Escolar Documentos
Profissional Documentos
Cultura Documentos
U15CET402 Strength of Materials
Enviado por
KarthiKeyanDireitos autorais
Formatos disponíveis
Compartilhar este documento
Compartilhar ou incorporar documento
Você considera este documento útil?
Este conteúdo é inapropriado?
Denunciar este documentoDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
U15CET402 Strength of Materials
Enviado por
KarthiKeyanDireitos autorais:
Formatos disponíveis
U15CET402 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS L T P C
2 2 0 3
Course Outcomes
After successful completion of this course, the students will be able to
CO1:find the deflection in beams and frames using Energy theorems.
CO2:analyze indeterminate beams.
CO3:analyze the long and short columns and determine the design loads.
CO4: assess the state of stress in three dimensions.
CO5:analyze the structural members using various theories of failures
CO6:solve problems involving unsymmetrical bending in structural members.
Pre-requisites:
1. Engineering Mechanics
2. Solid Mechanics
Course Assessment methods:
Direct Indirect
1. Internal tests Course End survey
2. Assignment
3. Presentation
4. End semester exam
CO/PO Mapping
(S/M/W indicates strength of correlation) S-Strong, M-Medium, W-Weak
COs Programme Outcomes(POs)
PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12
CO1 M S M
CO2 M S M
CO3 M S M
CO4 M S M
CO5 M S M
CO6 M S M
ENERGY PRINCIPLES 6+6Hours
Strain energy and strain energy density-strain energy in traction, problems on suddenly applied
loads and impact loads, strain energy in shear, flexure and torsion - Castigliano’s theorems -
principle of virtual work - application of energy theorems for computing deflections in beams
and trusses - Maxwell’s reciprocal theorems.
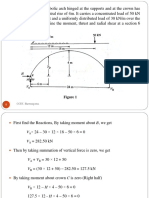
INDETERMINATE BEAMS 6+6Hours
Propped cantilever and fixed beams - fixed end moments and reactions for concentrated load
(central, non-central), uniformly distributed load, triangular load (maximum at centre and
maximum at end), theorem of three moments – analysis of continuous beams - support reactions
- shear force and bending moment diagrams for continuous beams.
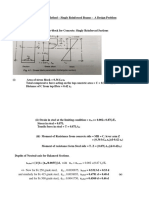
COLUMNS 6+6Hours
Eccentrically loaded short columns-middle third rule - core of section - Euler’s theory for long
columns - critical loads for prismatic columns with different end conditions; Rankine – Gordon
formula for eccentrically loaded columns.
STATE OF STRESS IN THREE DIMENSIONS 2+2Hours
Spherical and deviation components of stress tensor - determination of principal stresses and
principal planes (3 dimensions) - volumetric strain.
4+4Hours
THEORIES OF FAILURE
Theories of failure - principal stress dilatation - principal strain - shear stress - strain energy and
distortion energy theories - application in analysis of stress, load carrying capacity and design of
members –interaction problems and interaction curves - residual stresses.
6+6Hours
ADVANCED TOPICS IN BENDING OF BEAMS
Unsymmetrical bending of beams of symmetrical and unsymmetrical sections – shear flow -
shear centre - channel section - curved beams – Winkler Bach formula - stress concentration -
fatigue, fracture and creep
Theory:30Hrs Tutorial: 30Hrs Total :60Hrs
REFERENCES
1. Rajput R.K, “Strength of materials” (Mechanics of Solids), S. Chand (2015).
2. Bansal R.K,“ Strength of materials”, Lakshmi publication (2015).
3. PrakkashRao D.S,“ Strength of materials”, University Press, Hyderabad (2002).
4. Sadhu singh, “Strength of Materials”, Khanna Publishers, Delhi (2006).
5. KazimiS.M.A,”Solid mechanics” Tata Mc- raw-Hill Publications Ltd. New Delhi,
(2009).
6. Punmia B.C., Ashok kumarJain,Arunkumar Jain “ Theory of structures”,
Lakshmipublications (P) Ltd, New Delhi, (2011).
