Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
Cruz vs. CA
Enviado por
Sirci RamTítulo original
Direitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Cruz vs. CA
Enviado por
Sirci RamDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
Cruz vs. CA -G.R. No. 123340.
August 29, 2002
Facts: Lutgarda Cruz was charged with the crime of “Estafa through Falsification of Public Document” before
the Manila Regional Trial Court. Petitioner executed before a Notary Public in the City of Manila an Affidavit
of Self-Adjudication of a parcel of land stating that she was the sole surviving heir of the registered owner when
in fact she knew there were other surviving heirs. Since the offended party did not reserve the right file a separate
civil action arising from the criminal offense, the civil action was deemed instituted in the criminal case. On
January 28, 1994, petitioner received a copy of the decision. On February 10, 1994, petitioner filed by registered
mail a motion for reconsideration dated February 7, 1994, assailing the trial court’s ruling on the civil aspect of
the criminal case. Petitioner furnished the City Prosecutor a copy of the motion by registered mail. Left with no
recourse, petitioner filed a petition for certiorari and mandamus with the Court of Appeals to nullify the two
assailed orders of the trial court. Petitioner also asked the Court of Appeals to compel the trial court to resolve
her motion for reconsideration of the decision dated February 7, 1994.
After trial on the merits, the trial court rendered its decision dated January 17, 1994acquitting petitioner on the
ground of reasonable doubt. In the same decision, the trial court rendered judgment on the civil aspect of the
case, ordering the return to the surviving heirs of the parcel of land located in Bulacan.
Issue: Whether or not the RTC of Manila had jurisdiction over the civil aspect of the case?
Held: Yes. The RTC of Manila has jurisdiction to render judgment on the civil aspect of the Criminal Case.
There are three important requisites which must be present before court can acquire criminal jurisdiction. First,
the court must have jurisdiction over the subject matter. Second, the court must have jurisdiction over the territory
where the offense was committed. Third, the court must have jurisdiction over the person of the accused.
In the instant case, the trial court had jurisdiction over the subject matter as the law has conferred on the court the
power to hear and decide cases involving estafa through falsification of a public document. The trial court also
had jurisdiction over the offense charged since the crime was committed within its territorial jurisdiction. The
trial court also acquired jurisdiction over the person of accused-petitioner because she voluntarily submitted to
the court’s authority. Where the court has jurisdiction over the subject matter and over the person of the accused,
and the crime was committed within its territorial jurisdiction, the court necessarily exercises jurisdiction over all
issues that the law requires the court to resolve. One of the issues in a criminal case is the civil liability of the
accused arising from the crime. Article 100 of the Revised Penal Code provides that “[E]very person criminally
liable for a felony is also civilly liable.” Article 104 of the same Code states that “civil liability x x x includes
restitution.”
Você também pode gostar
- Cruz vs. CA Case DigestDocumento1 páginaCruz vs. CA Case DigestAlexandra Khadka0% (1)
- 026 DIGESTED Rosa Uy vs. CA and People - G.R. No. 119000Documento5 páginas026 DIGESTED Rosa Uy vs. CA and People - G.R. No. 119000Paul ToguayAinda não há avaliações
- 01 Cariaga Vs PeopleDocumento2 páginas01 Cariaga Vs PeopleRomarie Abrazaldo100% (4)
- Alonte V Savellano, Jr. (1998)Documento2 páginasAlonte V Savellano, Jr. (1998)AbbyElbamboAinda não há avaliações
- Macasaet Vs PeopleDocumento2 páginasMacasaet Vs PeopleLira HabanaAinda não há avaliações
- Tadeja Vs PeopleDocumento4 páginasTadeja Vs PeopleLindsay MillsAinda não há avaliações
- Antiporda Vs Garchitorena (Digested)Documento2 páginasAntiporda Vs Garchitorena (Digested)ksulaw2018100% (1)
