephritis: Genetic Factors Streptococcal InfectionsMary Rose Silva GargarAinda não há avaliações
- Ormoc Usaid Lccap - Full Draft Edited Version3Documento140 páginasOrmoc Usaid Lccap - Full Draft Edited Version3zimm pot100% (1)
- Integration of Buoyant Foundation To Container Van HousingDocumento158 páginasIntegration of Buoyant Foundation To Container Van HousingNavanitha PAinda não há avaliações
- Why Federalism Is The Better Form of Government For The PhilippinesDocumento2 páginasWhy Federalism Is The Better Form of Government For The PhilippinesEvan ReyesAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon Haiyan Appeal: A Reflection and PrayerDocumento14 páginasTyphoon Haiyan Appeal: A Reflection and PrayerphilipjudeacidreAinda não há avaliações
- Pre-Test: DirectionDocumento15 páginasPre-Test: DirectionAllona Fideles Hernandez100% (1)
- DRRM Lesson 5Documento15 páginasDRRM Lesson 5Eloiza May LoposAinda não há avaliações
- Term Paper TyphoonDocumento7 páginasTerm Paper Typhoonafdtvovhb100% (1)
- Task 5 - Aristotles Rhetorical TriangleDocumento7 páginasTask 5 - Aristotles Rhetorical TriangleJonah DelmundoAinda não há avaliações
- Geography HurricanesDocumento6 páginasGeography HurricanesYong Junseng Alson yjsAinda não há avaliações
- CBCP Monitor Vol. 18 No. 7Documento20 páginasCBCP Monitor Vol. 18 No. 7Areopagus Communications, Inc.Ainda não há avaliações
- Yap Gelect Task 2Documento2 páginasYap Gelect Task 2Arabella YapAinda não há avaliações
- 11-09-2013 Edition PDFDocumento32 páginas11-09-2013 Edition PDFSan Mateo Daily JournalAinda não há avaliações
- DRRR Week 3 Module 2Documento11 páginasDRRR Week 3 Module 2Jacquelyn PenoliarAinda não há avaliações
- 2019 Research 1ST SemDocumento29 páginas2019 Research 1ST SemIves MedinaAinda não há avaliações
- Typhoon YolandaDocumento2 páginasTyphoon YolandaYeth Colocar-manqueriaAinda não há avaliações
- News WritingDocumento14 páginasNews WritingSammy Figura Grubanzo100% (1)
- Updated Wind Zone and Contour MapsDocumento13 páginasUpdated Wind Zone and Contour MapsClethHirenAinda não há avaliações
- November 2013Documento4 páginasNovember 2013api-248807023Ainda não há avaliações
- Resilient Housing Case Study LocalDocumento7 páginasResilient Housing Case Study LocalWenchell CastenAinda não há avaliações
- RR Strategic Plan Barugo As of April 1 2014Documento25 páginasRR Strategic Plan Barugo As of April 1 2014Polcomar Ponferrada CanonceAinda não há avaliações
- Philippine Canadian Inquirer #527Documento32 páginasPhilippine Canadian Inquirer #527canadianinquirerAinda não há avaliações
- Providing Shelters To Survivors of Super Typhoon Haiyan in Molocaboc Island, Sagay City, Negros OccidentalDocumento3 páginasProviding Shelters To Survivors of Super Typhoon Haiyan in Molocaboc Island, Sagay City, Negros Occidentalcarlos-tulali-1309Ainda não há avaliações
- AGUINALDO, ROLAND JULIUS B.-Emergency Shelter Typologies: Determining Its Applicability in The Philippine EnvironmentDocumento71 páginasAGUINALDO, ROLAND JULIUS B.-Emergency Shelter Typologies: Determining Its Applicability in The Philippine EnvironmentRoland Julius Aguinaldo100% (3)
- Reaction Paper Super Typhoon YolandaDocumento3 páginasReaction Paper Super Typhoon YolandaDPDA DPDOAinda não há avaliações
- Informative SpeechDocumento3 páginasInformative Speechapi-313471773100% (3)
- ITs More Fun in The Philippines Vs Wow PhilippinesDocumento22 páginasITs More Fun in The Philippines Vs Wow PhilippinesN JoAinda não há avaliações
- Las Science 8 Melc 4 q2 Week-4Documento9 páginasLas Science 8 Melc 4 q2 Week-4Tonepher CaballeroAinda não há avaliações
- DRRM Contingency Plan FormatDocumento65 páginasDRRM Contingency Plan Formatma carol fabraoAinda não há avaliações
- Editorial Writing & Science Writing & Column WritingDocumento24 páginasEditorial Writing & Science Writing & Column WritingLhen Dimla - GarciaAinda não há avaliações
- A Case Study On The Disaster Preparednes PDFDocumento138 páginasA Case Study On The Disaster Preparednes PDFDonald Montano Dela TorreAinda não há avaliações
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNo EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (69)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterNo EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterAinda não há avaliações
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersNo EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersAinda não há avaliações
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincNo EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (137)
- So Others May Live: Coast Guard's Rescue Swimmers Saving Lives, Defying DeathNo EverandSo Others May Live: Coast Guard's Rescue Swimmers Saving Lives, Defying DeathNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastNo EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (31)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeNo EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (4)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesNo EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (21)
- The World Beneath: The Life and Times of Unknown Sea Creatures and Coral ReefsNo EverandThe World Beneath: The Life and Times of Unknown Sea Creatures and Coral ReefsNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (4)
- Civilized To Death: The Price of ProgressNo EverandCivilized To Death: The Price of ProgressNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (215)
- Rocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyNo EverandRocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (5)
- Alien Oceans: The Search for Life in the Depths of SpaceNo EverandAlien Oceans: The Search for Life in the Depths of SpaceNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (26)
- Ruthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterNo EverandRuthless Tide: The Heroes and Villains of the Johnstown Flood, America's Astonishing Gilded Age DisasterNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (12)
- Run the Storm: A Savage Hurricane, a Brave Crew, and the Wreck of the SS El FaroNo EverandRun the Storm: A Savage Hurricane, a Brave Crew, and the Wreck of the SS El FaroNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (39)
- A Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersNo EverandA Brief History of Earth: Four Billion Years in Eight ChaptersNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (113)
- When the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeNo EverandWhen the Sahara Was Green: How Our Greatest Desert Came to BeNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (6)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosNo EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosNota: 3.5 de 5 estrelas3.5/5 (8)
- When Humans Nearly Vanished: The Catastrophic Explosion of the Toba VolcanoNo EverandWhen Humans Nearly Vanished: The Catastrophic Explosion of the Toba VolcanoNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (34)
- Exploring Creation with Physical Science, 3rd EditionNo EverandExploring Creation with Physical Science, 3rd EditionNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (2)