Você também pode gostar
- ME 201 Mechanics of SolidsDocumento3 páginasME 201 Mechanics of SolidsSudeesh SudevanAinda não há avaliações
- Elementary Mechanics of Solids: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structure and Solid Body MechanicsNo EverandElementary Mechanics of Solids: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structure and Solid Body MechanicsAinda não há avaliações
- Bmee202l Mechanics-Of-Solids TH 1.0 67 Bmee202lDocumento3 páginasBmee202l Mechanics-Of-Solids TH 1.0 67 Bmee202lKrijayAinda não há avaliações
- ME 201 Mechanics of SolidsDocumento2 páginasME 201 Mechanics of SolidsUnnikrishnan TGAinda não há avaliações
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNo EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Som Mech SyllabusDocumento2 páginasSom Mech SyllabusVinay KorukondaAinda não há avaliações
- M.tech Machine SyllabusDocumento41 páginasM.tech Machine SyllabusSyed Faiz Quadri0% (1)
- WWW - Ktustudents.In: 1. Rattan, Strength of Materials, 2E Mcgraw Hill Education India, 2011Documento3 páginasWWW - Ktustudents.In: 1. Rattan, Strength of Materials, 2E Mcgraw Hill Education India, 2011SherwinAinda não há avaliações
- Stress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNo EverandStress Analysis Problems in S.I. Units: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionNota: 2.5 de 5 estrelas2.5/5 (4)
- Unit 1 Part 1Documento32 páginasUnit 1 Part 1ramamurthiAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Materials 2: The Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural MaterialsNo EverandMechanics of Materials 2: The Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural MaterialsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (14)
- 09St101 Applied Mathematics 3 0 0 100 ObjectiveDocumento37 páginas09St101 Applied Mathematics 3 0 0 100 ObjectiveThulasi Raman KowsiganAinda não há avaliações
- Stability of Structures: Principles and ApplicationsNo EverandStability of Structures: Principles and ApplicationsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (4)
- Probability and Statistics: Inferences Concerning ProportionsDocumento29 páginasProbability and Statistics: Inferences Concerning ProportionsMukesh Kumar PandeyAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainNo EverandStrength of Materials: An Introduction to the Analysis of Stress and StrainNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Pre Requisite: BE 100 Engineering MechanicsDocumento3 páginasPre Requisite: BE 100 Engineering MechanicsBalagopal VAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Sem III To VIDocumento103 páginasSyllabus Sem III To VIChetanAinda não há avaliações
- Course Code Course Name L-T-P:C Year 04 CE 6103 3-1-0-4 2015Documento2 páginasCourse Code Course Name L-T-P:C Year 04 CE 6103 3-1-0-4 2015Arun KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Unit #1 NotesDocumento192 páginasUnit #1 Notescopegob600Ainda não há avaliações
- Civilsyll PDFDocumento31 páginasCivilsyll PDFmohanAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Solid: PME3I101Documento3 páginasMechanics of Solid: PME3I101Anonymous kTVBUxrAinda não há avaliações
- CivilsyllDocumento131 páginasCivilsyllYashwanth YashuAinda não há avaliações
- CivilsyllDocumento32 páginasCivilsyllShrinidhi KulkarniAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical Engg SyllabusDocumento33 páginasMechanical Engg SyllabusKRISHNA KANT GUPTAAinda não há avaliações
- Department of Civil Engineering Revised Course Structure For M.Tech (Structural Engineering) (DT)Documento13 páginasDepartment of Civil Engineering Revised Course Structure For M.Tech (Structural Engineering) (DT)SaikrupaVempatiAinda não há avaliações
- 2010 Syllabus Civ PDFDocumento138 páginas2010 Syllabus Civ PDFManish Shashikant DharekAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of Solids: Mr. Y. B. Kumbhar Ybk - Aero@adcet - inDocumento19 páginasMechanics of Solids: Mr. Y. B. Kumbhar Ybk - Aero@adcet - inYogesh KumbharAinda não há avaliações
- 1 SemDocumento12 páginas1 SemShivam VermaAinda não há avaliações