- Macasaet V PeopleDocumento4 páginasMacasaet V PeopleJimenez Lorenz100% (1)
- Mobilia Products Vs UmezawaDocumento1 páginaMobilia Products Vs UmezawaPan Correo100% (3)
- Estrada Vs Ombudsman DigestDocumento3 páginasEstrada Vs Ombudsman Digest莊偉德75% (4)
- Republic v. Sunga L-38634Documento1 páginaRepublic v. Sunga L-38634AJEAinda não há avaliações
- Atienza Vs PeopleDocumento2 páginasAtienza Vs PeopleCMG100% (4)
- Trenas Vs People Case DigestDocumento1 páginaTrenas Vs People Case Digestsujee100% (2)
- Isip V PeopleDocumento3 páginasIsip V PeopleAsh Campiao50% (2)
- Magno V PeopleDocumento2 páginasMagno V Peoplekontribute100% (1)
- Zaldivia v. Reyes 211 Scra 277Documento2 páginasZaldivia v. Reyes 211 Scra 277AJE100% (2)
- Lachica Vs TormisDocumento2 páginasLachica Vs TormisBruce Estillote100% (1)
- Burgos Vs CA Case DigestDocumento1 páginaBurgos Vs CA Case DigestRay Carlo Ybiosa Antonio100% (1)
- Alarilla v. SandiganbayanDocumento2 páginasAlarilla v. SandiganbayanKing BadongAinda não há avaliações
- When Civil Action May Be Consolidated With Subsequent Criminal Action - Case No. 4Documento1 páginaWhen Civil Action May Be Consolidated With Subsequent Criminal Action - Case No. 4Khaiye De Asis AggabaoAinda não há avaliações
- Case Digest Magno V PP - G.R. No. 171542Documento3 páginasCase Digest Magno V PP - G.R. No. 171542JamesHarvey0% (1)
- A.M. NO. 1048, JULY 14, 1995: Reyes vs. GAADocumento4 páginasA.M. NO. 1048, JULY 14, 1995: Reyes vs. GAAPatrice Grace De CastroAinda não há avaliações
- Salazar v. PeopleDocumento2 páginasSalazar v. PeopleEcnerolAicnelav100% (3)
- 62 Valdepenas Vs PeopleDocumento2 páginas62 Valdepenas Vs PeoplePiaAinda não há avaliações
- Los Banos V PedroDocumento2 páginasLos Banos V PedroZoe Velasco100% (1)
- Pinote v. AycoDocumento2 páginasPinote v. AycoIldefonso Hernaez100% (3)
- 1) Miranda V TuliaoDocumento1 página1) Miranda V TuliaoASGarcia24100% (1)
- Sec de Lima vs. Reyes (2016)Documento6 páginasSec de Lima vs. Reyes (2016)Sam Leynes83% (6)
- Adalim-White VS BugtasDocumento5 páginasAdalim-White VS BugtasRiva Vivienne Joy ParejoAinda não há avaliações
- Crespo vs. MogulDocumento1 páginaCrespo vs. MogulMichelle Vale Cruz0% (1)
- Jimenez vs. PeopleDocumento2 páginasJimenez vs. Peopleiris virtudez100% (2)
- Ruiz Vs Judge BeldiaDocumento2 páginasRuiz Vs Judge BeldiaBryan Jay Nuique100% (1)
- Pinote V Ayco Case DigestDocumento2 páginasPinote V Ayco Case DigestVanessa C. Roa100% (2)
- Posadas v. OmbudsmanDocumento2 páginasPosadas v. OmbudsmanMark Co100% (5)
- Crisostomo Vs SandiganbayanDocumento3 páginasCrisostomo Vs SandiganbayanBruce Estillote100% (2)
- Pacoy Vs Cajigal - G.R. No. 157472 - Case DigestDocumento2 páginasPacoy Vs Cajigal - G.R. No. 157472 - Case DigestAbigail Tolabing50% (4)
- Domingo v. Sandiganbayan DigestDocumento2 páginasDomingo v. Sandiganbayan DigestDan Christian Dingcong Cagnan100% (3)
- Ocampo vs. AbandoDocumento1 páginaOcampo vs. AbandoKat Miranda100% (2)
- Garces Vs HernandezDocumento2 páginasGarces Vs HernandezquasideliksAinda não há avaliações
- Republic Vs Cojuangco Crim DigestDocumento2 páginasRepublic Vs Cojuangco Crim DigestCJ100% (3)
- 5,15 Okabe vs. Gutierrez and People vs. LadrilloDocumento4 páginas5,15 Okabe vs. Gutierrez and People vs. LadrilloInnah MontalaAinda não há avaliações
- Bayas vs. SandiganbayanDocumento2 páginasBayas vs. SandiganbayanKing Badong100% (2)
- Topic Date: Criminal Procedure 2EDocumento3 páginasTopic Date: Criminal Procedure 2EJasenAinda não há avaliações
- 20 Macasaet V PeopleDocumento2 páginas20 Macasaet V PeopleKeisha Mariah Catabay Lauigan100% (1)
- De Lima v. Guerrero: Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002Documento1 páginaDe Lima v. Guerrero: Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002ada9ablaoAinda não há avaliações
- Alva vs. CA (Case Digest)Documento2 páginasAlva vs. CA (Case Digest)Cherie Teves50% (2)
- People V BeginoDocumento2 páginasPeople V BeginoHannah MedesAinda não há avaliações
- Alfredo Mendoza v. People of The Philippines and Juno Cars, Inc.Documento2 páginasAlfredo Mendoza v. People of The Philippines and Juno Cars, Inc.Jillian Asdala100% (1)