- S. E. Mech. Engg. June 2013 PDFDocumento34 páginasS. E. Mech. Engg. June 2013 PDFDinesh PatilAinda não há avaliações
- UEMX2313Documento3 páginasUEMX2313Chang King HonAinda não há avaliações
- M.Tec in Civil - Structural Design Engineering: Singhania UniversityDocumento54 páginasM.Tec in Civil - Structural Design Engineering: Singhania UniversityPrashantAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of SolidsDocumento3 páginasMechanics of SolidsVishal SinghAinda não há avaliações
- School of Civil Engineering M. Tech. Program Specialization: Structural Engineering SyllabusDocumento13 páginasSchool of Civil Engineering M. Tech. Program Specialization: Structural Engineering SyllabusasdAinda não há avaliações
- Subject Code Title of The Subject L T P C BESBS1031 Basics of Mechanics 3 1 0 4Documento1 páginaSubject Code Title of The Subject L T P C BESBS1031 Basics of Mechanics 3 1 0 4Arya NayakAinda não há avaliações
- Unknown 7 2Documento3 páginasUnknown 7 2ahmad najihanAinda não há avaliações
- MOS-1, SlyDocumento2 páginasMOS-1, SlyManish KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Civil Engineering SyllabusDocumento137 páginasCivil Engineering SyllabusH S Vishwanath ShastryAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanics of SolidsDocumento1 páginaMechanics of SolidsMouna GuruAinda não há avaliações
- Som Syllabus (Ce2252)Documento1 páginaSom Syllabus (Ce2252)rajapratyAinda não há avaliações
- Anna University Syllabus Btech MechanicalDocumento160 páginasAnna University Syllabus Btech MechanicaljibinictAinda não há avaliações
- Syllabus Civil PGDocumento103 páginasSyllabus Civil PGTanmaya Kumar SahooAinda não há avaliações
- Pdfjoiner PDFDocumento11 páginasPdfjoiner PDFPratik Sarkar RebornAinda não há avaliações
- Structural AnalysisDocumento353 páginasStructural AnalysisRitik Singh100% (2)
- SOM CivilDocumento7 páginasSOM CivilVikram RaoAinda não há avaliações
- Ce010 601 Design of Steel StructuresDocumento11 páginasCe010 601 Design of Steel StructuresDev GajbeAinda não há avaliações
- MSM SyllabusfDocumento143 páginasMSM SyllabusfPrashantAinda não há avaliações
- Baddi University Syll of MEDocumento102 páginasBaddi University Syll of MEKunal KumbhaAinda não há avaliações
- Mech 325-Strength of Materials SyllabusDocumento2 páginasMech 325-Strength of Materials Syllabuspicefeati100% (1)
- Me 202 Advanced Mechanics of SolidsDocumento3 páginasMe 202 Advanced Mechanics of SolidsMohammed Asif NAinda não há avaliações
- Se Ce SyllabusDocumento23 páginasSe Ce SyllabusPrashant PatilAinda não há avaliações
- CE202 Structural AnalysisDocumento3 páginasCE202 Structural AnalysisBalagopal VAinda não há avaliações
- Mechanical EngineeringDocumento11 páginasMechanical Engineeringhyy5u6Ainda não há avaliações
- Applied MathamaticsDocumento55 páginasApplied MathamaticsthemobilekingAinda não há avaliações
- Vtu Civil Syllabus Rejinpaul PDFDocumento137 páginasVtu Civil Syllabus Rejinpaul PDFTabrez AhmedAinda não há avaliações
- SyllabusDocumento58 páginasSyllabusRediraAinda não há avaliações
- CE Strength of Materials I L T PC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivesDocumento4 páginasCE Strength of Materials I L T PC 3 0 0 3 ObjectivesAnonymous H7nsyCogAinda não há avaliações
- Introduction To Steel StructuresDocumento62 páginasIntroduction To Steel StructuresKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Student Centered TeachingDocumento56 páginasStudent Centered TeachingKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Unit 1Documento71 páginasUnit 1KarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Analysis - I, B. Tech., 4th Semester, Civil Engineering, Module-V, Part IDocumento54 páginasStructural Analysis - I, B. Tech., 4th Semester, Civil Engineering, Module-V, Part IKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Structural Analysis - I, B. Tech., 4th Semester, Civil Engineering, Module-V, Part - IIDocumento35 páginasStructural Analysis - I, B. Tech., 4th Semester, Civil Engineering, Module-V, Part - IIKarthiKeyan100% (1)