- Miranda v. Tuliao (DIGEST)Documento2 páginasMiranda v. Tuliao (DIGEST)Gennard Michael Angelo Angeles100% (8)
- 8 Layosa V RodriguezDocumento2 páginas8 Layosa V RodriguezArtemisTzyAinda não há avaliações
- Pacoy v. Judge CajigalDocumento2 páginasPacoy v. Judge CajigalquasideliksAinda não há avaliações
- Figueroa v. PeopleDocumento1 páginaFigueroa v. PeopleElaineMarcilla0% (1)
- Floresta V UbiadasDocumento2 páginasFloresta V UbiadasMarcial Gerald Suarez III100% (1)
- Enrile Vs PeopleDocumento2 páginasEnrile Vs Peoplelacbayen100% (1)
- Consoluella v. SandiganbayanDocumento2 páginasConsoluella v. SandiganbayanRanrave Marqueda Diangco100% (1)
- B3 Sanrio Company Vs LimDocumento2 páginasB3 Sanrio Company Vs LimBoletPascuaAinda não há avaliações
- HEIRS OF DELGADO V GonzalesDocumento2 páginasHEIRS OF DELGADO V GonzalesHannief Ampa21Ainda não há avaliações
- Cruz Vs PPDocumento1 páginaCruz Vs PPEA100% (1)
- Cruz V CA - Case DigestDocumento1 páginaCruz V CA - Case DigestAbigail TolabingAinda não há avaliações
- Cruz Vs CADocumento2 páginasCruz Vs CANadiel FerrerAinda não há avaliações
- Cudia vs. CADocumento2 páginasCudia vs. CASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Star LightDocumento3 páginasStar LightSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Macasaet Vs PeopleDocumento4 páginasMacasaet Vs PeoplegabbieseguiranAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Compendium ICT Policies FINAL12Documento244 páginas6th Compendium ICT Policies FINAL12Sirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- People Vs CincoDocumento1 páginaPeople Vs CincoSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Jing SpeeachDocumento2 páginasJing SpeeachSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Licyayo Vs PeopleDocumento1 páginaLicyayo Vs PeopleSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- People vs. TanDocumento3 páginasPeople vs. TanSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- MALTO v. PEOPLE - Criminal Law 2 - RA 7610 Anti-Child Abuse LawDocumento1 páginaMALTO v. PEOPLE - Criminal Law 2 - RA 7610 Anti-Child Abuse LawJCAinda não há avaliações
- Francisco vs. CADocumento1 páginaFrancisco vs. CASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Sec vs. RicDocumento3 páginasSec vs. RicSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- 6th Compendium ICT Policies FINAL12Documento244 páginas6th Compendium ICT Policies FINAL12Sirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- People vs. UrinaDocumento1 páginaPeople vs. UrinaSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- People vs. MendozaDocumento4 páginasPeople vs. MendozaSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Magno VS PeopleDocumento1 páginaMagno VS PeopleSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Cudia vs. CADocumento2 páginasCudia vs. CASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Francisco vs. CADocumento1 páginaFrancisco vs. CASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Pangilinan V CA 321 SCRA 72ADocumento1 páginaPangilinan V CA 321 SCRA 72ASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Palana v. PeopleDocumento2 páginasPalana v. PeopleRafaelAinda não há avaliações
- Magno VS PeopleDocumento1 páginaMagno VS PeopleSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Remedial Law Evidence Reviewer v1 0 PDFDocumento39 páginasRemedial Law Evidence Reviewer v1 0 PDFJoven Camus100% (1)
- 6th Compendium ICT Policies FINAL12Documento244 páginas6th Compendium ICT Policies FINAL12Sirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- PP vs. PurisimaDocumento2 páginasPP vs. PurisimaSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Cruz vs. CADocumento1 páginaCruz vs. CASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Work and Financial Plan FOR CY 2019: OfficeDocumento3 páginasWork and Financial Plan FOR CY 2019: OfficeSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- EvidenceDocumento4 páginasEvidenceSirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence Q and ADocumento6 páginasEvidence Q and ASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representative of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocumento4 páginasBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representative of The Philippines in Congress AssembledRC FloresAinda não há avaliações