- GCEK, BhawanipatnaDocumento2 páginasGCEK, BhawanipatnaKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- GCEK, BhawanipatnaDocumento4 páginasGCEK, BhawanipatnaKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- 11-1 Wan-Brief Intro Use of Mineral Admixture in Concrete-2-26Documento25 páginas11-1 Wan-Brief Intro Use of Mineral Admixture in Concrete-2-26KarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- About NIT Warangal:: "Learning Management System: "Documento2 páginasAbout NIT Warangal:: "Learning Management System: "KarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- GCEK, BhawanipatnaDocumento4 páginasGCEK, BhawanipatnaKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- P18SEE0001 Design of Bridges L T P J C 3 0 0 0 3: Pre-Requisites: NilDocumento2 páginasP18SEE0001 Design of Bridges L T P J C 3 0 0 0 3: Pre-Requisites: NilKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 5 CorrectedDocumento43 páginasChapter 5 CorrectedKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Challenges For Faculty Motivation in Heis: National Education Policy 2019Documento4 páginasChallenges For Faculty Motivation in Heis: National Education Policy 2019KarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Performance of Glass/Cladding of High-Rise Buildings in Hurricane KatrinaDocumento7 páginasPerformance of Glass/Cladding of High-Rise Buildings in Hurricane KatrinaKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Current Long Span BridgesDocumento28 páginasCurrent Long Span BridgesKarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Program Schedule: Day 1 1st July 2019Documento2 páginasProgram Schedule: Day 1 1st July 2019KarthiKeyanAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 13Documento22 páginasChapter 13RohitGupta0% (1)
- Astm Section 3 Wear and Erosion G 38 - 01 - RZM4Documento8 páginasAstm Section 3 Wear and Erosion G 38 - 01 - RZM4Rony AgistaAinda não há avaliações
- Design of Slabs For ResidentialDocumento12 páginasDesign of Slabs For ResidentialWilbert ReuyanAinda não há avaliações
- Understanding Overhead Crane Deflection and CriteriaDocumento3 páginasUnderstanding Overhead Crane Deflection and Criteriaram_babu_59Ainda não há avaliações
- Flexural Design of Singly Reinforced Beam Sections by LSMDocumento12 páginasFlexural Design of Singly Reinforced Beam Sections by LSMKallem KiranmayiAinda não há avaliações
- Ex3 LTBeamDocumento27 páginasEx3 LTBeamYoussef AliAinda não há avaliações
- PRTIND-SESK-DCR-SS-0001 - Design CriteriaDocumento16 páginasPRTIND-SESK-DCR-SS-0001 - Design CriteriaPhạm Quốc ViệtAinda não há avaliações
- Mohr's TheoremsDocumento91 páginasMohr's TheoremsSandeep_Ajmire90% (10)
- DraftDocumento27 páginasDraftisaudkAinda não há avaliações
- SA Lab Manual - 6 ExpDocumento23 páginasSA Lab Manual - 6 ExpAkbar HamidAinda não há avaliações
- Concreto Armado - Ghoneim - Design - of - Reinforced - Concrete - Structure - Volume - 3 PDFDocumento425 páginasConcreto Armado - Ghoneim - Design - of - Reinforced - Concrete - Structure - Volume - 3 PDFJaniiiiooooAinda não há avaliações
- Slab DesignDocumento20 páginasSlab Designmanoj_structureAinda não há avaliações
- Taguchi Orthogonal ArraysDocumento3 páginasTaguchi Orthogonal ArraysGautham Shankar0% (1)
- Atkins - Almas-TowerDocumento12 páginasAtkins - Almas-TowerAshish BorkarAinda não há avaliações
- Beam DesignDocumento84 páginasBeam DesignFoo He XuanAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Materials University Question PaperDocumento2 páginasStrength of Materials University Question PaperSaravanan KumarAinda não há avaliações
- Strength of Material 2Documento6 páginasStrength of Material 2viv_1971Ainda não há avaliações
- Serviceability MBMADocumento2 páginasServiceability MBMAabdulloh_99100% (1)
- Mackay Flex Isolators CatalogueDocumento142 páginasMackay Flex Isolators Cataloguemuss21Ainda não há avaliações
- WRD 12 (653) IS 5620 Recommendation For Structural Design Criteria For Low Head Slide Gates (Third Revision)Documento32 páginasWRD 12 (653) IS 5620 Recommendation For Structural Design Criteria For Low Head Slide Gates (Third Revision)Anup MitraAinda não há avaliações