- Evidence Q and ADocumento6 páginasEvidence Q and ASirci RamAinda não há avaliações
- Lim vs. CaDocumento1 páginaLim vs. CaabethzkyyyyAinda não há avaliações
- Universal Robina CorpDocumento4 páginasUniversal Robina CorpChristian ParadoAinda não há avaliações
- CompuFill v. Delhaize AmericaDocumento7 páginasCompuFill v. Delhaize AmericaPriorSmartAinda não há avaliações
- HNLU - Essay Competition BrochureDocumento7 páginasHNLU - Essay Competition BrochureBar & BenchAinda não há avaliações
- American and Scandinavian Legal RealismDocumento15 páginasAmerican and Scandinavian Legal RealismJigarJadavAinda não há avaliações
- Appeal Motion To Quash Service State Illinois 1133555 - R23Documento7 páginasAppeal Motion To Quash Service State Illinois 1133555 - R23sbhasin1100% (1)
- MAL Digest 2012 eDocumento242 páginasMAL Digest 2012 eMariam PetrosyanAinda não há avaliações
- The Jones Act: Philippines Table of ContentsDocumento2 páginasThe Jones Act: Philippines Table of ContentsMyrna B RoqueAinda não há avaliações
- The Inquistition Is UnconstitutionalDocumento2 páginasThe Inquistition Is UnconstitutionalAnthony J. FejfarAinda não há avaliações
- Rule71 Contempt Marantan vs. Diokno BangcolaDocumento3 páginasRule71 Contempt Marantan vs. Diokno BangcolaGeds DAinda não há avaliações
- 3:10-cv-00257 #127Documento7 páginas3:10-cv-00257 #127Equality Case FilesAinda não há avaliações
- Ra 9344Documento24 páginasRa 9344odycuaAinda não há avaliações
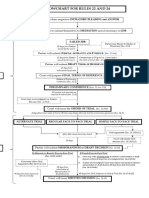
- FLOWCHART of Rules 22 and 24Documento1 páginaFLOWCHART of Rules 22 and 24Stewart Paul TorreAinda não há avaliações
- Furnco Constr. Corp. v. Waters, 438 U.S. 567 (1978)Documento15 páginasFurnco Constr. Corp. v. Waters, 438 U.S. 567 (1978)Scribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- Dp-Certificate of Departmental Permission-PpscDocumento1 páginaDp-Certificate of Departmental Permission-Ppscfazalulbasit9796Ainda não há avaliações
- Term PaperDocumento10 páginasTerm PaperMylene CanezoAinda não há avaliações
- Record For Benson V Vilosola Amended Complaint W Exhibits AZ 201000977Documento103 páginasRecord For Benson V Vilosola Amended Complaint W Exhibits AZ 201000977Christopher Earl StrunkAinda não há avaliações
- In Re Vicente SottoDocumento2 páginasIn Re Vicente SottoJimi Solomon100% (1)
- United Arab Emirates: Arab Political Systems: Baseline Information and Reforms - UAEDocumento17 páginasUnited Arab Emirates: Arab Political Systems: Baseline Information and Reforms - UAEWanttoemigrate RightnowAinda não há avaliações
- Royal Rutter vs. Placido Esteban (GR No. L-3708, 93 Phil 68, 18 May 1953)Documento2 páginasRoyal Rutter vs. Placido Esteban (GR No. L-3708, 93 Phil 68, 18 May 1953)Archibald Jose Tiago Manansala100% (1)
- Two (2) Requisites For The Judicial Review of Administrative Decision/ActionsDocumento1 páginaTwo (2) Requisites For The Judicial Review of Administrative Decision/ActionsMei MeiAinda não há avaliações
- Sebastian V Bajar DigestDocumento2 páginasSebastian V Bajar Digestjeffdelacruz100% (2)
- LegalForms - (20) Motion To Post BailDocumento3 páginasLegalForms - (20) Motion To Post BailIsidore Tarol IIIAinda não há avaliações
- The Commission of Sati (Prevention) Act 1987Documento6 páginasThe Commission of Sati (Prevention) Act 1987navinkapilAinda não há avaliações
- Yangco v. CFIDocumento1 páginaYangco v. CFItrishahaAinda não há avaliações
- Amgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 388Documento3 páginasAmgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 388Justia.comAinda não há avaliações
- Porterfield v. Lott, 4th Cir. (1998)Documento12 páginasPorterfield v. Lott, 4th Cir. (1998)Scribd Government DocsAinda não há avaliações
- Uniform Bonding Code What Is Bonding AllDocumento46 páginasUniform Bonding Code What Is Bonding Allmlo356100% (7)
- Prayas InternshipDocumento17 páginasPrayas InternshipShivam GuptaAinda não há avaliações
- Motion Quash Subpoena ED MIDocumento28 páginasMotion Quash Subpoena ED MIdammonAinda não há avaliações