- Design of SpringsDocumento80 páginasDesign of SpringsRohan SinghAinda não há avaliações
- Design of MonorailDocumento24 páginasDesign of MonorailSherwin PonsAinda não há avaliações
- STRC03 ReinforcedConcrete Part1 0717 PDFDocumento112 páginasSTRC03 ReinforcedConcrete Part1 0717 PDFnickAinda não há avaliações
- Excel For Civil EngineeringDocumento9 páginasExcel For Civil Engineeringsocmaster100% (2)
- Filigree Slabs TestingDocumento6 páginasFiligree Slabs Testingmulti5torpeAinda não há avaliações
- Chapter 10 - Composite Beams: Example ProblemsDocumento3 páginasChapter 10 - Composite Beams: Example ProblemsJULIUS CESAR G. CADAOAinda não há avaliações
- Behaviour of Laterally Loaded Piles in Cohesionless SoilsDocumento3 páginasBehaviour of Laterally Loaded Piles in Cohesionless SoilsInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyAinda não há avaliações
- Kingspan PIR Datasheet King Zip Roof July 2020Documento10 páginasKingspan PIR Datasheet King Zip Roof July 2020Georgios PAinda não há avaliações
- Design and Analysis of A Tapered Composite Leaf Spring K. Diwakar, N. Bhaskar, A. Surendra, Y. Uday Kumar & C. Srikar RaoDocumento11 páginasDesign and Analysis of A Tapered Composite Leaf Spring K. Diwakar, N. Bhaskar, A. Surendra, Y. Uday Kumar & C. Srikar RaoRôpíp PhanAinda não há avaliações
- D 2164 Â " 83 R94 RDIXNJQTODNSOTRFMQDocumento8 páginasD 2164 Â " 83 R94 RDIXNJQTODNSOTRFMQdorbarelAinda não há avaliações
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignNo EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (138)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNo EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindAinda não há avaliações
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresNo EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresNota: 1 de 5 estrelas1/5 (2)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignNo EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (19)
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!No EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (3)
- Onshore Structural Design Calculations: Power Plant and Energy Processing FacilitiesNo EverandOnshore Structural Design Calculations: Power Plant and Energy Processing FacilitiesNota: 4.5 de 5 estrelas4.5/5 (13)
- Non-destructive Testing and Evaluation of Civil Engineering StructuresNo EverandNon-destructive Testing and Evaluation of Civil Engineering StructuresJean-Paul BalayssacAinda não há avaliações
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsAinda não há avaliações
- SAM: One Robot, a Dozen Engineers, and the Race to Revolutionize the Way We BuildNo EverandSAM: One Robot, a Dozen Engineers, and the Race to Revolutionize the Way We BuildNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (5)
- Mechanics of Flow-Induced Sound and Vibration, Volume 2: Complex Flow-Structure InteractionsNo EverandMechanics of Flow-Induced Sound and Vibration, Volume 2: Complex Flow-Structure InteractionsAinda não há avaliações
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsNo EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (1)
- Digital Twin Development and Deployment on the Cloud: Developing Cloud-Friendly Dynamic Models Using Simulink®/SimscapeTM and Amazon AWSNo EverandDigital Twin Development and Deployment on the Cloud: Developing Cloud-Friendly Dynamic Models Using Simulink®/SimscapeTM and Amazon AWSAinda não há avaliações
- Artificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsNo EverandArtificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsNota: 5 de 5 estrelas5/5 (3)
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsNo EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (16)
- The AI Generation: Shaping Our Global Future with Thinking MachinesNo EverandThe AI Generation: Shaping Our Global Future with Thinking MachinesNota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (2)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.No EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Nota: 4 de 5 estrelas4/5 (5)